Aerobic fermentation systems and methods
A technology of aerobic fermentation and aeration system, which is applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, sterilization methods, bioreactor/fermenter combinations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0092] The following examples are provided to illustrate the performance of various aspects of the systems 100, 200 described in this disclosure.
example 1
[0094] aeration oxygen mass transfer
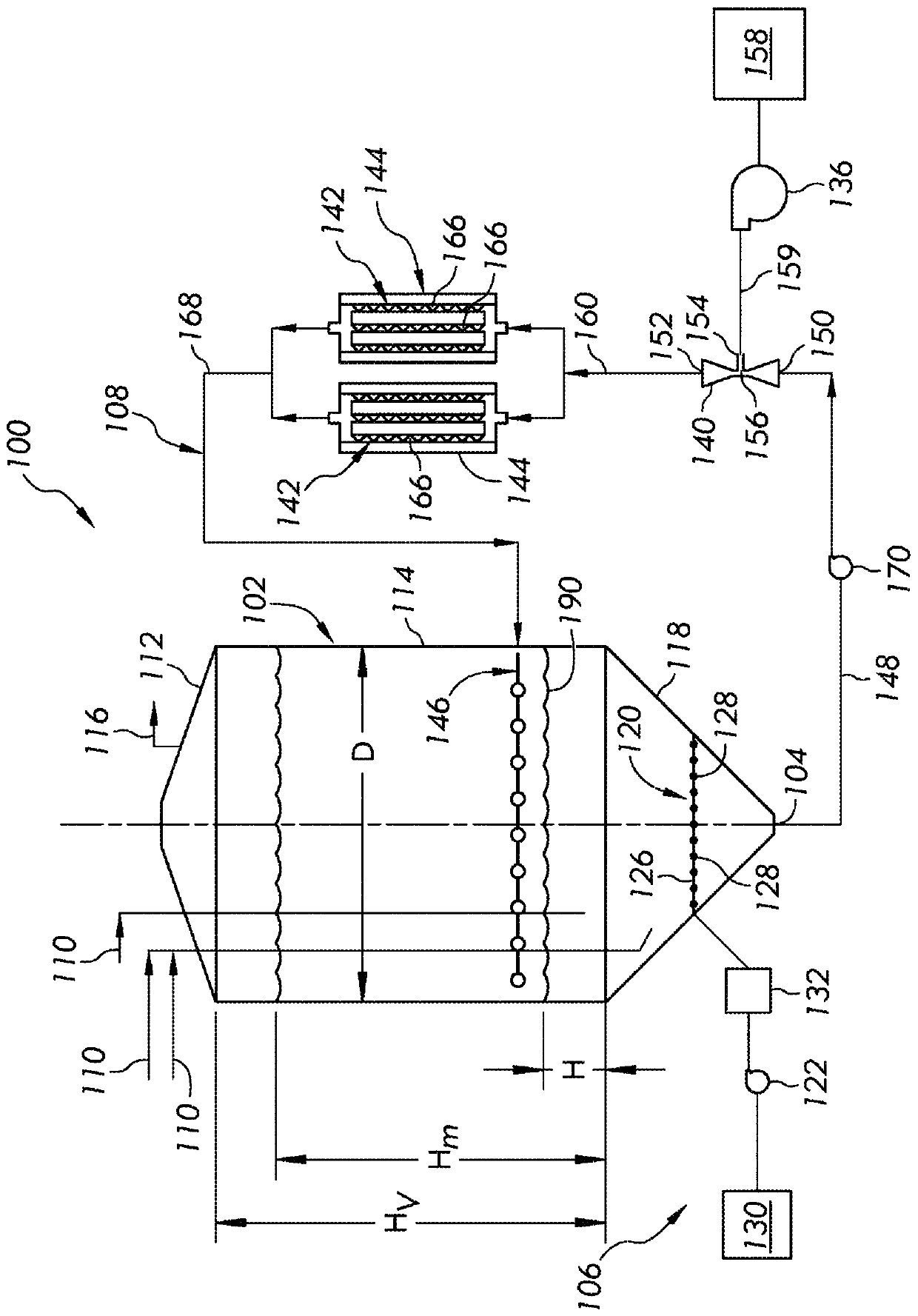
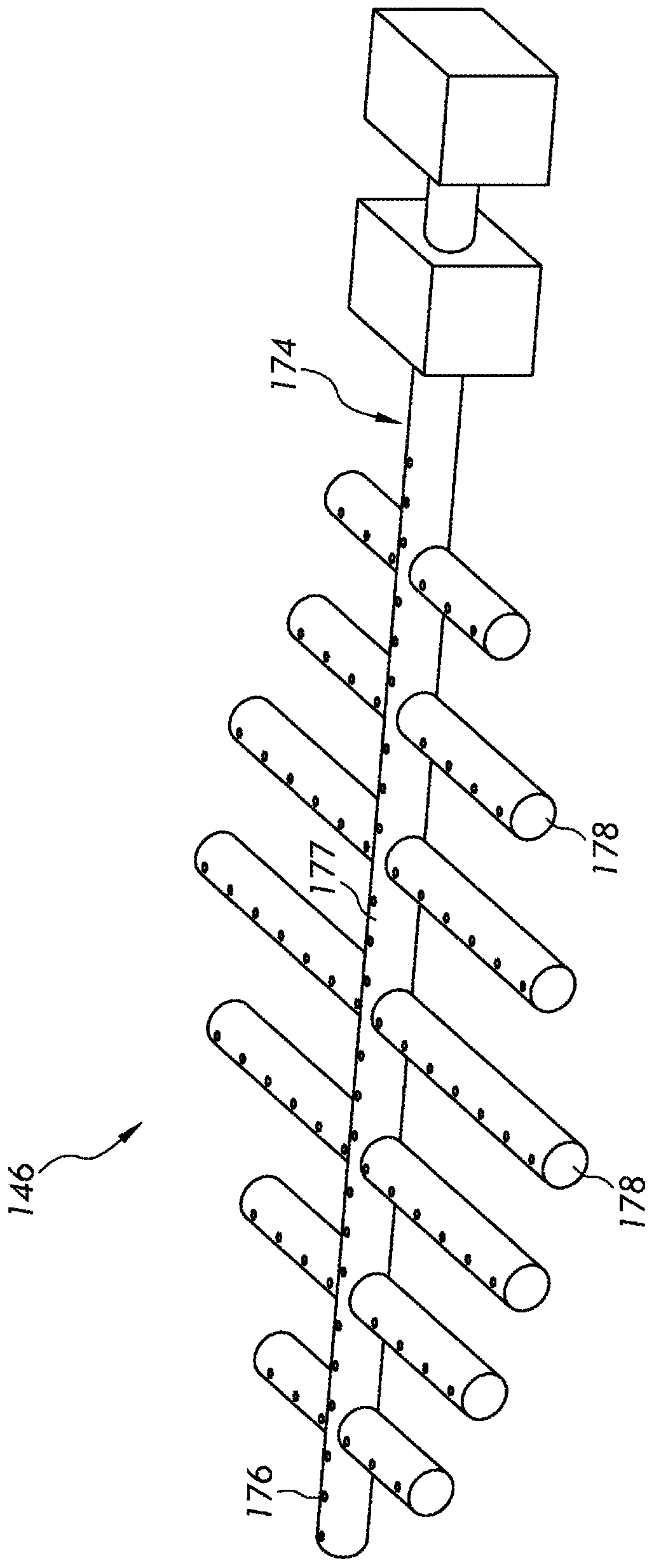
[0095] Experiments were performed to determine the volumetric mass transfer coefficient k for delivery throughout the vessel of an aerobic fermentation system L a is 0.1 / s(s -1 ) is an appropriate magnification standard. Experiments were conducted in an 1800 gallon vessel with an aeration system fluidly coupled to the vessel. The inner diameter D of the container is 66 inches and the height H of the straight side V is 120". Change the height H of the liquid in the container by adding more liquid to the container or draining a portion of the existing contents. Between 3 feet and 8 feet of liquid corresponding to an aspect ratio (H / D) of 0.55 to 1.5 Experiments were carried out at a range of heights H. In each experiment, the liquid used was water at a nominal temperature of 18°C to 20°C. Air was introduced into the vessel through an air sparger with a nominal outside diameter of approximately 50 inches, and used Pneumatically control...
example 2
[0109] Oxygen mass transfer in a recirculation loop with a static mixer
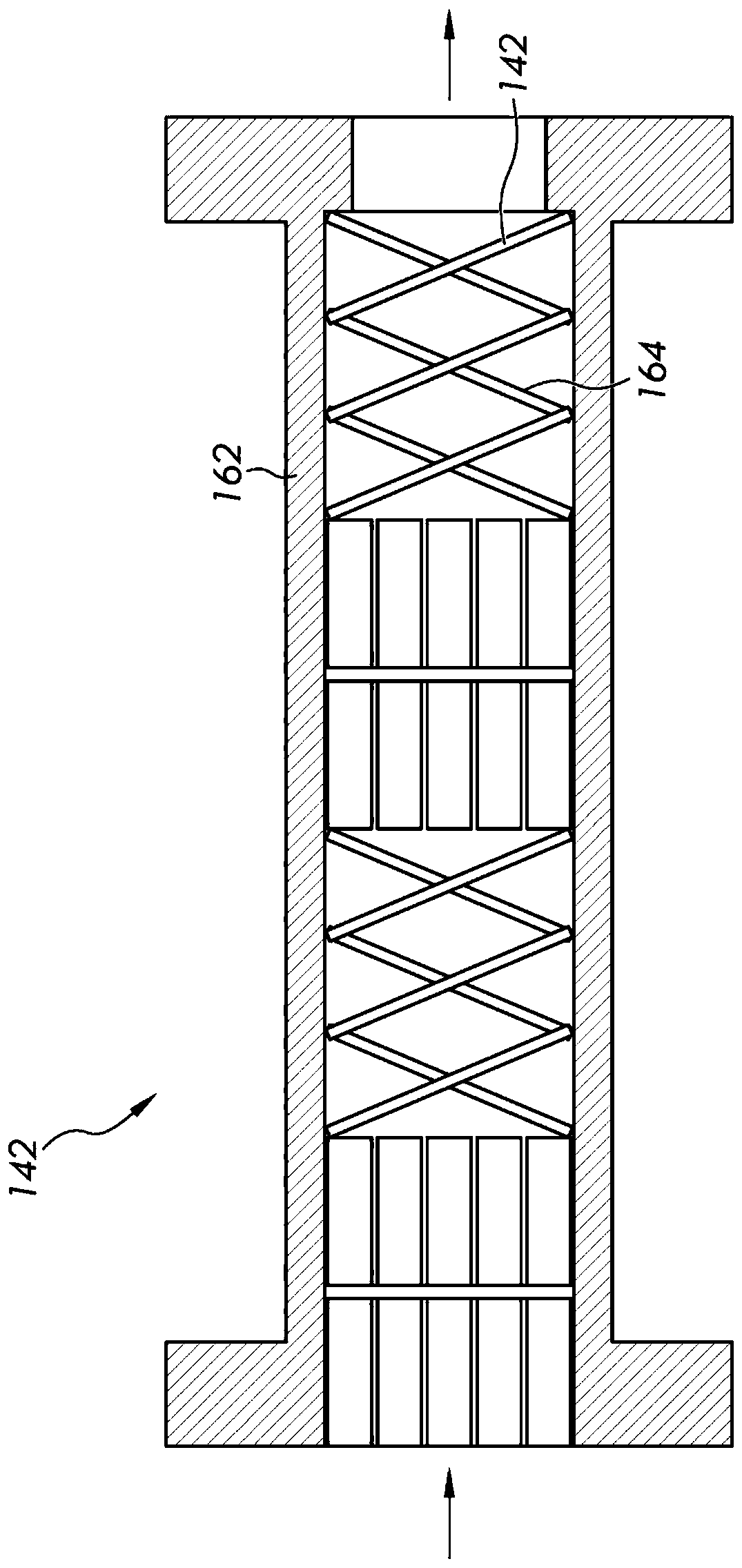
[0110] Increasing the oxygen mass transfer rate by circulating the fermentation composition through the recirculation loop 108 can provide improved performance during certain stages of the aerobic fermentation process. For example, this occurs during the growth phase of a microbial population (microorganisms), when compared to conventional operation of an aerobic fermentation process, a much greater oxygen mass transfer rate is required to maintain an oxygen mass transfer rate equal to or greater than that achieved by microorganisms When metabolism consumes the level of dissolved oxygen. As previously discussed herein, limiting the length of the recirculation can reduce fouling of recirculation loop surfaces. This means that the residence time of the fermented composition in the recirculation loop is shorter. Thus, recirculation can be designed to provide greater oxygen transfer rates than aeration sys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com