Patents
Literature
169 results about "Genetic linkage map" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diffusion tensor imaging white matter fiber clustering method
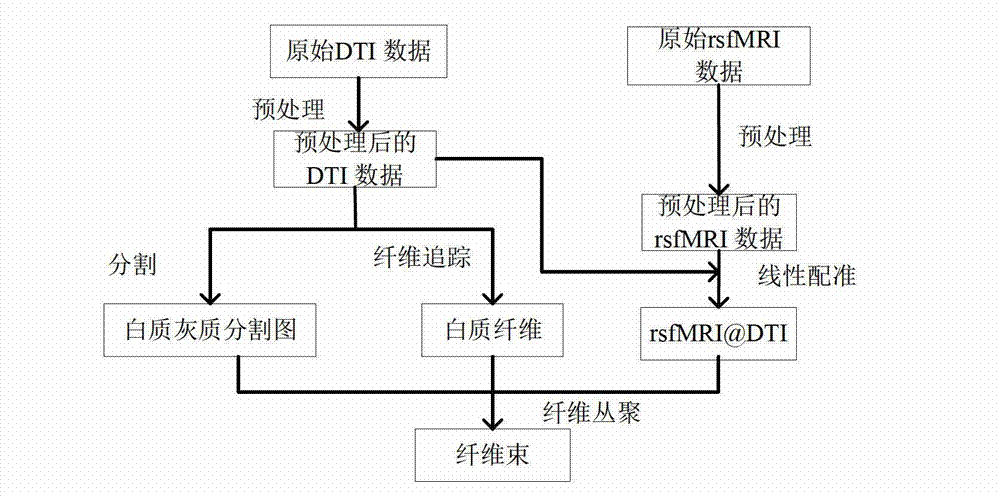
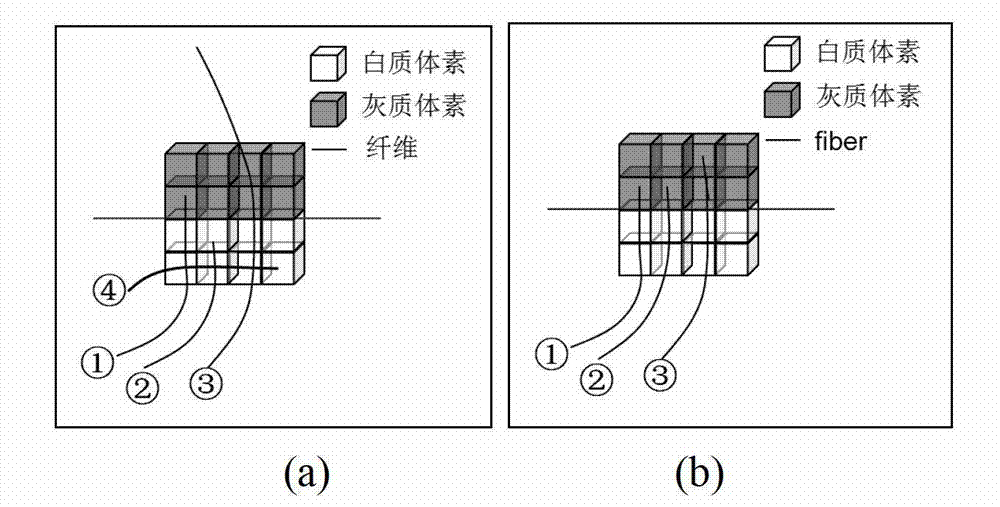
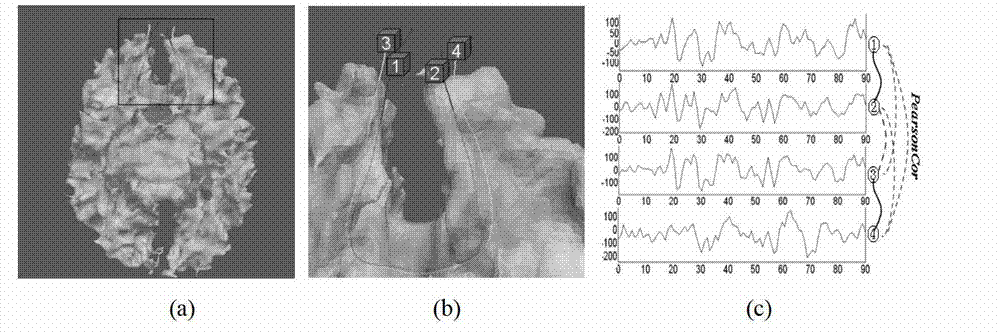
The invention provides a diffusion tensor imaging white matter fiber clustering method. The method includes the steps of pre-processing original rsf magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data and the original diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) data, registering the pre-processed rsf MRI data into a DTI space, respectively conducting fiber tracking and brain tissue segmentation on the pre-processed DTI data, conducting fiber projection on white matter fiber which can not reach grey matter or exceed a grey matter surface in a white matter fiber obtained by DTI, then calculating functional similarities among the white matter fiber, obtaining a matrix of the similarities and clustering by adopting an affine spread clustering algorithm. Fiber bundle has functional independence, accuracy without need to relay on of a genetic linkage map and require complicated registration.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
SSR molecular marker primer based on transcriptome data of azalea as well as screening method and application of SSR molecular marker primer
InactiveCN105969767AAvoid it happening againEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenetic diversity
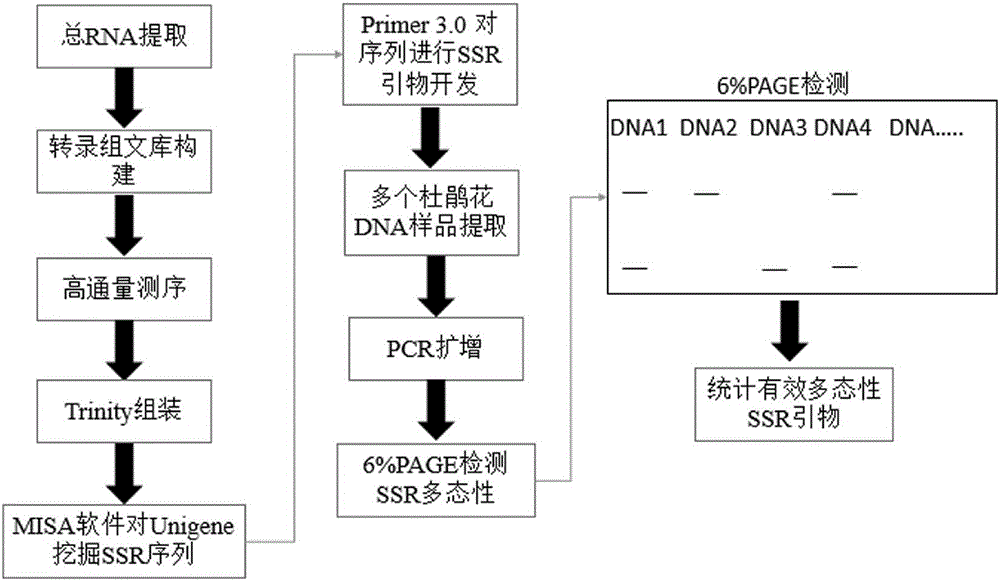
The invention discloses an SSR molecular marker primer based on transcriptome data development and specific application of the SSR molecular marker primer, belonging to the technical field of biology. The primer is obtained based on development of a transcriptome sequence. By virtue of primer designs of carrying out batch screening on lots of sequencing data based on transcriptome sequencing to obtain an SSR sequence and carrying out SSR marking, the obstacles that the SSR molecular markers of the azalea are few, the development efficiency is low, and the like are overcome. The validity of the SSR primer is verified by virtue of different varieties of azaleas, and foundation is laid for the research of genetic diversity of the azaleas, the constitution of genetic linkage maps, the assistant breeding of the molecular marker, and the like.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV
Molecular marker for assisted selective breeding of upland cotton with greensickness resistant traits
InactiveCN102080080AReduce workloadEnsure consistencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
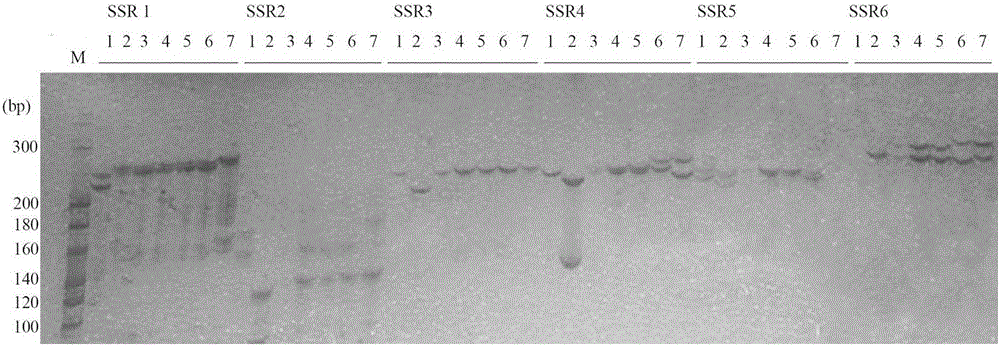
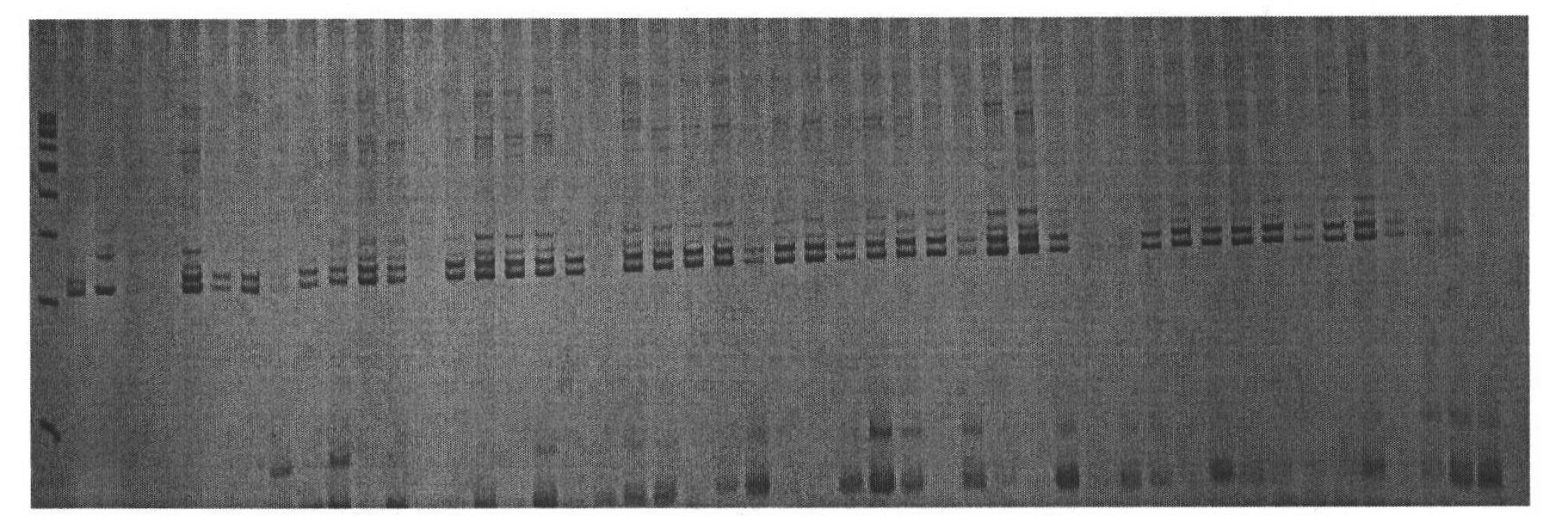
The invention relates to a molecular marker for assisted selective breeding of upland cotton with greensickness resistant traits, belonging to the technical field of genetic breeding of cotton. Three SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) markers for assisted selective breeding of the upland cotton resisting greensickness can be obtained by constructing a molecular marker genetic linkage map in upland cotton seeds to carry out QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) positioning on the greensickness resistant traits and selecting remarkable SSR markers entering a linkage group section and the SSR makers linked with disease-resistant QTLs to screen different upland cotton plant systems. The three markers comprise marker primers and a primer combination and are suitable for greensickness-resistant molecular marker-assisted selective breeding of the upland cotton. The plant systems resisting the greensickness can be obtained by using the obtained molecular marker to carry out greensickness-resistant molecular marker-assisted selection on different upland cotton plant systems.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker closely linked with oil content character of rapes and application
ActiveCN102766627AQuick filterIncrease costMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceMarker-assisted selection
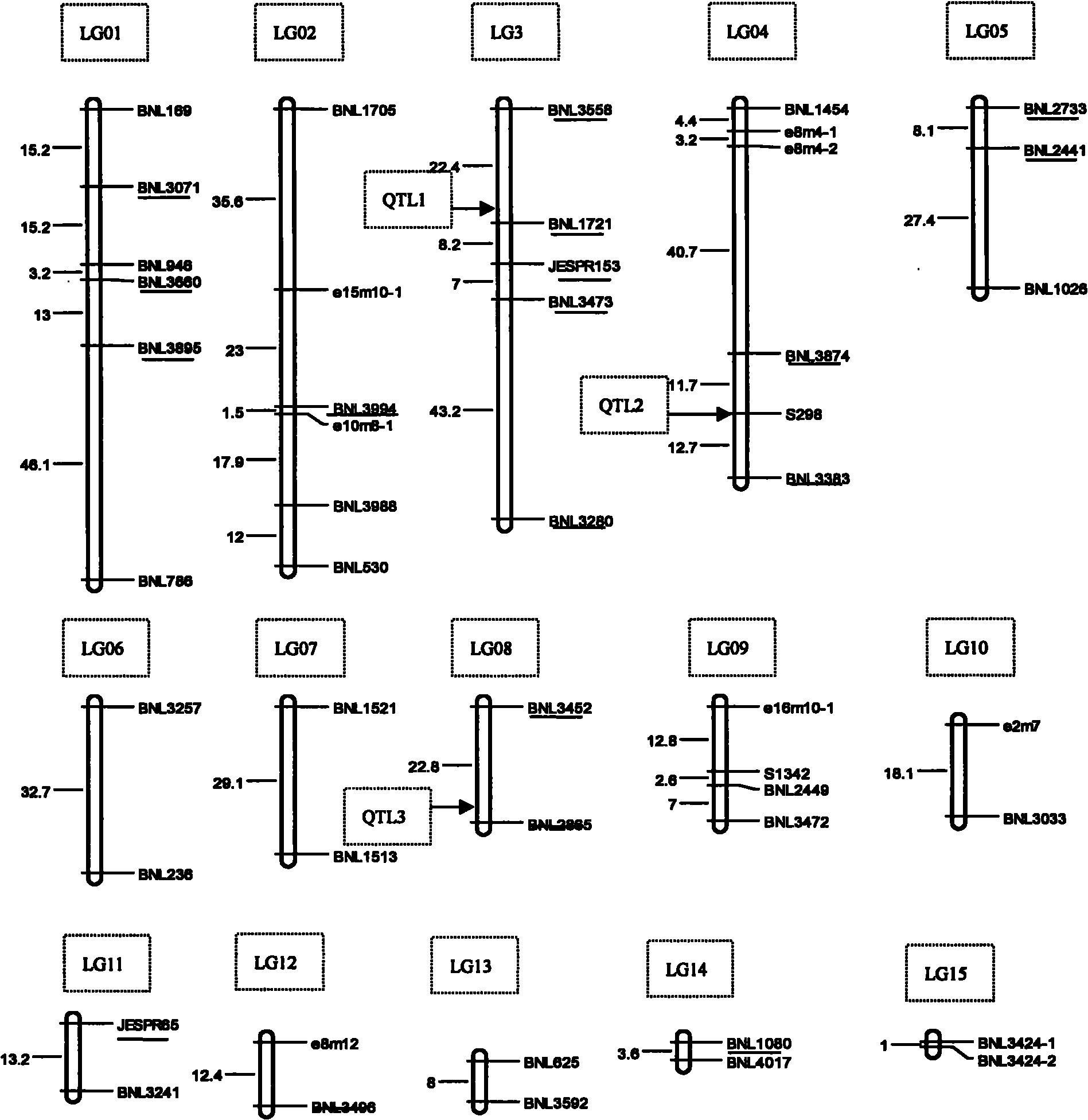
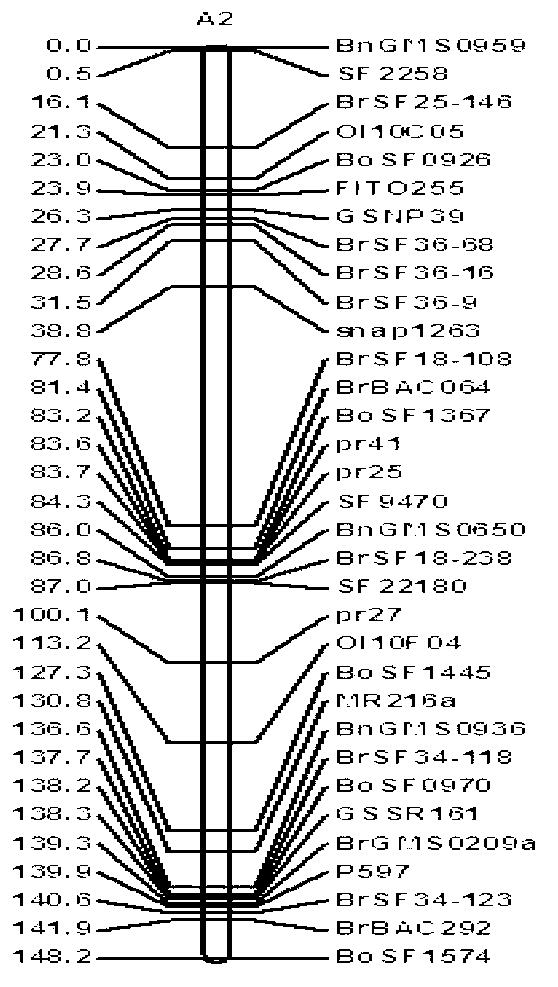
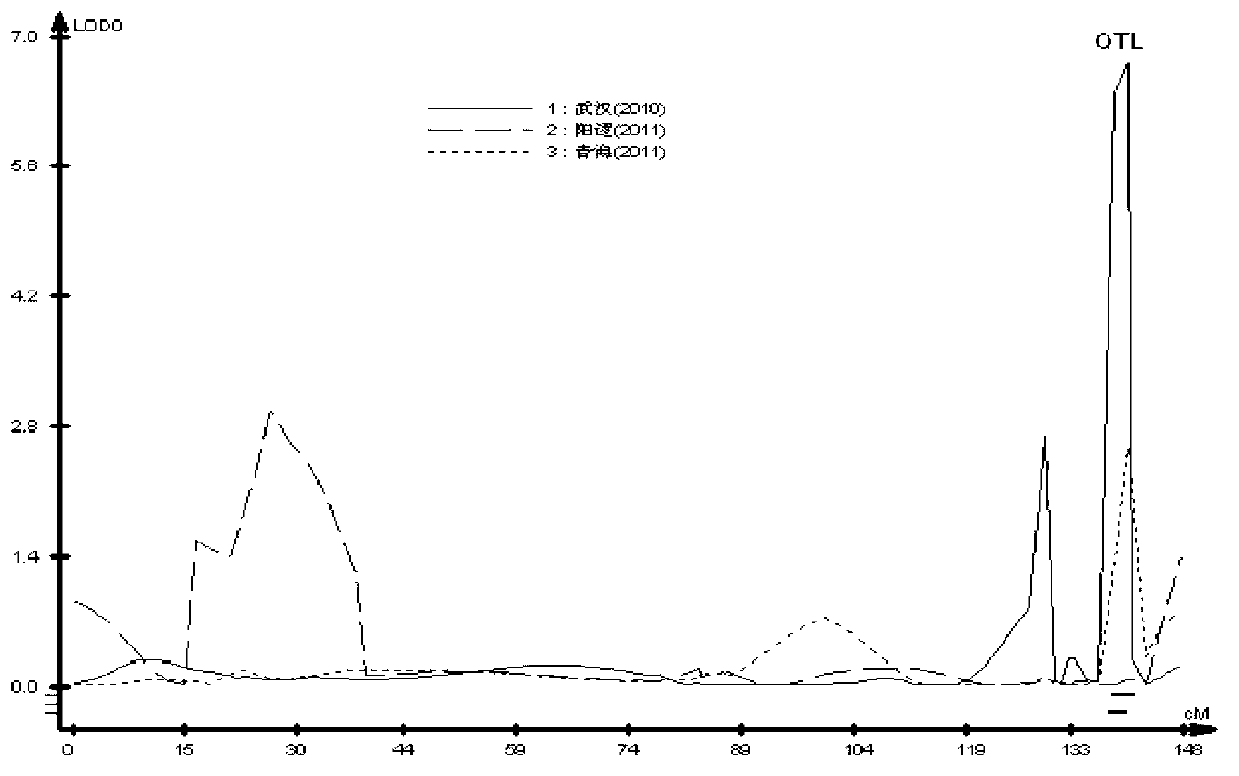
The invention discloses a molecular marker closely linked with an oil content character of the rapes and an application of the molecular marker. The molecular marker BrSF34-123 closely linked with the oil content character of the rapes comprises the following screening steps: 1) hybridizing a cabbage type rape variety zy036 and 51070 so as to obtain a DH generation segregation population; 2) designing a primer to polymorphically screen a parent, and establishing a genetic linkage map; 3) carrying out an field experiment and harvesting for the DH generation segregation population to obtain a phenome database of the oil content; and 4) carrying out QTL (quantitative trait locus) detection by combining the genetic linkage map of the developed high-density molecular marker with a genotype of the segregation population and the phenome database of the oil content to obtain the molecular marker closely linked with the oil content character of rapes. Therefore, the marker is utilized to be conducted for marker-assisted selection, thereby being capable of quickly screening the strains with high oil content for breeding the oil content of the rapes, being definite in breeding selection target and saving cost.
Owner:武汉中油种业科技有限公司
Prepn process and application of sea island cotton EST SSR marker
The present invention belongs to the field of cotton breeding technology, and is especially the preparing technology of sea island cotton EST-SSR primer sequence and its application in cotton genetic diversity evaluation, molecular genetic linkage construction and TQL location of important cotton characters. The preparation process includes the following steps: establishing cDNA library of sea island cotton strain Pima3-79 fiber development and selecting EST of partial bases; designing SSR lateral wing primer; taking total DNA with plant leaf; amplifying with the designed primer; calculating the polymorphism information content of each pair of primers and performing cluster and main coordinate analysis of taken total DNA; and integrating the amplified EST-SSR to corresponding linkage group and performing TQL location of important cotton characters. The preparation results are also given.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker for single fruit weight main-effect quantitative trait loci (QTL) of Dangshansu pear fruit and application thereof
ActiveCN102140455AHigh contribution rateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPEARAgricultural science
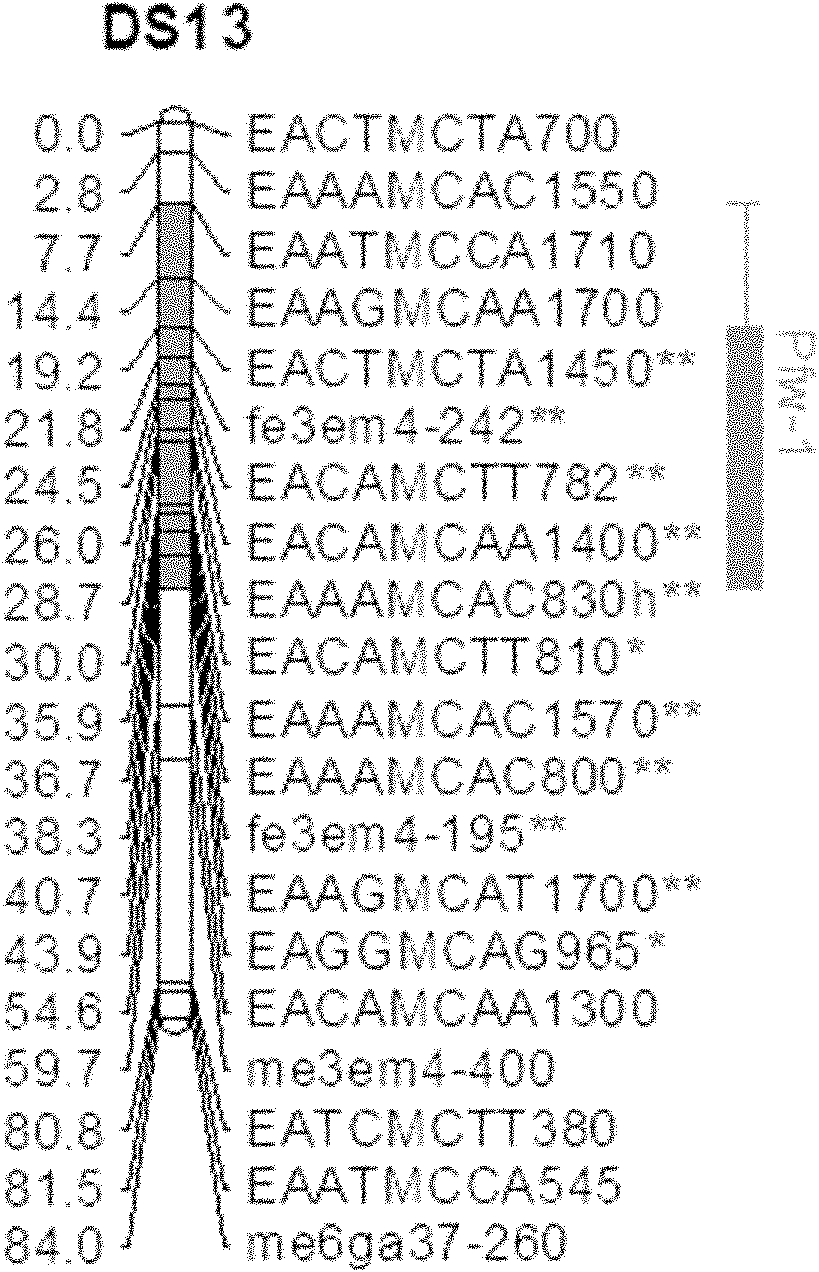
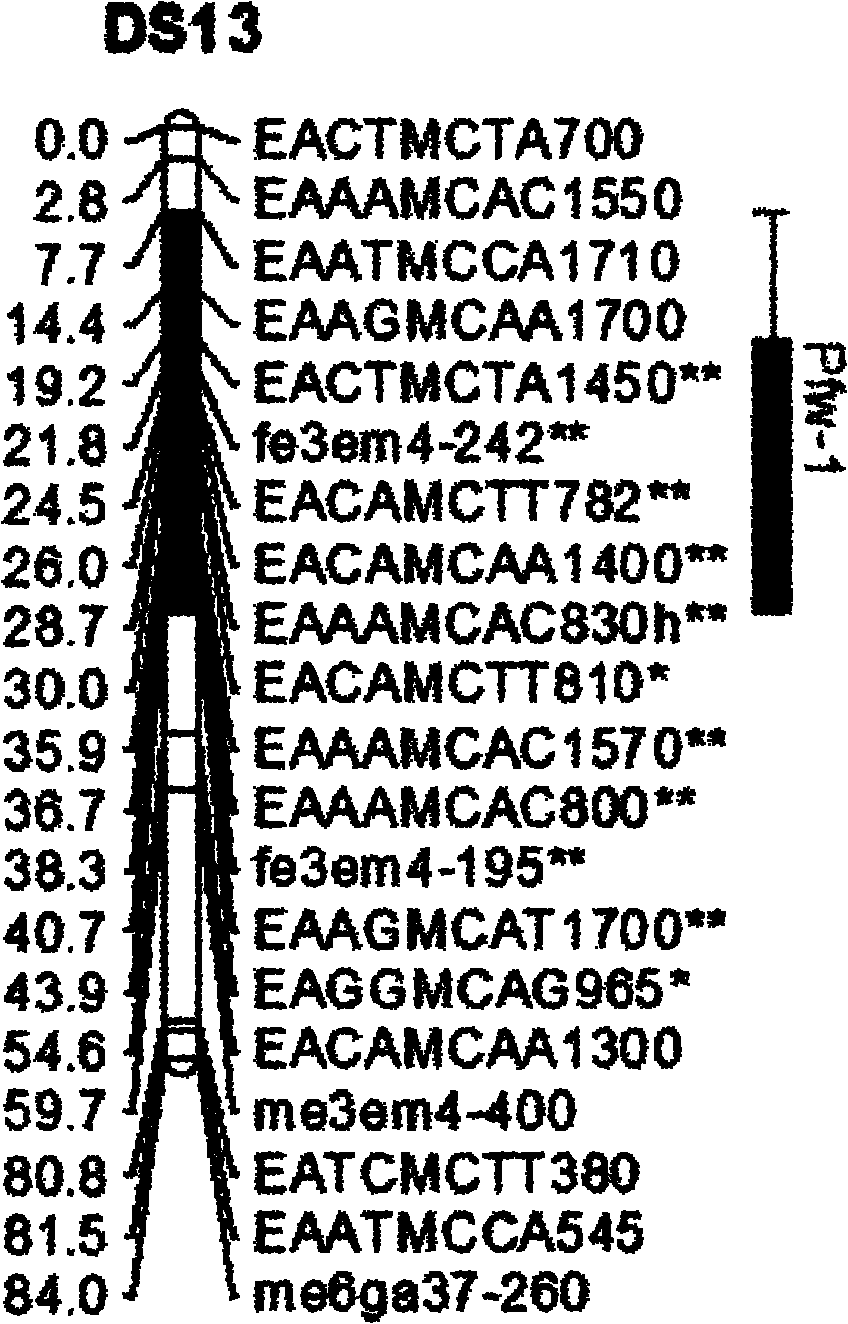
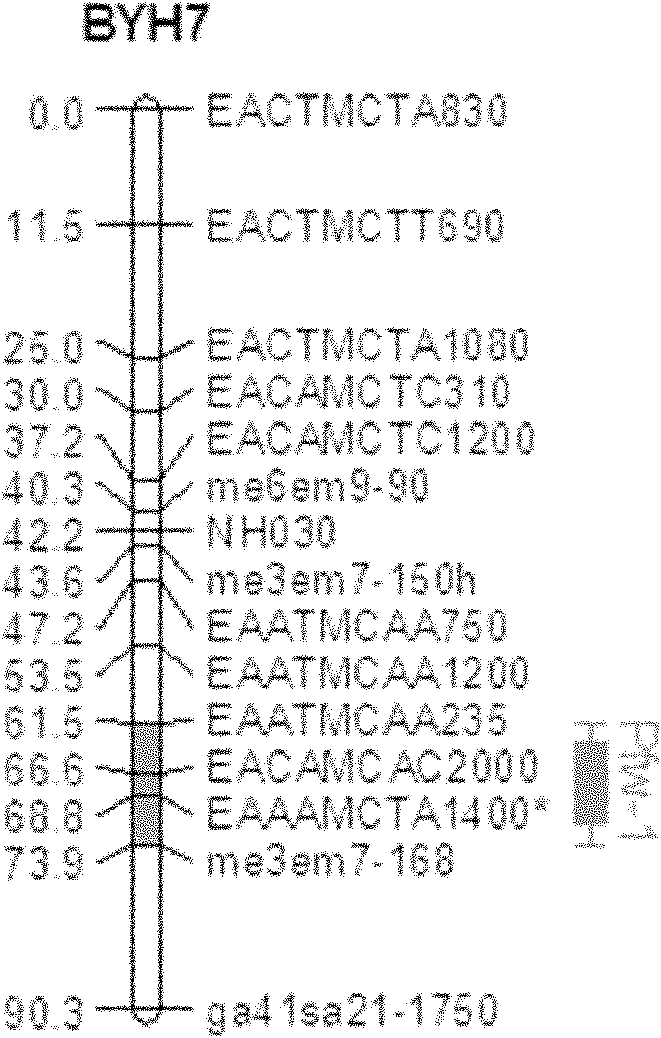
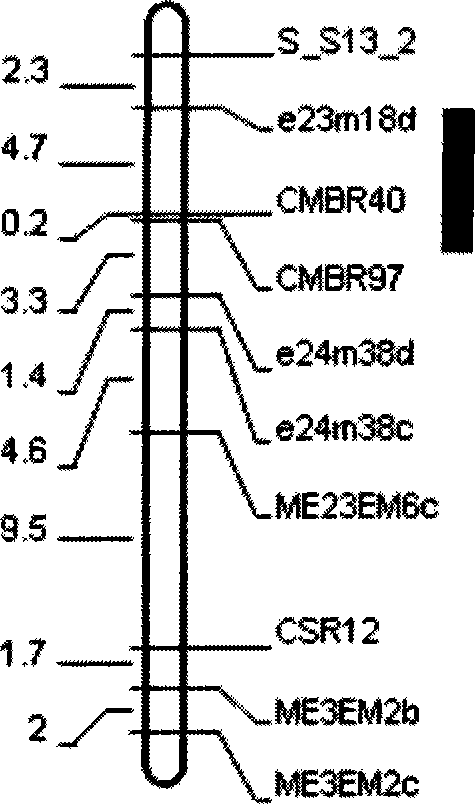
The invention belongs to the field of inheritance breeding, and relates to a molecular marker for a single fruit weight main-effect quantitative trait loci (QTL) of Dangshansu pear fruit and application thereof. A genetic linkage map of Dangshansu pear is constructed by utilizing sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), simple sequence repeats (SSR) and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP), phenotypic identification on the single fruit weight of the fruit is combined, a group is analyzed through interval mapping, the presence of the main-effect QTL is detected on the 13th linkage group of the Dangshansu pear, and the 48.8 percent of single fruit weight can be interpreted. A molecule closest to the main-effect QTL Pfw-1 is marked as fe3em4-242p* and the distance is 0cM. The obtained molecular marker for the single fruit weight main-effect QTL has important theoretical and practical guidance significance for quickening the genetic improvement progress of pear varieties and improving breeding selection efficiency.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for establishing microsatellite molecular marker of scylla paramamosain
InactiveCN101886070AEasy to operateImprove the efficiency of constructing microsatellite markersMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSequence analysisEnzyme digestion
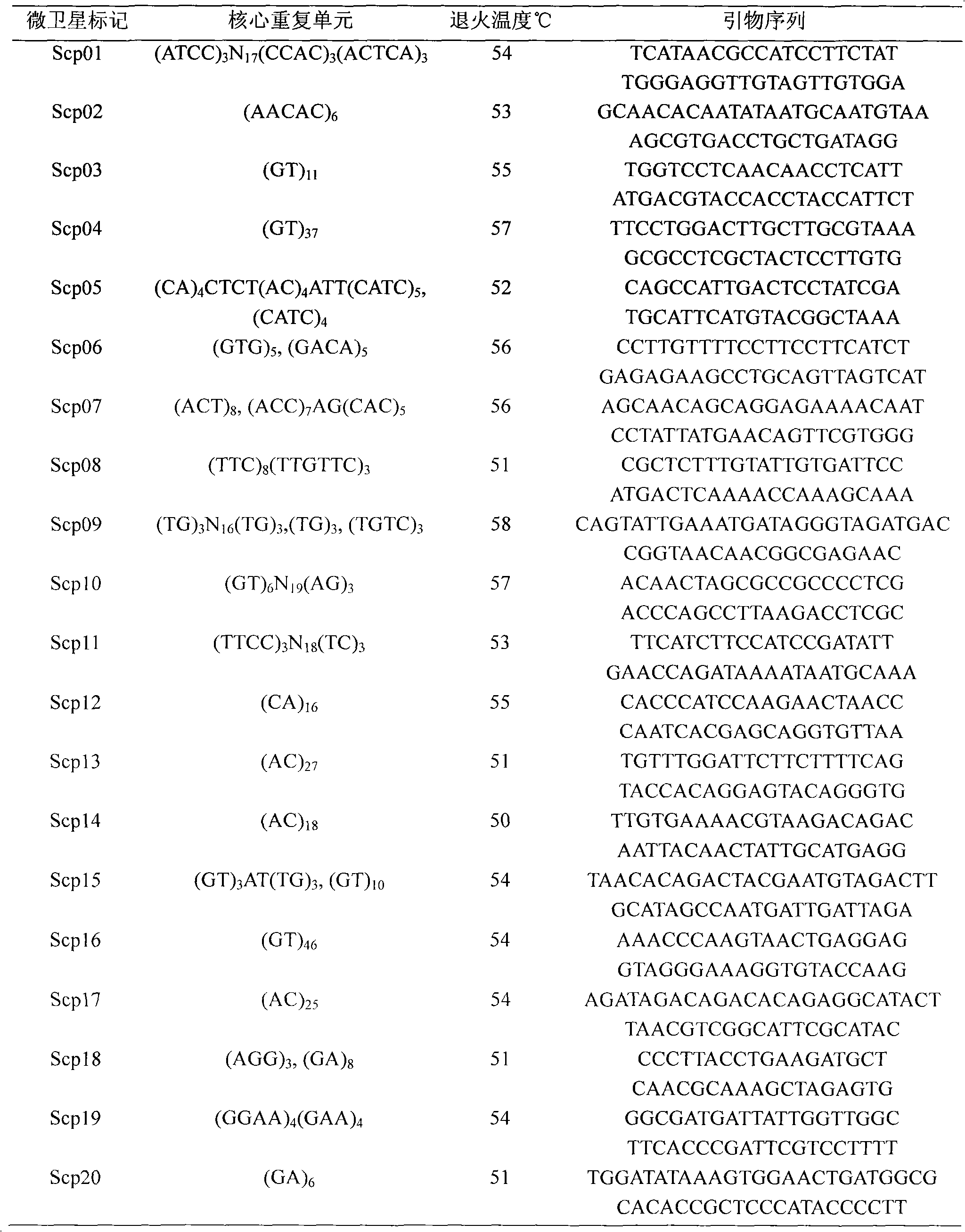
The invention relates to a method for establishing a microsatellite molecular marker of scylla paramamosain. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting genome DNA of the scylla paramamosain; performing enzyme digestion on the genome DNA, jointing and pre-amplifying; hybridizing an amplification product, a probe and a magnetic bead and performing secondary PCR amplification; cloning and sequencing the amplification product; analyzing the sequence and designing a microsatellite specific primer; performing PCR amplification on the genome DNA of different geographic groups or individuals in the group; and performing 6 percent modified polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to detect the PCR amplification product so as to obtain a polymorphic map of genetic variation of the scylla paramamosain. The method has a good application prospect in the fields such as genetic variation analysis of the scylla paramamosain, germplasm resource protection and management, genetic linkage map establishment, marker-assisted breeding and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Cucumber powdery mildew resistance main effect QTL compact linkage molecule labeling method and applying method
InactiveCN101240342AReduce manpowerReduce the waste of equipment and material resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyEarly generation
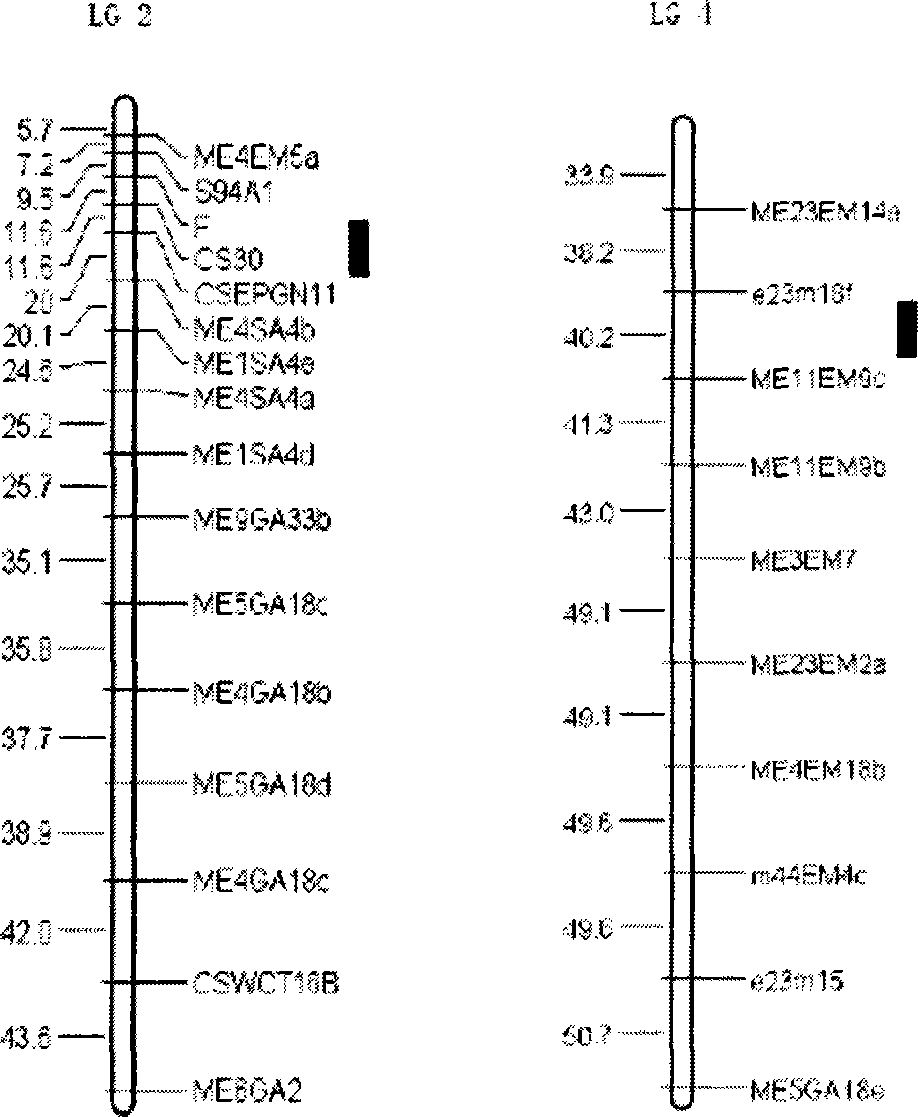
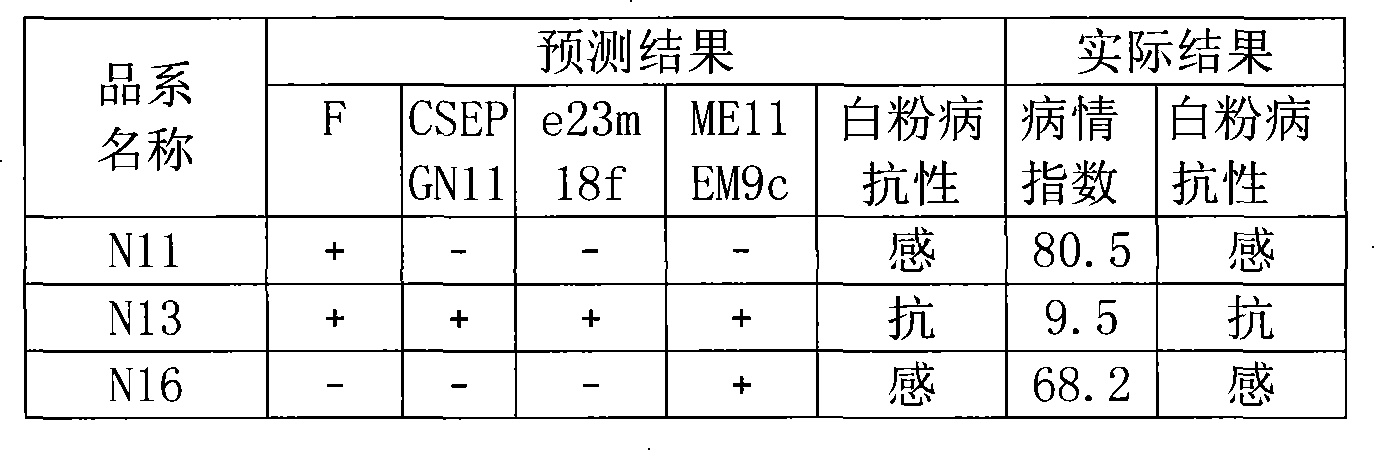
The present invention relates to a molecular marker method closely linked with major QTL for powdery mildew of cucumber resistance, belonging to the field of biological technology. The invention comprises the following steps: hybridizing susceptible variety S94 of powdery mildew of cucumber with susceptible variety S06 of powdery mildew of cucumber, getting hybrid F1; acquiring F7 generation recombinant inbred lines by filial generation single seed descent method; separating DNA of individual cucumber leaves and performing PCR amplification; analyzing data and constructing cucumber genetic linkage map for molecular marker; applying to statistical analysis and QTL location; and determining molecular markers F, CSEPGN11, e23m18f and ME11EM9c linked with major QTL for resistance source S06 powdery mildew. The coincidence rate between the identification result of the invention and the field resistance has improved from 94 percent to 100 percent. By the molecular markers linked with major QTL for resistance source S06 powdery mildew, progeny and derived varieties thereof for the specific resistant source can be selected in early generation seedling without the influence of environment condition, saving cost and improving breeding and selection efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for screening and detecting single-nucleotide polymorphic site G642A of marsupenaeus japonicus
InactiveCN104611460AEasy to identifyEasy constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenotyping
The invention discloses a method for screening and detecting a single-nucleotide polymorphic site G642A of marsupenaeus japonicus, and relates to the marsupenaeus japonicas. A specific primer is designed by a PAMSA method, so that verification and genotyping of a single-nucleotide polymorphic mark of the marsupenaeus japonicas can be conveniently and quickly performed through polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; the method has the advantages of low screening and detecting expense, high simplicity, convenience and quickness in operation and the like; by the method, parentage determination of the marsupenaeus japonicas, establishment of a genetic linkage map, and other researches are facilitated; under the condition that information of the single-nucleotide polymorphic site of a genome DNA of the marsupenaeus japonicas is unknown, through transcriptome mixed sample sequencing, and by virtue of bioinformatic analysis, the single-nucleotide polymorphic site G642A is screened; the specific primer is designed by the PAMSA method, so that the single-nucleotide polymorphic site G642A of the marsupenaeus japonicas can be conveniently and quickly detected, verified and genotyped through the polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the screening and detecting expense is low and the operation is simple, convenient and quick.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
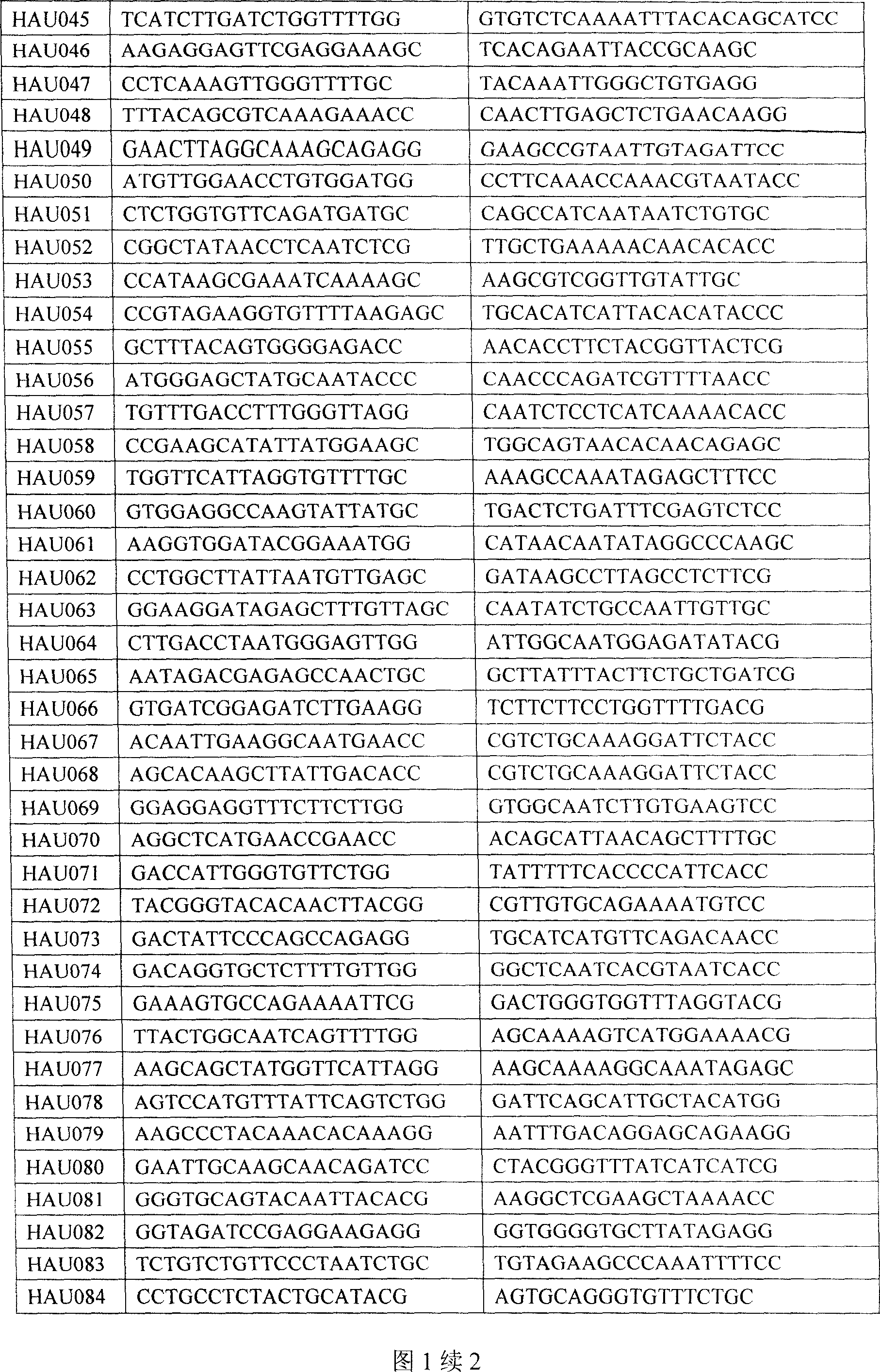
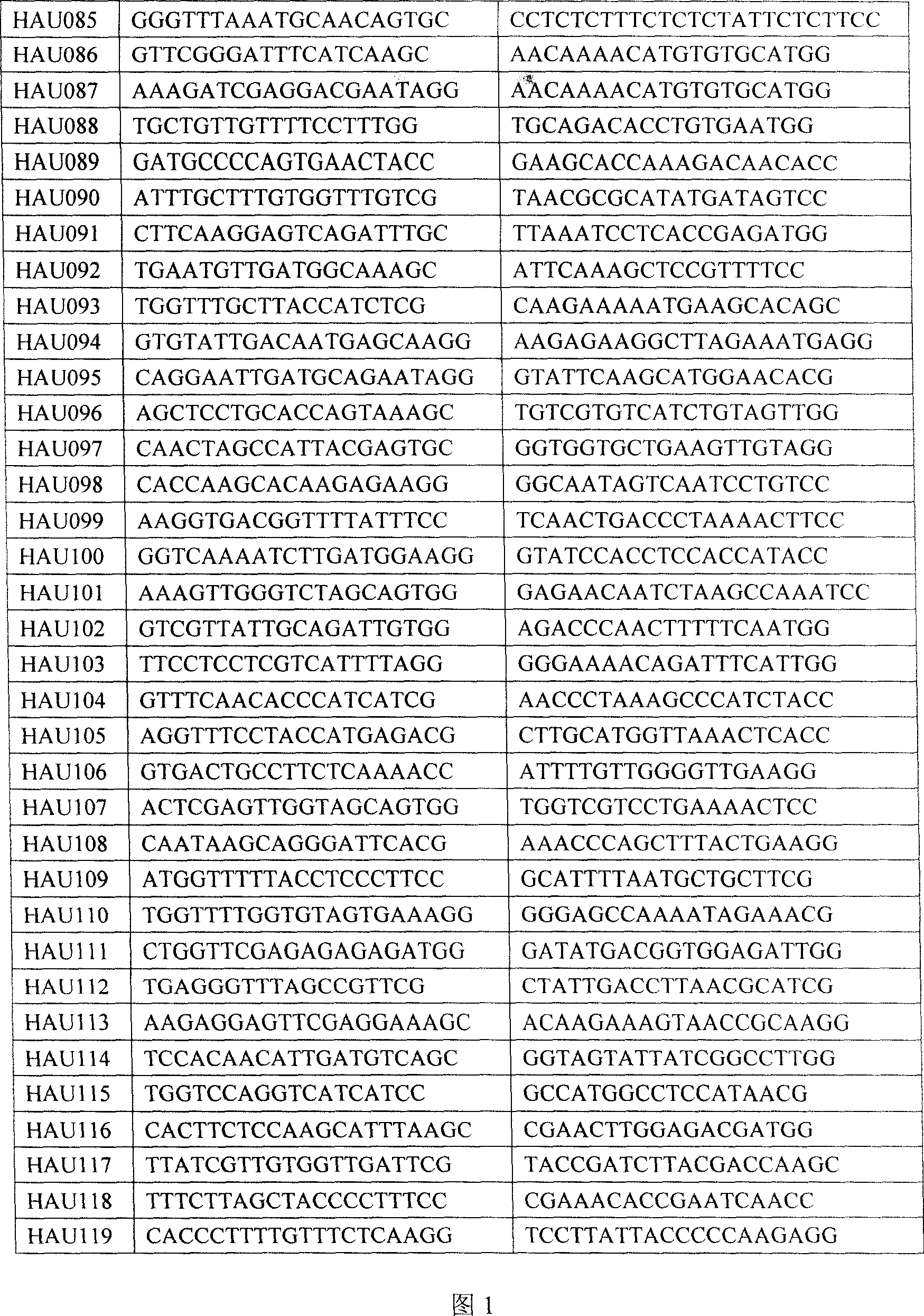
Method for building cotton fiber transcription genetic linkage map by EST-SSR sign
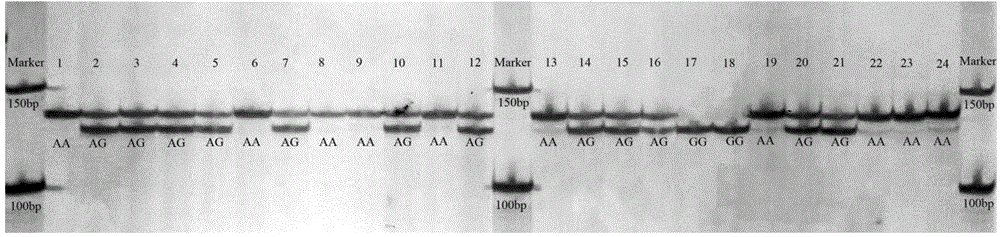
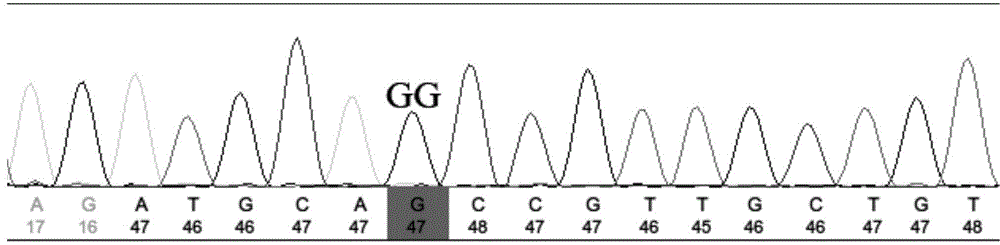
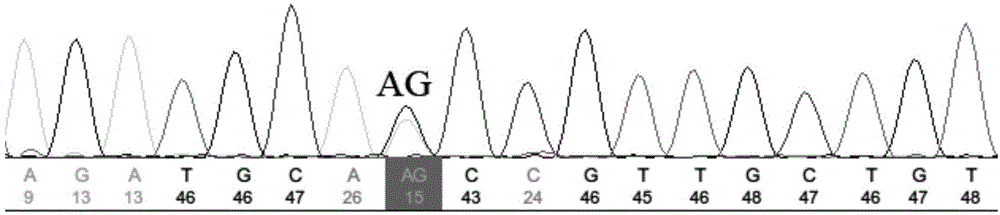
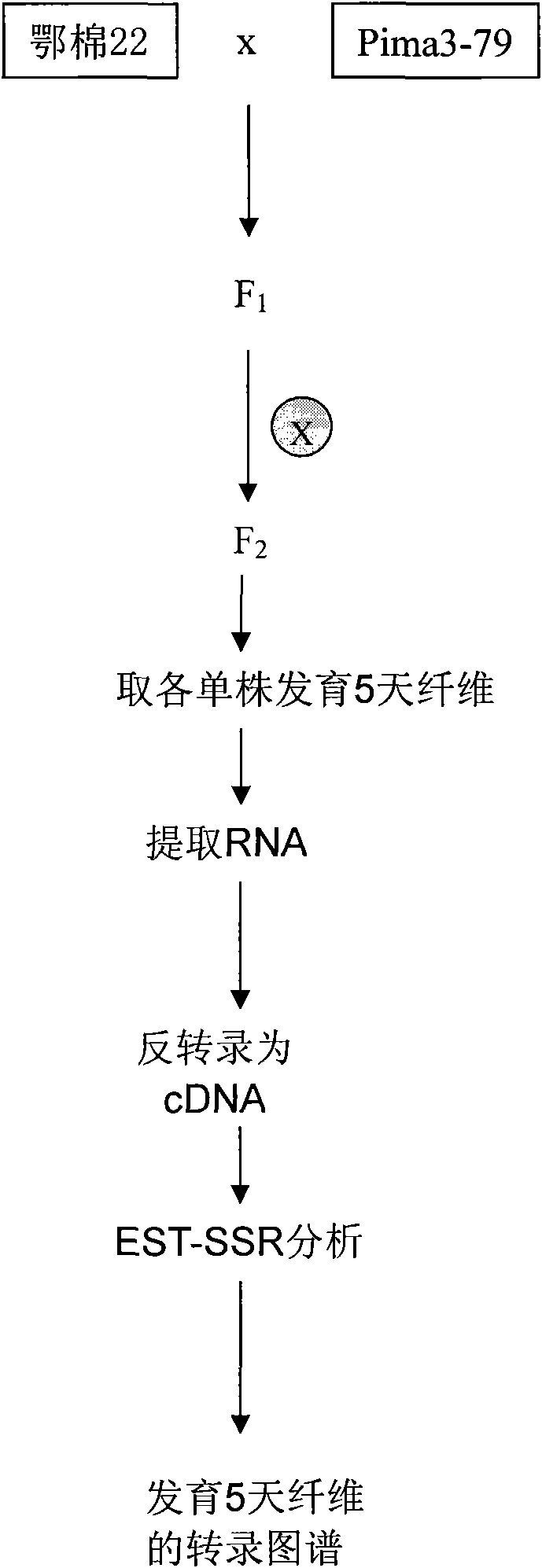
InactiveCN101880714AThe method is simple and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementFiberAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of cotton molecule breeding, particularly relating to a method for building a cotton fiber transcription genetic linkage map by EST-SSR signs. The method comprises the following steps: taking gossypium barbadense Pima 3-79 as a male parent and Gossypium hirsutum Emian 22 as a female parent, and hybridizing to obtain F1; planting F1, and causing F1 to be inbreeded to obtain F2; taking the F2 single plant as a starting material for the fiber transcription map to be plotted; extracting the RNA of the fiber of the field F2 single plant in 5 days after the single plant blooms, and carrying out reverse transcription of the RNA into cDNA to be served as a plotting group of the transcription map; utilizing the reported EST-SSR primer and the primer shown by a self-designed sequence table SEQ ID NO:1-90 to carry out the plotting group analysis to the F2 single plant by a denatured polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis; and finally, analyzing data by MAPMAKER / EXP.3.0 mapping software, and manufacturing and obtaining the transcription map. Compared with the existing method, the method of the invention is simple and practical, has accurate QTL positioning and is convenient for cloning genes relevant to cotton fiber development.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Rhododendron fortunei SSR primer pair based on transcriptome sequencing development, screening method and application
ActiveCN109468405AFast wayAccurate methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence analysisGenetic diversity
The invention discloses a rhododendron fortunei SSR primer pair based on transcriptome sequencing development, a screening method and application, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The primers are obtained on the basis of transcriptome sequencing and sequence analysis, on the basis of transcriptome sequencing, a large number of data are screened, a unigene sequence which is rich in SSR sites is acquired and SSR labeled primers are designed, and the barriers of a small number of rhododendron fortunei SSR molecular markers and low development efficiency at present are overcome. By arhododendron fortunei group, the effectiveness of the SSR primers is verified, and a foundation is laid for genetic research such as rhododendron fortunei genetic diversity research, genetic linkagemap, QTL positioning and molecular marker-assisted breeding.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV
Detection method of turbot FF0901 microsatellite marker by utilizing specific primers
InactiveCN101705295AEasy to detectEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementNegative strandGenetics
The invention discloses a detection method of a turbot FF0901 microsatellite marker by utilizing specific primers, comprising the following steps: firstly extracting turbot genomic DNA; then utilizing a sequence containing a microsatellite in an enrichment library of the turbot microsatellite; designing specific primers at two ends of the sequence as a positive strand 5'-TTACGCTTCGCATCGCTCAT-3', and a negative strand 5'-TGCCAGGCCACCAGACG-3'; carrying out PCR amplification on the turbot genomic DNA; separating the obtained PCR product through modified polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; analyzing strips generated on the product to obtain a turbot genetic polymorphism map. The method of the invention is suitable for the detection technologies of turbot population genetic marker, genealogy authentication, genetic linkage map construction and the like; the PCR amplification product presents better polymorphism in turbot population detection; and the method of the invention can rapidly acquire a genetic variation map of the turbot FF0901 microsatellite marker, and conveniently, rapidly, accurately and intuitively detect each individual genotype of the turbot.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Brassica juncea EST-SSR (expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat) marker primer group based on development of transcriptome sequence
ActiveCN104846093AOvercoming the Rare ProblemAdd raw dataMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMarker-assisted selection
The invention discloses a brassica juncea EST-SSR (expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat) marker primer group based on development of a transcriptome sequence, and belongs to the technical field of biologics. The brassica juncea EST-SSR marker primer group has the advantages that the primer group is obtained on the basis of development of the transcriptome sequence; on the basis of transcriptome sequencing, a large amount of sequence information is processed by batches, and the finding of an SSR sequence and the primer design of an SSR marker are performed, so as to overcome the defects of fewer SSR markers, low development efficiency and the like in the present brassica juncea; as the brassica juncea and brassica campestris are different materials, the effectiveness and universality of SSR primer are verified, and a foundation is laid for the development of the brassica juncea SSR primer, the auxiliary selecting of the molecule marker, the building of the genetic linkage map, the evaluation of genetic diversity, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
SOYBEAN ANTI-POD-SHATTERING MAJOR QTLqPD05, AND MAPPING METHOD AND APPLICATION THEREOF
PendingUS20190333602A1Increase ratingsIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsHigh densityGenetics
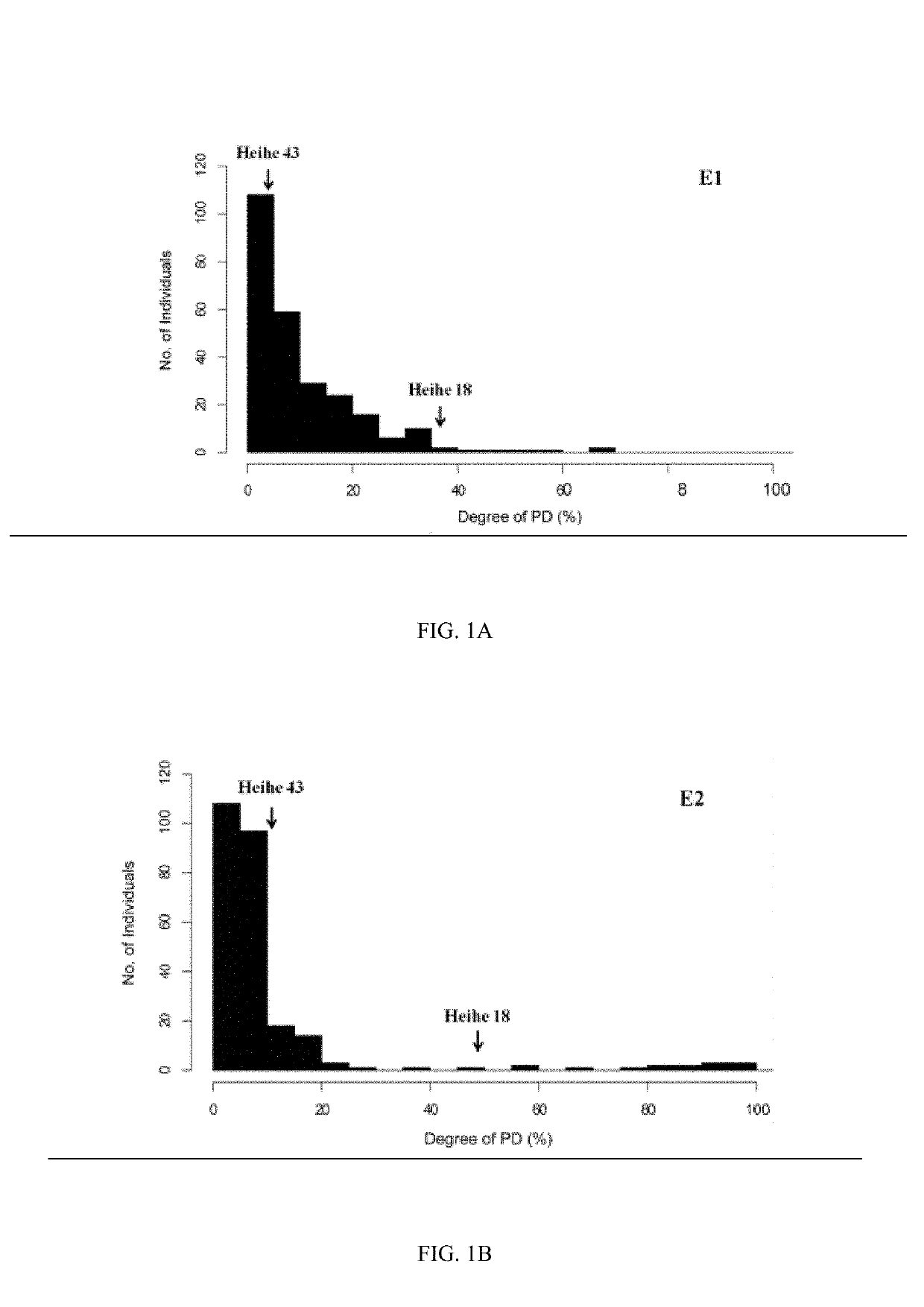
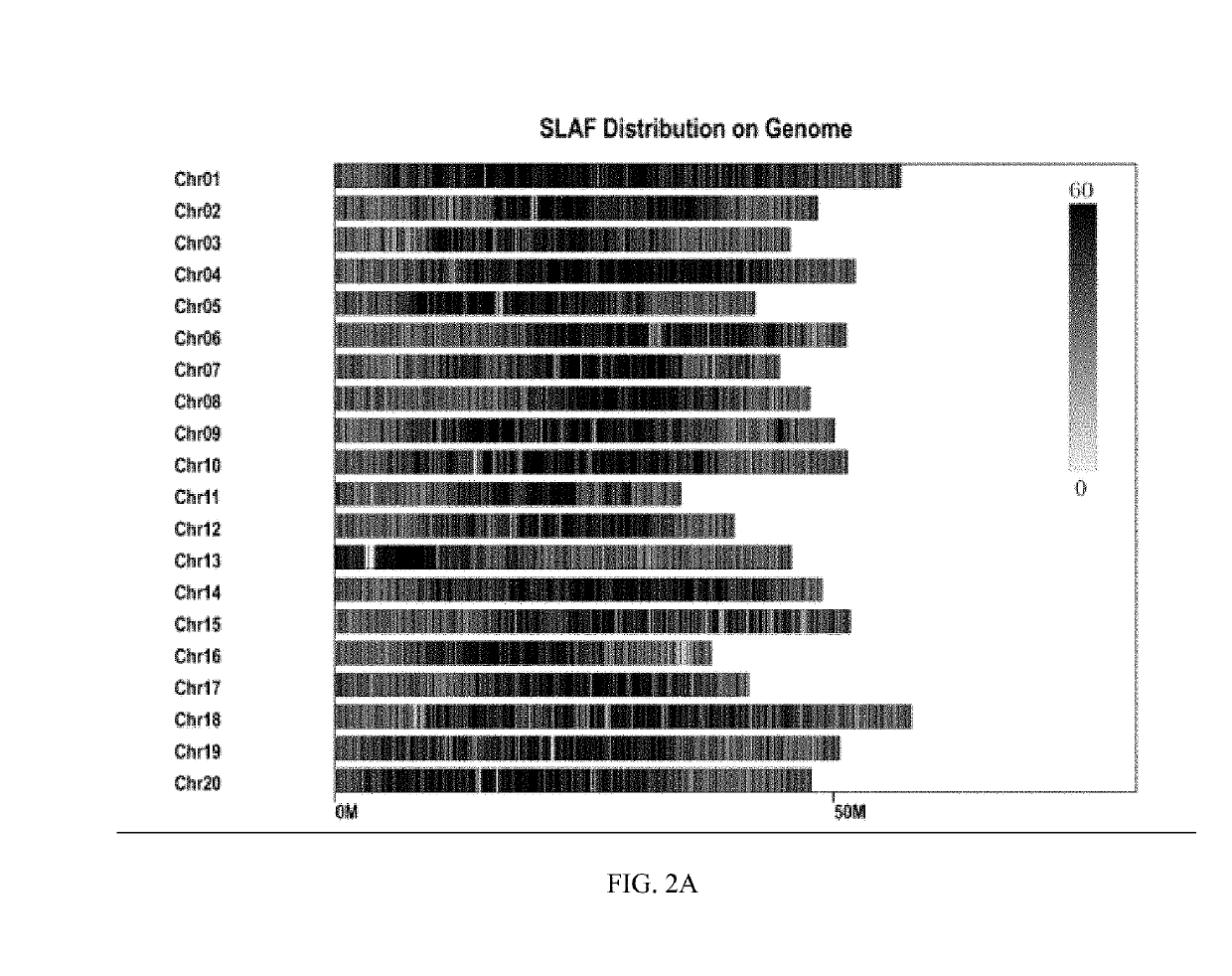
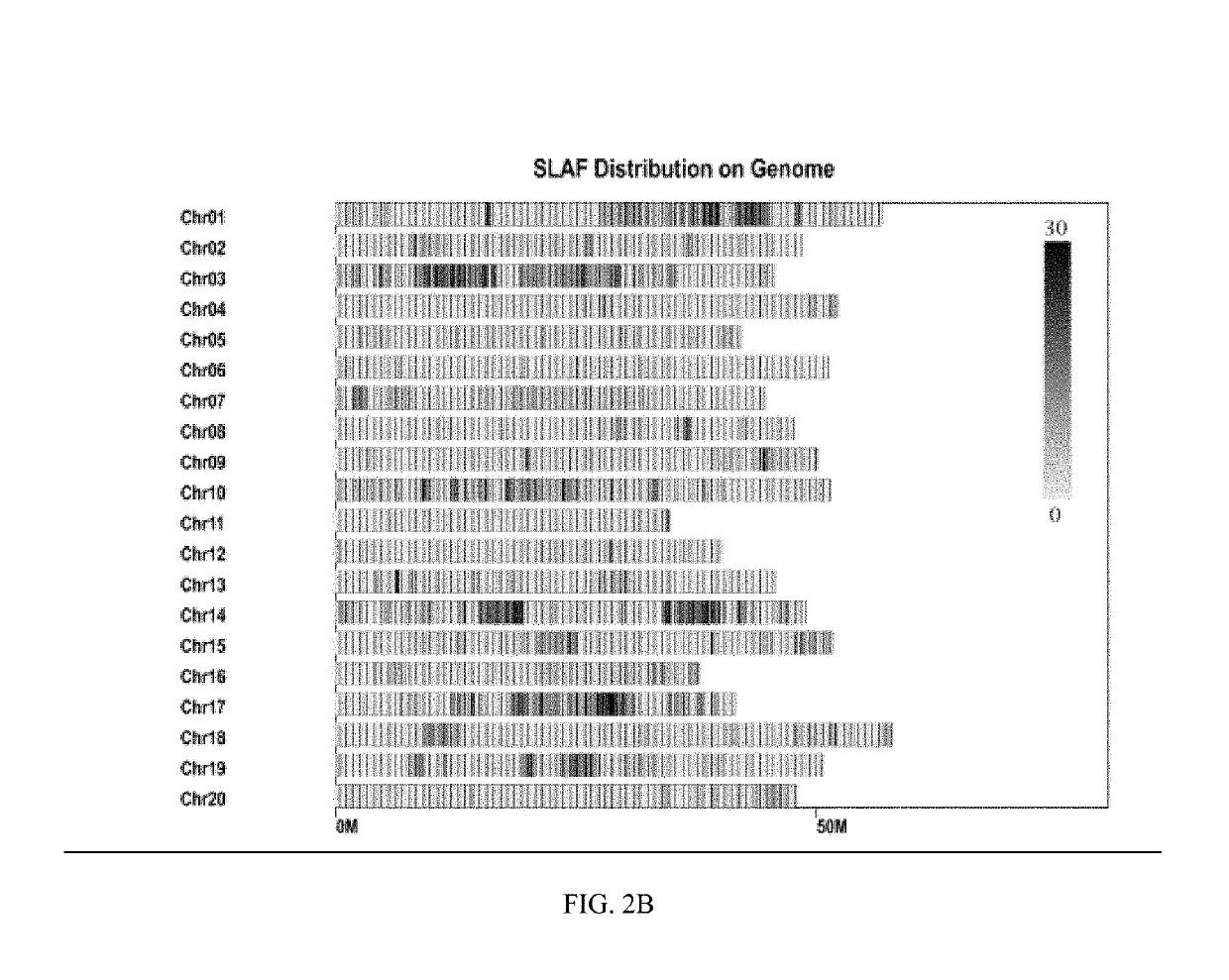
The present invention provides a soybean anti-pod-shattering major QTLqPD05, and a mapping method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of QTL mapping. The soybean anti-pod-shattering major QTL is mapped on the chromosome 5 of soybean at a physical position between 40448596-40703417. For the method for mapping the soybean anti-pod-shattering major QTL, a SLAF marker is screened at the whole genome level of the soybean by utilizing a SLAF-seq sequencing technology, so as to explore the QTLs related to pod shattering from this population. By using a material of a RIL7 population which has pod-shattering soybean and anti-pod-shattering soybean as the parents, a high-density genetic linkage map covering the whole genome of soybean is constructed, and QTL mapping of the anti-pod-shattering trait is carried out on this population to obtain QTLs related to anti-pod-shattering. In addition to this, the construction of the high-density genetic linkage map and the identification of the novel QTLs related to anti-pod-shattering specific to this population provide a reference for efficient QTL mapping of soybean.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker of single fruit weight major quantitative trait loci (QTL) of August red pyrus L. fruits and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN102154273AHigh contribution rateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsAmplified fragment length polymorphism
The invention belongs to the field of genetic breeding, and provides a molecular marker of single fruit weight major quantitative trait loci (QTL) of August red pyrus L. fruits and application of the molecular marker. The genetic linkage map of August red is constructed by using SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism), SSR (simple sequence repeats) and AFLP (amplified fragment length polymorphism), phenotype identification on single fruit weight of pyrus L. is combined, and an interval mapping method is used to analyze linkage groups, thus major QTL is detected on the seventh linkage group of August red and can explain 30.9% of characteristics of single fruit weight. The point which is the nearest to the major QTL site Pfw-1 is marked to be EACAMCAC-2000m, and the nearest distance is 1.019cM. The obtained titratable acid major QTL molecular marker has significant theoretical and practical means for quickening genetic improvement process of pyrus L. varieties and improving breeding selection efficiency.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Towel gourd fruit bitter taste gene LaBt and molecular marker used for auxiliary selection for bitter taste property of fruit
ActiveCN108486128AAchieve synthesisOvercoming the disadvantages of the method of tasting and identifying the bitterness of fruitsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesGeneticsBitter tastes
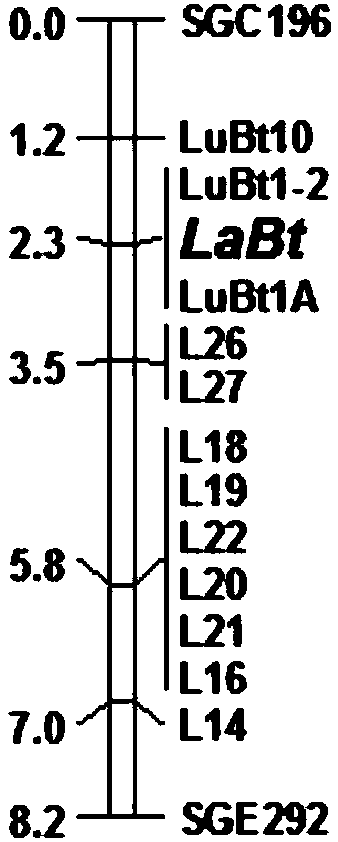
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and more specifically relates to a Luffa acutangula roxb bitter taste site LaBt genome sequence, a CDS sequence, a protein sequence, and a common towel gourd genome sequence corresponding to the site, a polymorphic marker for difference development according to a sequence between the above Luffa acutangula roxb and the common towel gourd. Though a molecular marker technology, a genetic linkage map of the towel gourd is constructed, the towel gourd bitter taste gene LaBt is positioned, an InDel molecular marker LuBt1-2 co-separated with the LaBt gene is obtained, an auxiliary selection system of the molecular marker is established, and the genome sequence of the site is obtained. The gene is helpful for auxiliary selection of the molecular marker for bitter taste property of towel gourd fruit, overcomes the disadvantages of sensory tasting and identification of the bitter taste of the fruit, and has the advantages of labor savingand time saving.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Set of mung bean InDel molecular markers and development method thereof
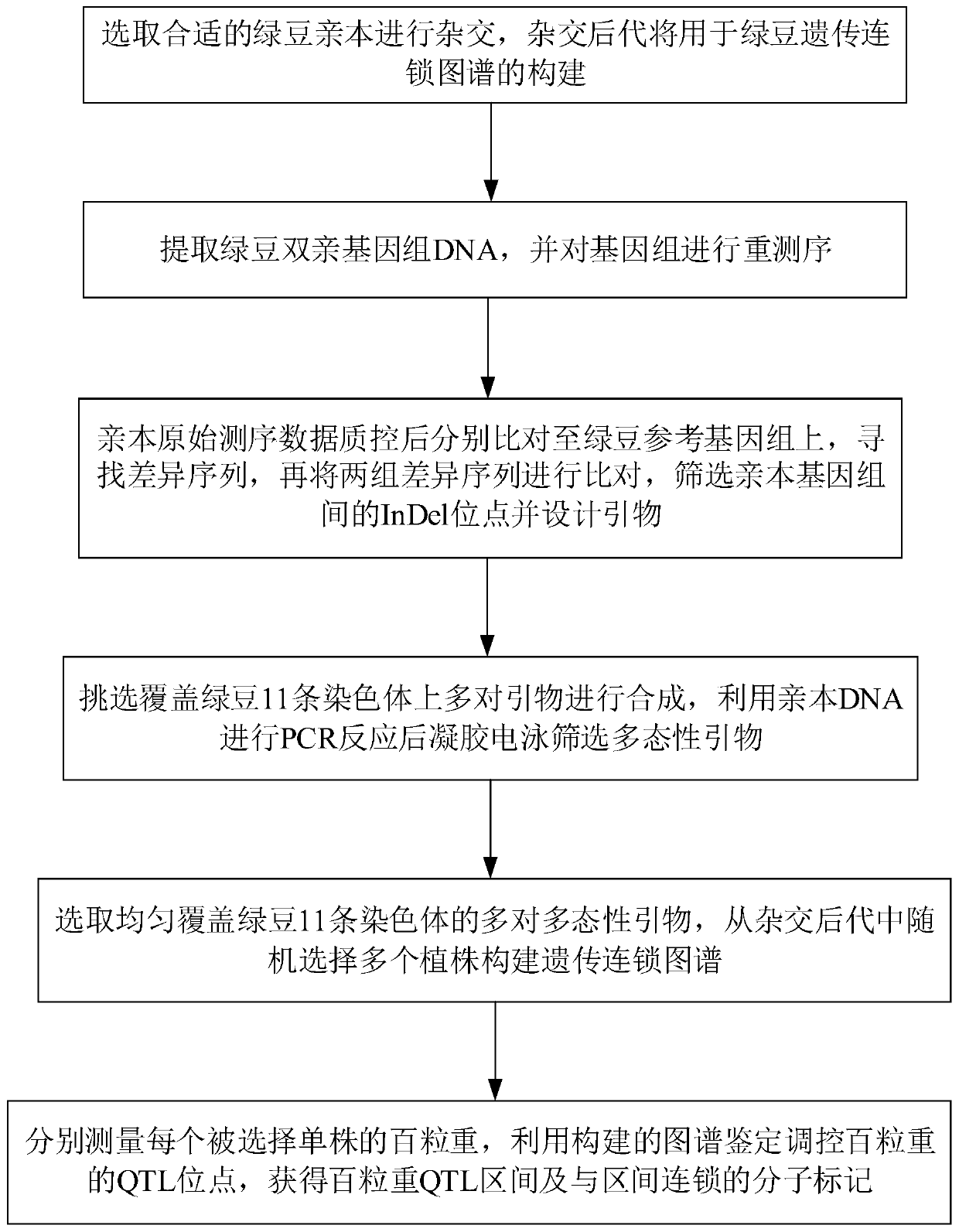
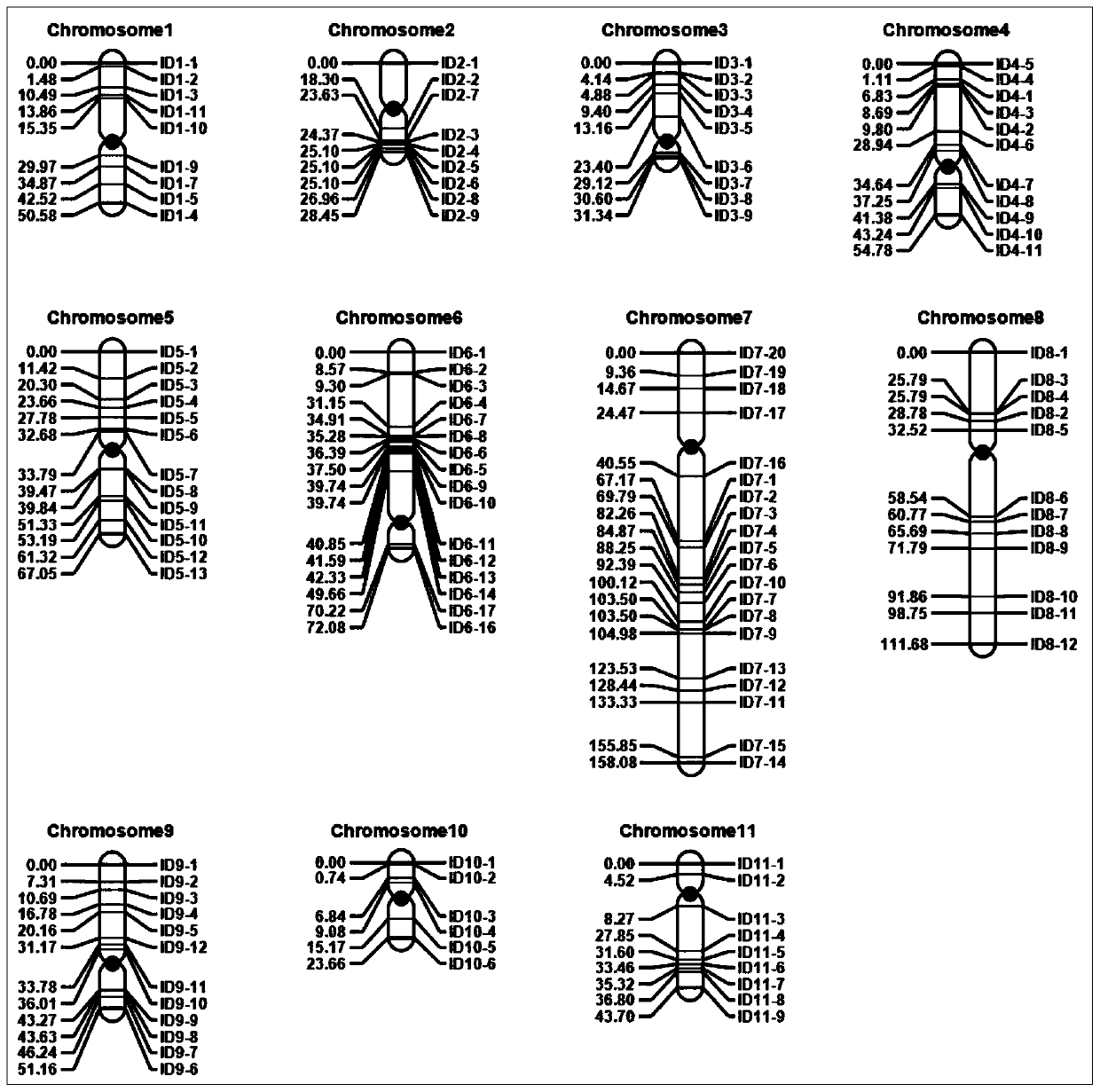
ActiveCN110656200AIncrease success rateRaise the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyPlantlet
The invention discloses a set of mung bean InDel molecular markers and a development method thereof. The development method comprises the steps: mung bean parents are selected to be hybridized so as to construct a mung bean genetic mapping population; parent genomes are re-sequenced; parental sequencing data are subjected to quality control and then compared to mung bean reference genomes to screen differential sequences, then InDel loci between the parental genomes are screened, finally primers are designed for the InDel loci, and the multiple pairs of primers are obtained; the polymorphic primers evenly covering 11 chromosomes of mung beans are selected, and a plurality of filial generation plants are selected at random to construct a mung bean genetic linkage map; and the hundred-grainweight per plant is measured, quantitative trait loci (QTL) for controlling and adjusting the hundred-grain weight are identified, and QTL intervals and the linked markers are obtained. The success rate and the polymorphic primer ratio of primer design are increased, polymorphism is better, and the genetic linkage map constructed through the InDel markers can be used for identification of the QTLof quantitative traits and is beneficial to important gene identification of the mung beans and assistant breeding of the molecular markers.
Owner:CROP INST ANHUI PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Group of cabbage mustard InDel molecular markers as well as development method and application thereof
ActiveCN110791550AIncrease success rateHigh polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a group of cabbage mustard InDel molecular markers as well as a development method and an application thereof, which relate to the technical field of molecular markers. The cabbage mustard InDel molecular marker provided by the invention comprises primer pairs corresponding to 60 sites, and the nucleotide sequences of the primer pairs are shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 to SEQ ID NO.120. The marker developed by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, good stability and high polymorphism; the primer pairs are good in stability, are uniformly distributed in 9 linkage groups, can be used for positioning of important agronomic trait genes of cabbage mustard, genetic diversity analysis, fingerprint construction, genome-wide association analysis and genetic linkage map construction or molecular marker-assisted selective breeding, and can improve the working efficiency.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLES GUANGDONG PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Seed number per pod character major gene site of rape and application thereof
InactiveCN102226189AThe detection method is convenient and fastPrecise screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationField experimentGenotype Analysis
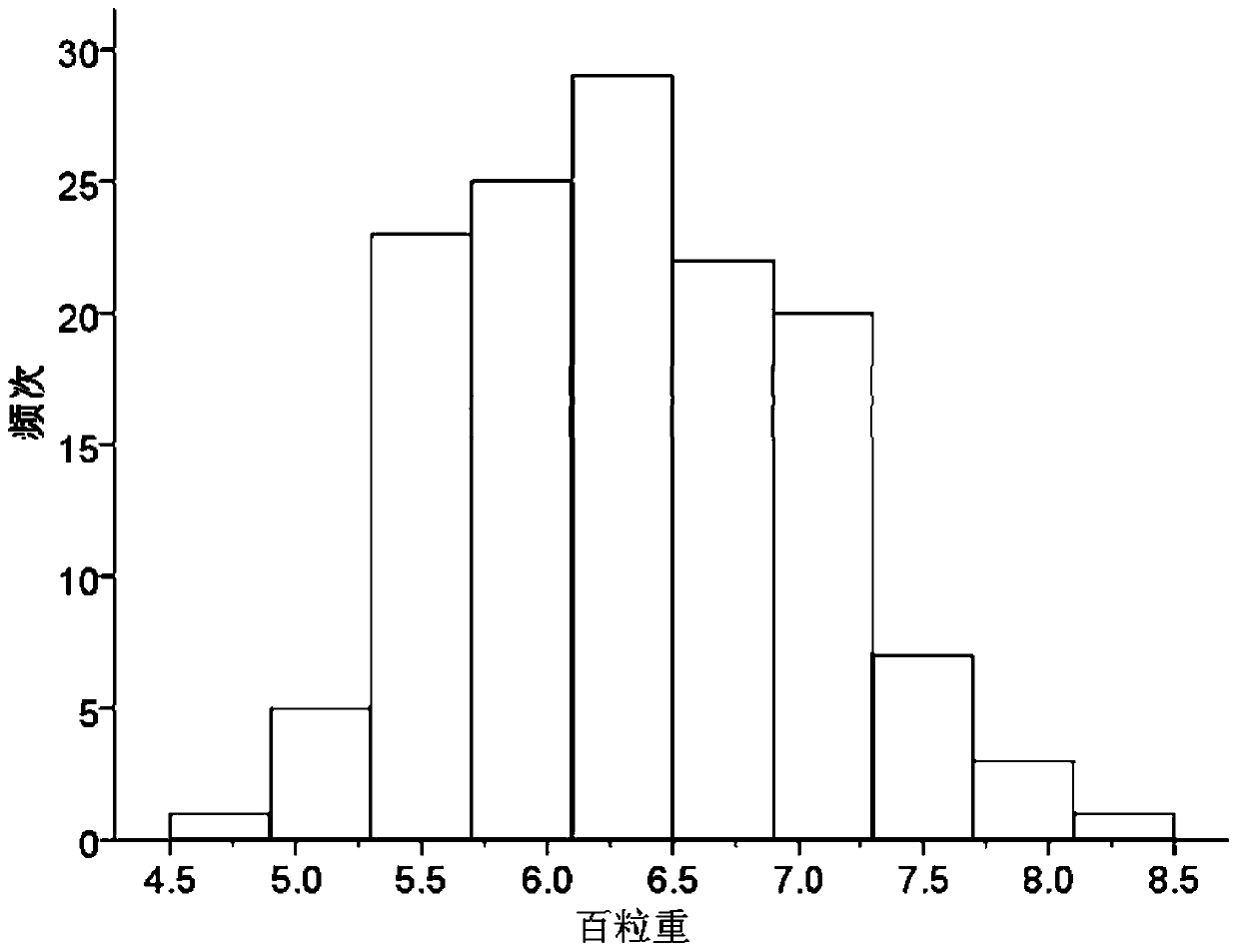
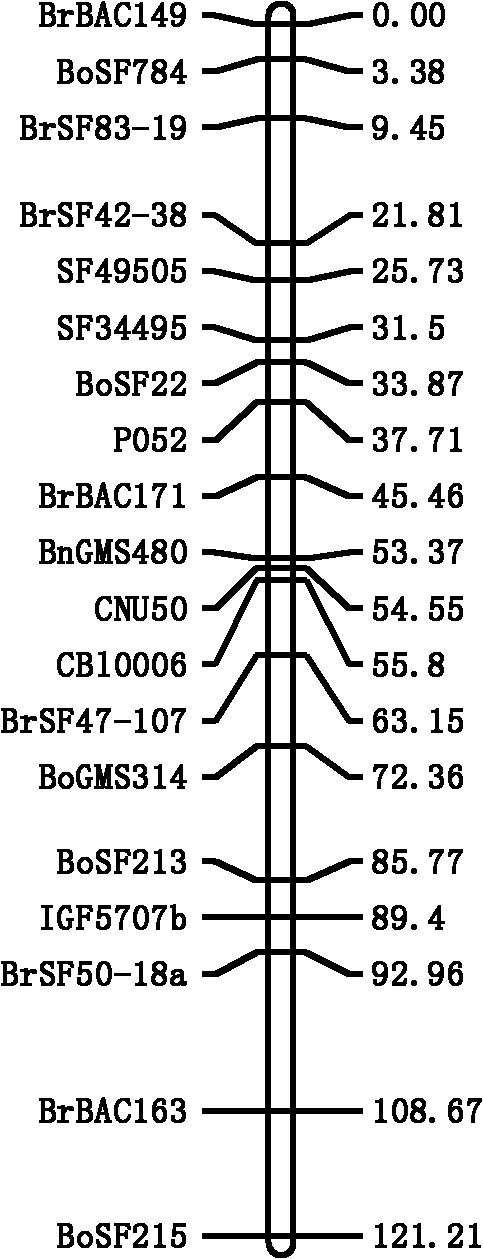
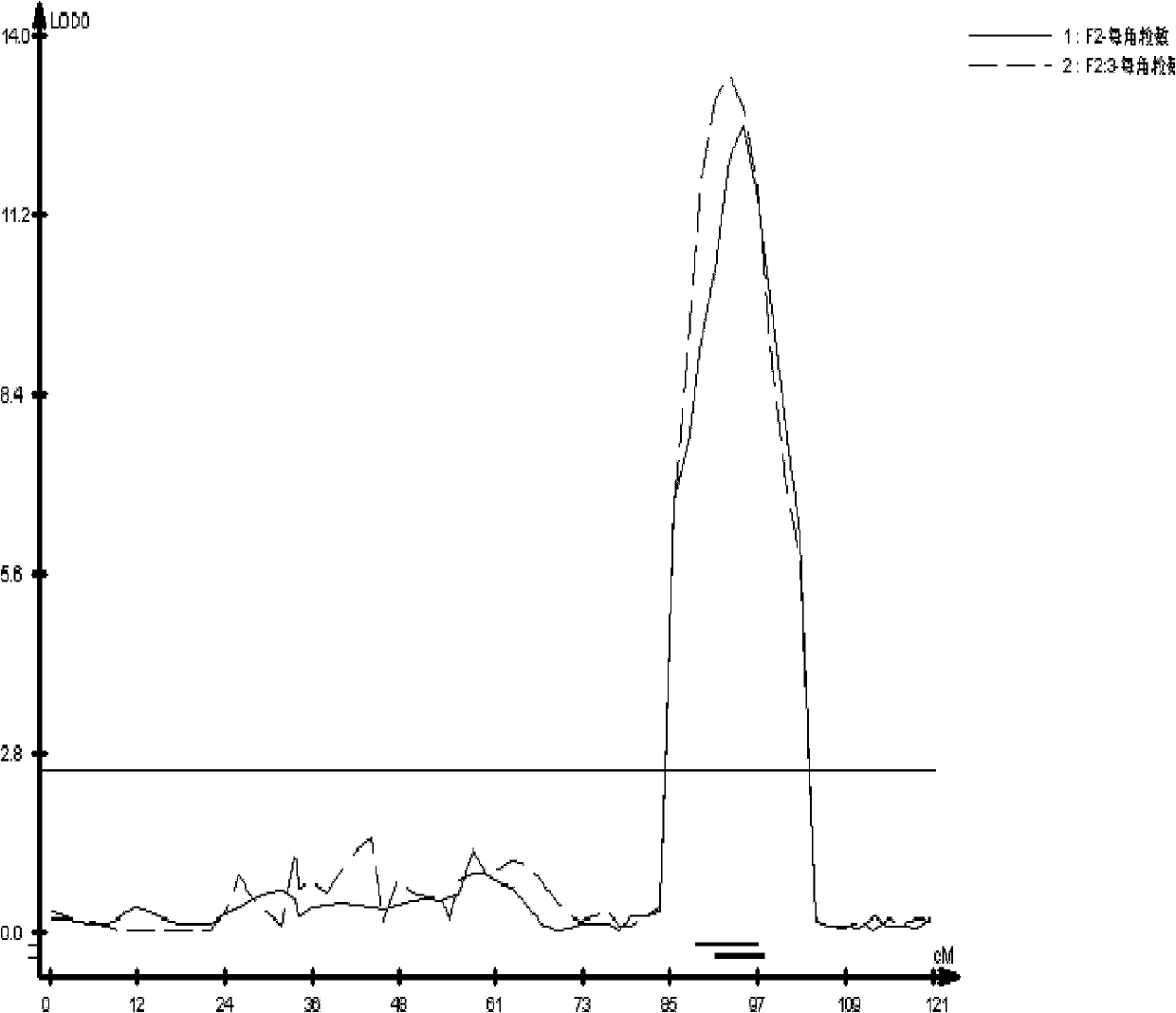
The invention discloses a seed number per pod character major gene site of rape and application thereof. The process comprises the following steps: (1) hybridizing by Brassica napus variety with obvious difference on each seed number per pod character; (2) carrying out polymorphism screening for parent DNA by public and developed SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) and SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) primers, and building a genetic linkage map by molecular mark gene type analysis to an F2-generation segregation population; (3) obtaining the phenotype data of each seed number per pod character by field experiments and variety research to F2 and F2:3 segregation population; and (4) combining the gene type and the phenotype data of the segregation population to carry out QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) detection. The major gene site qQN.A6 and the molecular marker BrSF50-18 for controlling seed number per pod of rape on an A6 linkage group are obtained. The F3 generation derived from two parents is analyzed by the marker, and an individual plant with the marker is kept. A variety research result shows that the ratio of the seed number per pod is 83.4% higher than the F3 individual plate of F2:F3 family mean value, and thus, the marker is used for assisted selection to greatly improve the selection efficiency of high-yield breeding.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rice salt-tolerant QTL, positioning method, molecular marker and application thereof
PendingCN110512020AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRe sequencingAgricultural science
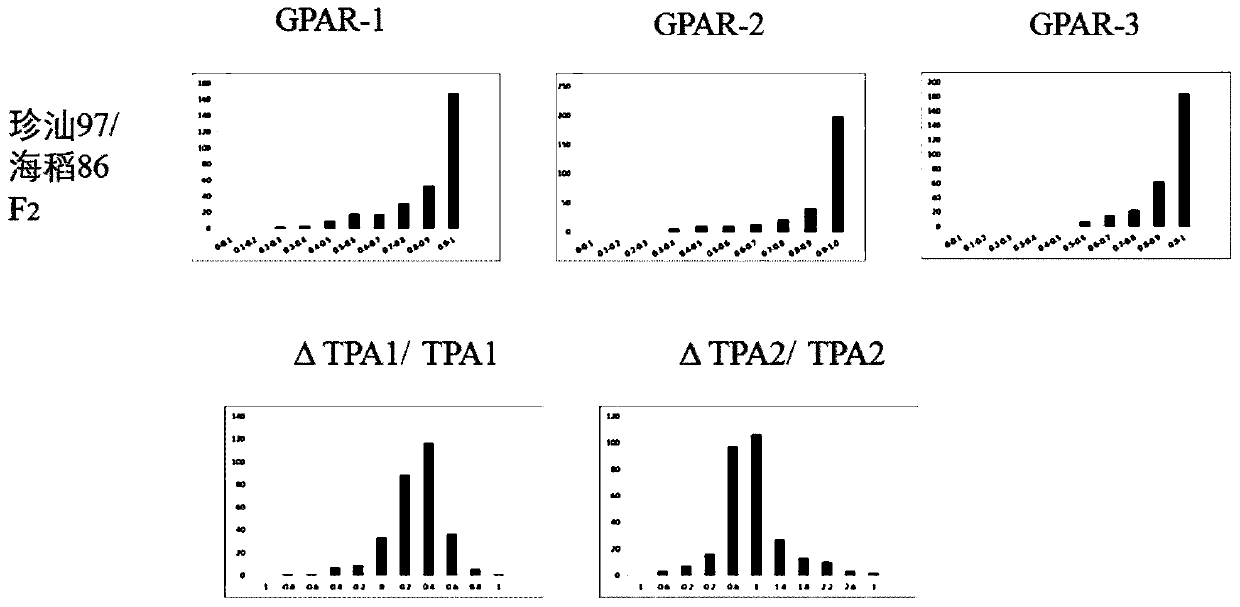
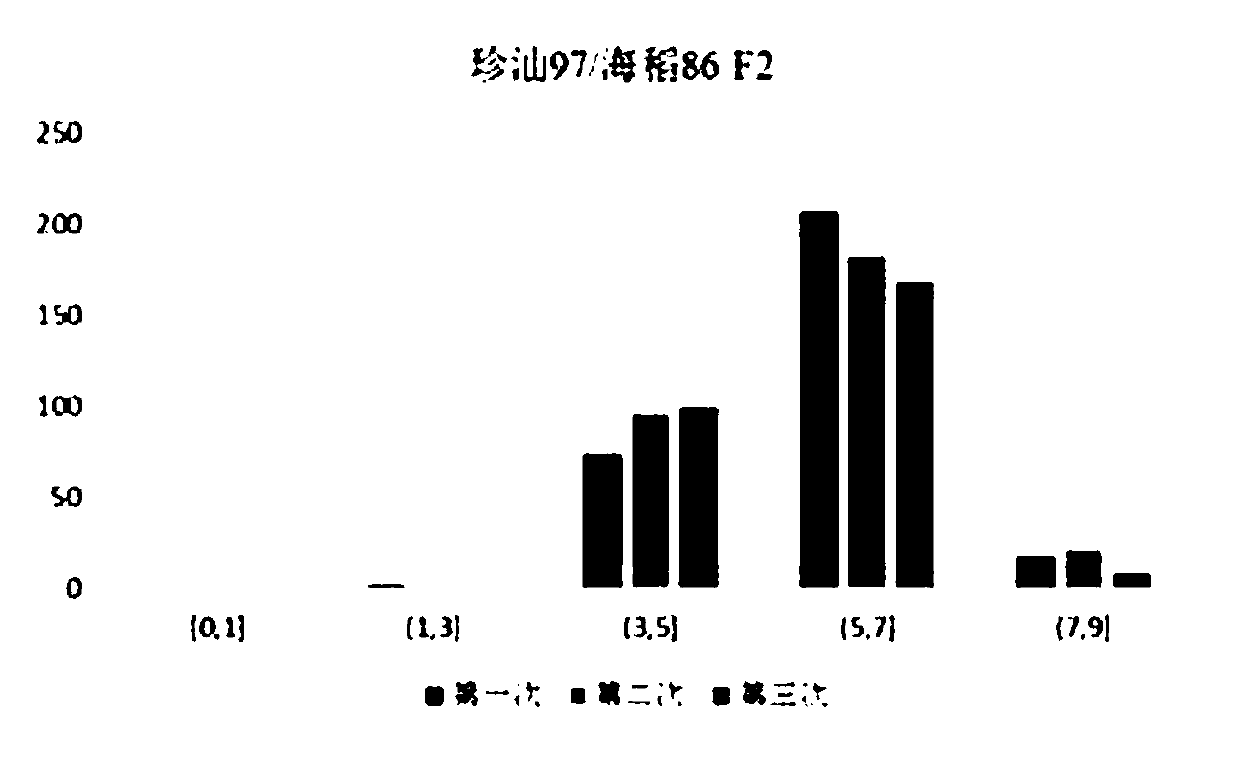
The invention belongs to the field of genetic crop gene engineering technology, and particularly relates to rice salt-tolerant QTL, a positioning method, a molecular marker and application thereof. According to the research, sea rice 86 used as a salt-tolerant parent and a salt-sensitive parent Zhenshan 97 are used for constructing a segregation population; potted plant salt stress phenotype identification is carried out on F2, a genetic linkage map obtained through re-sequencing is combined to carry out positioning of salt-tolerant quantitative trait locus, and a molecular marker is developedfor positioned sections. Thereby, screening of salt-tolerant rice can be rapidly and accurately achieved.
Owner:WUHAN HAITAO INT BIOTECH CO LTD
Molecular marker of pot shattering resistance trait major gene locus of rapes and application
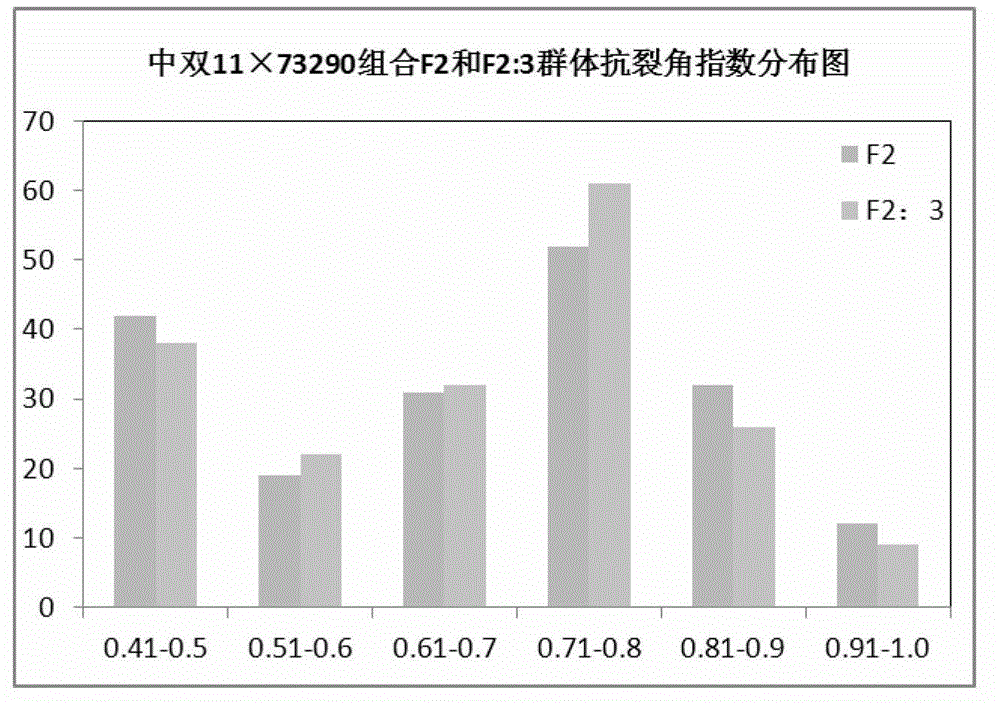
ActiveCN102747080AImprove accuracySelection inefficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceField experiment
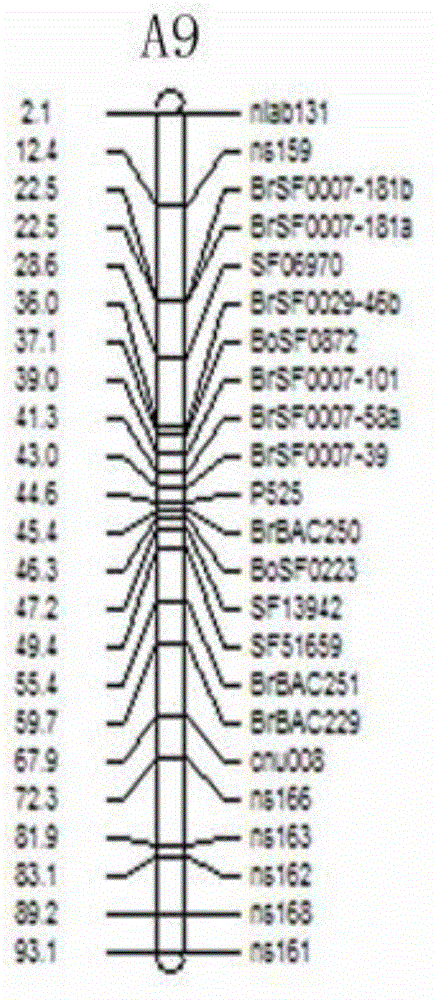
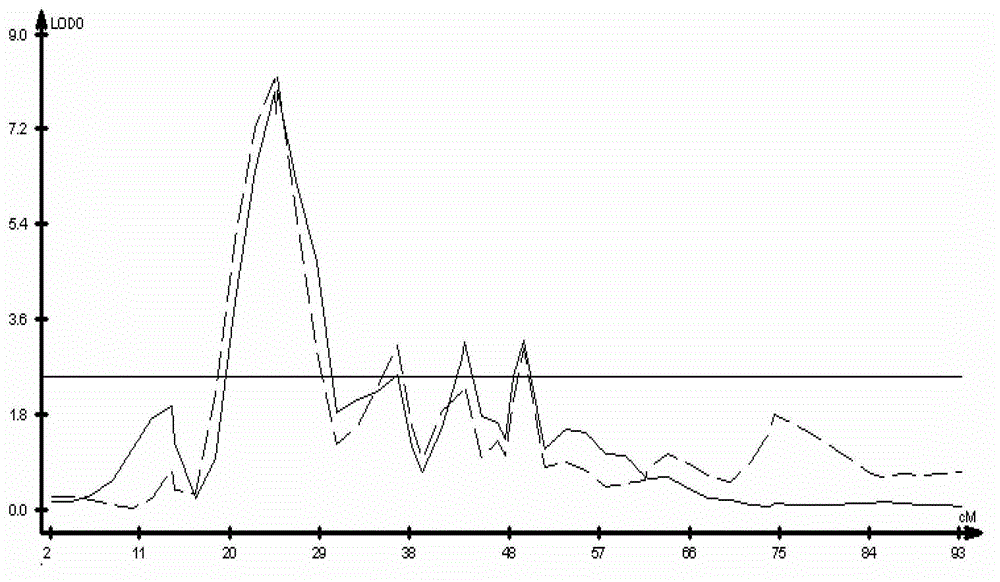
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a pot shattering resistance trait major gene locus of rapes and an application. The steps are as follows: 1) hybridizing double 11 variety and 73290 variety (which have obvious differences in the pot shattering resistance traits) in a cabbage type rape varieties, and carrying out selfing on progenies to obtain F2 and F2:3 segregation populations with the segregated pod shattering resistance traits; 2) carrying out polymorphic screening on parent DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by utilizing an SSR (simple sequence repeat) primer, and establishing a genetic linkage map by carrying out SSR molecular marker genotyping on the F2 progeny segregation populations; 3) carrying out field experiments and plant inquisition on the F2 and F2:3 segregation populations so as to obtain phenotype data of the pod shattering resistance traits; and 4) carrying out QTL (quantitative trait locus) detection by combining with the developed high-density molecular marker genetic linkage map and genotype and the phenotype data of the segregation populations, utilizing QTL Cart2.5 software to obtain the major gene locus Psr.A9 for controlling the pod shattering resistance of the rapes on a cabbage type rape A9 linkage group and also obtain the molecular marker BrSF0007-39 closely linked with the major gene locus. The selection efficiency of breeding with the pod shattering resistance can be greatly improved by utilizing the marker for assistant selection.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Portunus pelagicus polymorphic microsatellite molecular marker, identification method and application
ActiveCN107937395ARapid identificationIdentification of large quantitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence analysisGenomic DNA
The invention relates to a portunus pelagicus polymorphic microsatellite molecular marker, an identification method and application. The identification method comprises the following steps: portunus pelagicus genomic DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) extraction, simplified genomic library construction and high-throughput sequencing, sequence analysis and microsatellite primer designing, and microsatellite marker polymorphism evaluation. According to the identification method disclosed by the invention, 17983 microsatellite loci are identified, and 16 microsatellite markers having molecular polymorphism are screened out. The identification method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple and safe, the accuracy is high, a result is true and reliable, and the like,and is capable of being used for quickly and massively obtaining portunus pelagicus microsatellite markers; the technical method disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to numerous species having no reference genome because of no need to know genomic information in advance, and has a wide popularization and application potential; in addition, a candidate tool can be provided for population genetic variation evaluation, genetic relationship identification and genetic linkage map construction of portunus pelagicus by 16 pairs of polymorphic microsatellite marker primers obtained by themethod.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Pistacia chinensis bunge microsatellite loci, primer and application
ActiveCN106399497AHigh polymorphismImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationChinese pistachioEnrichment methods
The invention is aimed at providing pistacia chinensis bunge microsatellite loci, a primer and application, and provides the twelve pistacia chinensis bunge microsatellite loci, and the primer for designing the microsatellite loci and detecting the population genetic variation of pistacia chinensis bunge. The twelve microsatellite loci are obtained from a pistacia chinensis bunge genome through a magnetic bead enrichment method and a fluorescent label sequencing technology, the specific primer is designed according to flanking sequences of two ends of a microsatellite, the amplification result has high polymorphism and stability and can be used for the fields of population genetic diversity detection, genetic relationship identification, establishment of a genetic linkage map, molecular mark assisted breeding and the like of pistacia chinensis bunge.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIV QIANJIANG COLLEGE
Primer group, marking method and application of EST-SSR (Expressed Sequence Tag-Simple Sequence Repeats) molecular marker of macrobrachium nipponense
InactiveCN103484459AAchieve molecular markersImplement initial applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyCrustacean
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biological DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) marking technologies and applications thereof and particularly relates to a sieving method and application of an EST (Expressed Sequence Tag) microsatellite marker (EST-SSR (Simple Sequence Repeats)) of a macrobrachium nipponense as a freshwater economic shelled animal. By using an EST-SSR marking technology, the hereditary feature and group structure of a macrobrachium nipponense breeding group can be researched, the primary application of a molecular marker in macrobrachium nipponense breeding can be realized, and a foundation is laid for carrying out auxiliary molecular marker breeding through constructing a high-density macrobrachium nipponense genetic linkage picture and locating the important economic character of a QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus).
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Watermelon flesh color character major gene locus, and InDel molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN107254542AVariation StableEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenotypeGenetic linkage map
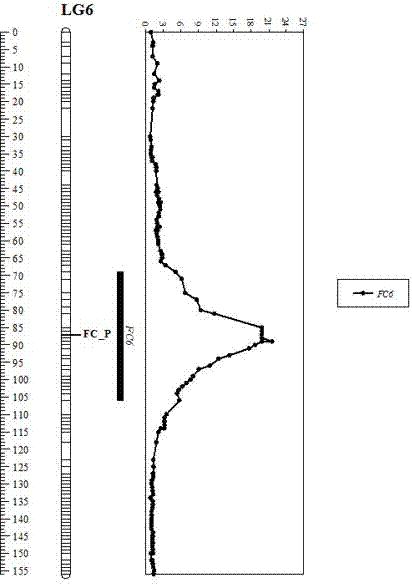
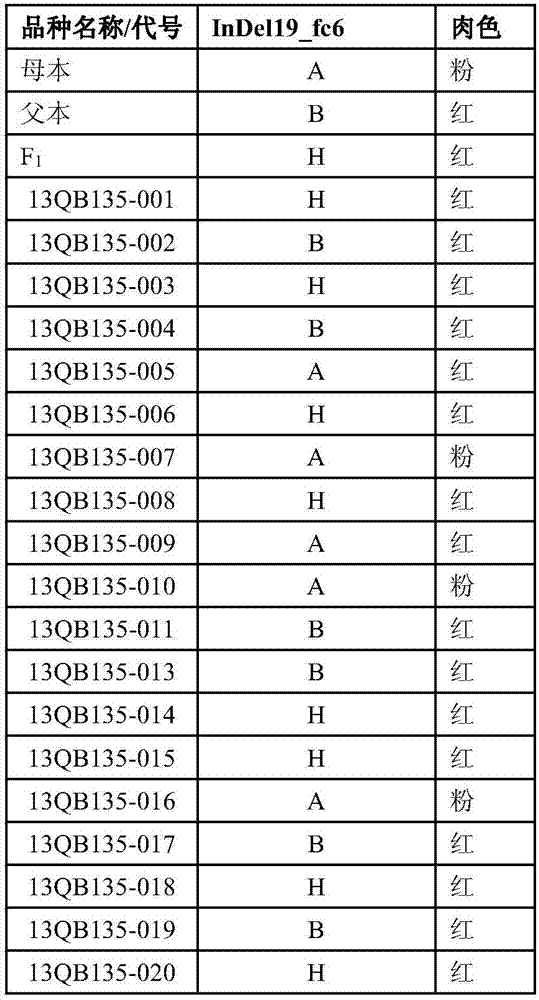
The invention discloses a watermelon flesh color character major gene locus, and an InDel molecular marker and an application thereof. A genetic linkage map of an F2 group cross-bred by female parents and male parents of which the flesh colors are pink and red is combined and phenotype identification of the flesh color is carried out on the female parents, the male parents, an F1 group and the F2 group; QTL primary positioning is carried out by adopting an Rqtl-IM-binary method; the InDel primer is designed by combining resequencing of the parents; polymorphism screening is carried out on the female parents, the male parents and the F1 group by using the InDel primer and genotype identification is carried out by using the polymorphic InDel primer in the F2 group; and map construction is carried out by using JoinMap4.0. Through the technical measures, the watermelon flesh color character major gene locus FC6 is obtained and an insertion and deletion molecular marker InDel19-fc6 tightly linked with the flesh color is prepared. A novel method can be provided for identification of the watermelon flesh color, the improvement process of the watermelon flesh color is accelerated and the breeding accuracy and the selection efficiency are improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Cucumber downy mildew resistance main effect QTL linkage molecule labeling method and applying method
InactiveCN101240343AReduce workloadImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSelf-pollinationGenotype
The present invention relates to a molecular marker method linked with major QTL for cucumber downy mildew resistance and an application method, belonging to the field of biological technology. The molecular marker method: getting F2 filial generation by self-pollination of hybrid F1; acquiring F7 generation recombinant inbred lines by filial generation single seed descent method; describing the gene type of each strain of the recombinant inbred lines; constructing genetic linkage map for molecular marker; testing the downy mildew resistance of each strain of the recombinant inbred lines; and composite interval mapping for interval possible located in QTL. The application method: hybridizing S94 and derive verities thereof with other cucumbers and multiplying to F2 generation; separating genome DNA of single cucumber plant, and testing whether each cucumber plant has molecular marker method linked with major QTL for cucumber downy mildew resistance. The invention develops an efficient, rapid breeding technology, selects breeding variety with conventional downy mildew, reduces workload of breeder, and improves precise of selection and breeding efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Primers and kit for detecting molecular marker linked to major QTL for controlling corn stalk strength, detection method for detecting corn stalk strength, and applications of primers, kit and detection method
InactiveCN109295248AEasy to operateThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceUltimate tensile strength
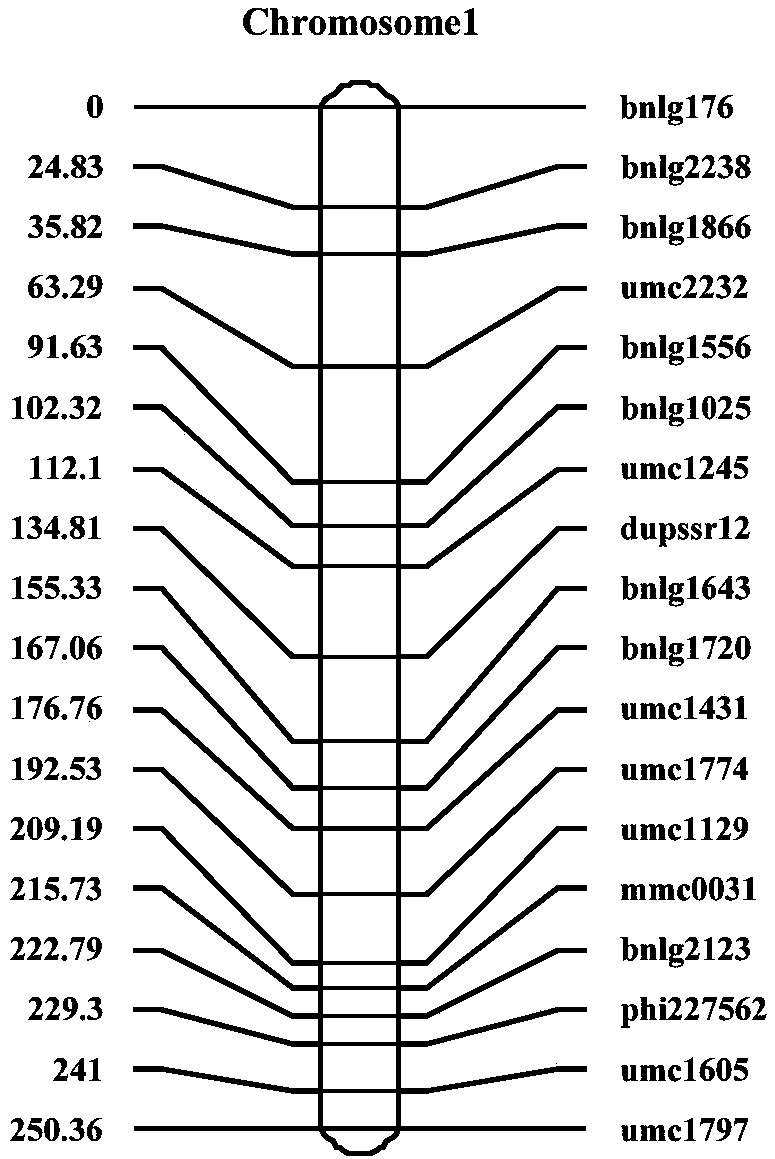
The invention relates to primers and a kit for detecting a molecular marker linked to major QTL for controlling corn stalk strength, a detection method for detecting corn stalk strength, and applications of the primers, the kit and the detection method, and belongs to the technical field of corn genetic breeding and molecular biology. According to the present invention, a recombinant selfing linepopulation containing 241 families is constructed through Zheng 58*D863F, and genetic linkage map analysis is performed, such that four QTL for controlling corn stalk strength are detected, wherein the high stalk strength major QTL qRPR1.07 is identified simultaneously at the position 1.07 of the chromosome 1 of the corn from Hainan Ledong and Henan Yuanyang Demonstration Base, and is positioned between two SSR markers bnlg1556 and umc2232 so as to explain nearly 20% of genetic variation; and the molecular marker linked to the major QTL for controlling corn stalk strength can directionally andprecisely screen corn materials with high stalk strength at the early stage of growth so as to save the breeding cost and the breeding time, and is used for lodging-resistant breeding of corn.
Owner:河南省农业科学院作物设计中心
Quick detection method for Scylla paramamosain by microsatellite markers from functional genes
InactiveCN101787395AFast detection methodThe detection method is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmScylla paramamosain
The invention relates to a quick detection method for Scylla paramamosain by microsatellite markers from functional genes, which comprises the following steps: (1) extracting genomic DNA of the Scylla paramamosain; (2) acquiring a gene sequence containing microsatellite repeats according to a functional gene sequence of the Scylla paramamosain in a GeneBank database; (3) designing microsatellite marker primers; (4) performing PCR amplification on the genomic DNA of different geographic population or different individuals in the population of the Scylla paramamosain; and (5) detecting a PCR product by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The detection method has the advantages of quickness, accuracy, sensitivity and the like, and can intuitively detect genotypes of different individuals of the Scylla paramamosain so as to quickly acquire a polymorphic map for hereditary variation at functional gene microsatellite loci of the Scylla paramamosain; and the microsatellite markers can be applied to the fields such as hereditary variation analysis of the Scylla paramamosain, germ plasm resource protection and management, genetic linkage map construction and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Hermaphrodite laver dihaploid colony building method
InactiveCN106069717ASolve hybridSolving details such as the identification of heterozygous filamentsCultivating equipmentsPlant genotype modificationClaviceps purpureaSporophyte
The invention discloses a hermaphrodite laver dihaploid colony building method. The method comprises taking hermaphrodite laver thalluses (gametophytes) with obvious color difference as cross parents, carrying out mixed cultivation on father and mother thalluses with antheridiums, collecting carpospores, selecting the carpospores with germ tubes, carrying out single culture to obtain protonema (sporophore), carrying out induction to obtain conchospore of the protonema, carrying out culture to obtain macroscopic F1 thalluses, wherein if 90% or more of the thalluses contain amphiphilic color chimeras, the thalluses are used for building of a dihaploid colony, separating all color blocks of the four-color block chimera, acquiring monospores or single isolated cells of each one of the color blocks, carrying out culture to obtain macroscopic thalluses, carrying out single thallus culture and autofertilization to obtain pure thallus of each one of color blocks of the four-color block chimera and building a dihaploid colony. The method solves problems of hermaphrodite laver dihaploid colony building and lays the foundation of genetic linkage map construction.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
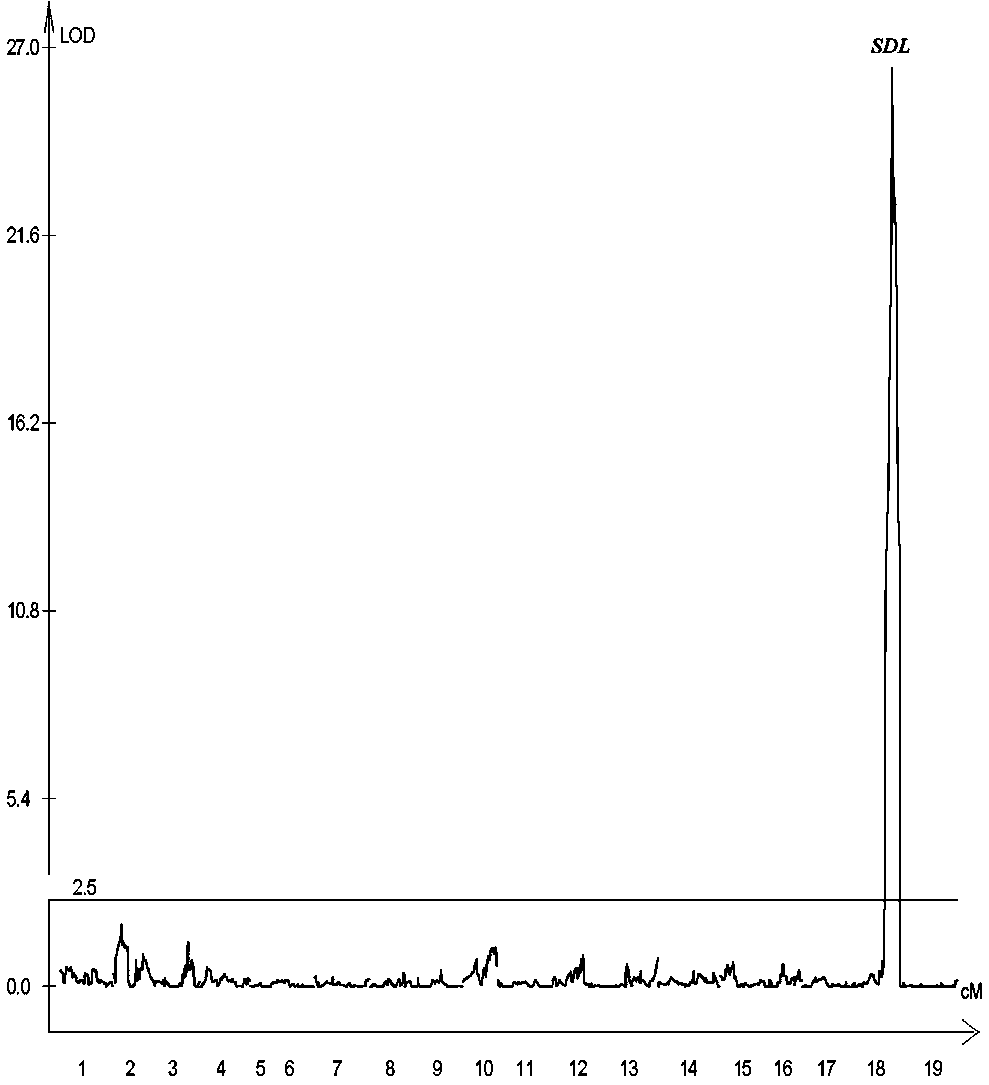
SNP molecular marker for grape fruit seedless major QTL site SDL and application
ActiveCN107723378AGuaranteed accuracyEasy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVitis viniferaAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of grape molecular breeding, and particularly provides a molecular marker for a grape fruit seedless major QTL site and an application. An RAD-seq method is utilizedfor sequencing and constructing a joint genetic linkage map of a female parent 'Red Globe' and a male parent 'Centenial Seedless', identification is carried out in combination with a grape fruit phenotype, and an interval mapping method is utilized for QTL analysis, then the presence of the major QTL site (i)SDL( / i) is detected in combination with a 18th linkage group in the genetic linkage map,a contribution rate of the major QTL site is 77.9%, and two SNP markers closely linked to the site are SDL1 and SDL2, with a genetic distance of 124kb. The SNP molecular marker for the grape fruit seedless major QTL site obtained in the invention can be used for early screening of grape fruit seedless traits, and has important theoretical and practical guiding significance for improving the breeding efficiency.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU FRUIT RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com