Method for replicating or amplifying circular DNA
A circular and linear technology, applied in the direction of DNA preparation, recombinant DNA technology, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem that template circular DNA cannot be multiplied
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
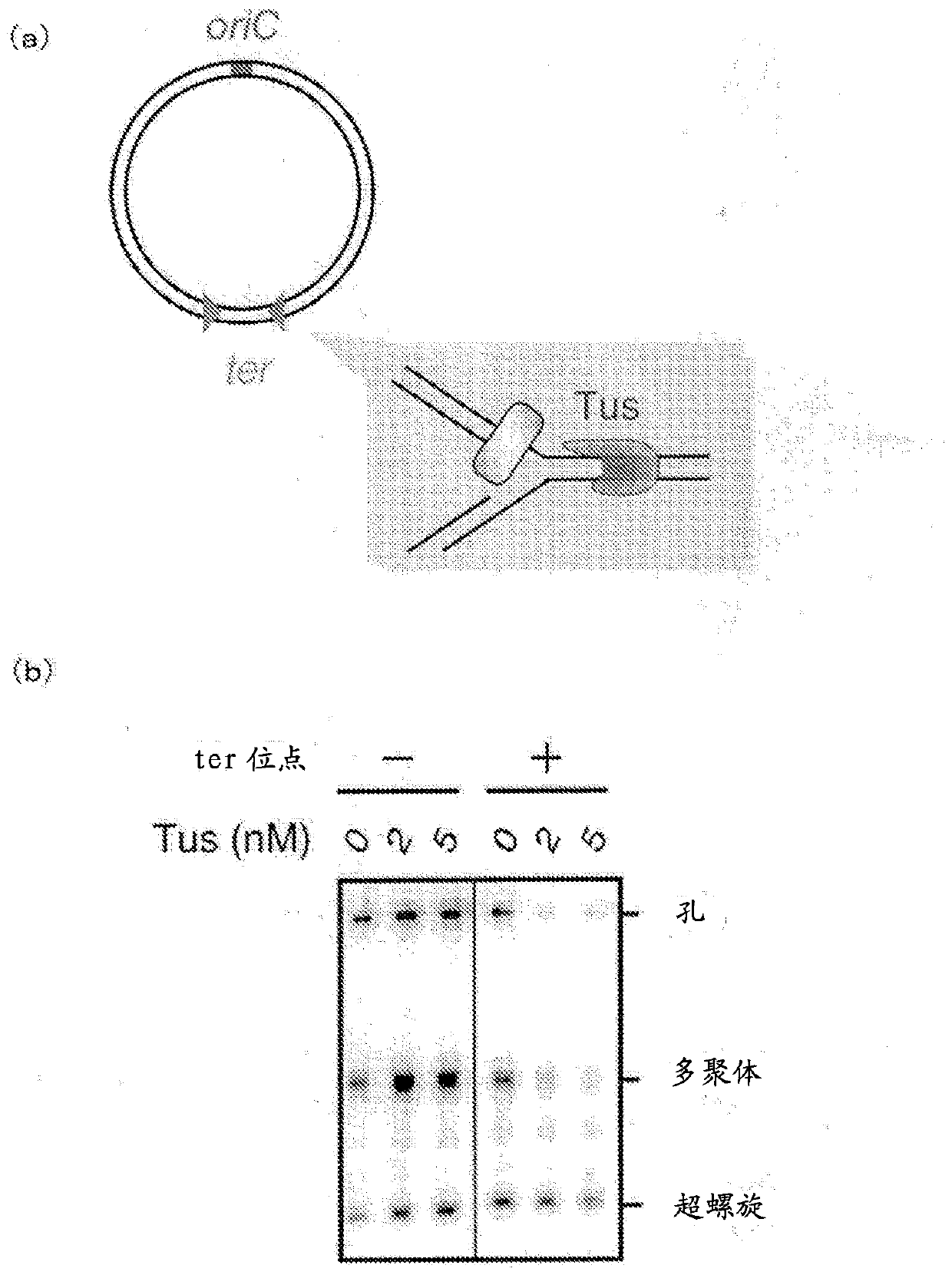
[0267] Example 1: Replication of circular DNA accompanied by DNA multimer inhibition using terminator sequence ter and Tus protein
[0268]
[0269] The circular DNA used as a template is prepared as follows. Insert the oriC fragment into the M13mp18 plasmid vector to make an 8.0kb circular DNA. Insert a DNA fragment ((5’-ACTT) containing two opposing ter sequences (underlined) into the region on the opposite side of oriC in the 8.0kb circular DNA TAGTTACAACATAC TTATT-N 176 -AATAA GTATGTTGTAACTA AAGT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 26)), made into 8.0kb circular DNA with ter inserted ( image 3 (A)). The 8.0 kb circular DNA inserted with ter was used as the template DNA, and the 8.0 kb circular DNA was used as the control DNA without ter sequence.
[0270] Tus is produced and prepared from the E. coli expression strain of Tus through a process including affinity column chromatography and gel filtration column chromatography.
[0271] A reaction solution having the composition shown in Table 1 an...
Embodiment 2
[0291] Example 2: Circular DNA with DNA multimer inhibition using site-specific recombination sequences dif and XerCD copy
[0292]
[0293] The dif sequence (SEQ ID NO: 22) is contained in the region on the opposite side of oriC of the circular DNA, and a 12 kb circular DNA with dif inserted as a template ( Figure 4 (A)). Specifically, using Escherichia coli expressing the recombinant proteome of lambda phage, a cassette containing oriC and kanamycin resistance genes and the 4.2 kb region and downstream of the dif upstream side of the chromosome of Escherichia coli were prepared by intracellular recombination reaction. A circular DNA with a target length of 6.0 kb on the side.
[0294] As a control DNA without dif sequence, the 8.0 kb circular DNA described in Example 1 was used.
[0295] XerCD is purified and prepared from the E. coli co-expression strain of XerC and XerD through a process including ammonium sulfate precipitation and affinity column chromatography.
[0296] The ...
Embodiment 3
[0301] Example 3: The influence of the position of ter sequence or dif sequence in circular DNA In Examples 1 and 2, the template DNA was prepared in such a way that the ter sequence or the dif sequence was located in the region on the opposite side of oriC in the circular DNA. In Example 3, a replication / amplification reaction was performed on circular DNA in which the ter sequence or the dif sequence was arranged near or adjacent to oriC.
[0302]
[0303] In order to construct a 15kb circular DNA, the E. coli genome was used as a template to amplify and prepare a 15kb DNA fragment without oriC.
[0304] As the circular DNA in which the ter sequence was arranged in the vicinity of oriC, a 15kb-ori-ter circular DNA was prepared as follows. The ori-ter cassette was connected to the 15 kb DNA fragment described above and circularized to produce ( Figure 5 ). The sequence of the ori-ter box (0.38 kb) is as follows, with ter sequences (underlined) outward at both ends of the oriC b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com