Novel biomarkers for non-invasive identification/warning of fatty liver in dairy cows
A biomarker, fatty liver disease technology, applied in the fields of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine, can solve problems such as unfavorable animal welfare, poor prognosis and complicated infectious diseases, and achieve the effect of high diagnostic application value, low cost and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
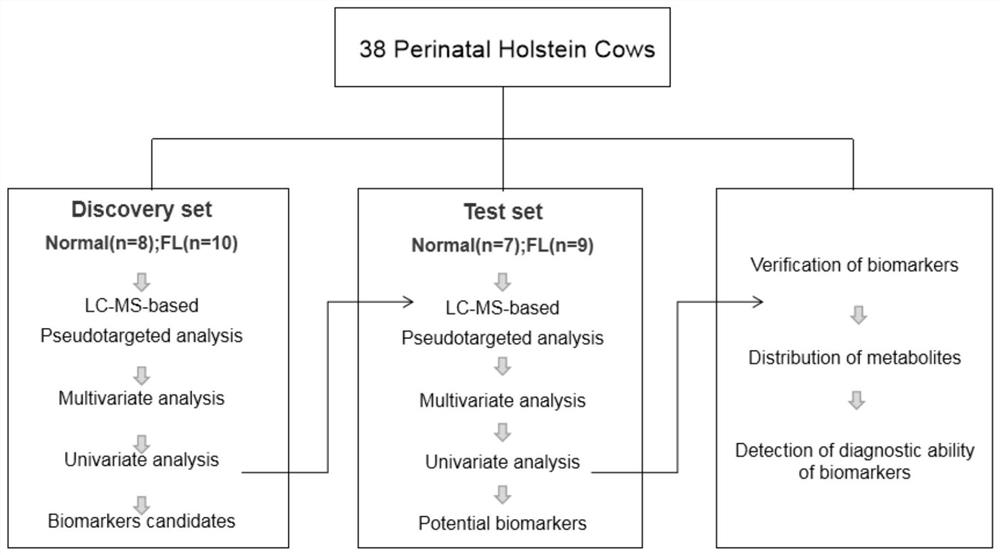
[0057] Example 1: Screening and Discovery of Candidate Markers - Screening and Discovery of Differential Metabolite Markers in a Liver Biopsy Diagnostic Population
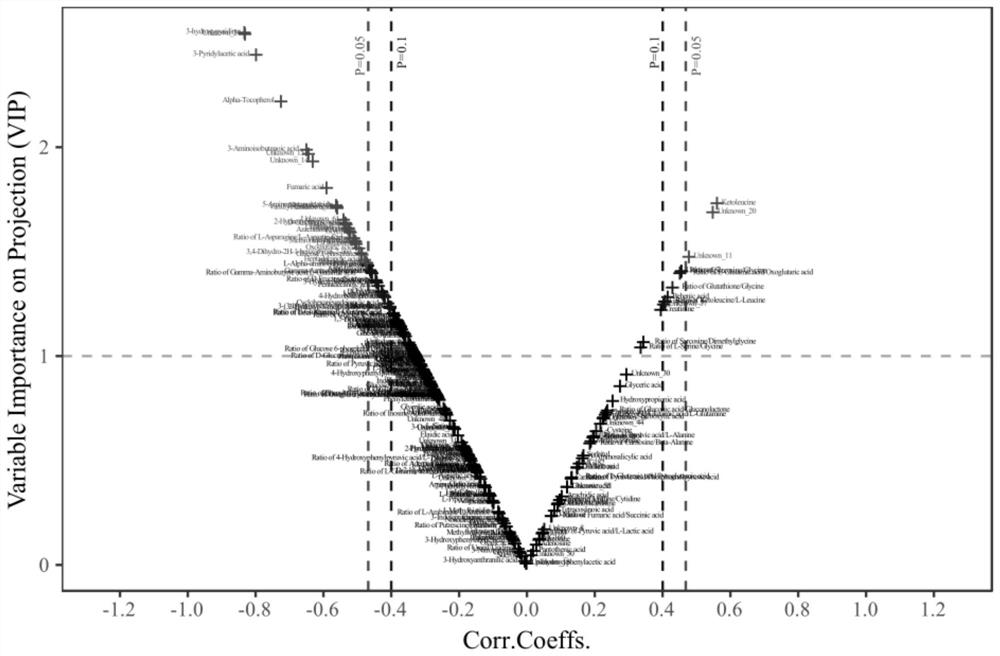
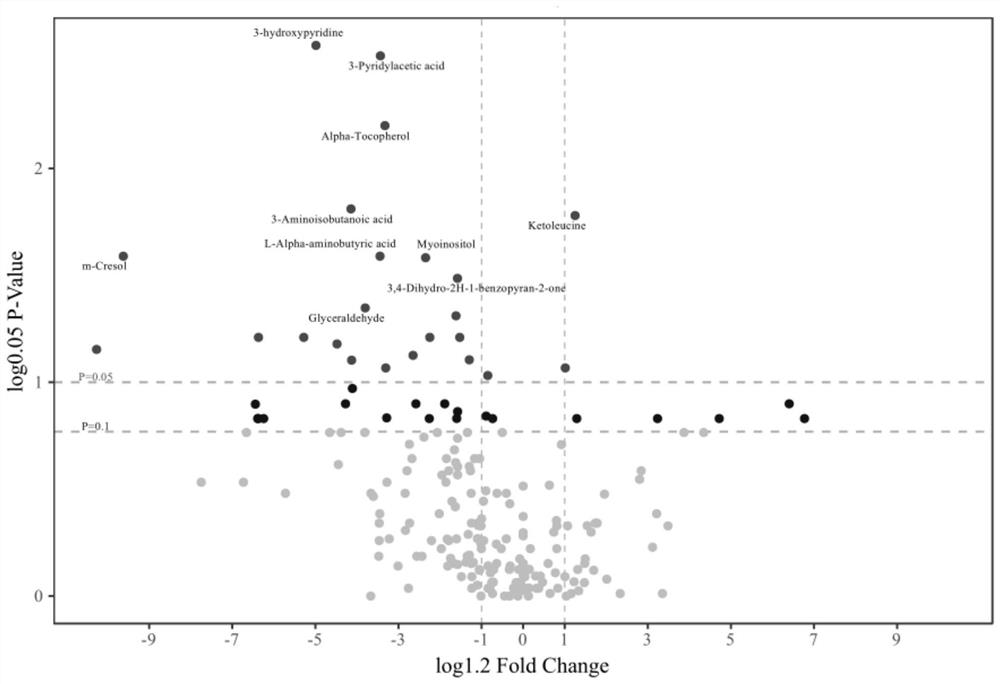
[0058] First, 18 dairy cows were selected as the Discovery set, and were divided into normal group (n=8) and diseased group (n=10) through liver tissue biopsy. The feces and urine of dairy cows were collected, and detected by mass spectrometry Differential distribution of molecular metabolites in normal and diseased groups. The model detection of metabolites showed that the distribution of differences between the two groups was significant, and the model was reliable. Differential markers were screened by two statistical analysis methods: VIP (Variable importance in projection) multidimensional test, with VIP>1 and P figure 2 ); single-dimensional T test, with P image 3 ), take the intersection of the candidate markers screened by the two methods ( Figure 4 ), and finally get the candidate difference markers of ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2: Screening of potential biomarkers - verification of differential expression of candidate markers in other groups of individuals
[0060] Select 16 dairy cows as the Test set, the purpose is to verify the candidate differential markers of the Discovery set through an independent sample group; through the results of traditional clinical serum indicators, B-ultrasound fluoroscopy and comprehensive veterinary diagnosis, it is divided into suspected Normal group (n=7) and suspected disease group (n=9), collect feces and urine, according to the method identical with embodiment 1:: VIP (Variable importance in projection) multidimensional test ( Figure 5 ), one-dimensional T-test ( Image 6 ), take the intersection of the candidate markers screened by the two methods ( Figure 7 ) for mass spectrometry detection of small molecule metabolites, statistical analysis, and finally screened out the candidate differential markers of the Test set.
[0061] Compare the can...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3: Validation of identification capability of 3 potential biomarkers - violin plot and ROC curve.
[0067] The violin plot shows ( Figure 8 ), compared with normal cows, L-Alpha-aminobutyric acid in feces and 3-Nitrotyrosine in urine were significantly down-regulated, while Behenic acid in feces was significantly up-regulated. ROC curve analysis shows that (such as Figure 9-Figure 11 ), the AUC value of each marker is higher than that of traditional clinical biochemical indicators, and has higher clinical diagnostic application value; moreover, the combined diagnostic results of the three fecal and urinary biomarkers show higher diagnostic application value ( The AUC value can reach 0.988, Table 2).
[0068] In the application of dairy farming, by detecting the relative content of these three biomarkers in cow feces or urine, dairy cows with potential fatty liver disease can be identified and detected. This biomarker provides a new technology and method for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com