Rice salt-tolerant QTL, positioning method, molecular marker and application thereof
A technology of molecular marker and positioning method, applied in the field of genetic engineering of genetic crops, can solve the problems of being easily affected by the environment and genetic background, and difficult to identify.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1F2
[0030] Example 1 F2 population salt stress phenotype identification
[0031] Zhenshan 97 is more sensitive to salt damage, while Haidao 86 is more salt-tolerant. The F2 population was obtained by crossing Haidao 86 and Zhenshan 97: Zhenshan 97 / Haidao 86F2 (300 individual plants).
[0032] In the summer of 2017, the F2 single plant was first planted in the rice experimental field of Huazhong Agricultural University by transplanting. At the peak tillering stage of the plant, 6 tillers of relatively uniform size were separated from each individual plant, 3 of which were planted in the field for taking leaf samples and subsequent collection of inbreds, and the other 3 were planted individually in potted blue barrels (barrel depth 30cm, upper mouth diameter 20cm) to do the stress test. Salt stress was started when the transplanted tillers resumed growth and before heading.
[0033] The salt stress was carried out three times, and the specific stress time and detection time of th...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Construction of Example 2 Genetic Linkage Map
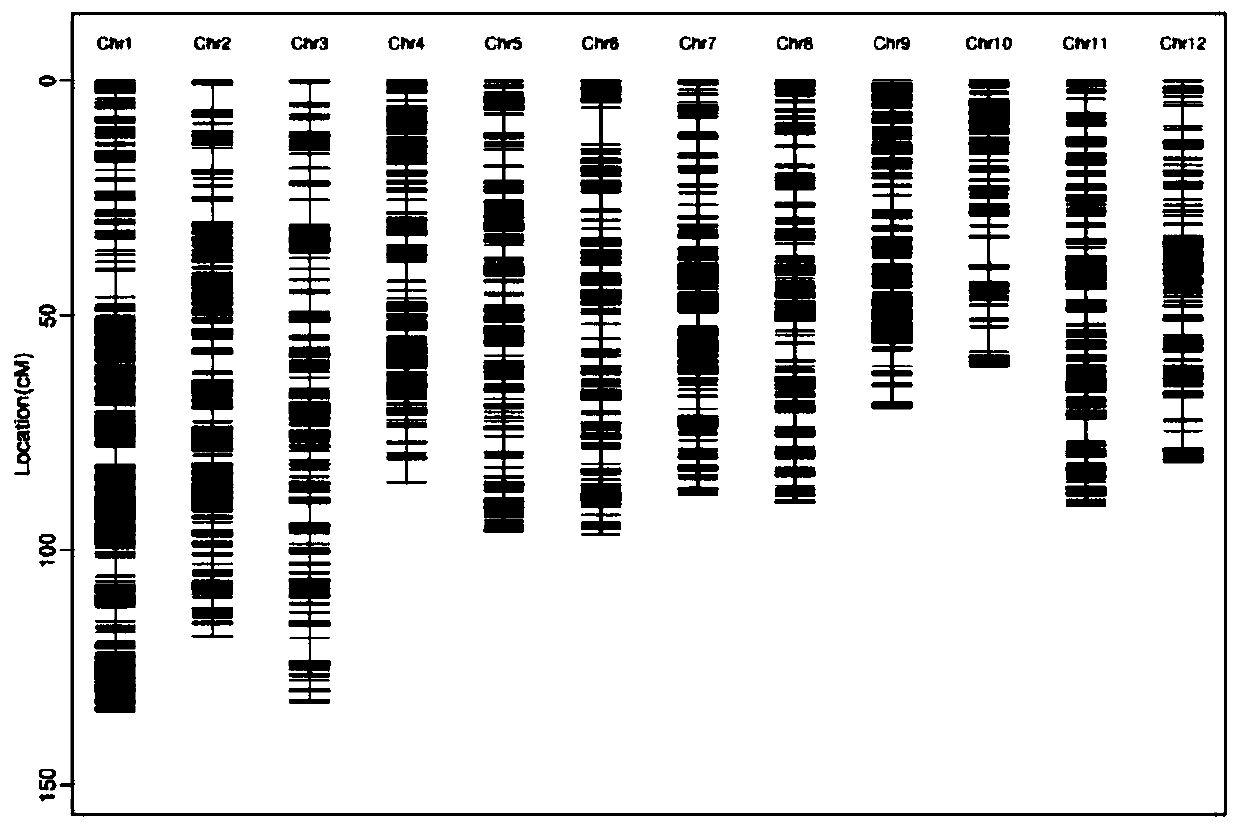
[0041] The construction of the genetic map was completed by the sequencing company GENOSEQ. The main process includes the preparation of test materials (rice leaves), library construction and sequencing, variation detection and construction of genetic linkage maps. That is to use the ddRAD seq (double digested restrict-site associated DNA sequencing) technology based on the next-generation sequencing platform to resequence 500 individuals from the F2 population. The data obtained from the resequencing were compared to the Nipponbare reference genome (MSU7.0) for variation detection (including SNP and InDel). Using WinQTLCart 2.5 to scan QTLs for salt tolerance and analyze genetic effects. The genotype data and phenotype data were imported into the analysis software WinQTLCart 2.5, the Kosambi mapping function and the composite interval mapping (CIM) mapping method were selected, the walk speed was set to 0.5cM, and the th...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 Salt tolerance phenotype analysis and QTL mapping based on F2 population
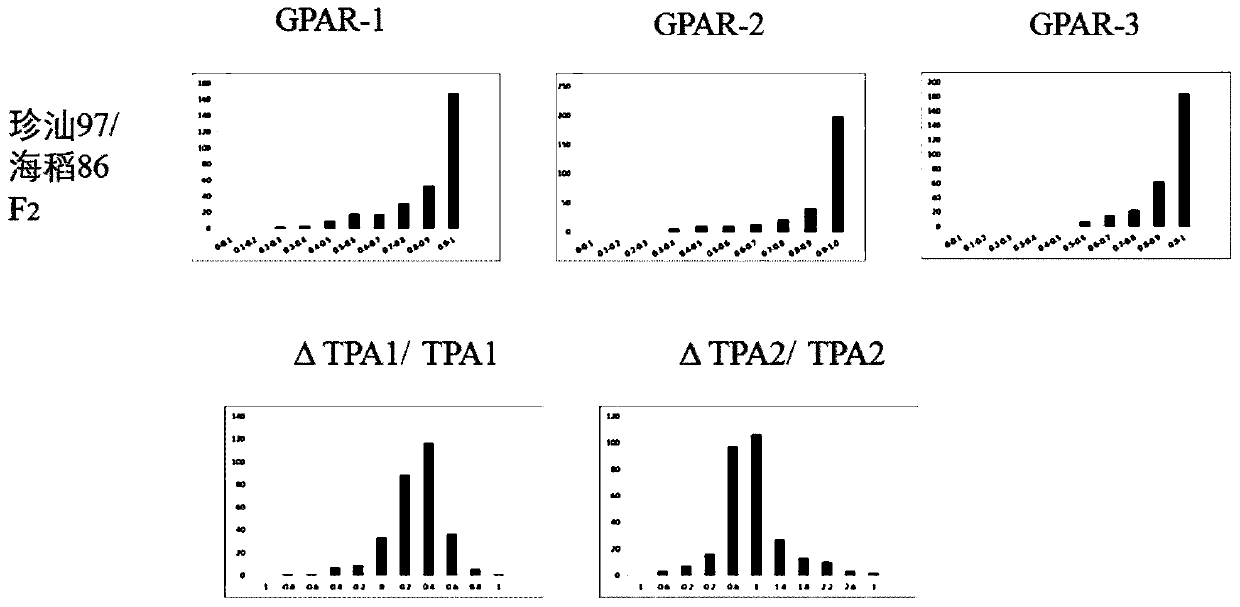
[0048] A single F2 plant is divided into three rice stalks of the same size and growth, which is equivalent to three repetitions. Image traits GPAR and manual rating can be directly used to evaluate salt tolerance, and ΔTPA / TPA can reflect plant growth rate. The frequency distribution of GPAR and ΔTPA / TPA obtained by three phenotype photographs is as follows: figure 1 shown. The GPAR values in the two F2 populations were skewed, and both showed a trend that the greater the GPAR value, the greater the frequency, and the values of most plants were between 0.9-1. ΔTPA / TPA presents a skewed normal distribution.
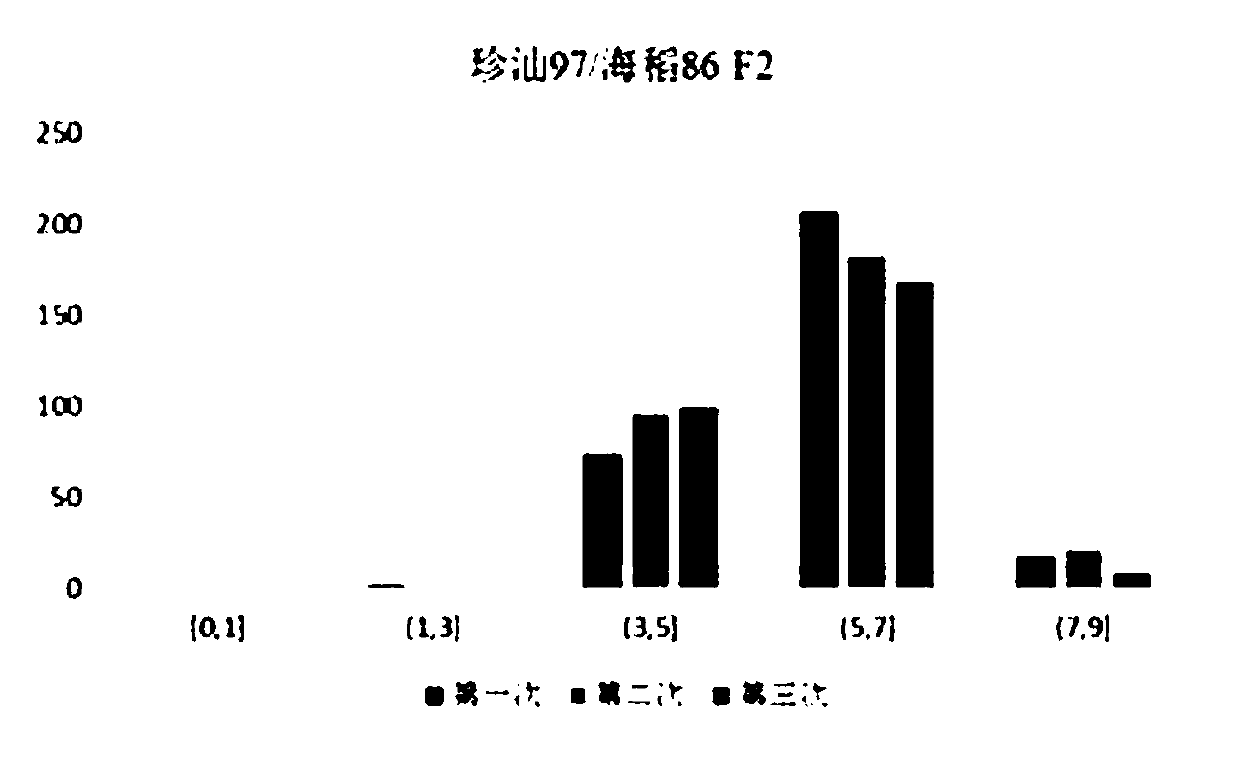
[0049] In order to reduce human error, the first one of each F2 picture was selected and scored independently by two persons, and the average value was taken as the score of salt damage rating. as follows figure 2 Shown are the frequency distributions of three artificial ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com