A Method for Absolute Quantification of Microbial Community Based on Multiple Internal Standard System
A microbial community, absolute quantitative technology, applied in the field of biotechnology and omics analysis, can solve problems such as failure to specifically reflect the microbial succession law, errors, and inability to quantify biomass, to shorten sample processing time, reduce errors, and cost. reduced effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
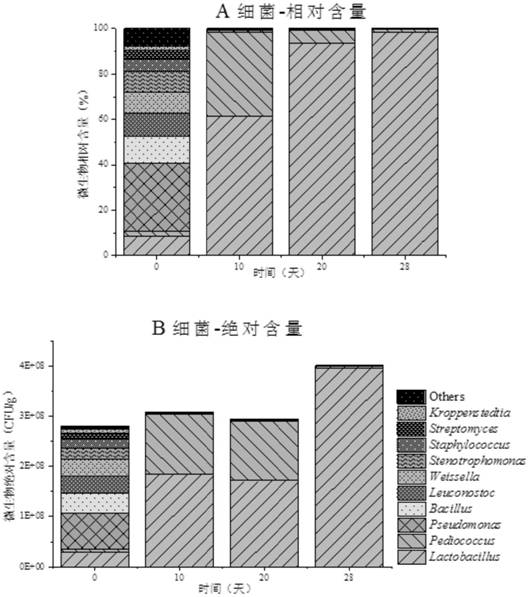
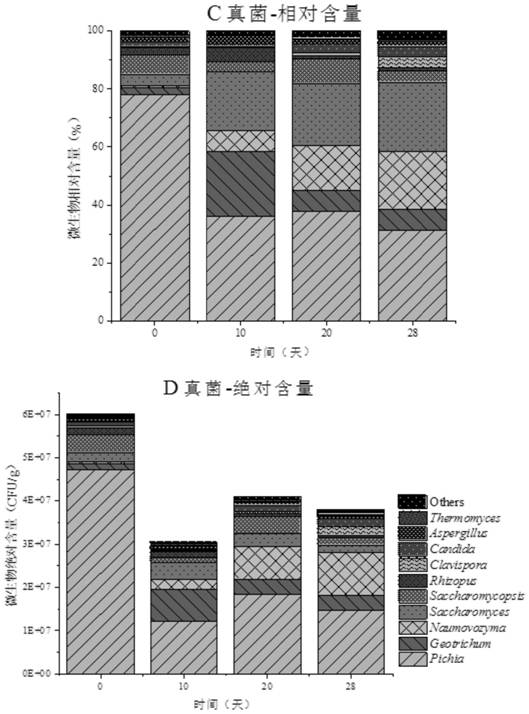
[0037] Take the microbial changes in the brewing process of a liquor as an example:
[0038] 1. Sequence design of the top 10 OTU units with the most content in bacteria and fungi in the brewing system (Table 1, 2), and random sequence design according to their average sequence length and GC% content to avoid the bias of amplification , from nearly 300 random sequences, the average similarity with the top 10 OTU sequences in the in situ system is all lower than 50%, which can be well distinguished from the microorganisms in the in situ system (Table 1 and 2) The 10 sequences (Table 3) are the designed sequences.
[0039] Table 1 Bacterial reference sequence information
[0040]
[0041] Table 2 fungal reference sequence information
[0042]
[0043] Table 3 Random sequence design information.
[0044]
[0045]
[0046]
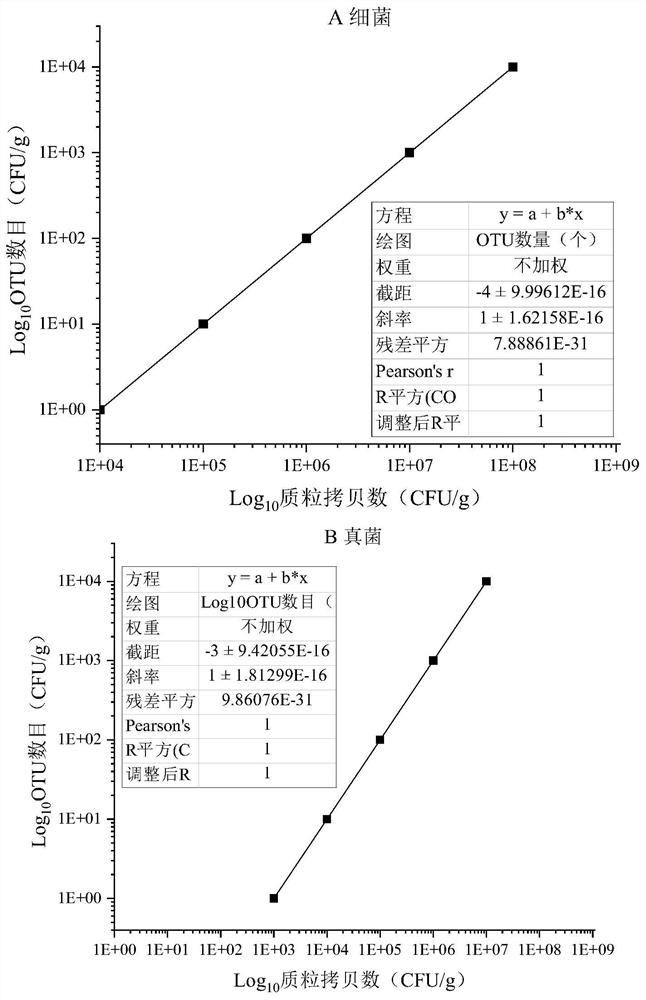
[0047] 2. In order to avoid the bias of amplification, select the general primer pair of bacterial V3-V4 region and fungal ITS2 region durin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com