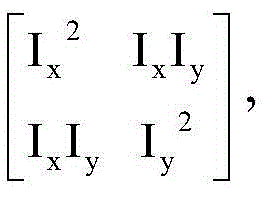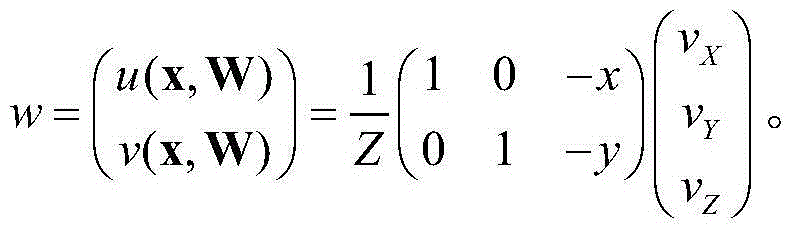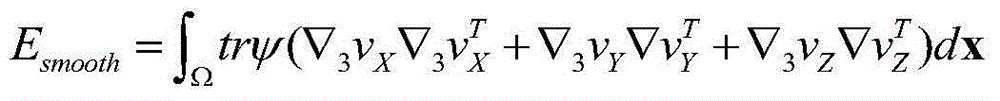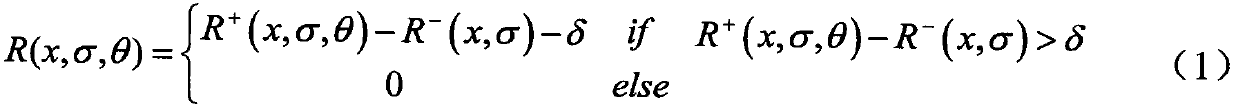Patents
Literature
102 results about "Diffusivity tensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a type of magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) which uses the rate at which water diffuses between cells to gather information about the internal structures of the body. The diffusion rate varies around barriers between different structures in the body, and this trait can be used to create a complex and detailed map of internal structures with the assistance of DTI.
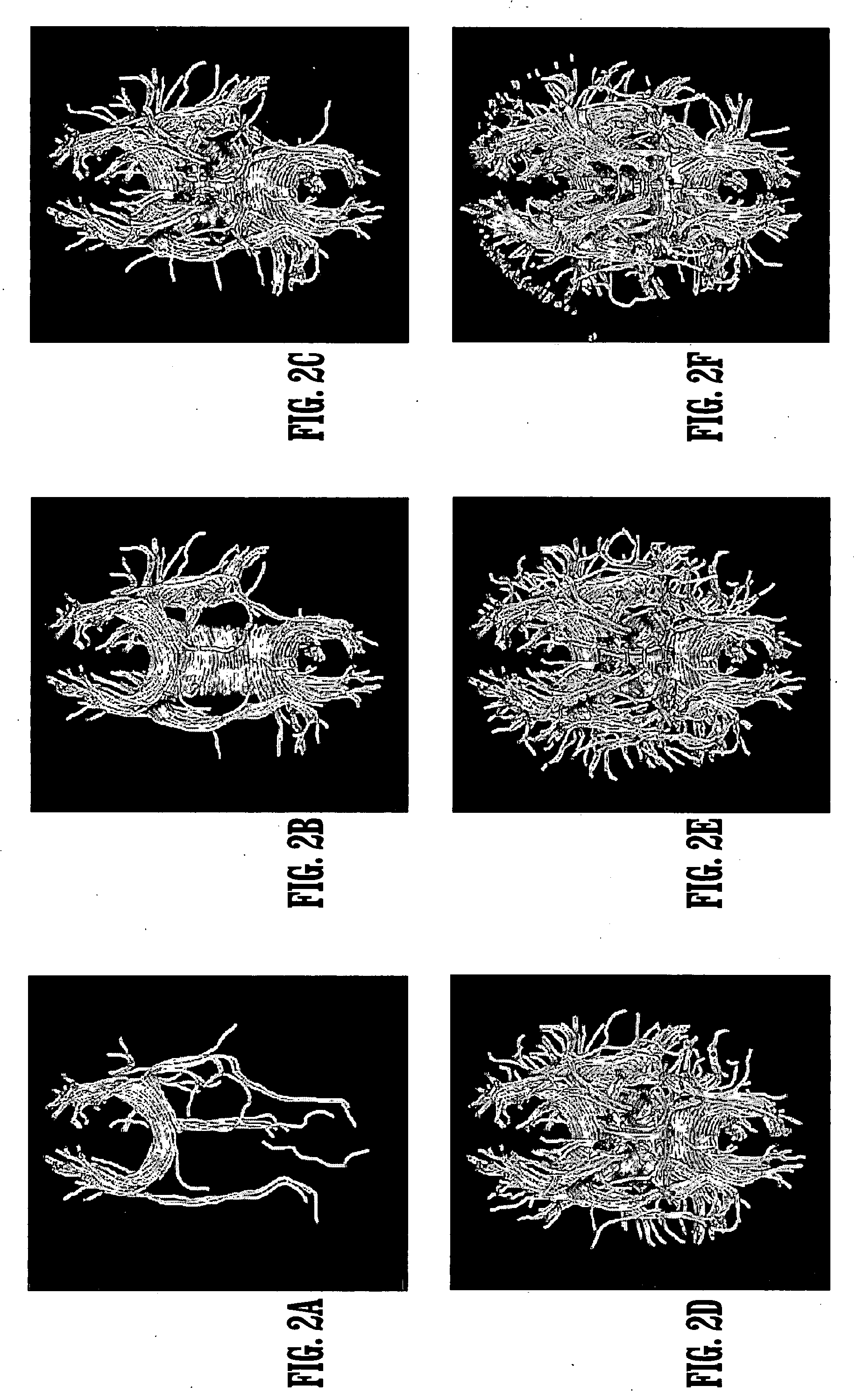
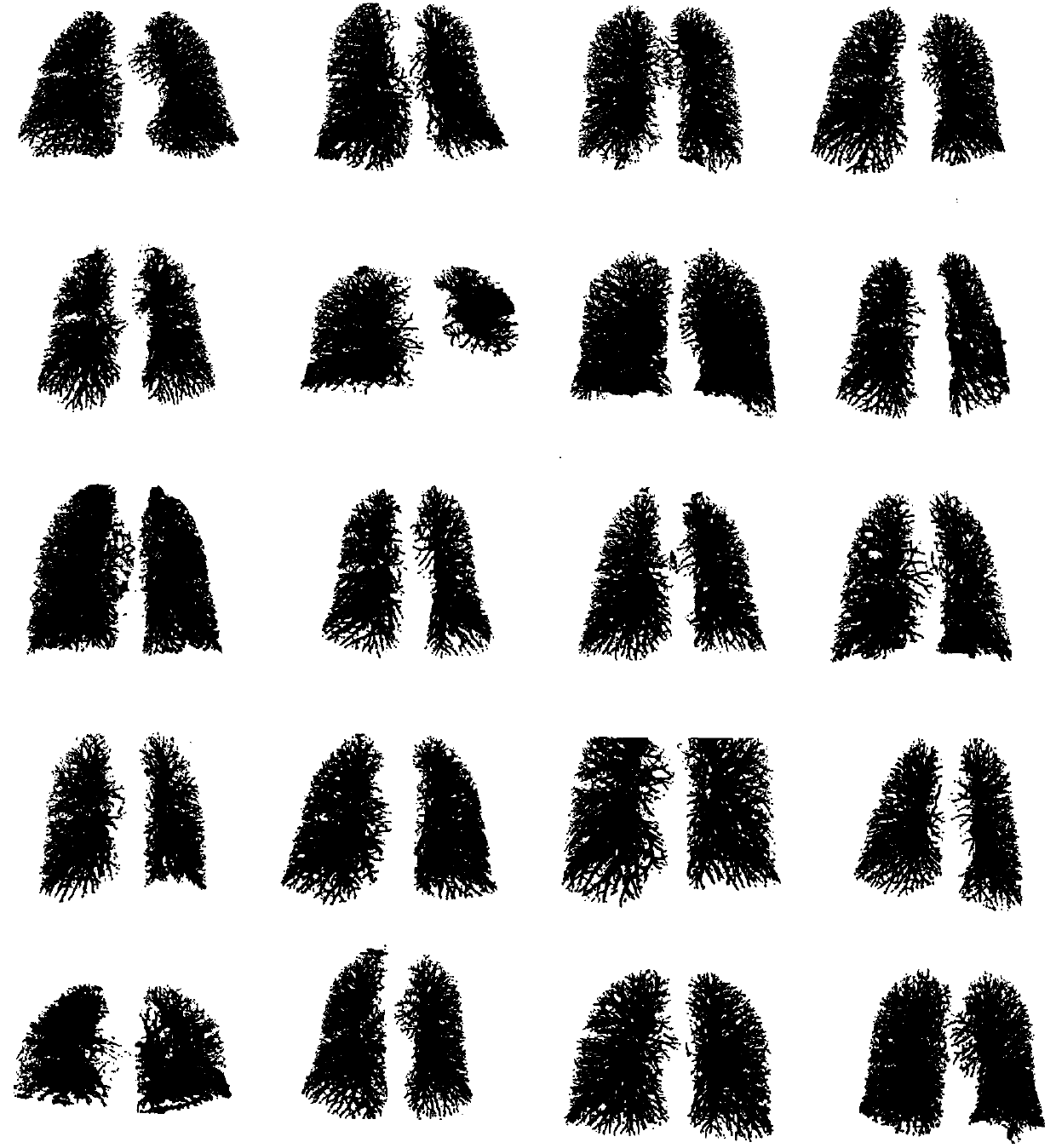
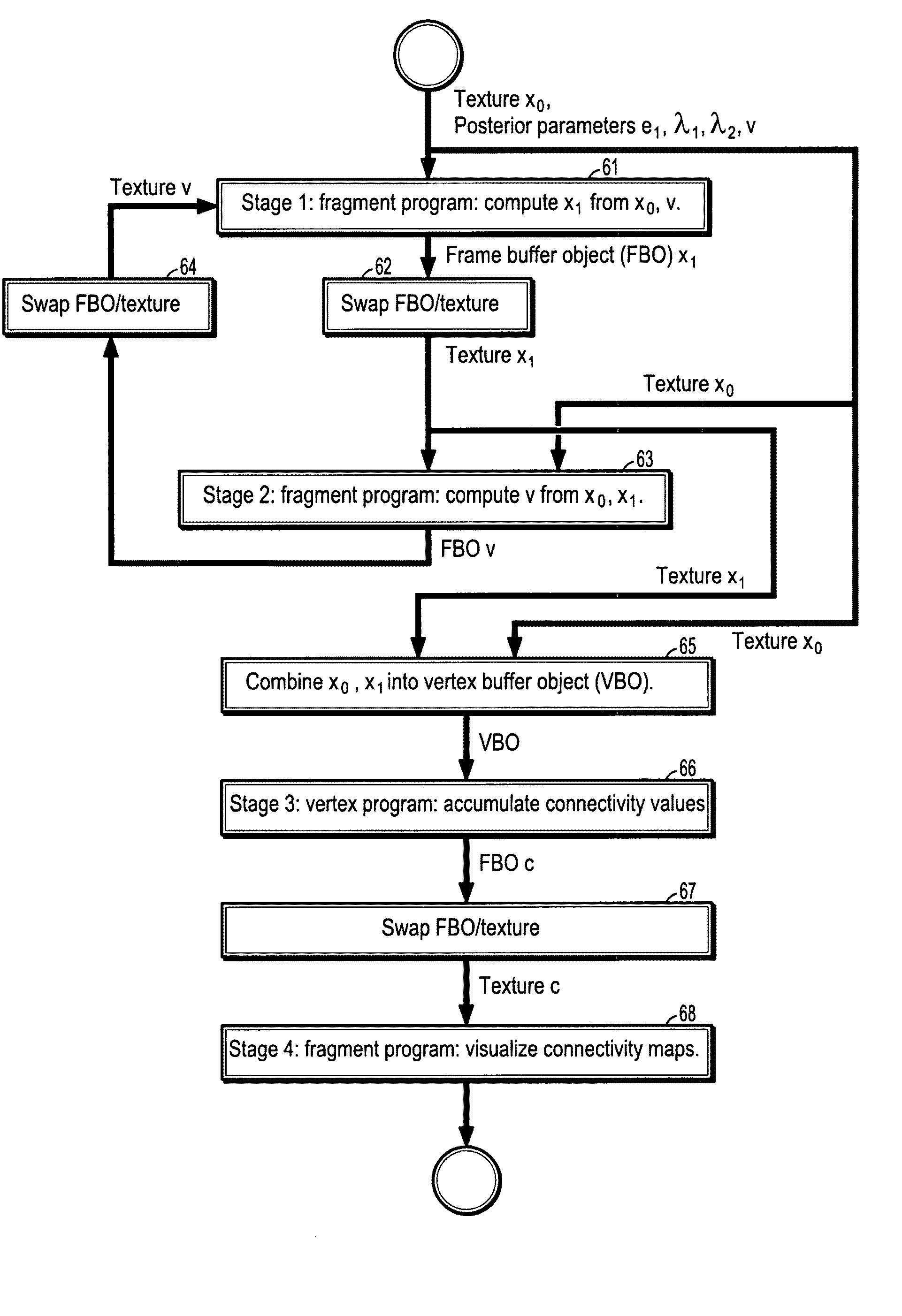
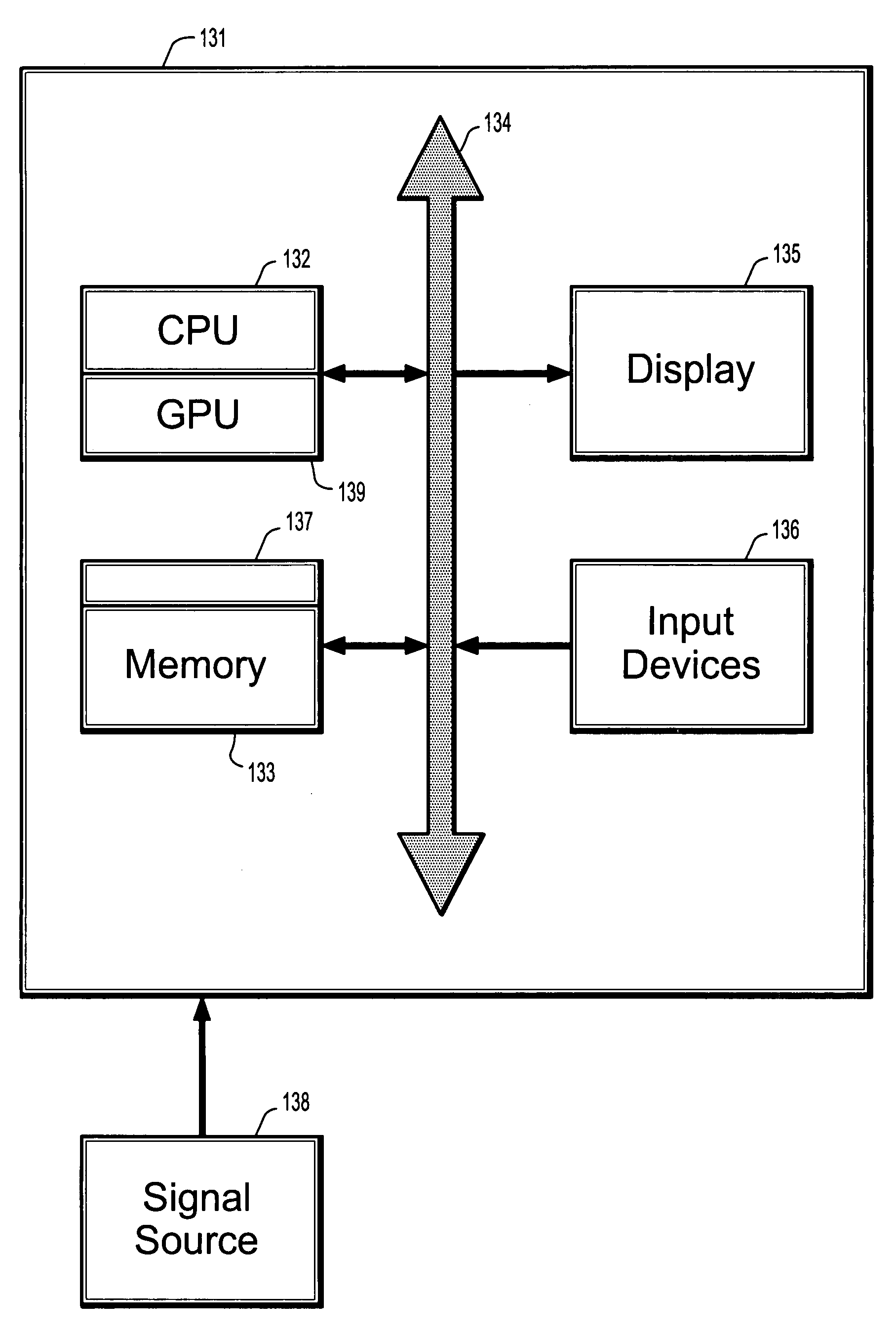
System and method for stochastic DT-MRI connectivity mapping on the GPU
InactiveUS7672790B2Highly parallelizableDrawing from basic elementsMagnetic measurementsGraphicsDiffusion
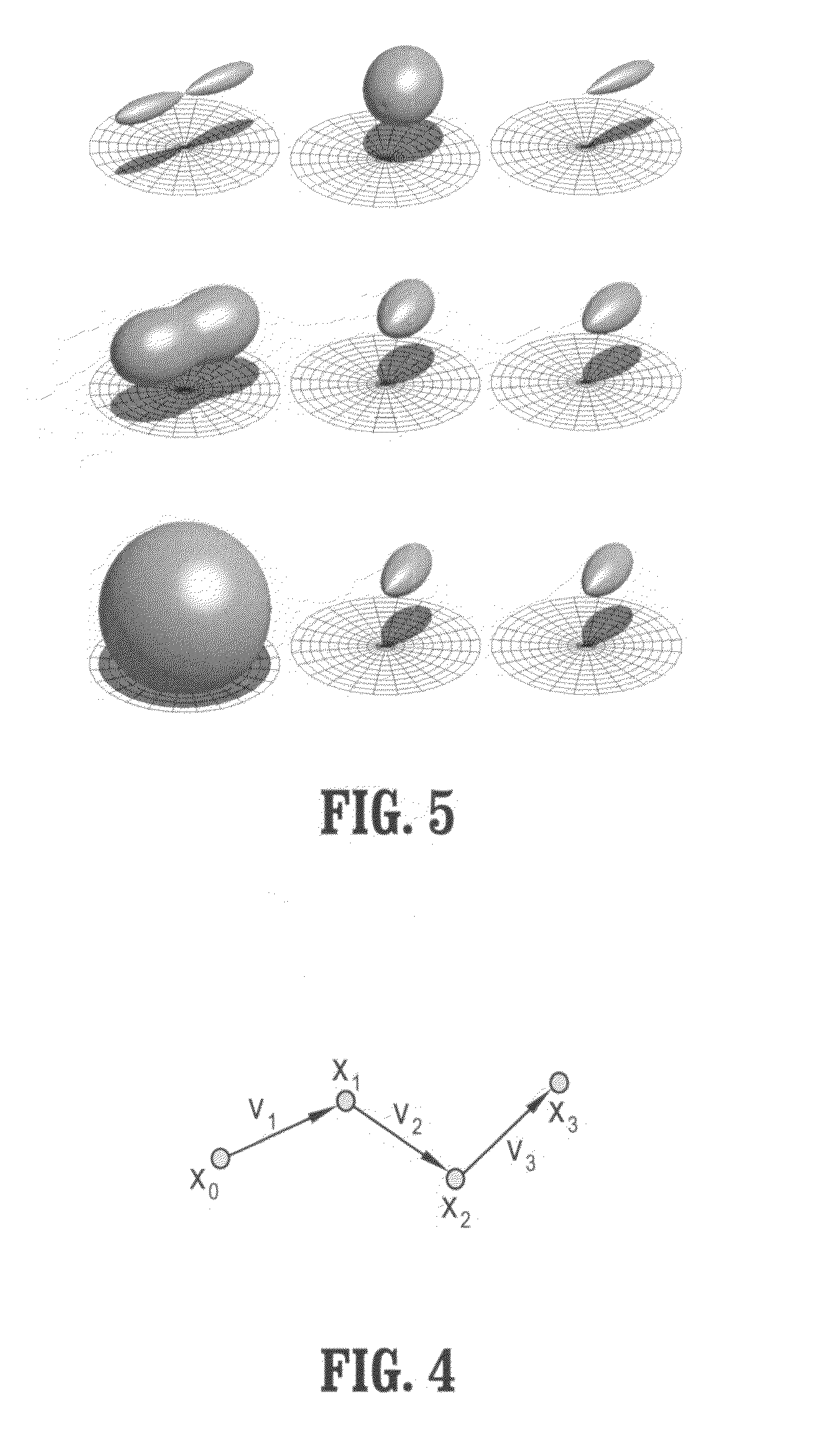
A graphics processing unit implemented method for fiber tract mapping from diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging data includes providing a diffusion tensor magnetic resonance brain image volume, initializing a set of fiber positions in a 3D set of points, fiber displacements, and a posterior distribution for an updated fiber displacement in terms of the initial displacements and diffusion tensors, randomly sampling a set of updated fiber displacements from said posterior distribution, computing a new set of fiber positions from said initial fiber positions and said updated fiber displacements, wherein a fiber path comprises a set of fiber points connected by successive fiber displacements, accumulating connectivity values in each point of said 3D set of points by additive alpha-blending a scaled value if a fiber path has passed through a point and adding zero if not, and rendering said connectivity values.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Correction of the effect of spatial gradient field distortions in diffusion-weighted imaging
ActiveUS6969991B2Convenient distanceMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionField of viewIsocenter
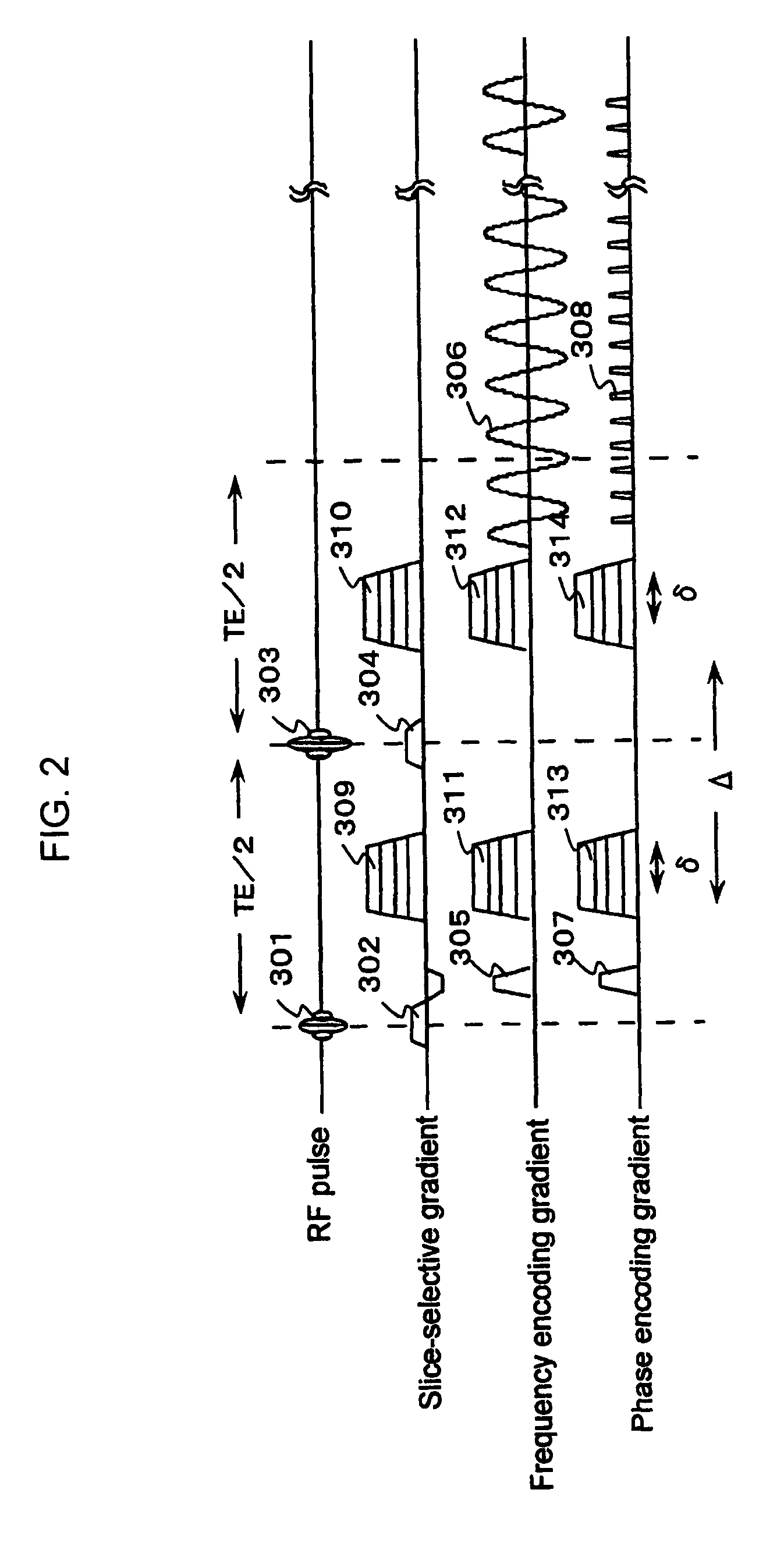
A general mathematical framework is formulated to characterize the contribution of gradient non-uniformities to diffusion tensor imaging in MRI. Based on a model expansion, the actual gradient field is approximated and employed, after elimination of geometric distortions, for predicting and correcting the errors in diffusion encoding. Prior to corrections, experiments clearly reveal marked deviations of the calculated diffusivity for fields of view generally used in diffusion experiments. These deviations are most significant with greater distance from the magnet's isocenter. For a FOV of 25 cm the resultant errors in absolute diffusivity can range from approximately −10 to +20 percent. Within the same field of view, the diffusion-encoding direction and the orientation of the calculated eigenvectors can be significantly altered if the perturbations by the gradient non-uniformities are not considered. With the proposed correction scheme most of the errors introduced by gradient non-uniformities can be removed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
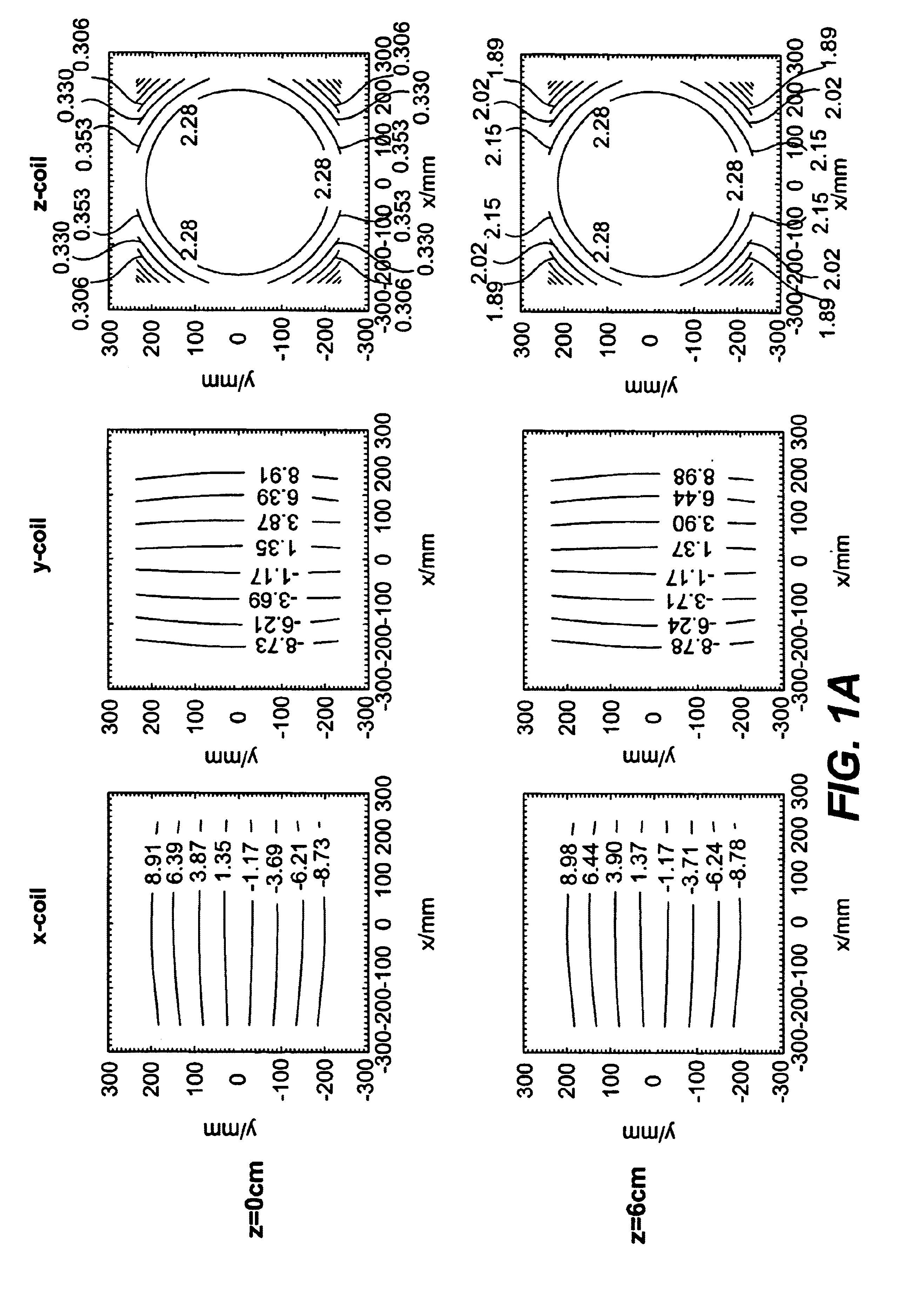
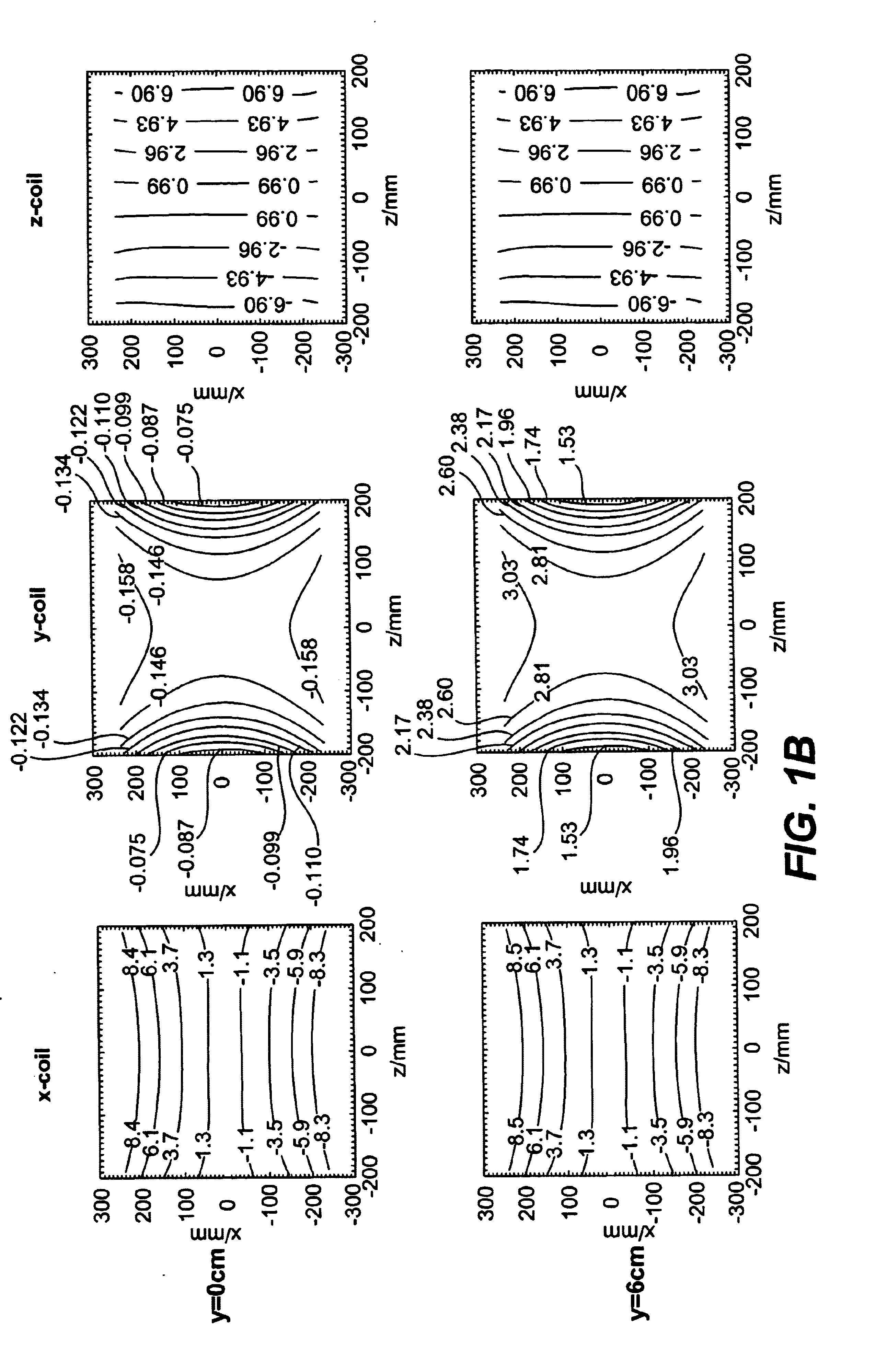
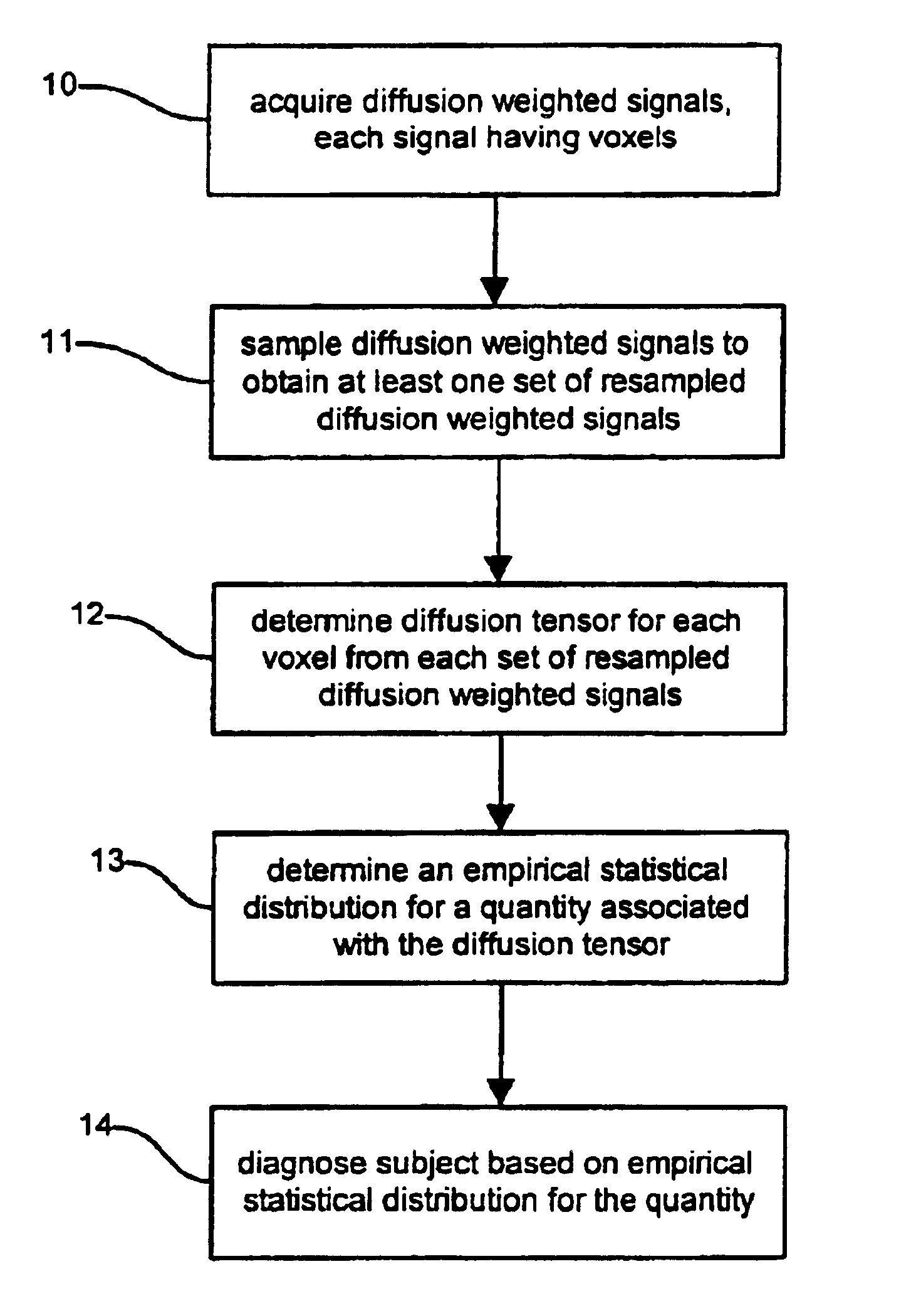
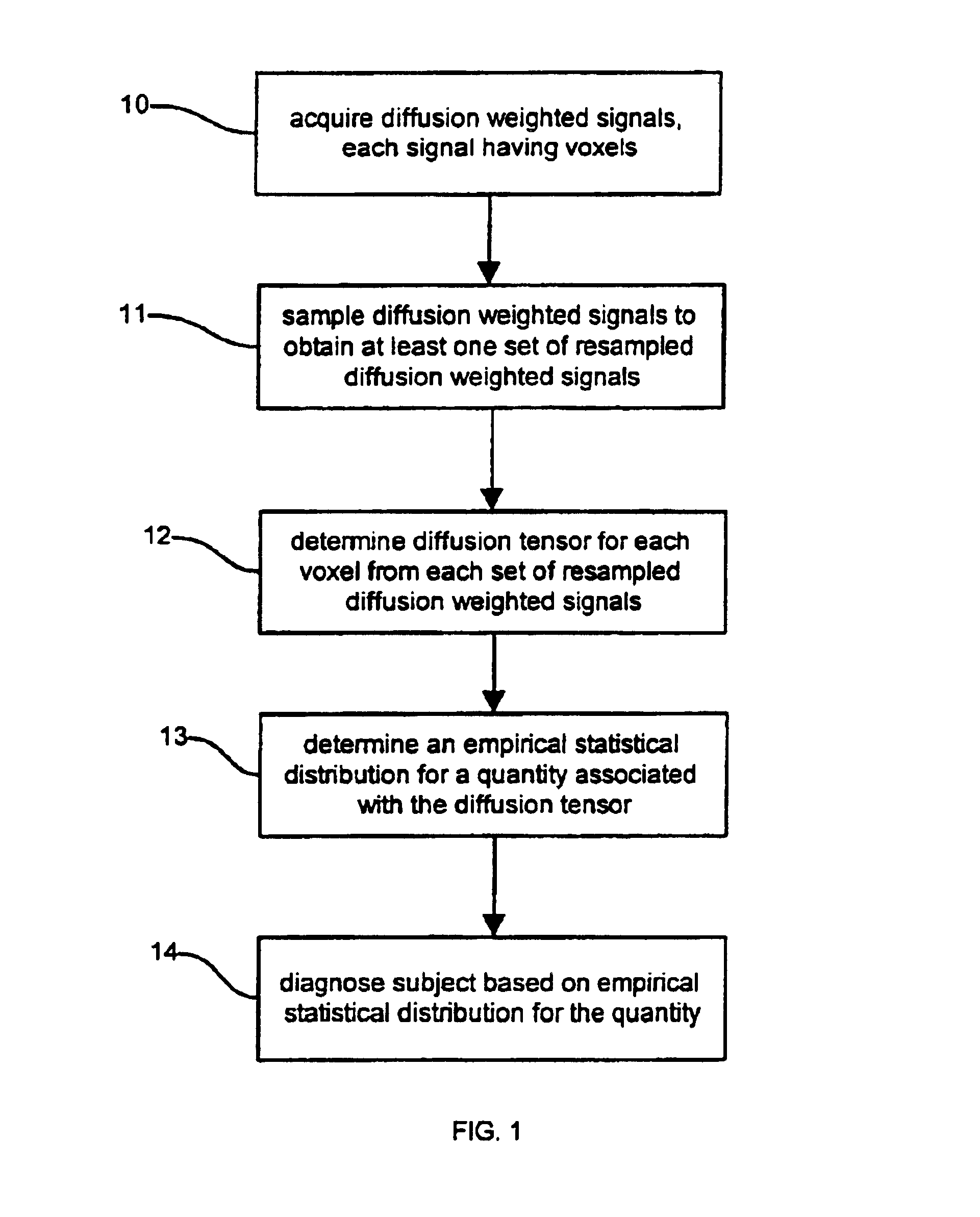
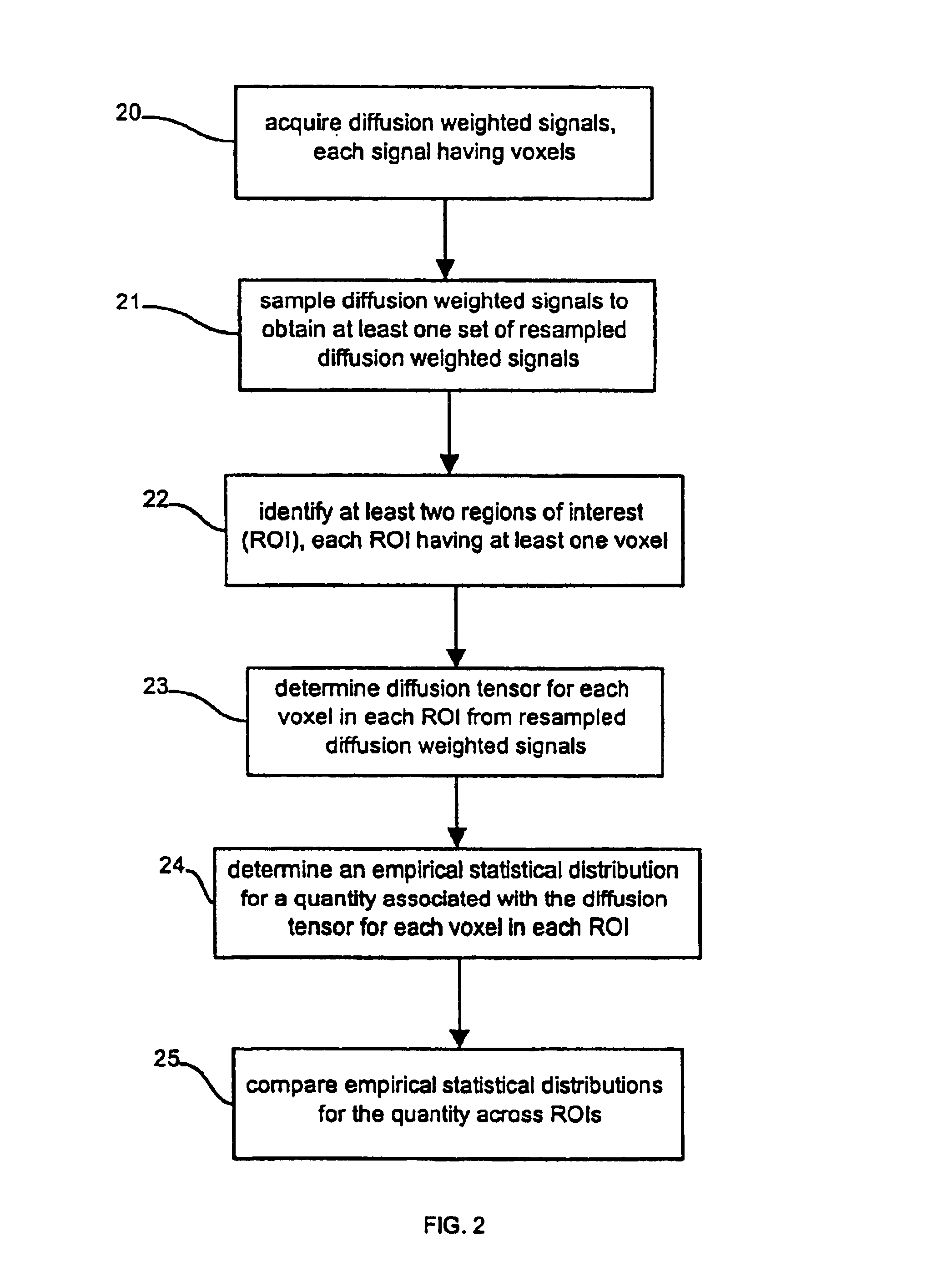
Determination of an empirical statistical distribution of the diffusion tensor in MRI
InactiveUS6845342B1Easy to learnLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNuclear monitoringDiffusionVoxel
Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance signals are analyzed. Diffusion weighted, signals are acquired, each signal having a plurality of voxels (10). The diffusion weighted signals are sampled to obtain at least one set of resampled diffusion weighted signals (11). A diffusion tensor for each voxel is determined from each set of the resampled diffusion weighted signals (12). An empirical statistical distribution is determined for a quantity associated with the diffusion tensor from the diffusion tensors determined from the at least one set of the resampled diffusion weighted signals (13).
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF
Automated fiber tracking of human brain white matter using diffusion tensor imaging
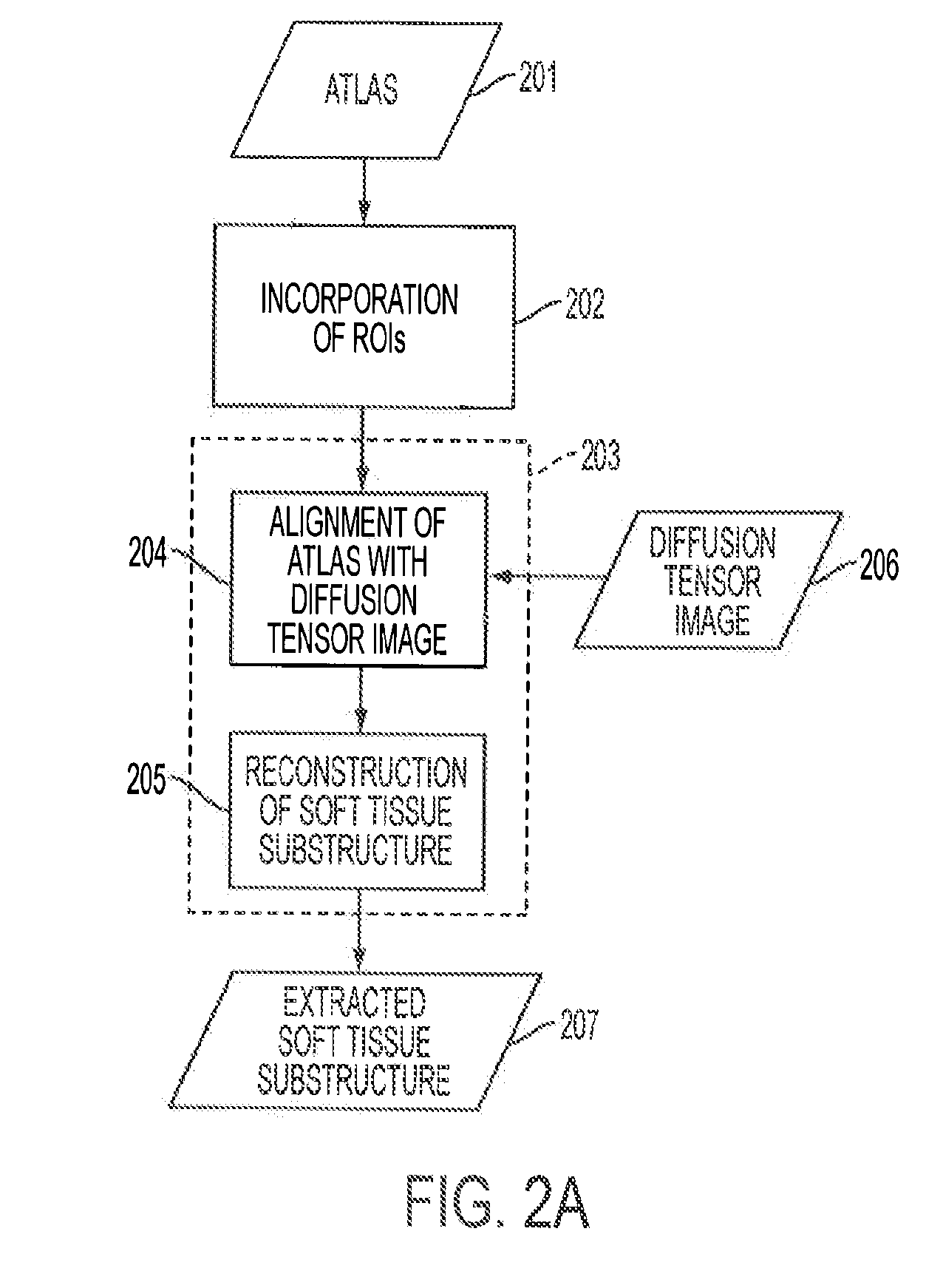
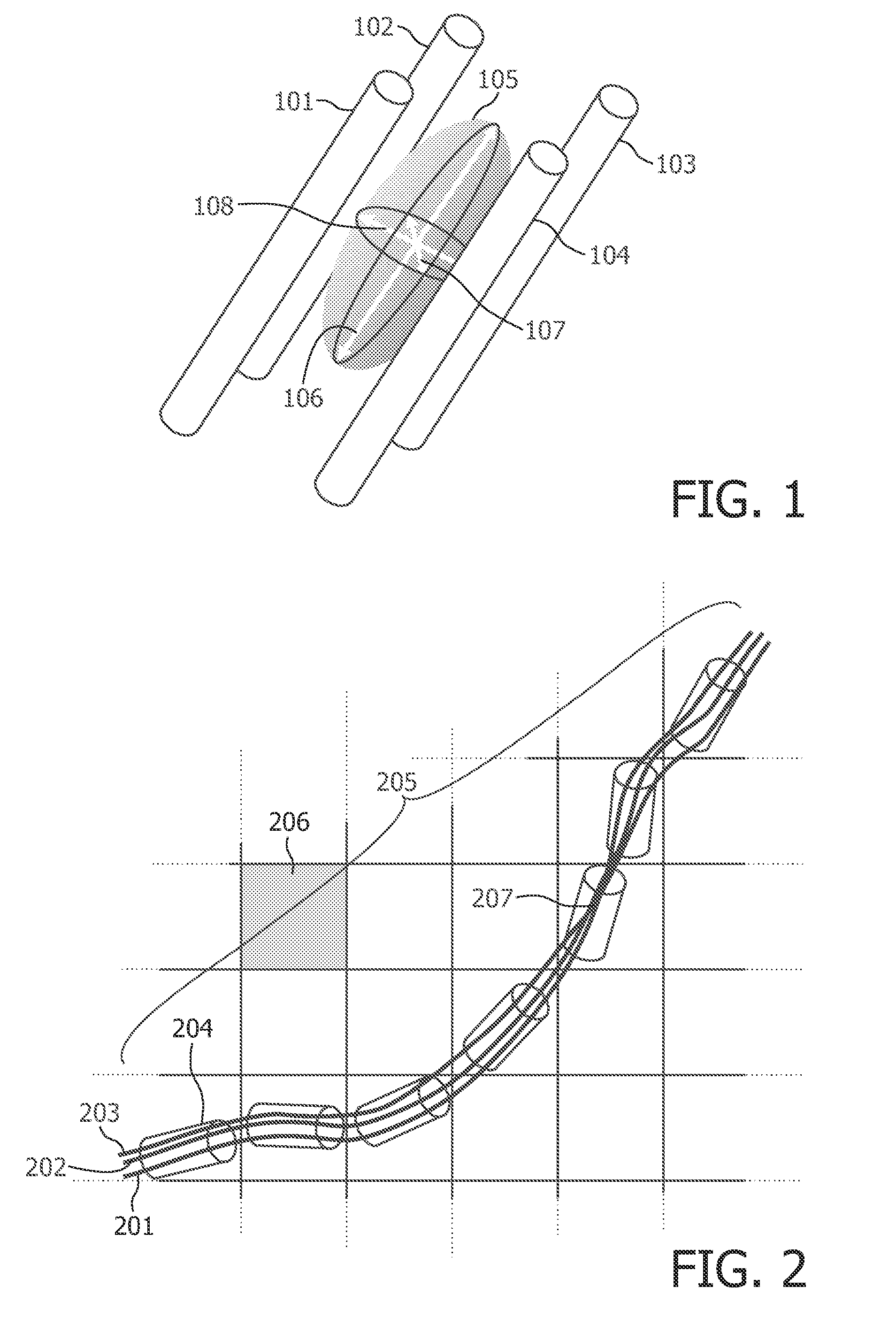
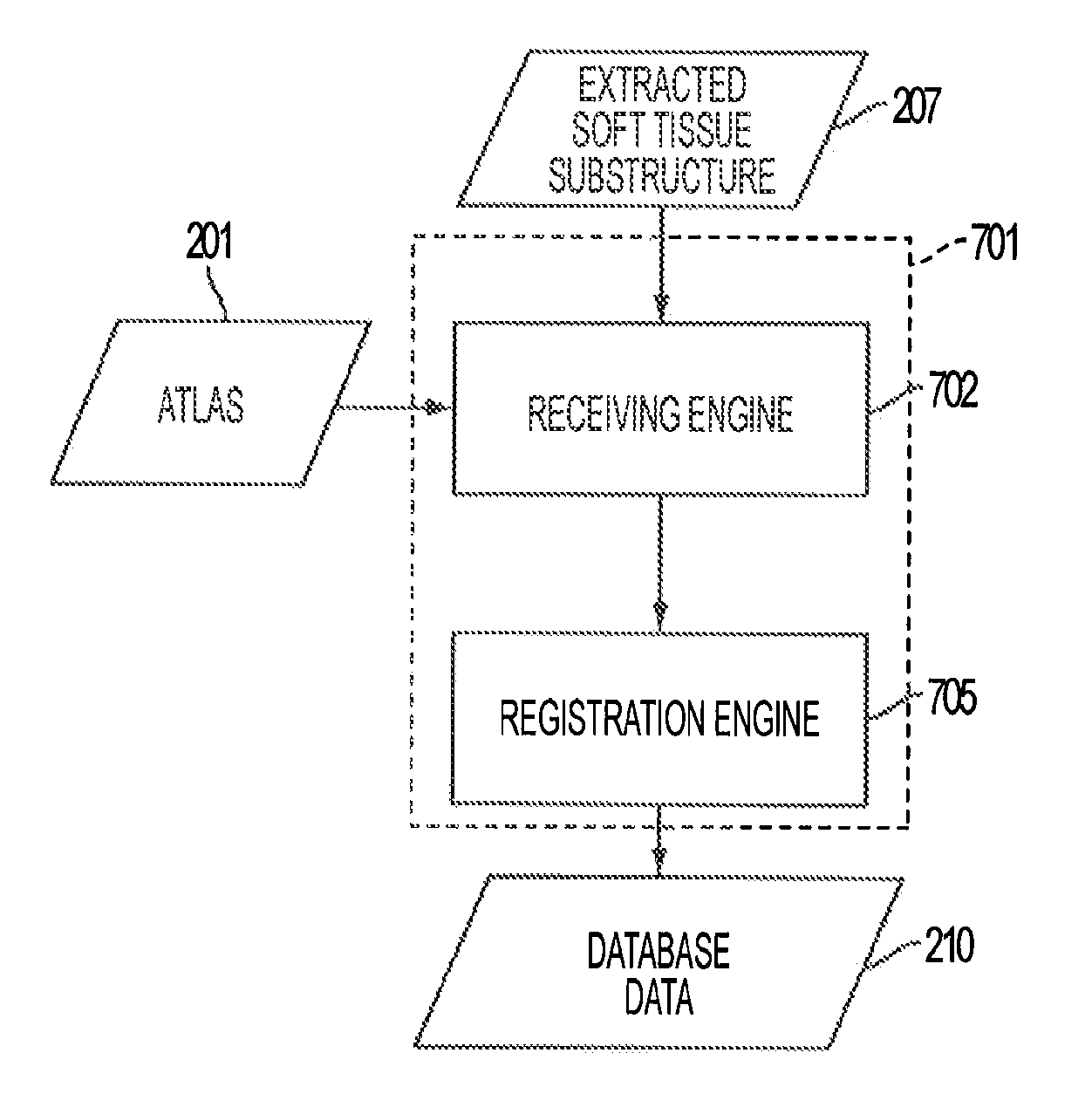
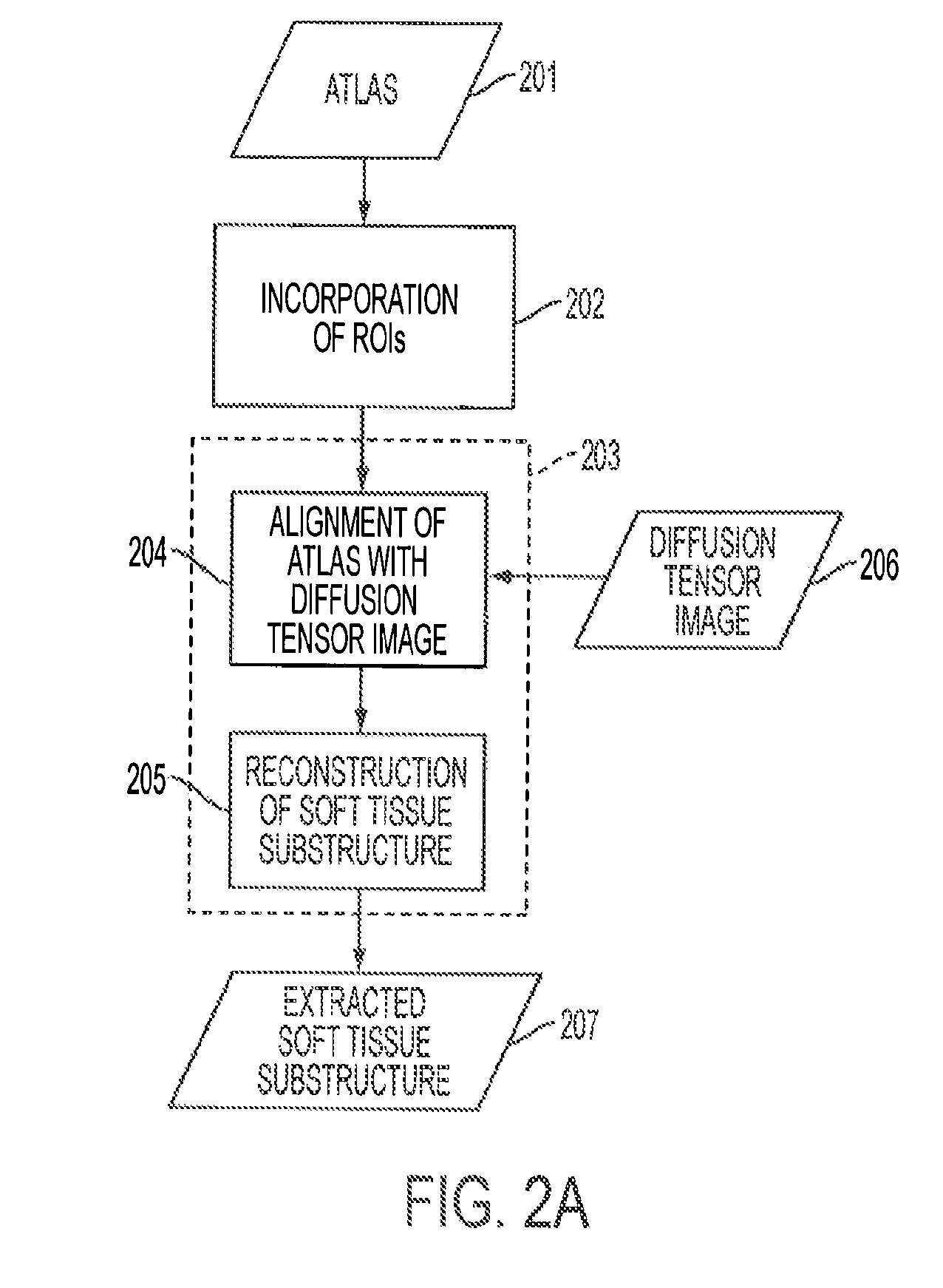
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, comprising: a MRI scanner; a signal processing system in communication with the magnetic resonance imaging scanner to receive magnetic resonance (MR) signals for forming magnetic resonance images of a subject under observations; a data storage unit in communication with the signal processing system, wherein the data storage unit contains database data corresponding to a soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The database data includes information identifying at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The signal processing system is adapted to process MR signals received from the MRI scanner to automatically identify at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
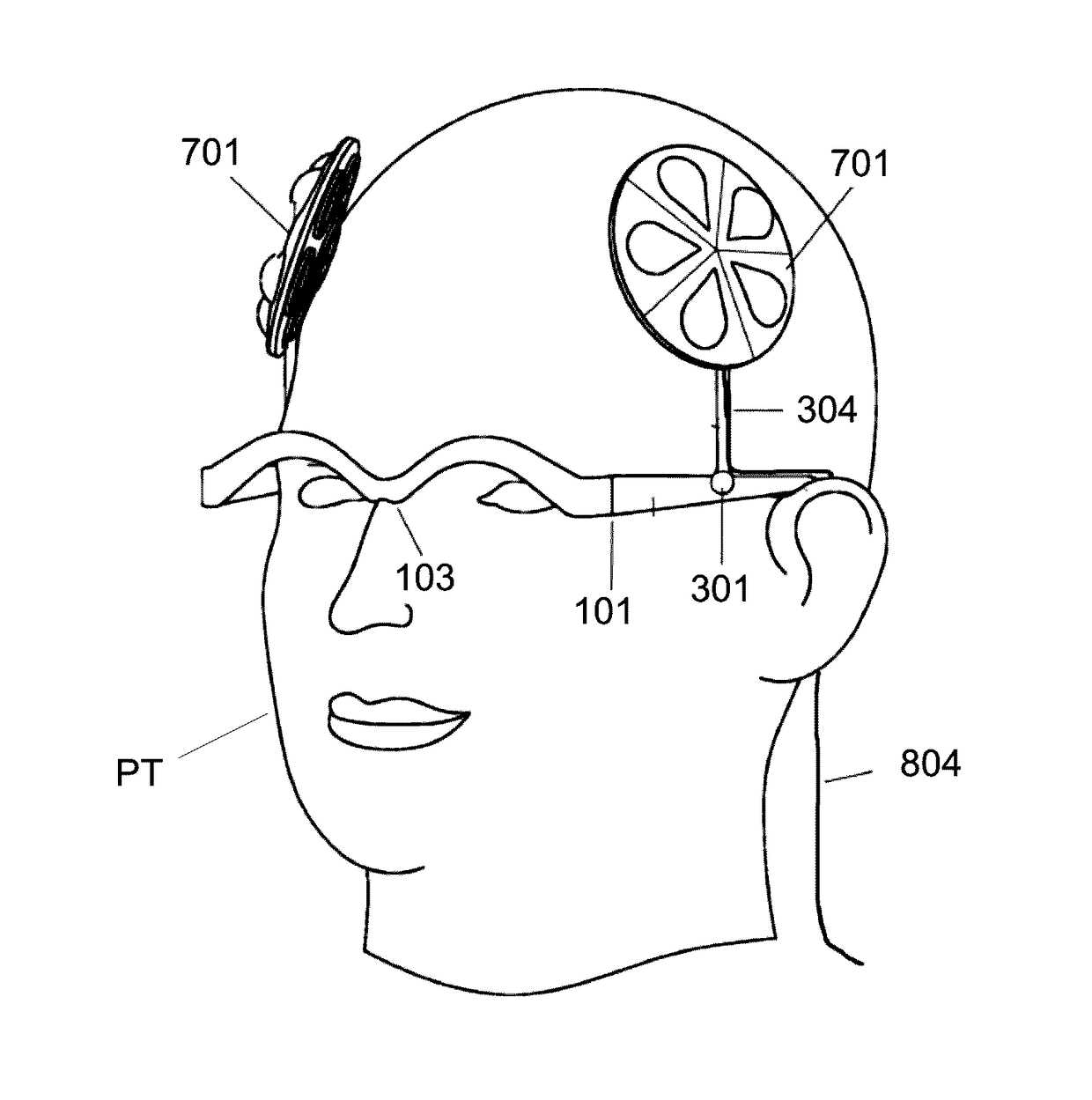
System for variably configurable, adaptable electrode arrays and effectuating software
ActiveUS20170087367A1Improve cognitive abilityAccurate informationElectroencephalographyUltrasound therapyDiseasePresent method
Electrical non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS) delivers weak electrical currents to the brain via electrodes that are affixed to the scalp. NIBS can excite or inhibit the brain in areas that are impacted by that electrical current during and for a short time following stimulation. Electrical NIBS can be used to change brain structure in terms of increasing white matter integrity as measured by diffusion tensor imaging. Together the electrical NIBS can induce changes in brain structure and function. The present methods and devices are adaptable to and configurable for facilitating the enhancement of brain performance, and the treatment of neurological diseases and tissues. The present methods and devices are advantageously designed to utilize modern electrodes deployed with, inter alia, various spatial arrangements, polarities, and current strengths to target brain areas or networks to thereby enhance performance or deliver therapeutic interventions.
Owner:STIMSCI INC
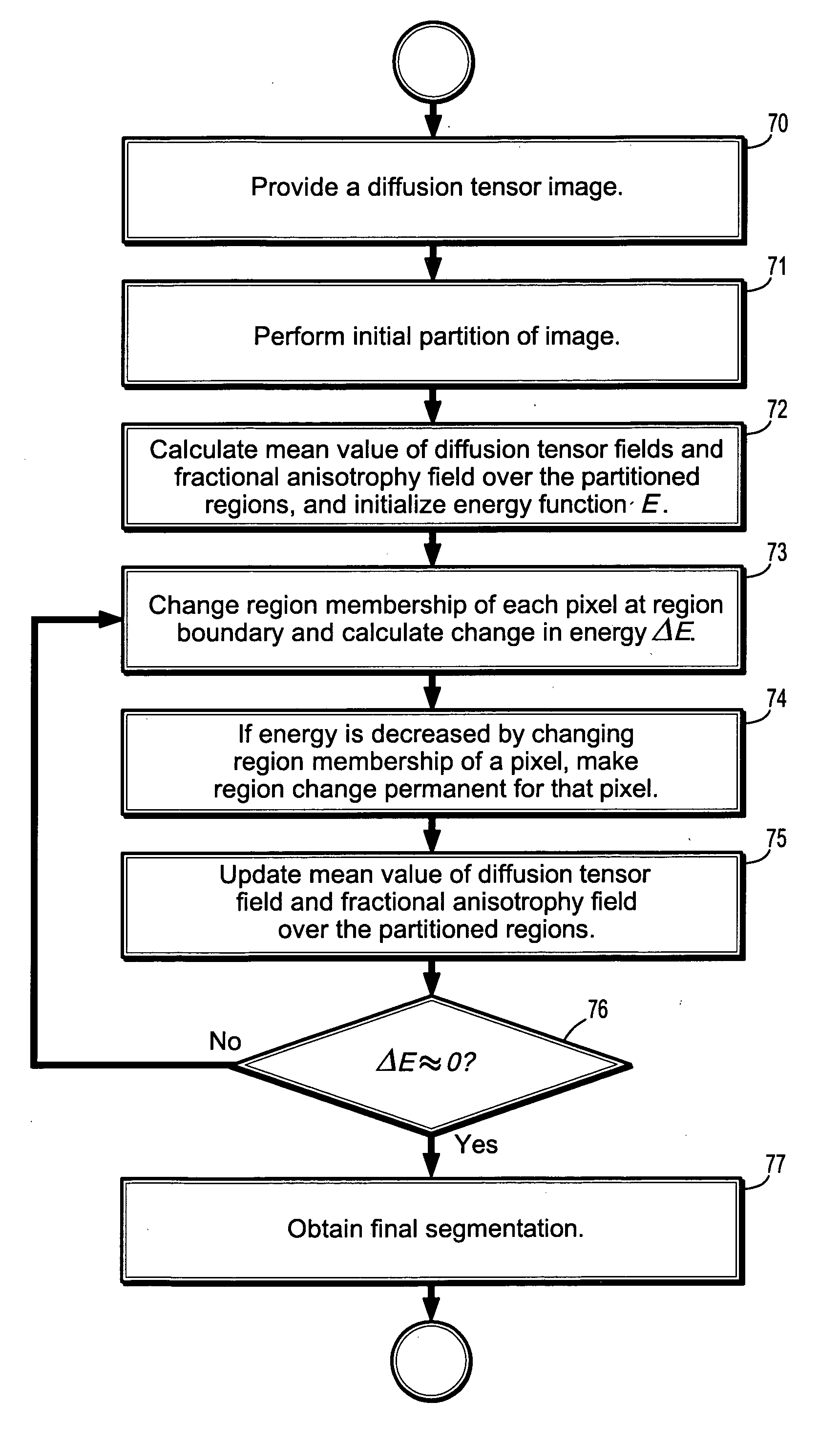
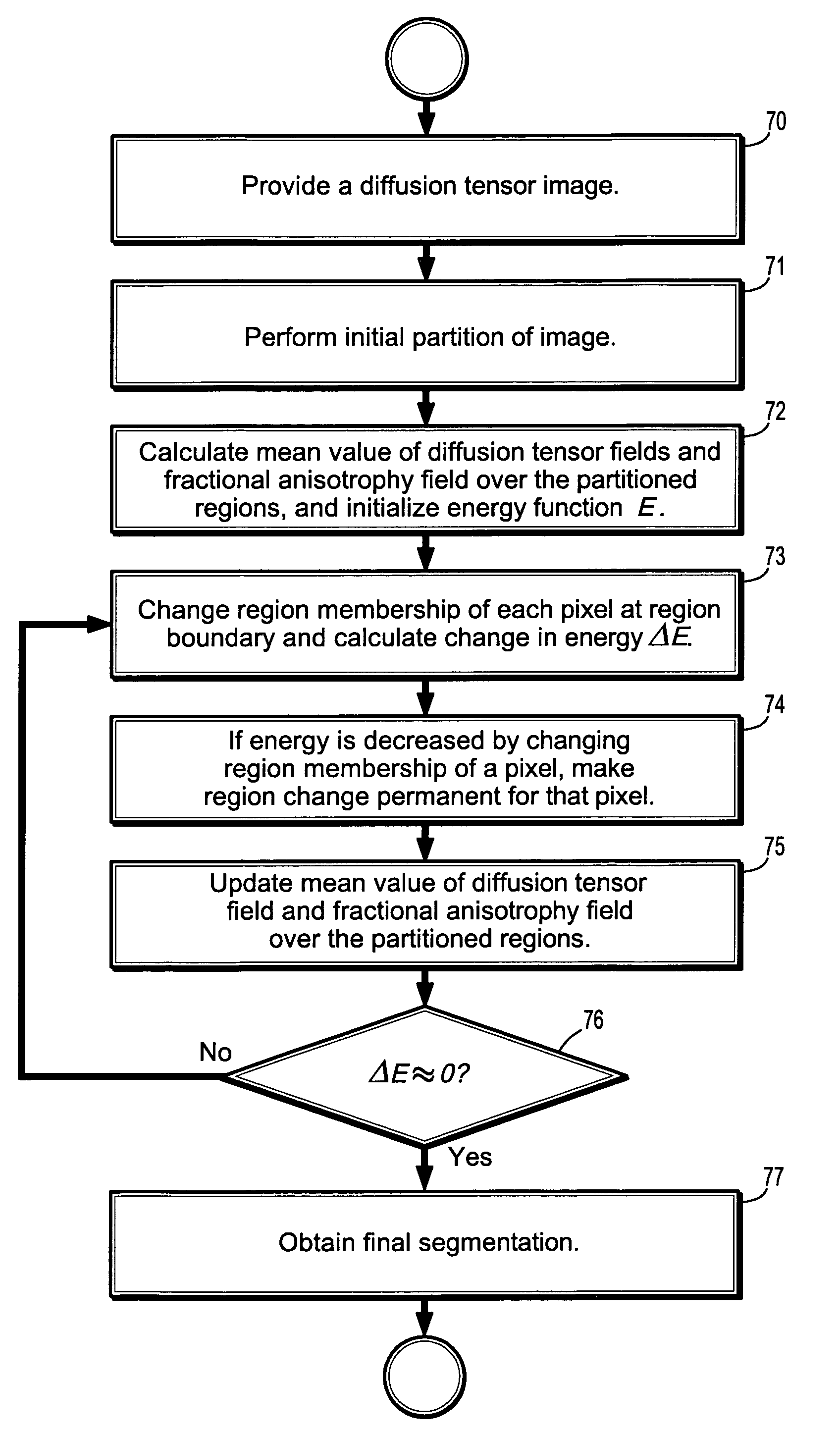
System and method for fast tensor field segmentation
InactiveUS20060158447A1Facilitates efficient segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionEnergy functional
Segmenting a digitized image includes providing a diffusion tensor field image, partitioning the image into 2 regions, each point being assigned to one of the regions, associating a level-set function with each region, the level-set function having a negative value in one region and a positive value in the other region, calculating a mean value of the diffusion tensor field over each of 2 regions, initializing an energy defined as a functional of level-set functions and diffusion tensor field, changing the region membership of each point in the image if the energy functional value decreases as a result of region membership change and updating said mean value of said diffusion tensor field over each of 2 regions, and obtaining a segmentation of the image when the magnitude of the change of the energy function value resulting from changing the region membership of a point is less then a predetermined threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
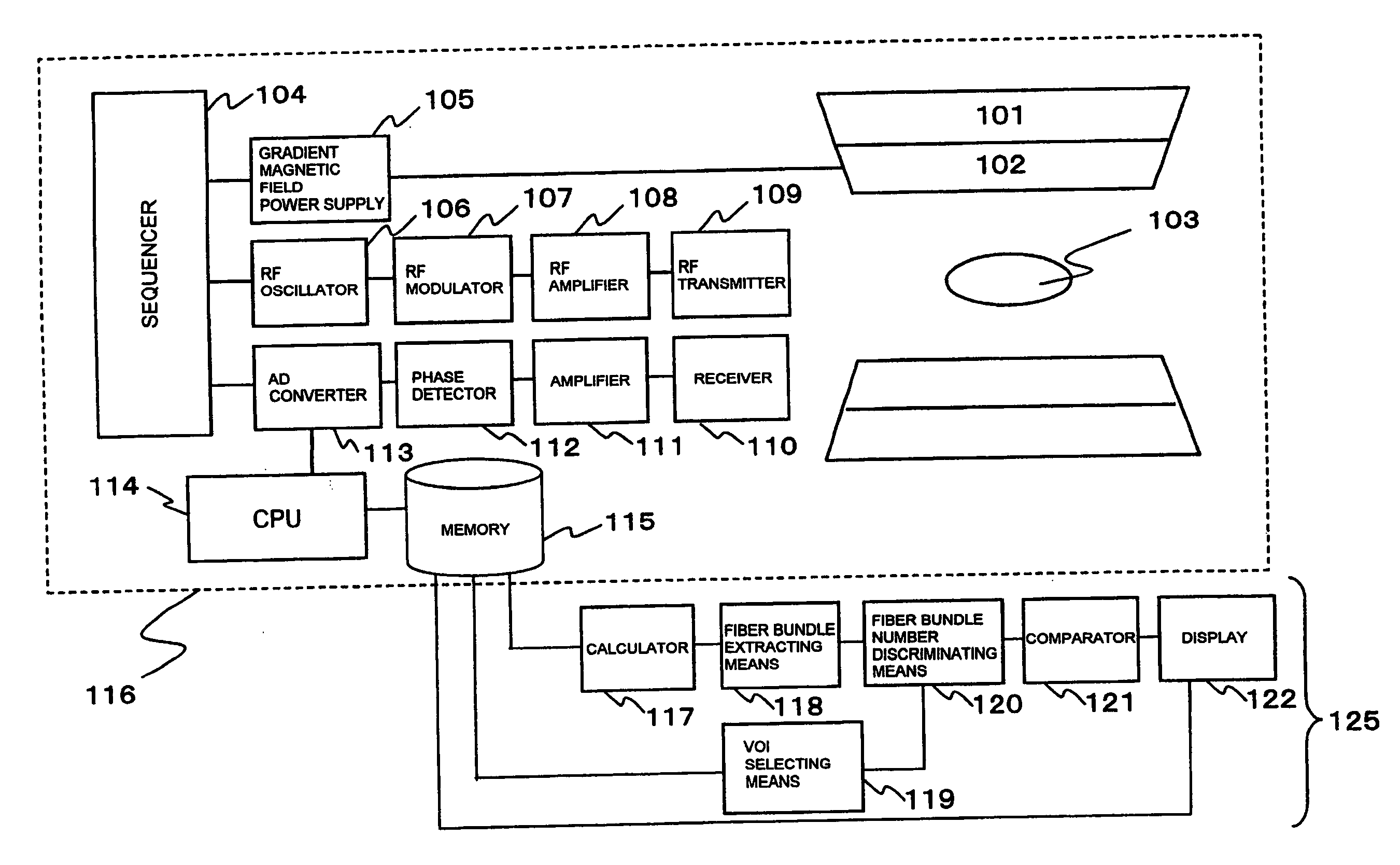
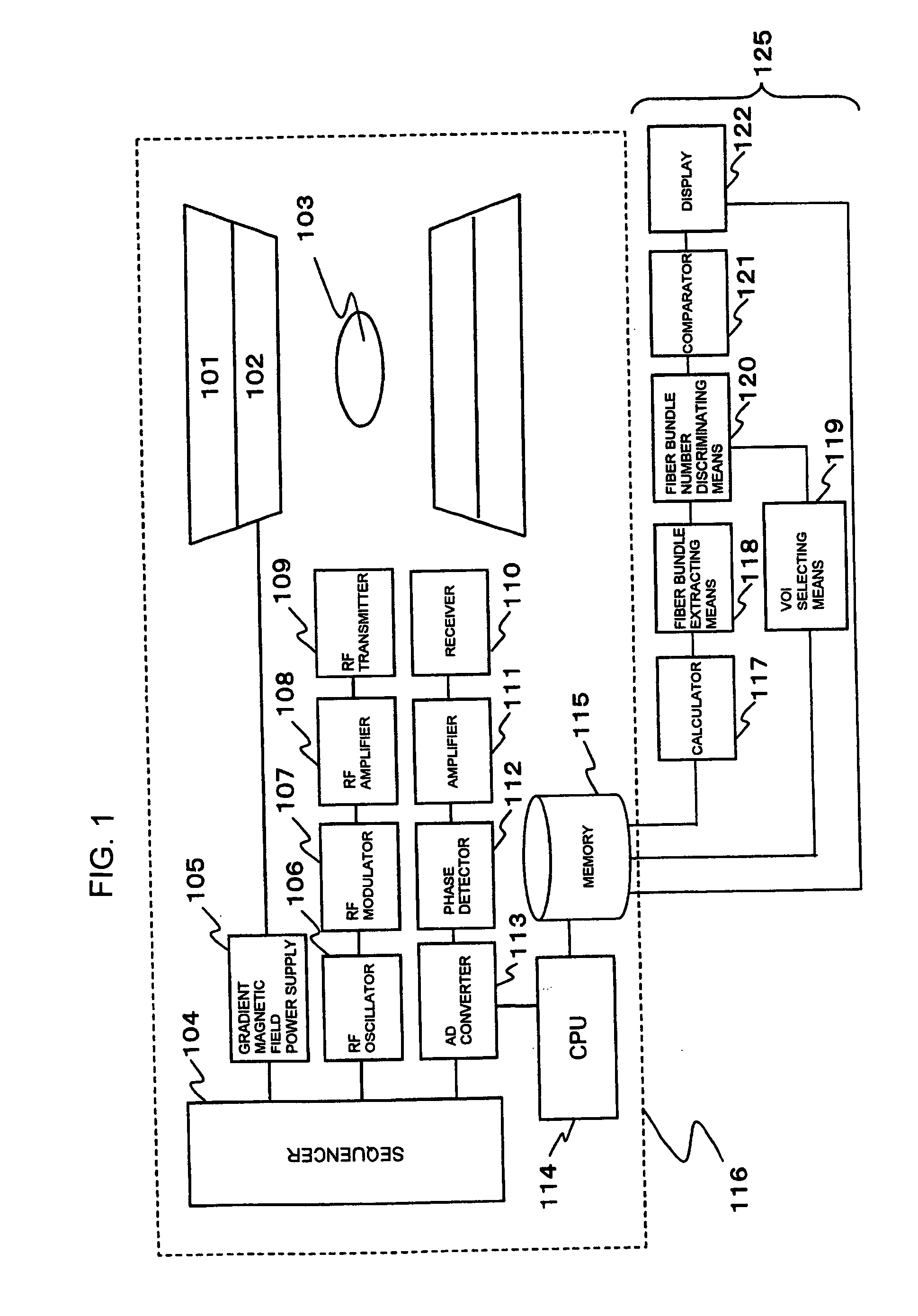
NMR measurement system and NMR image processing system for neural fiber bundles with volume of interest (VOI) optimization
InactiveUS7834627B2Number of fiber bundles can be quantitatively figured outMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
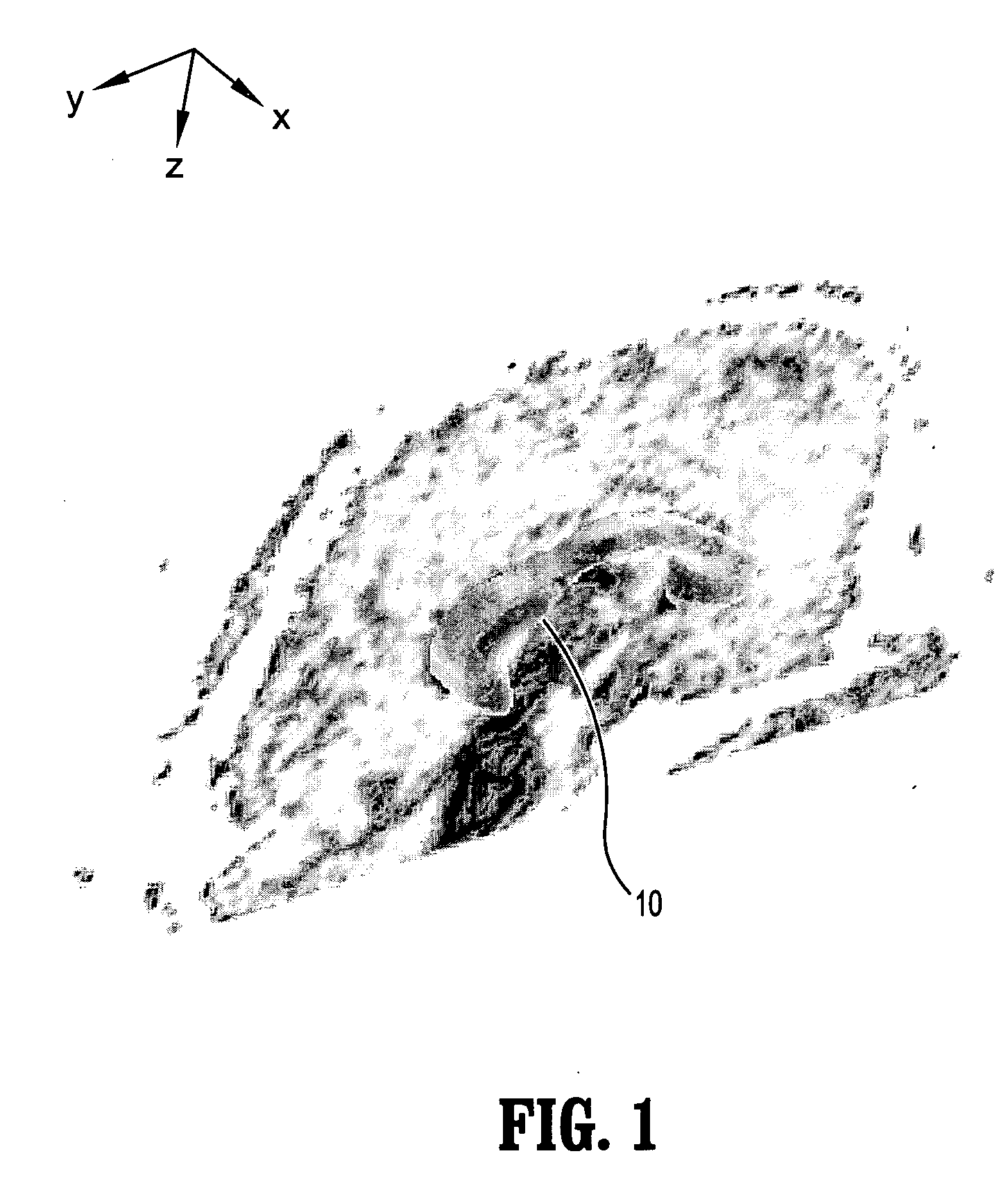
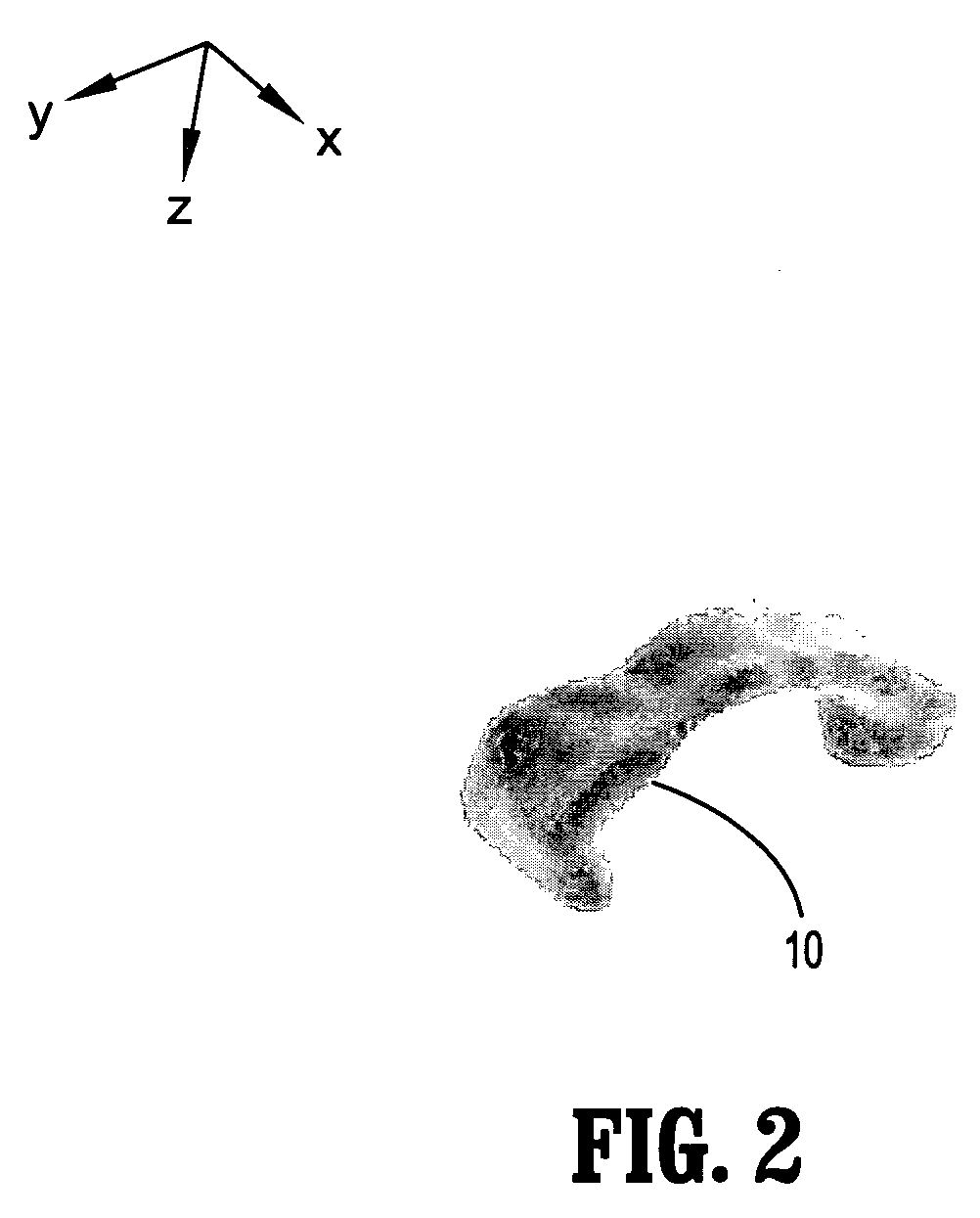
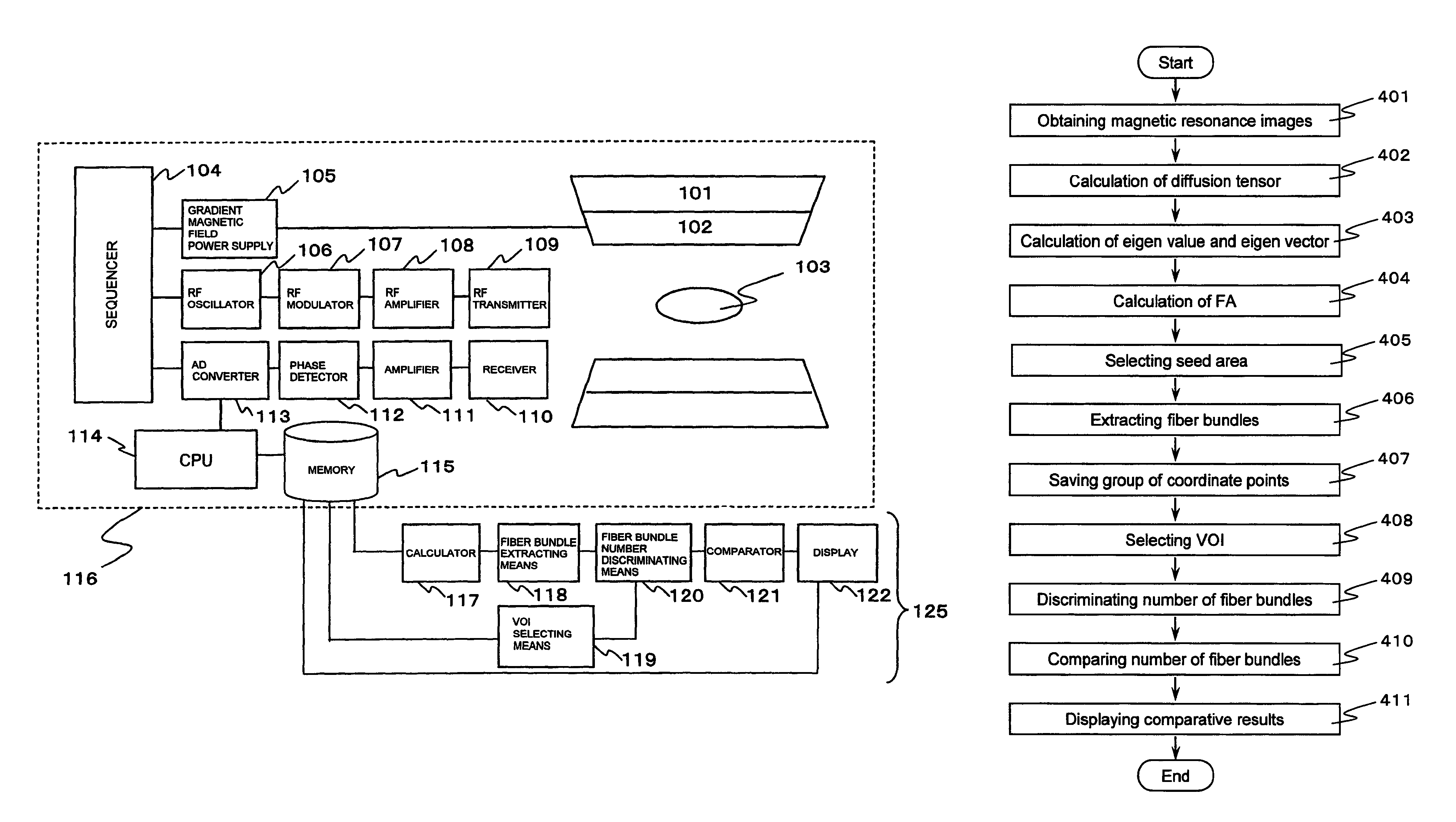
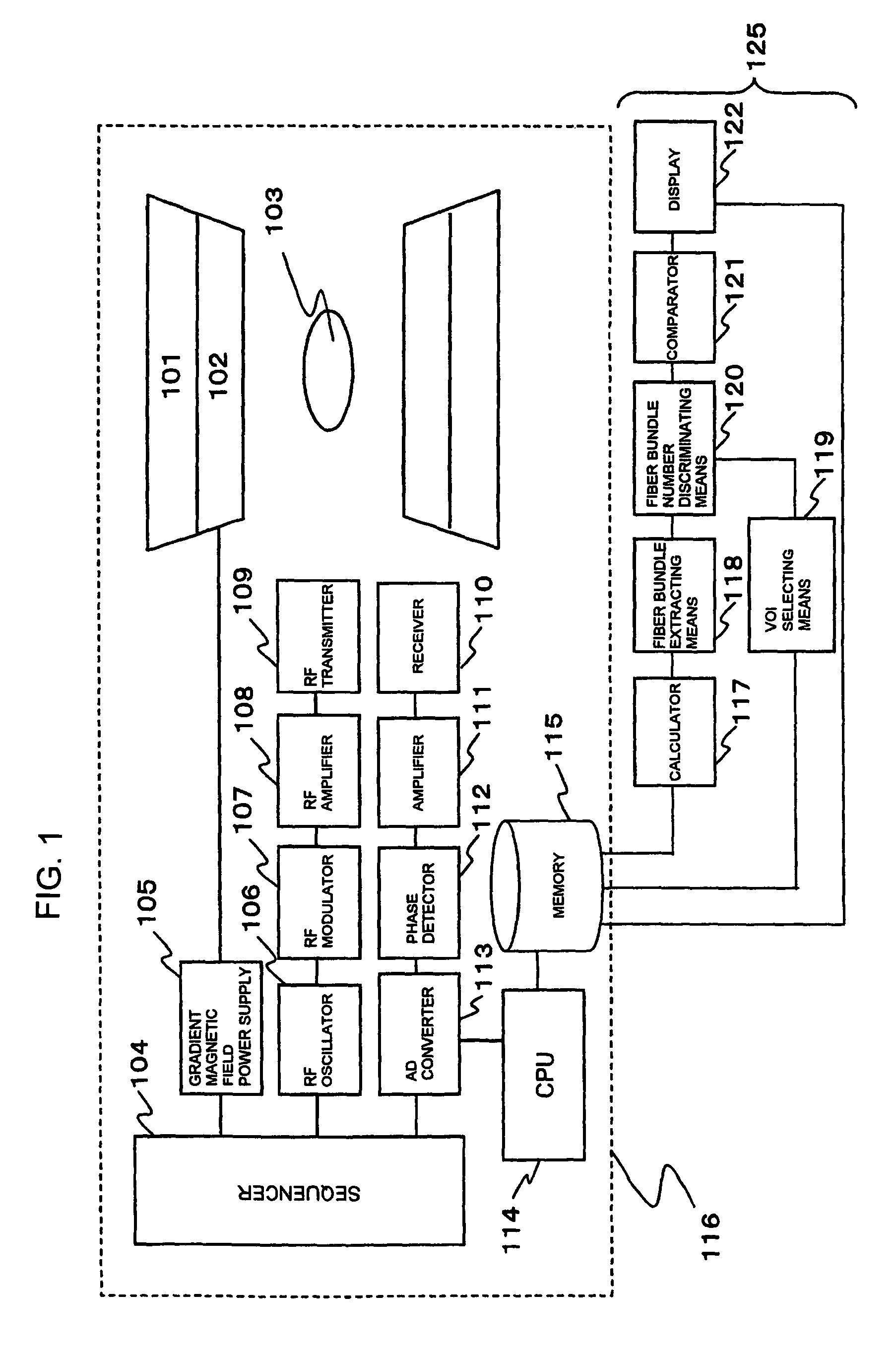
The present invention provides a measurement system and an image processing system for quantitatively figuring out the fiber bundles which are passing through any VOI. A static magnetic field and an RF signal are applied to a subject, and a nuclear magnetic resonance signal is received from the subject (401). Diffusion tensor is calculated from the nuclear magnetic resonance signals (402). As to a target area for receiving the nuclear magnetic resonance signal from the subject, fiber bundles passing through multiple predetermined origins, respectively, are extracted in a form of a group of coordinate points for each of the fiber bundles, based on the diffusion tensor calculated by the calculating means (406). At least one VOI is set for the target area for receiving the nuclear magnetic resonance signal (408). Out of the multiple fiber bundles extracted by the fiber bundle extracting means, the fiber bundles having at least one coordinate point of the group of coordinate points being included in the VOI are discriminated and the number of which is counted (409).
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Two-dimensional image-assisted depth image enhancement method
InactiveCN106408524AGuaranteed Depth DiscontinuityGuaranteed depth uniformityImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageDiffusivity tensor
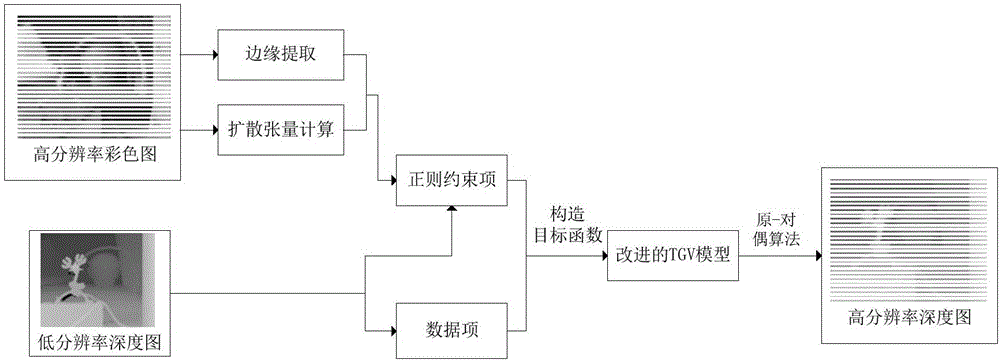
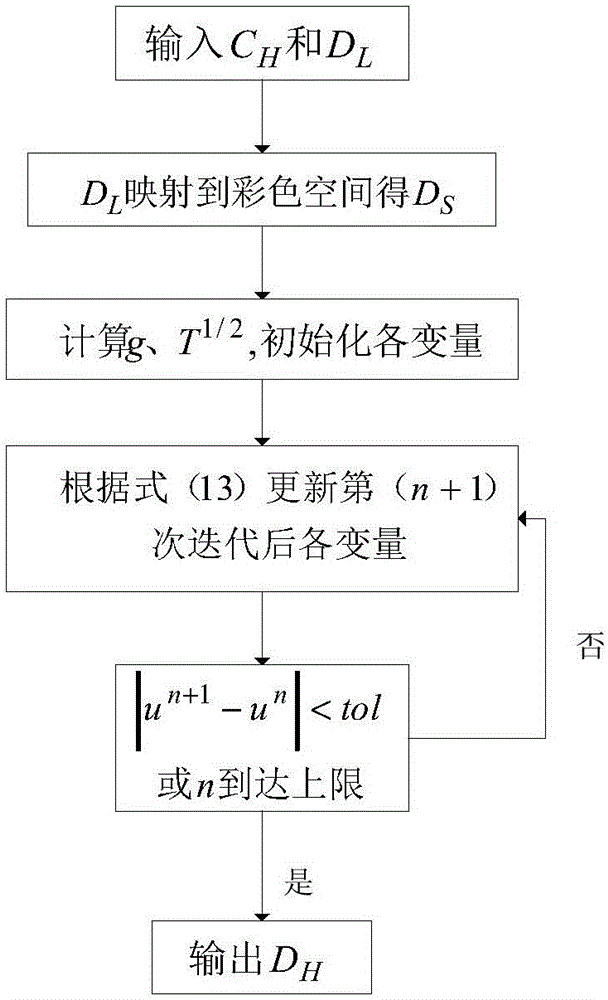
The invention discloses a two-dimensional image-assisted depth image enhancement method. The method includes the steps of utilizing a ToF camera and a high-resolution color camera to obtain a low-resolution depth image and a high-resolution color image of a same scene, and mapping a low-resolution depth map to a high-resolution color space; constructing data items of an objective function according to reconstruction constraints of a depth image; utilizing edge information of the color image to perform weighting on a regularization model, introducing diffusion tensor to a second-order generalized total variation model, and forming a regularization model for characteristics of the depth image; and solving through iterative reweighting and a primal-dual algorithm, so as to obtain a reconstruction result. The two-dimensional image-assisted depth image enhancement method provided by the invention can effectively solve the problems of low resolution, unclear margin and existence of noise of the depth image, and effectively protects the edge structure of the image.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Diffusion tensor imaging white matter fiber clustering method
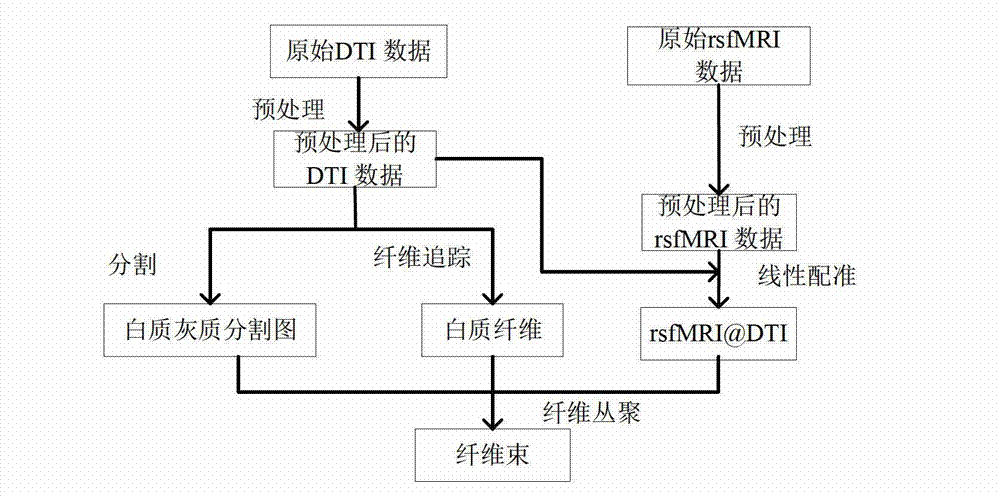
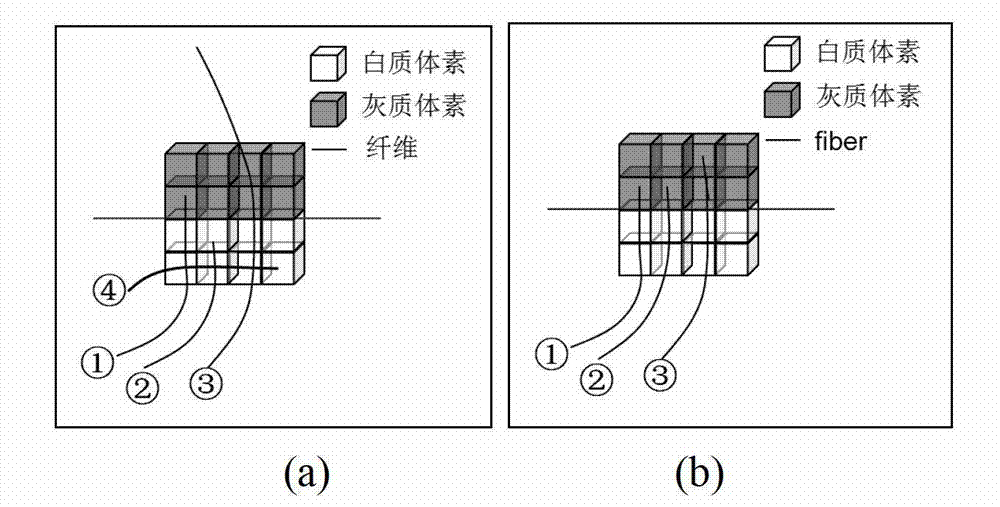
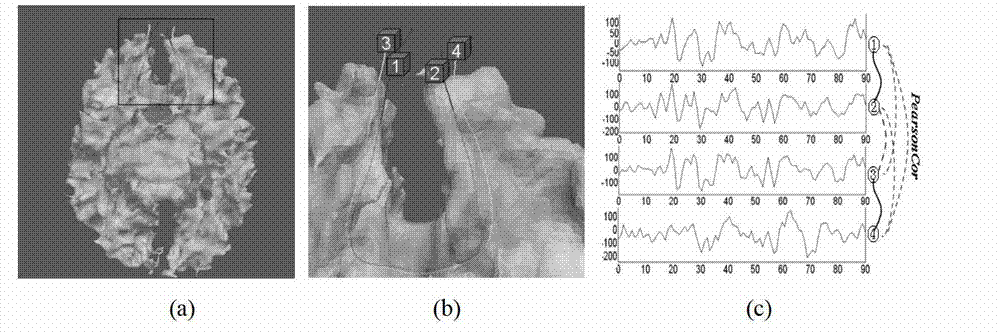
The invention provides a diffusion tensor imaging white matter fiber clustering method. The method includes the steps of pre-processing original rsf magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data and the original diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) data, registering the pre-processed rsf MRI data into a DTI space, respectively conducting fiber tracking and brain tissue segmentation on the pre-processed DTI data, conducting fiber projection on white matter fiber which can not reach grey matter or exceed a grey matter surface in a white matter fiber obtained by DTI, then calculating functional similarities among the white matter fiber, obtaining a matrix of the similarities and clustering by adopting an affine spread clustering algorithm. Fiber bundle has functional independence, accuracy without need to relay on of a genetic linkage map and require complicated registration.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Earthquake image structure guiding noise reduction method based on regularization mixed norm filtering
ActiveCN103489163AImprove signal-to-noise ratioPreserve Texture EdgesImage enhancementDiffusionEigenvalues and eigenvectors
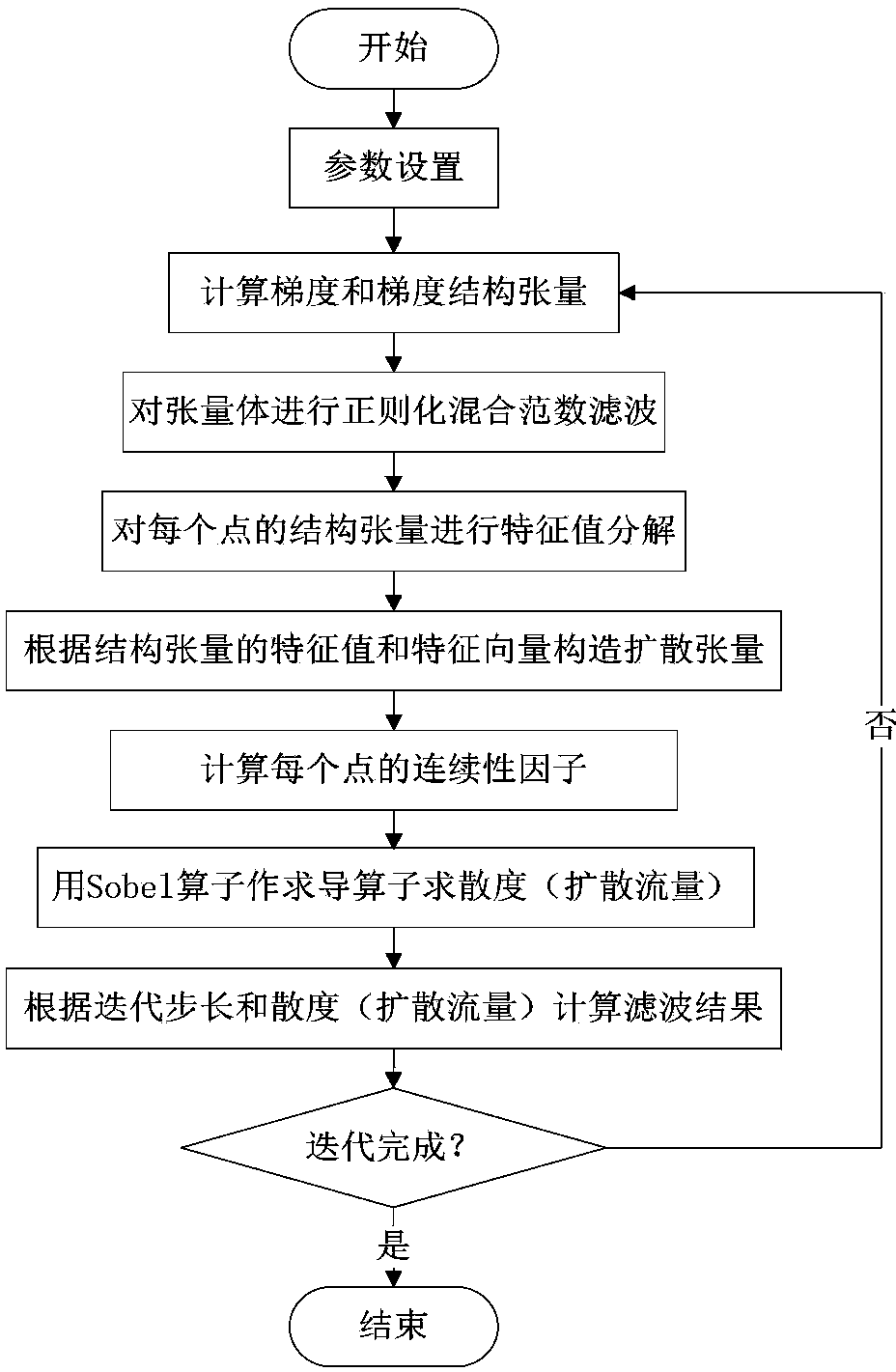
The invention discloses an earthquake image structure guiding noise reduction method based on regularization mixed norm filtering. The earthquake image structure guiding noise reduction method includes the following steps that a gradient structure tensor is solved for an input three-dimensional earthquake image; regularization mixed norm filtering is conducted on the gradient structure tensor; a diffusion tensor is designed according to the eigenvalue and eigenvector of the filtered gradient structure tensor; continuity factors are calculated, the continuity factors at the position of a boundary fault feather edge and the like are close to zero, and the maintain performance of the structure is achieved; a sobel operator serves as a derivation operator so that divergence can be calculated. By means of the earthquake image structure guiding noise reduction method based on regularization mixed norm filtering, the textured edge information of earthquake-related data can be reserved, Gaussian noise, ultra Gaussian noise and sub Gaussian noise can be effectively suppressed, and therefore an efficient noise reduction method is achieved.
Owner:OPTICAL SCI & TECH (CHENGDU) LTD
Measurement system and image processing system for neural fiber bundles
InactiveUS20080122440A1Number of fiber bundles can be quantitatively figured outNumber of fiber bundles included in the VOI can be discriminatedMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusionNerve fiber bundle
The present invention provides a measurement system and an image processing system for quantitatively figuring out the fiber bundles which are passing through any VOI. A static magnetic field and an RF signal are applied to a subject, and a nuclear magnetic resonance signal is received from the subject (401). Diffusion tensor is calculated from the nuclear magnetic resonance signals (402). As to a target area for receiving the nuclear magnetic resonance signal from the subject, fiber bundles passing through multiple predetermined origins, respectively, are extracted in a form of a group of coordinate points for each of the fiber bundles, based on the diffusion tensor calculated by the calculating means (406). At least one VOI is set for the target area for receiving the nuclear magnetic resonance signal (408). Out of the multiple fiber bundles extracted by the fiber bundle extracting means, the fiber bundles having at least one coordinate point of the group of coordinate points being included in the VOI are discriminated and the number of which is counted (409).
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
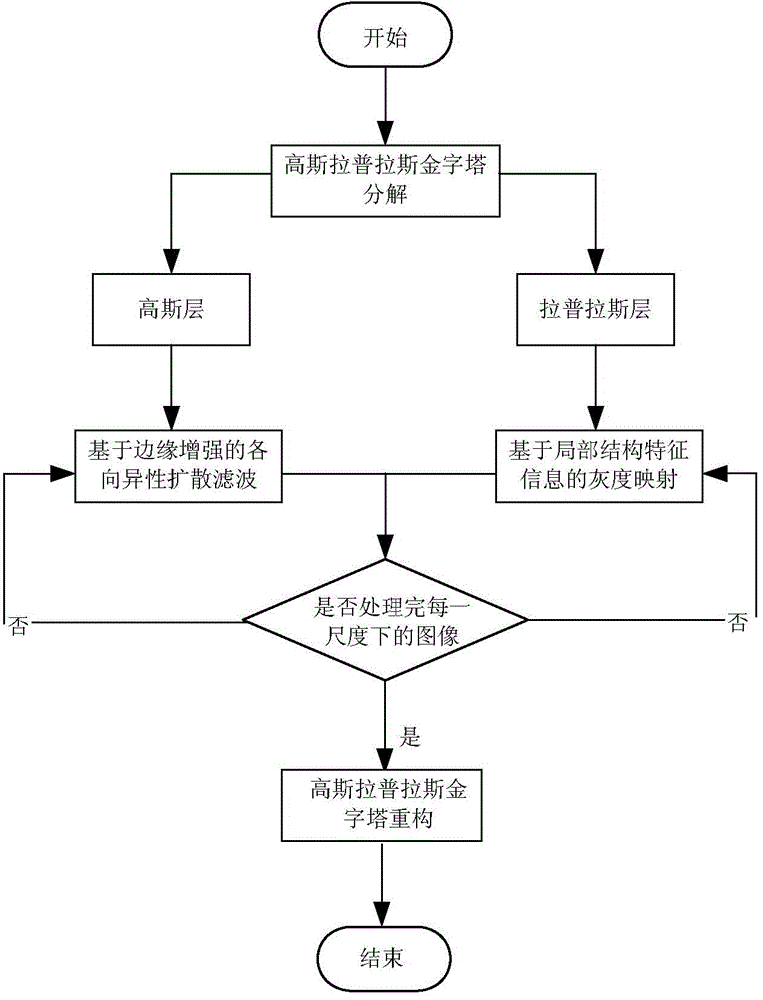
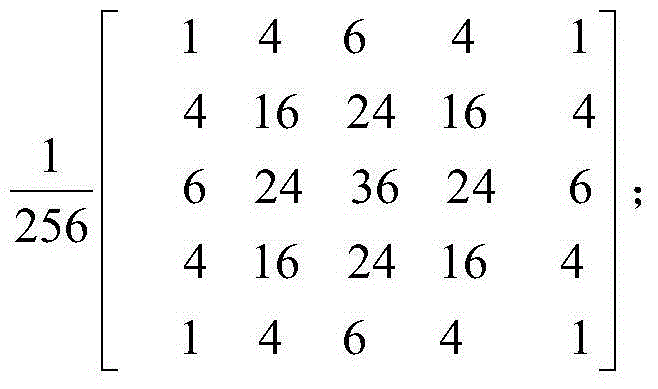
Adaptive denoising method for ultrasonic image
The invention discloses an adaptive denoising method for an ultrasonic image. The adaptive denoising method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining the ultrasonic image; (2) performing Gaussian-Laplacian pyramid decomposition on the ultrasonic image and obtaining Gaussian layers and Laplacian layers at different scales; (3) calculating a structure tensor and a diffusion tensor of the Gaussian layer at each scale and performing anisotropic diffusion filtering treatment on the Gaussian layer at the scale; (4) according to a characteristic value of the structure tensor of the Gaussian layer, designing a grey mapping curve, and performing grey mapping on the Gaussian layer at the scale according to the grey mapping curve; (5) repeating the steps (3) and (4) for multiple times and performing the same treatment on the Gaussian layer and the Laplacian layer at each scale; (6) performing reverse reconstruction on the treated Gaussian layer and Laplacian layer and obtaining a denoised ultrasonic image; (7) outputting the denoised ultrasonic image. The adaptive denoising method can inhibit edge enhancement and spots of the image and is simple in algorithm and strong in adaptability.
Owner:WUHAN BEBEL HEALTH BIOTECH
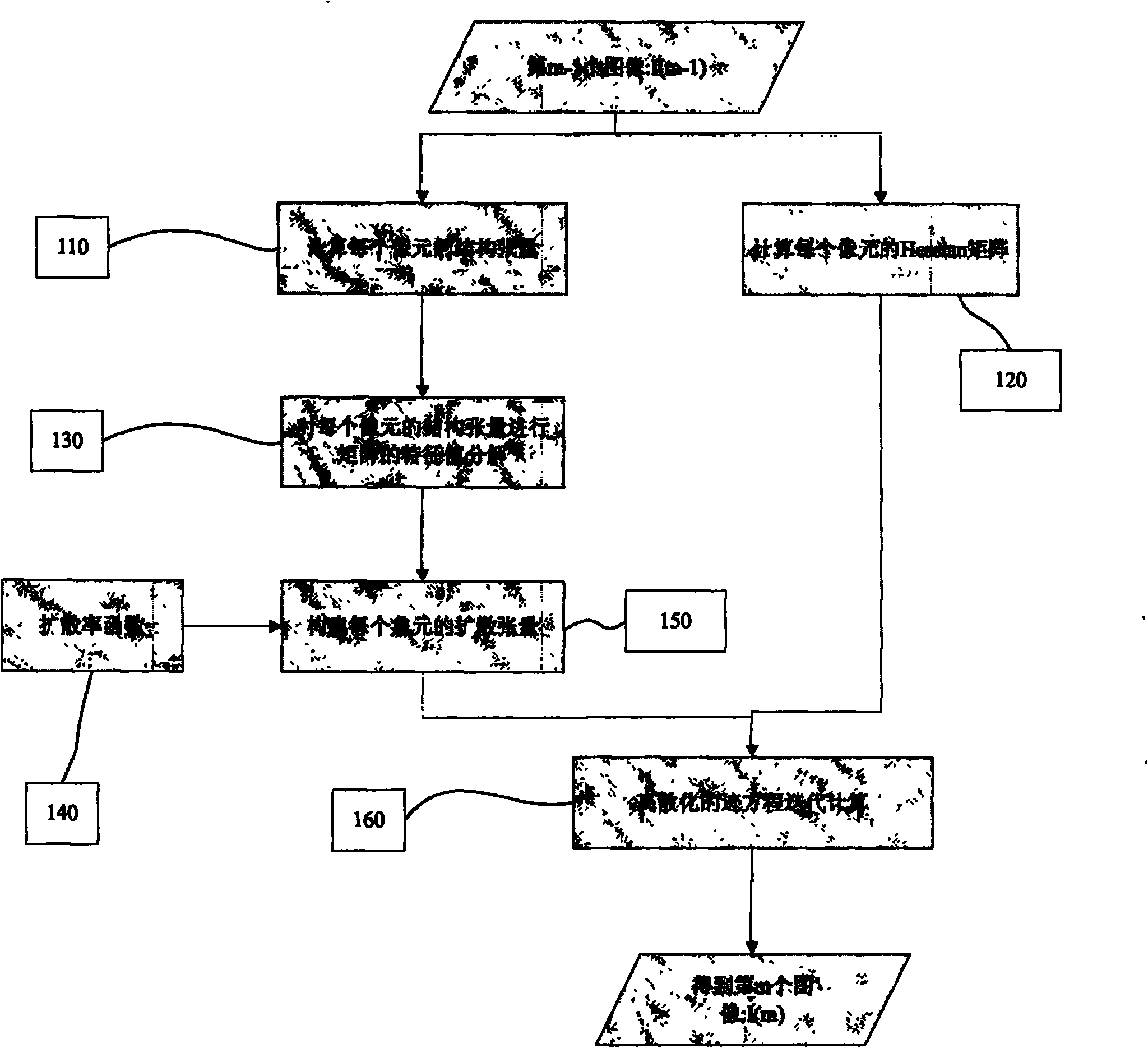
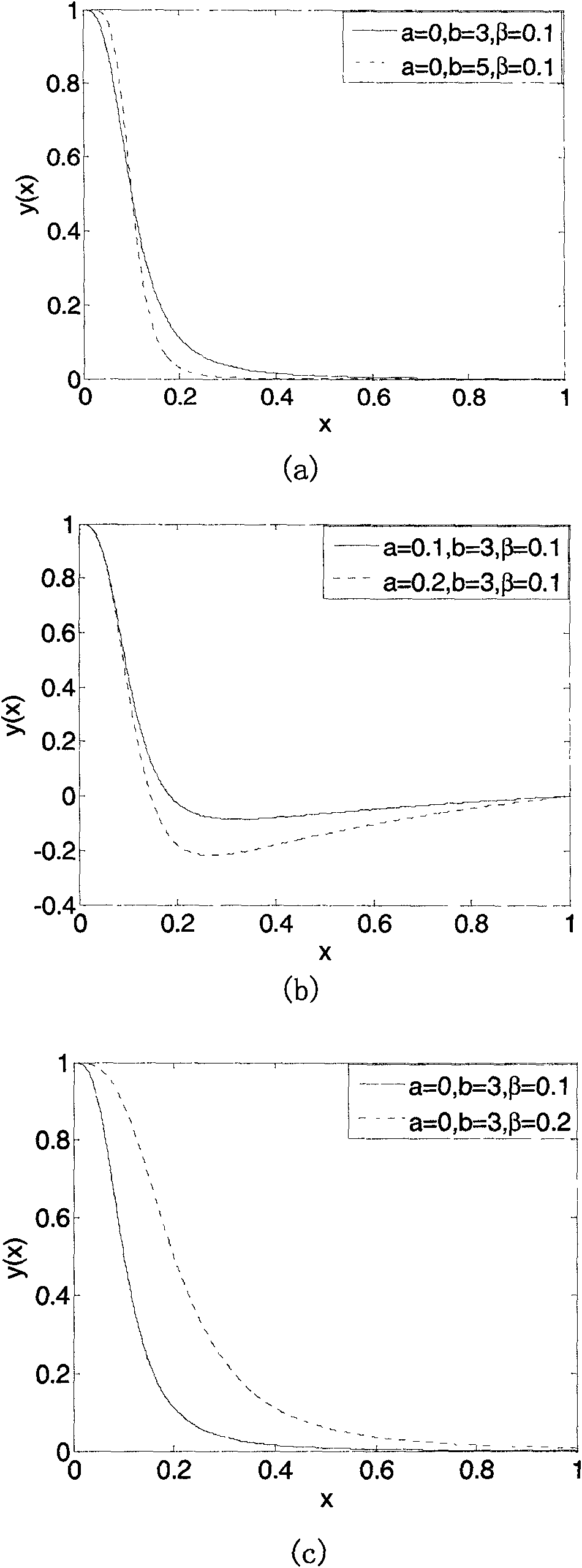
Method for denoising and enhancing anisotropic diffusion image with controllable diffusion degree
The invention discloses a method for denoising and enhancing an anisotropic diffusion image with controllable diffusion degree based on a track model. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, calculating a structure tensor and a Hessian matrix of each pixel point; secondly, decomposing the characteristic values of the structure tensor of each image point; thirdly, constructing a diffusion tensor of each image point, enabling the characteristic vector of the diffusion tensor to be the characteristic vector of the structure tensor, making the characteristic value as a function of the diffusion rate, i.e., a function of the characteristic value of the structure vector, and making the diffusion degree controllable by adjusting the parameter of the function; and finally, iteratively solving the track model. By adopting the method, the image can be effectively denoised and enhanced.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
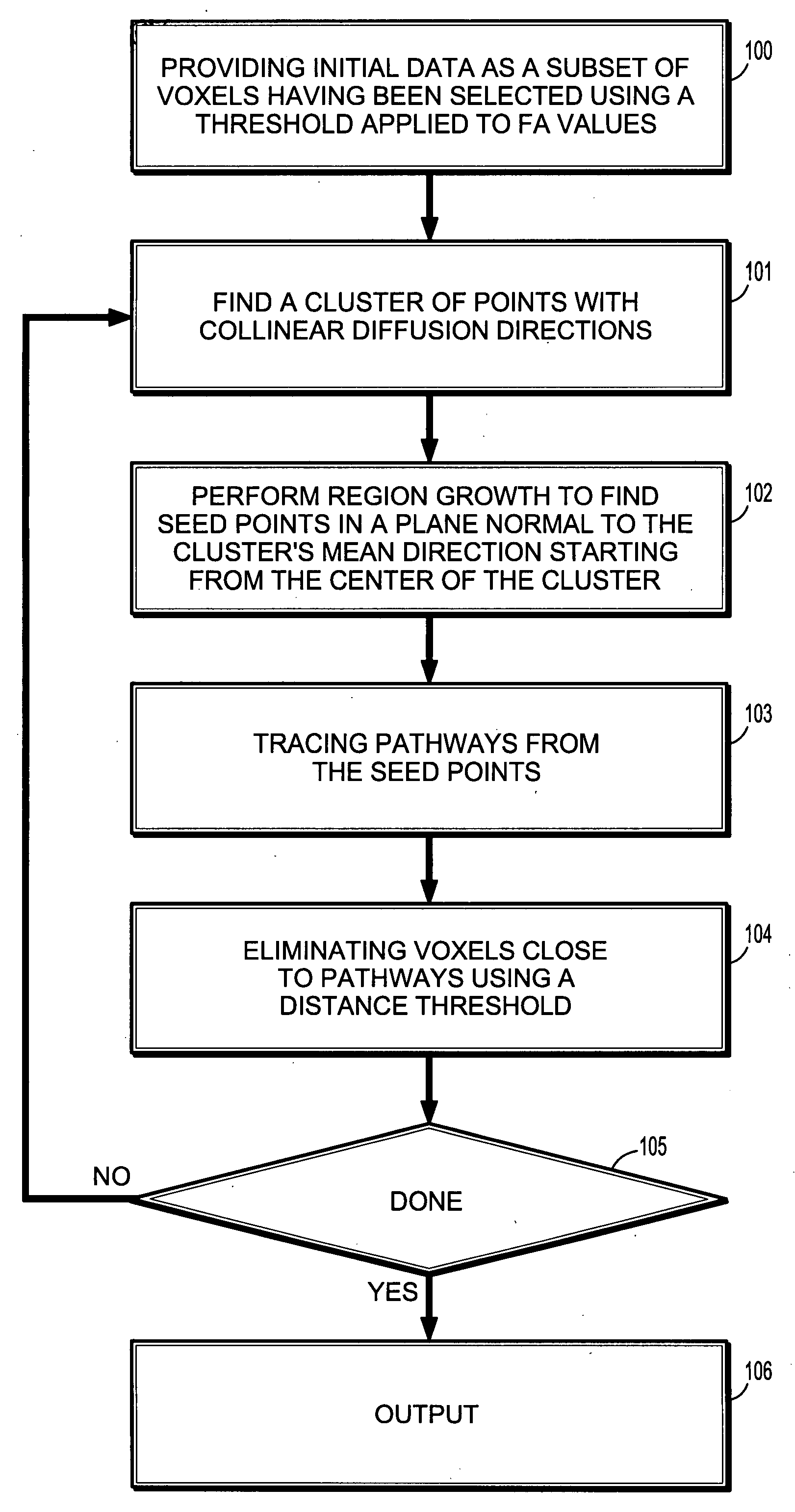
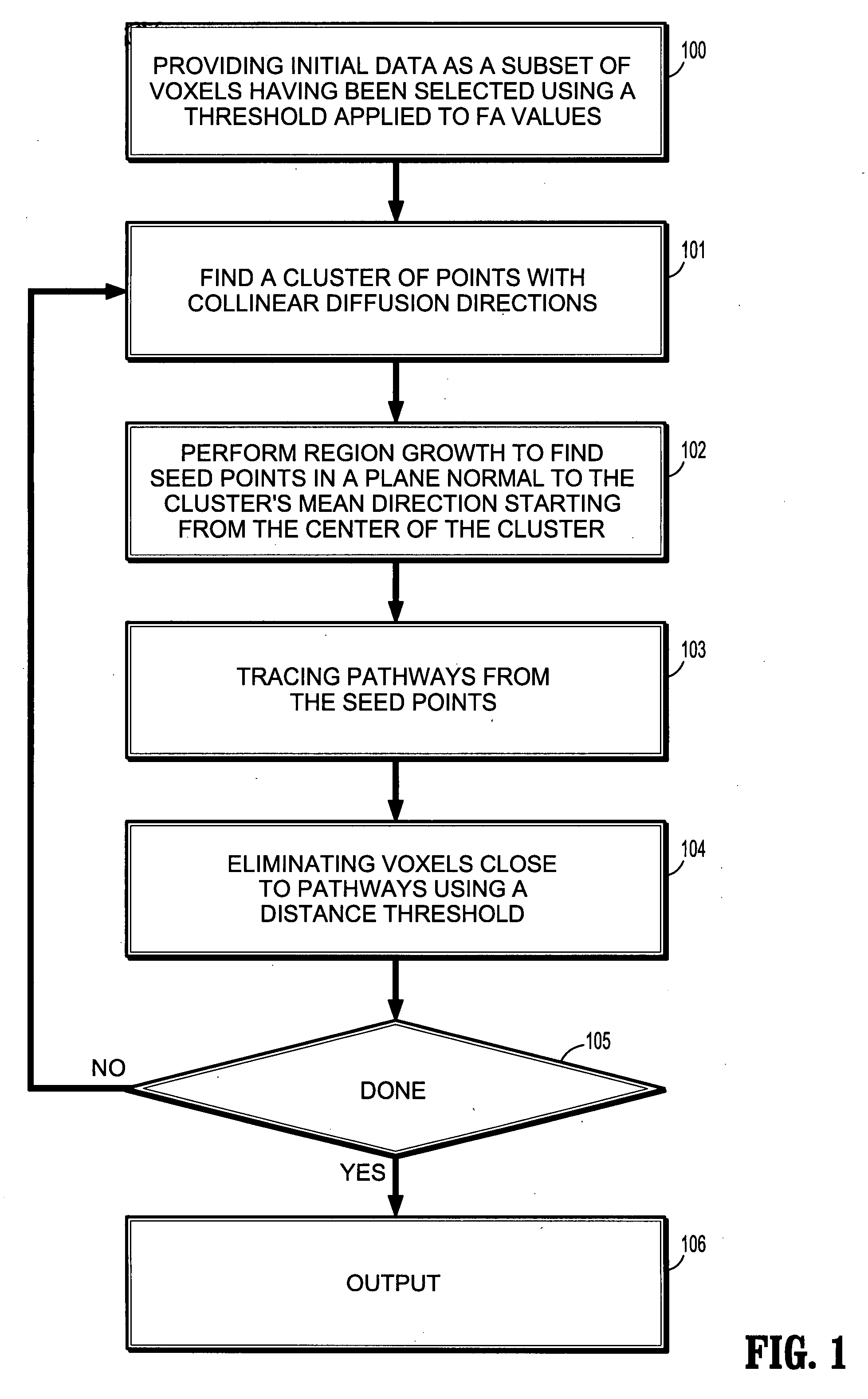
Detection of fiber pathways
A computer-implemented method for detection of fiber pathways includes determining initial data as a subset of voxels that have been selected from a diffusion tensor image by applying a threshold to fractional anisotropy values, determining a cluster of points with highly collinear diffusion directions, and performing region growth to find suitable seed points in a plane that is normal to the cluster's mean direction, starting from the center of the cluster. The method further includes tracing pathways from the seed points, eliminating voxels of the subset from the initial data that are close to any of the pathways using a distance threshold, displaying a visualization of a selection of voxels used as seed points and of the pathways traced from the seed points.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
System and method for stochastic dt-mri connectivity mapping on the GPU
InactiveUS20080109171A1Highly parallelizableDrawing from basic elementsMagnetic measurementsFiberDiffusion
A graphics processing unit implemented method for fiber tract mapping from diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging data includes providing a diffusion tensor magnetic resonance brain image volume, initializing a set of fiber positions in a 3D set of points, fiber displacements, and a posterior distribution for an updated fiber displacement in terms of the initial displacements and diffusion tensors, randomly sampling a set of updated fiber displacements from said posterior distribution, computing a new set of fiber positions from said initial fiber positions and said updated fiber displacements, wherein a fiber path comprises a set of fiber points connected by successive fiber displacements, accumulating connectivity values in each point of said 3D set of points by additive alpha-blending a scaled value if a fiber path has passed through a point and adding zero if not, and rendering said connectivity values.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
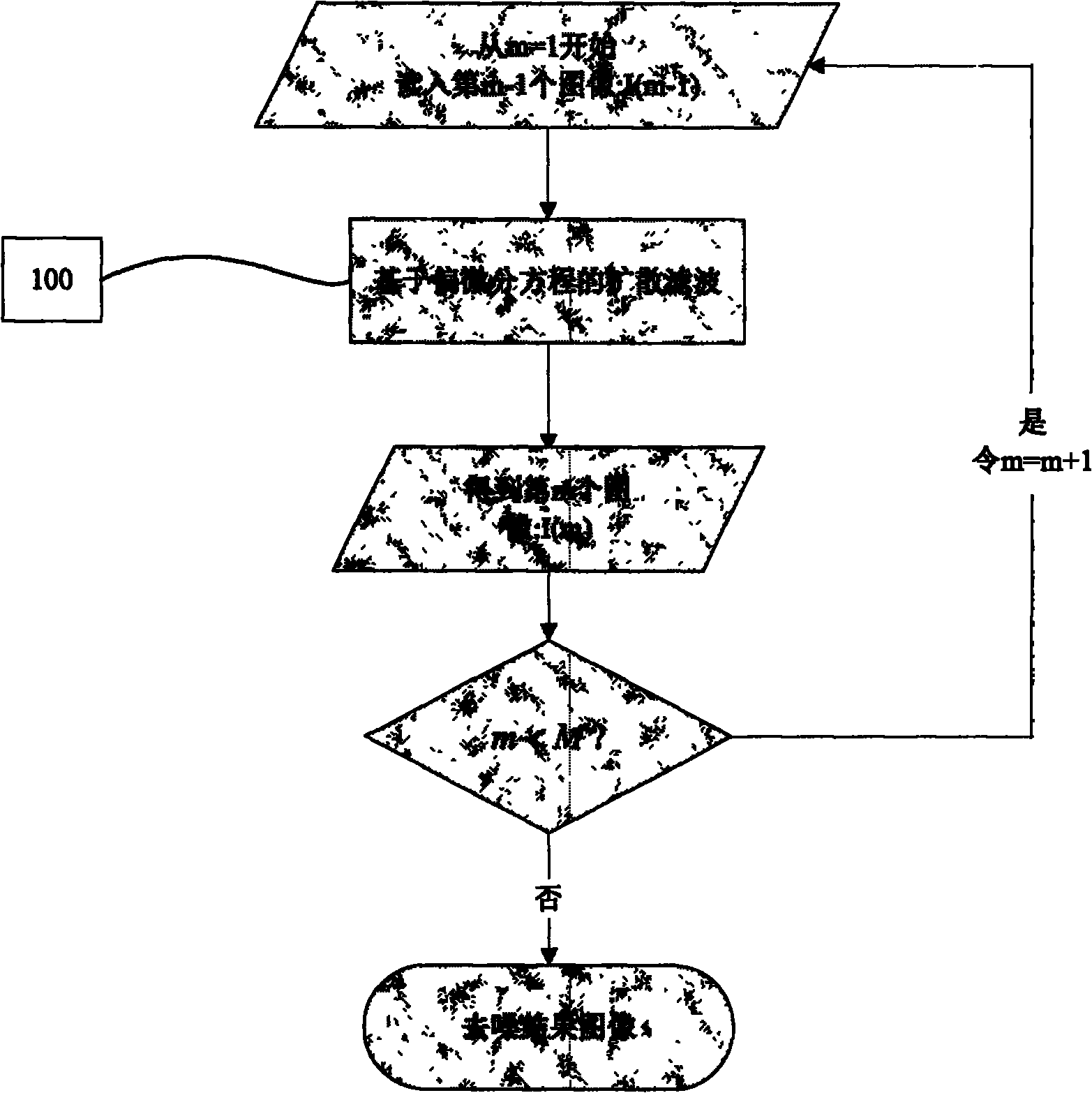
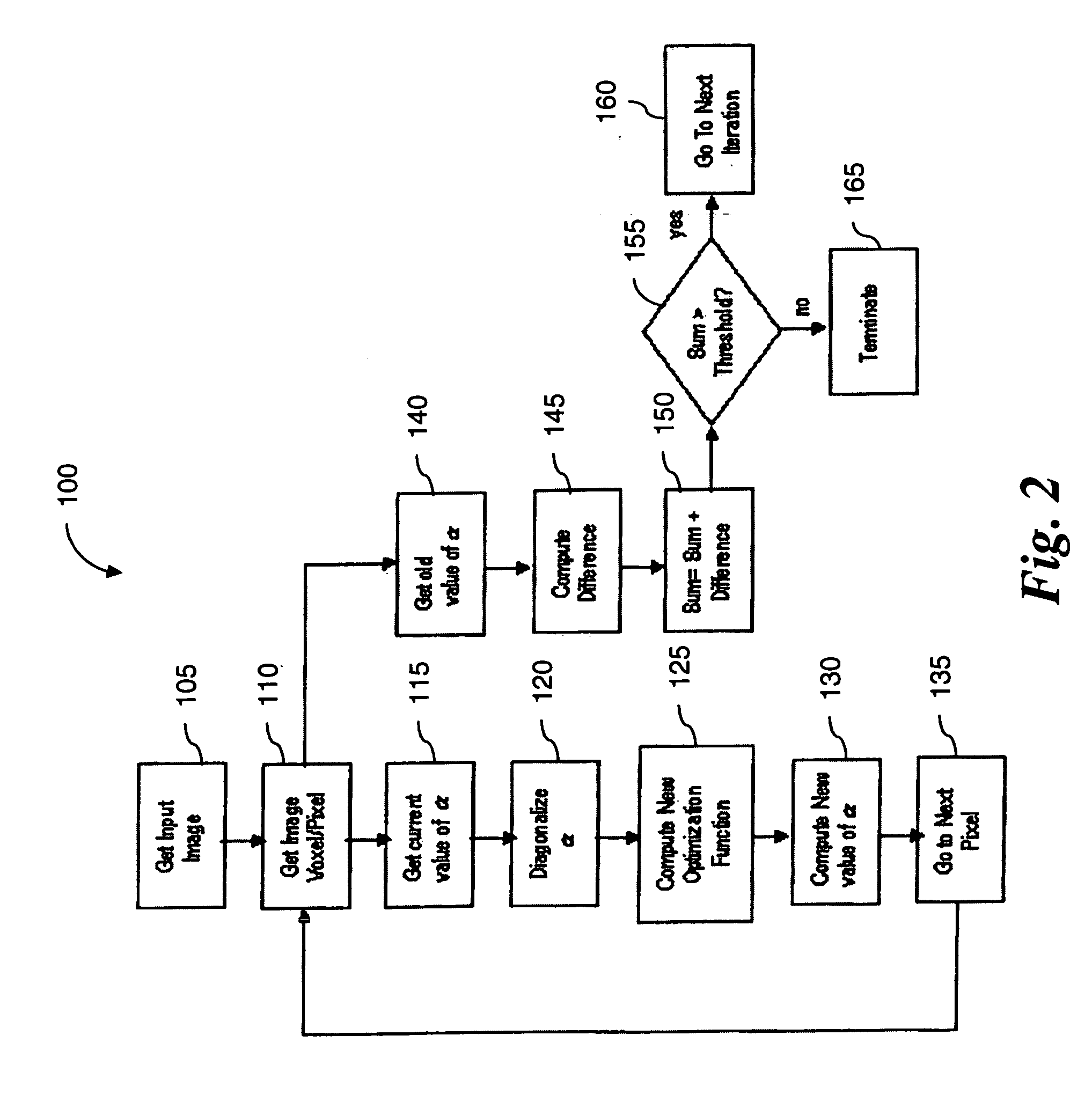
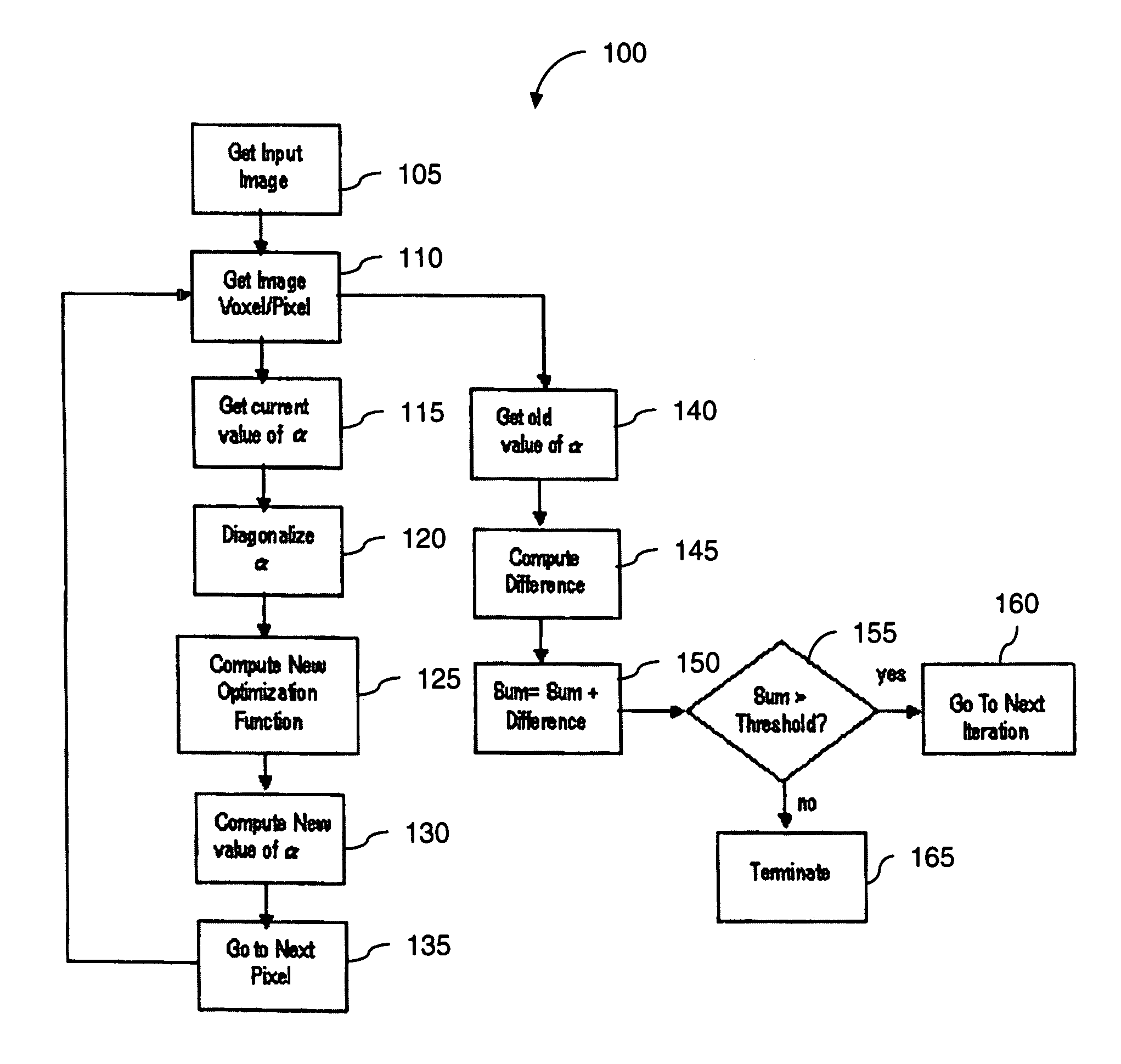
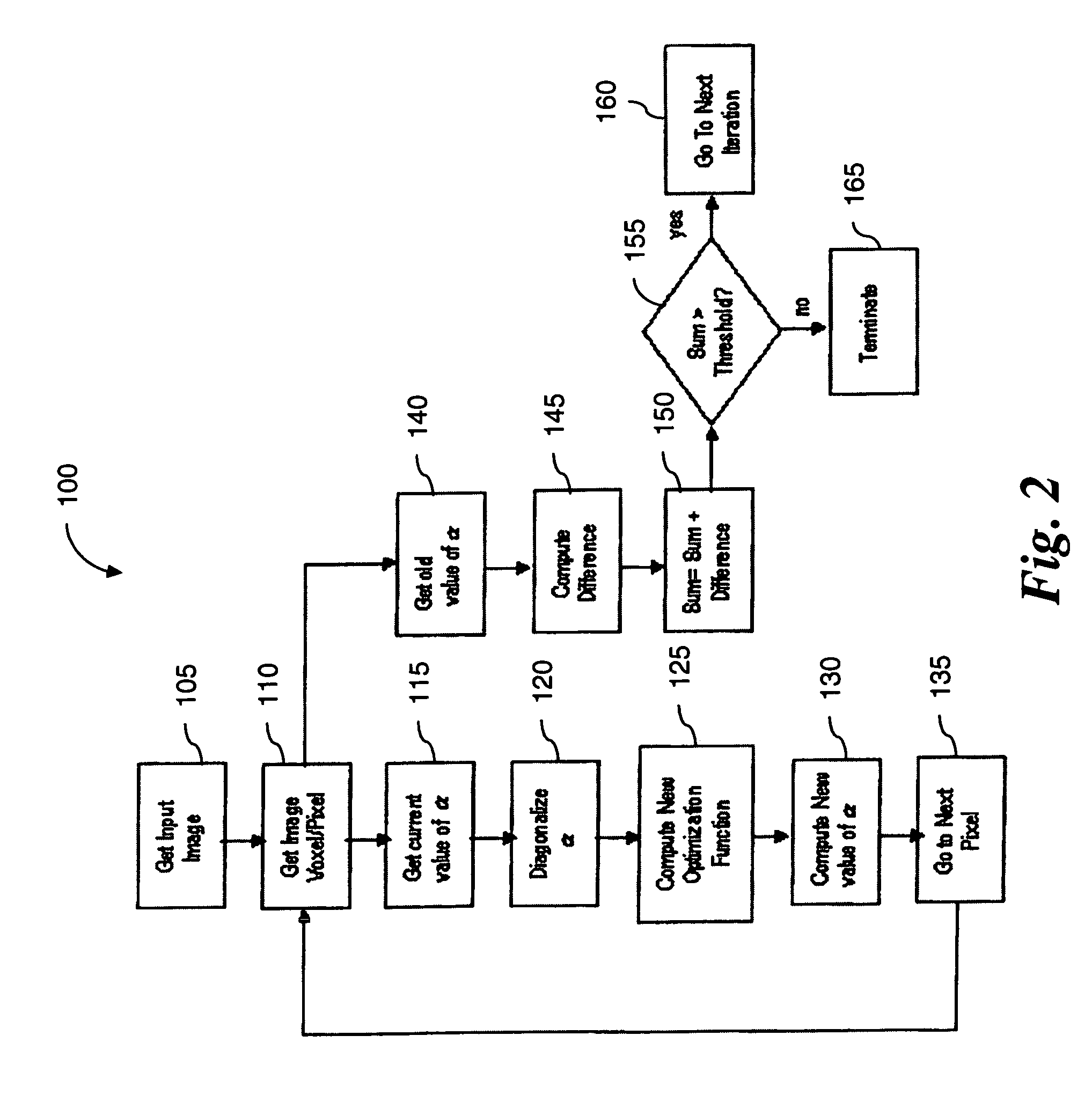
Noise reduction in diffusion tensor imaging data using bayesian methods
InactiveUS20060165308A1Reduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisExpectation–maximization algorithmDiffusion
A method and computer program product for reducing noise in diffusion tensor imaging data utilizes an optimization function performed on voxels or pixels of the image. The optimization function includes a neighborhood relevance component that considers diffusion tensor matrices from neighboring pixels or voxels. The neighborhood relevance component is modeled as a Markov Random Field. The method includes an iteration that seeks convergence of an Expectation Maximization algorithm performed on the diffusion tensor matrices.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Noise reduction in diffusion tensor imaging data using bayesian methods
InactiveUS7355403B2Reduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionExpectation–maximization algorithm
A method and computer program product for reducing noise in diffusion tensor imaging data utilizes an optimization function performed on voxels or pixels of the image. The optimization function includes a neighborhood relevance component that considers diffusion tensor matrices from neighboring pixels or voxels. The neighborhood relevance component is modeled as a Markov Random Field. The method includes an iteration that seeks convergence of an Expectation Maximization algorithm performed on the diffusion tensor matrices.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
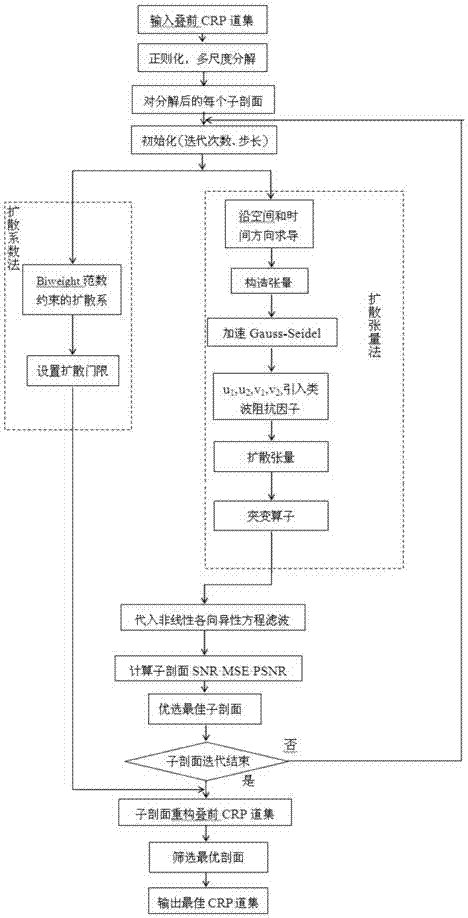
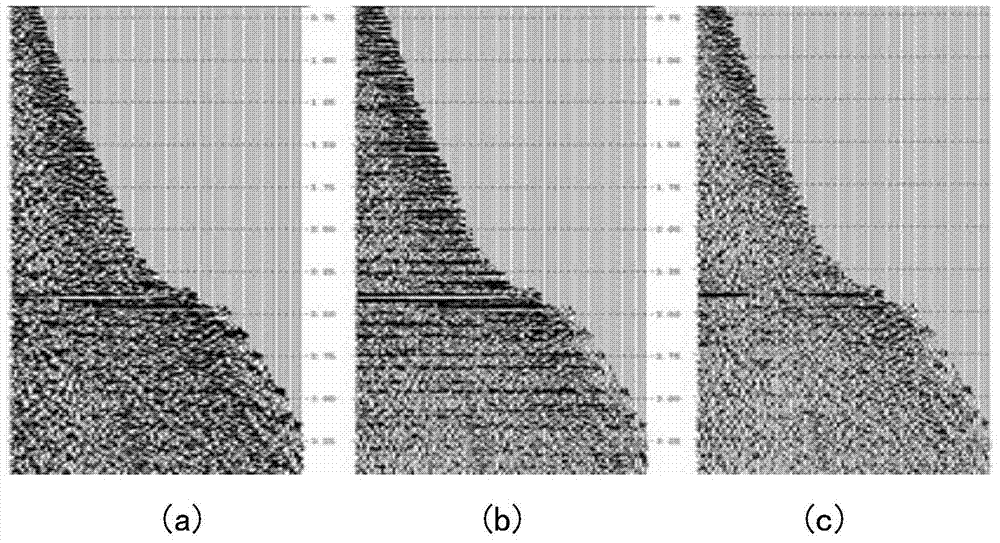
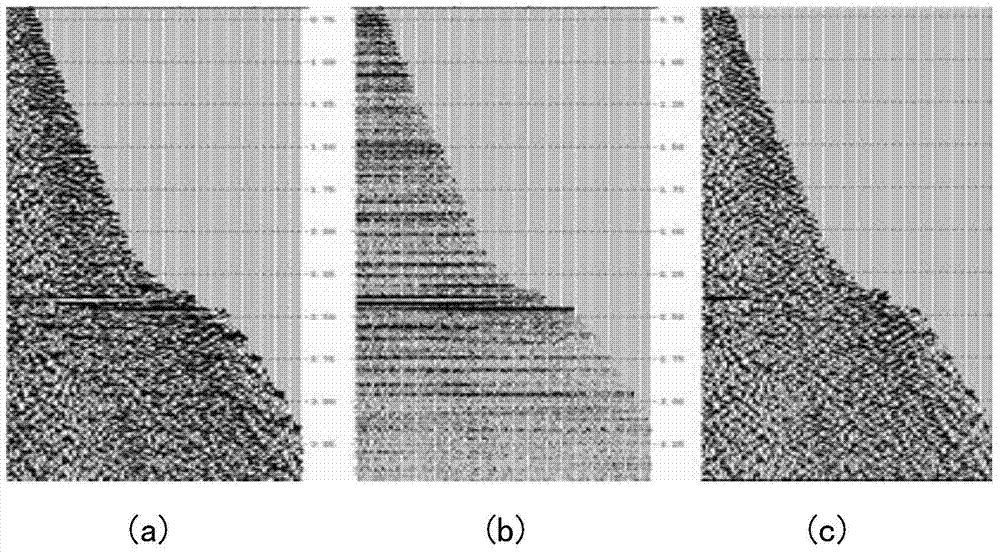
Multi-scale anisotropic diffusion filtering method based on pre-stack CRP trace sets
ActiveCN103926616AImprove robustnessImprove accuracySeismic signal processingMultiscale decompositionDiffusion
The invention relates to a multi-scale anisotropic diffusion filtering method based on pre-stack CRP trace sets. The method includes the steps that firstly, the input pre-stack CRP trace sets are regularized; secondly, multi-scale decomposition is conducted through a two-dimensional Mallat algorithm, and each decomposed sub section is initialized; thirdly, a diffusion threshold value is obtained through a diffusion coefficient method, and the sixth step is executed; after diffusion tensor parameters are obtained based on anisotropic diffusion of a diffusion tensor method, the parameters are substituted into a nonlinear anisotropic equation so as to conduct anisotropic diffusion filtering, and the fourth step is executed; fourthly, the SNR, the MSE and the PSNR of the sub sections obtained after each iteration are calculated, and then the optimal earthquake sub section is optimized; fifthly, processing of the fourth step is executed on all the sub sections obtained after anisotropic diffusion filtering, and the sixth step is executed; sixthly, pre-stack CRP trace set nondestructive reconstruction is conducted on information of all the iterated sub sections through a two-dimensional Mallat reconstruction algorithm, and then the optimal pre-stack CRP trace set is output after reconstruction. The multi-scale anisotropic diffusion filtering method can be widely applied to the processing process of various oil exploration earthquake data.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
System and method for fast tensor field segmentation
Segmenting a digitized image includes providing a diffusion tensor field image, partitioning the image into 2 regions, each point being assigned to one of the regions, associating a level-set function with each region, the level-set function having a negative value in one region and a positive value in the other region, calculating a mean value of the diffusion tensor field over each of 2 regions, initializing an energy defined as a functional of level-set functions and diffusion tensor field, changing the region membership of each point in the image if the energy functional value decreases as a result of region membership change and updating said mean value of said diffusion tensor field over each of 2 regions, and obtaining a segmentation of the image when the magnitude of the change of the energy function value resulting from changing the region membership of a point is less then a predetermined threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Fibre tracking on the basis of macroscopic information
ActiveUS20100079140A1Good segmentation resultImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A diffusion data processing apparatus comprising a segmenter arranged to segment the diffusion tensor data according to at least one segmentation model representing at least part of a fiber bundle. The segmentation model may comprise macroscopic and / or microscopic information. This leads to a segmentation of the fiber bundle that is robust and less influenced by non-perfections of the data set, such as low signal-to-noise ratio, partial voluming, or other imaging artifacts.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Automated fiber tracking of human brain white matter using diffusion tensor imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, comprising: a MRI scanner; a signal processing system in communication with the magnetic resonance imaging scanner to receive magnetic resonance (MR) signals for forming magnetic resonance images of a subject under observations; a data storage unit in communication with the signal processing system, wherein the data storage unit contains database data corresponding to a soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The database data includes information identifying at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation. The signal processing system is adapted to process MR signals received from the MRI scanner to automatically identify at least one soft tissue substructure encompassed by the soft tissue region of the subject under observation.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
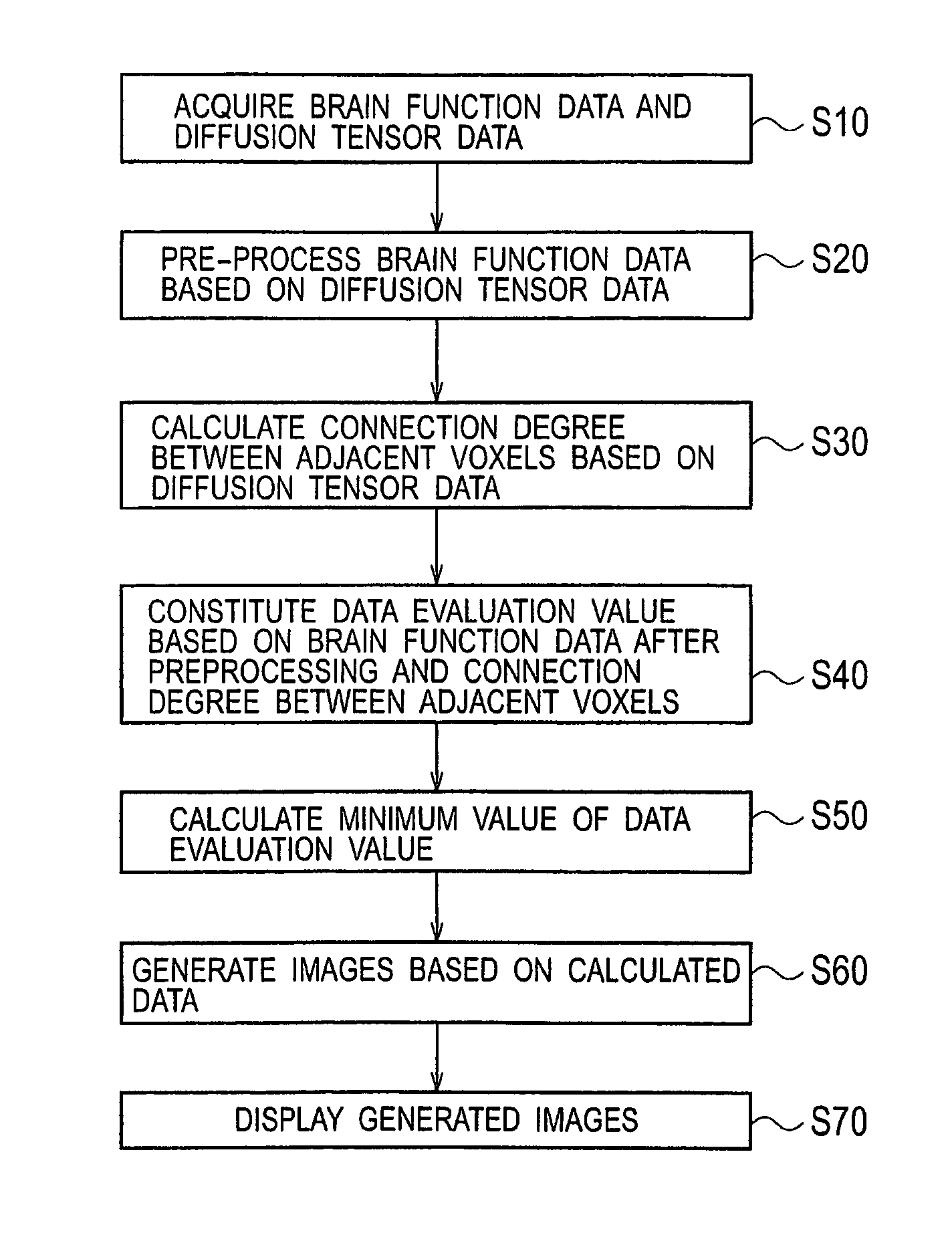
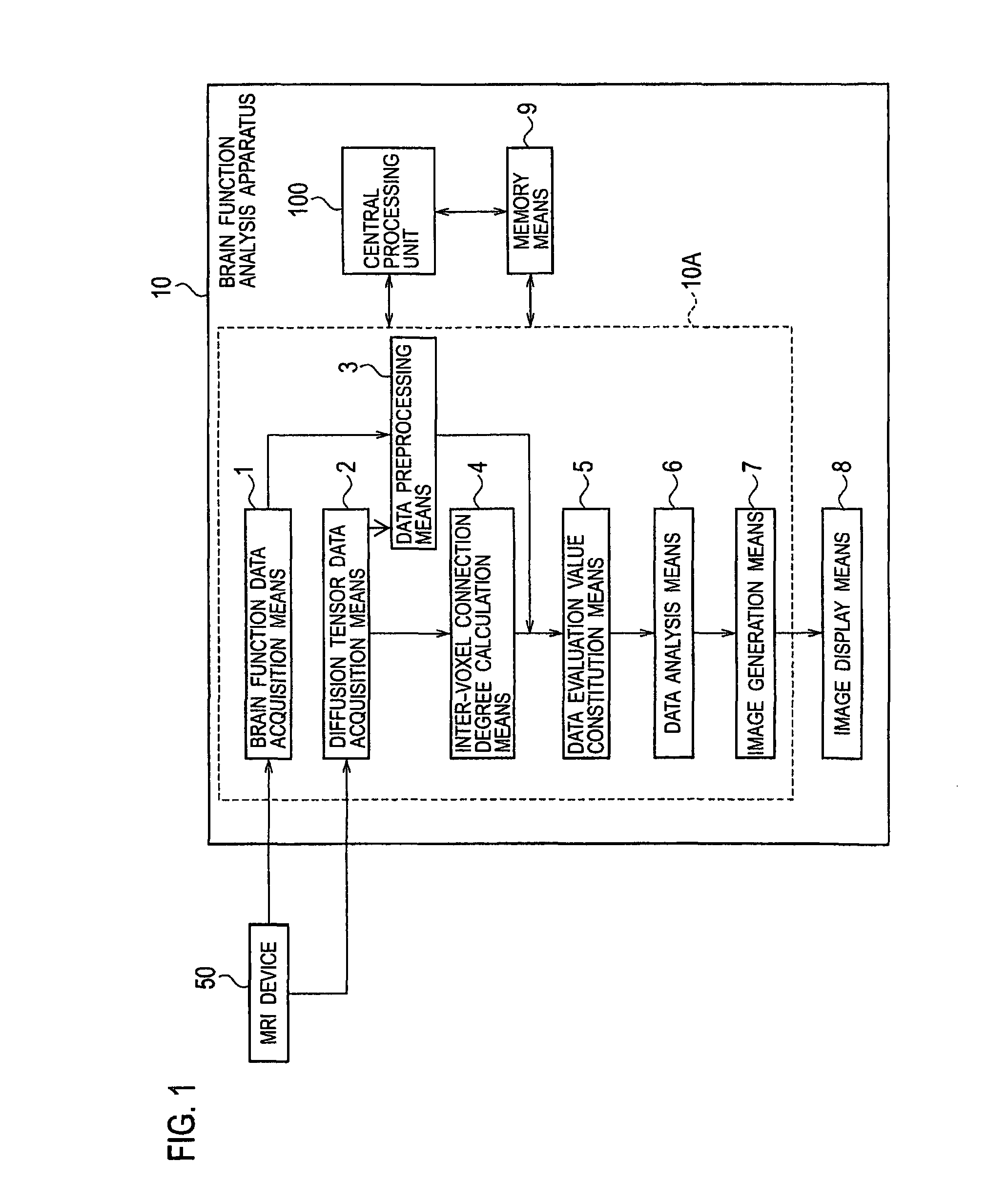
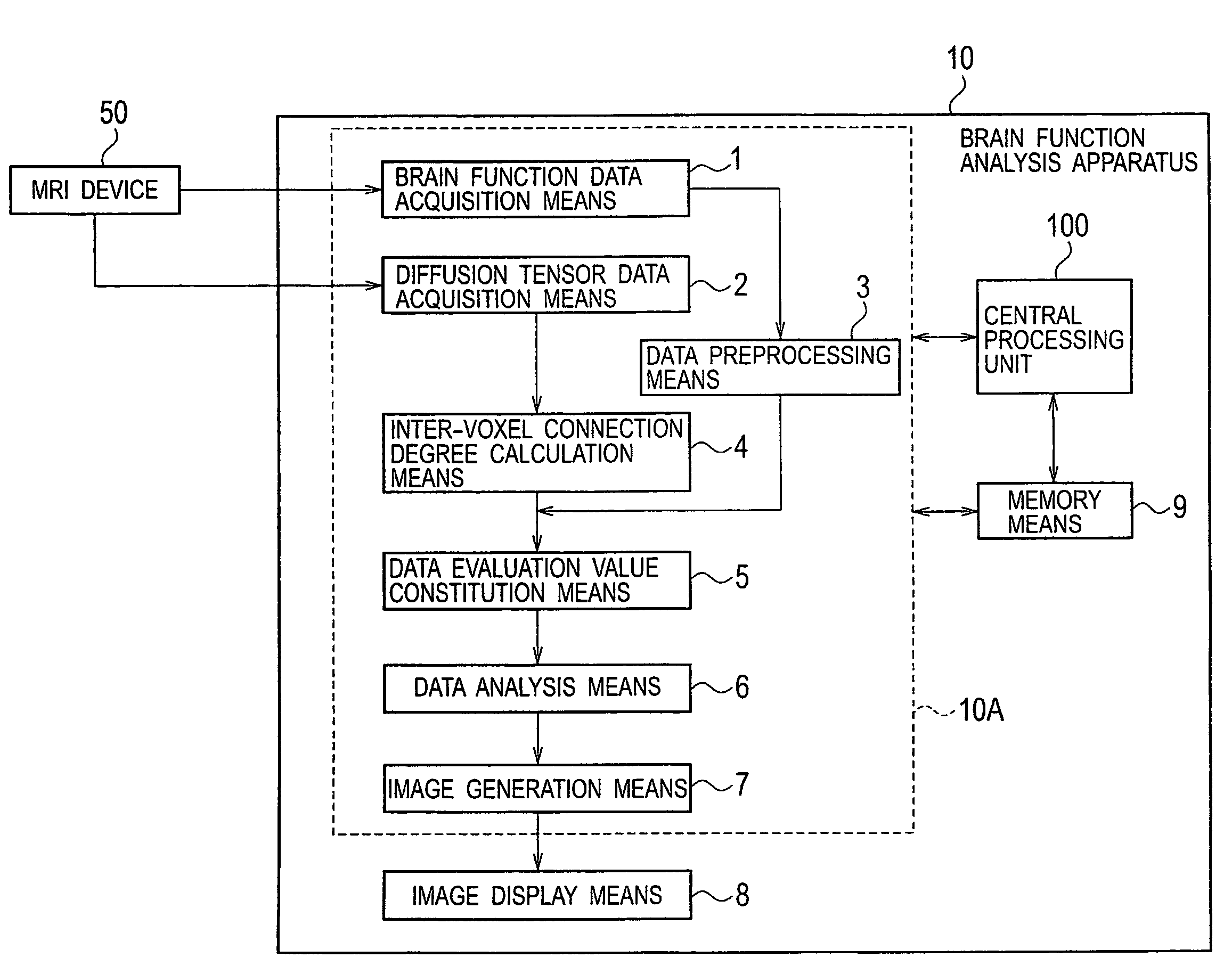
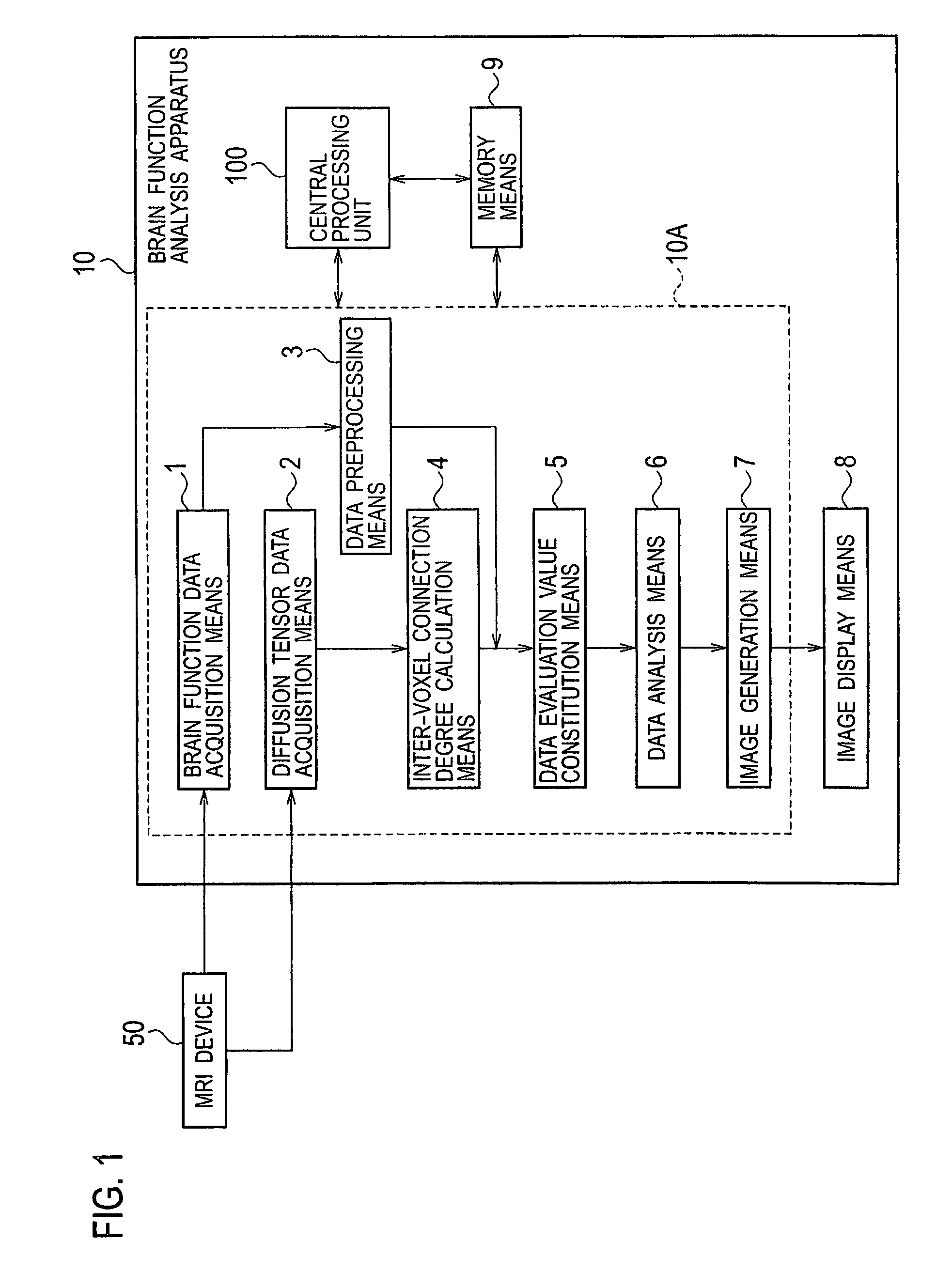
Brain function analysis apparatus and method
There is provided a method including, acquiring brain function data and diffusion tensor data, calculating a connection degree between voxels adjacent to each other based on the diffusion tensor data, constituting a data evaluation value based on the brain function data and the connection degree between the adjacent voxels, subjecting the data evaluation value to nonparametric regression analysis, and forming and displaying images based on results of the analysis.
Owner:TOKYO DENKI UNIVERSITY
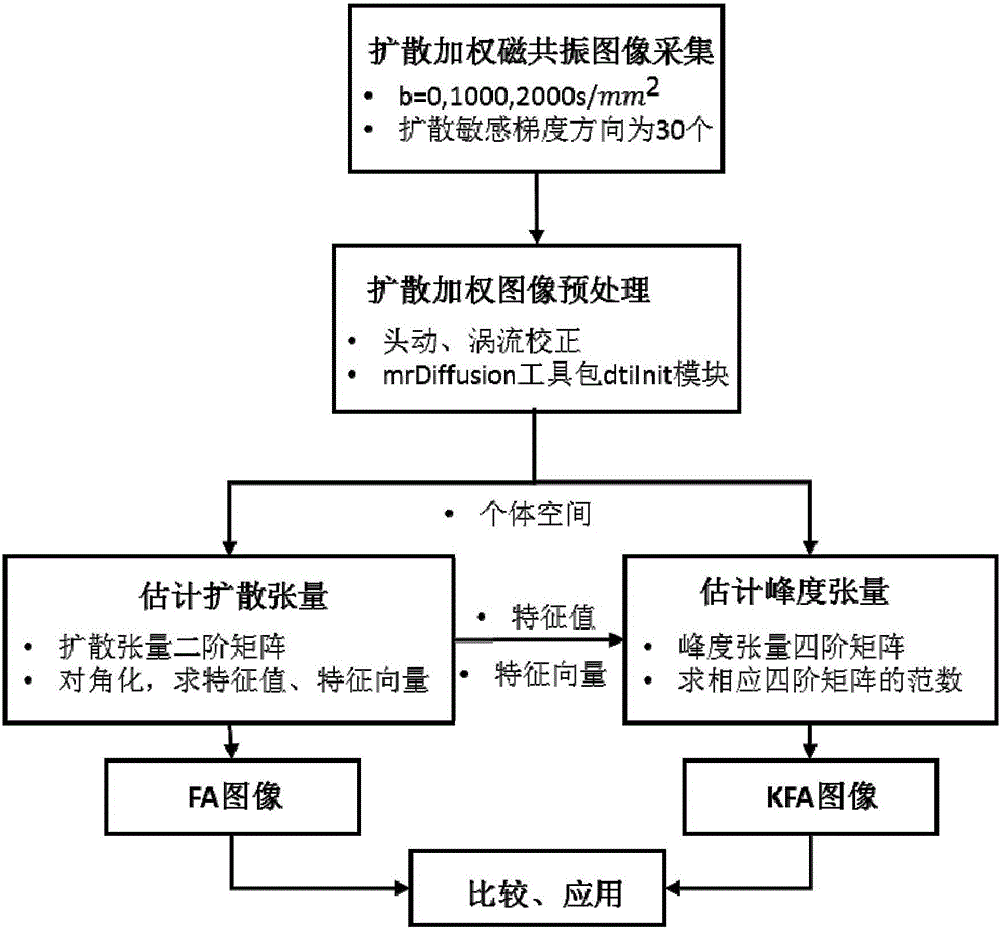
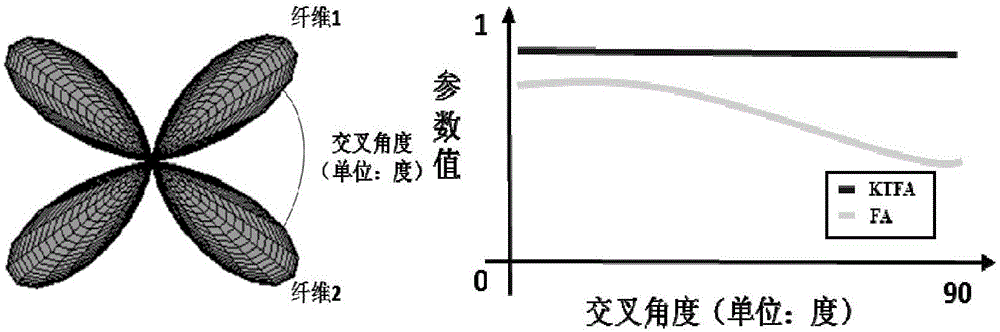
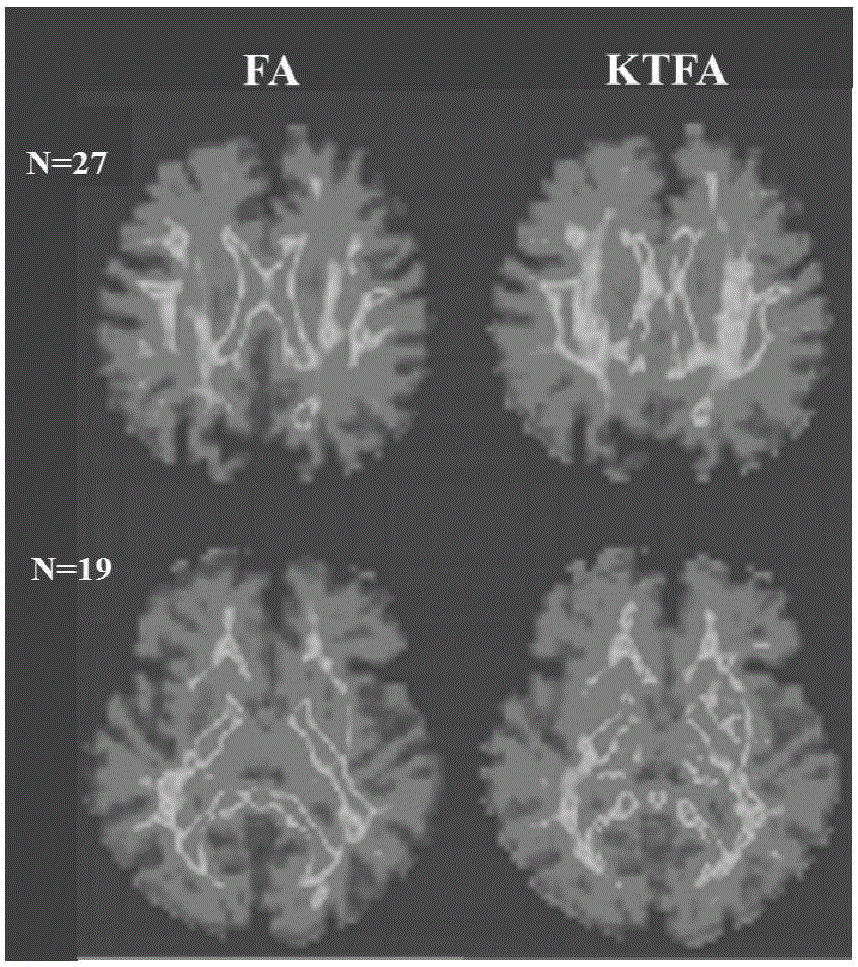
Fractional anisotropy microstructure characteristic extraction method based on kurtosis tensor and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN105842642ALow number of crossoversDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFiberMedical equipment
The invention relates to the image processing and medical instrument technology field and provides a burgeoning parameter extraction method of biological tissue anisotropy detection, wherein the method is used for clinic application. An analysis method of reconstructing and quantizing a clear, refine and highly-stable biological-tissue microcosmic anisotropy characteristic and a correlation apparatus are obtained. In a technical scheme used in the invention, based on the kurtosis-tensor fractional anisotropy microstructure characteristic extraction method, a subject collects multiple b value diffusion weight images of tissues along a plurality of diffusion sensitivity gradient directions on a magnetic resonance scanner; after the diffusion weight images are preprocessed, in an individual space, a second-order diffusion tensor and a fourth-order kurtosis tensor matrix reflecting a water molecule diffusion distribution probability density function characteristic in the tissues are acquired through fitting; through matrix operation, the corresponding fractional anisotropy FA and kurtosis tensor fractional anisotropy KTFA are acquired; and combining a characteristic parameter, a nerve fiber microstructure characteristic is acquired. The method and the apparatus are mainly used in medical equipment designing and manufacturing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
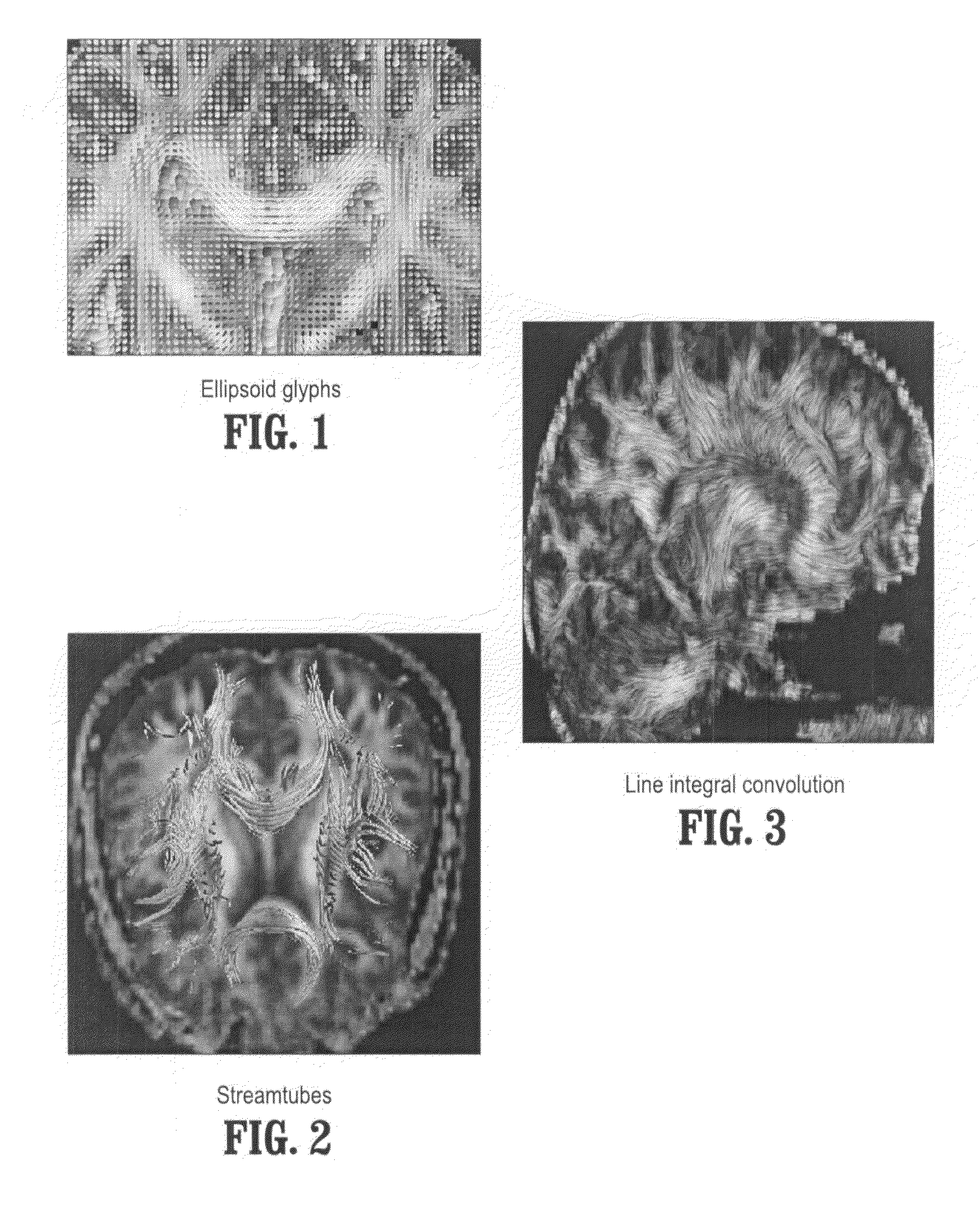
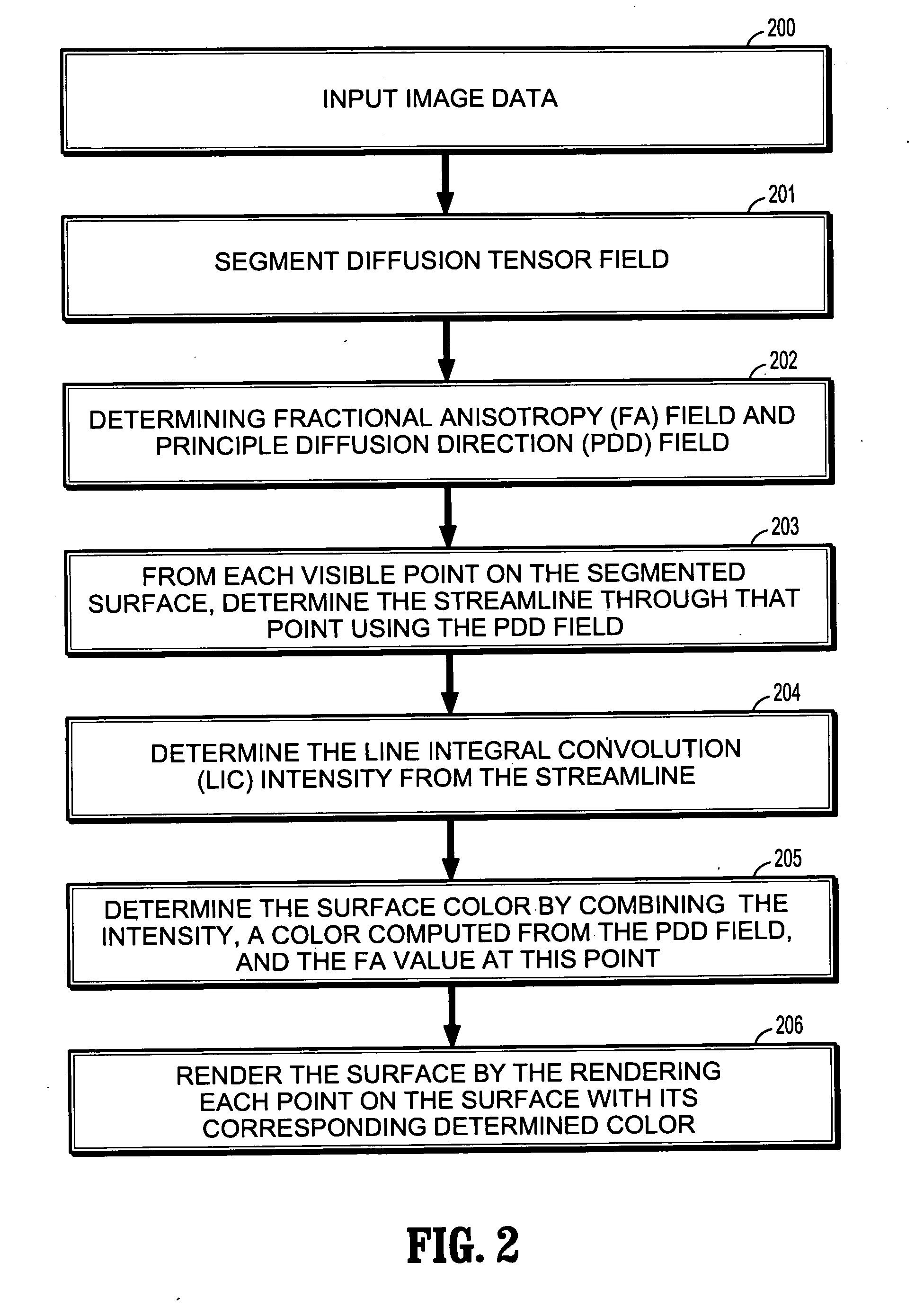
Diffusion tensor surface visualization
InactiveUS20060176488A1Magnetic measurementsScattering properties measurementsDiffusionChemical physics
A computer implemented method for diffusion tensor visualization includes receiving diffusion weighted image slice data, segmenting a diffusion tensor field from the diffusion weighted image slice data to determine a three-dimensional triangular mesh, and determining a fractional anisotropy field and a principle diffusion direction field of the diffusion tensor field. The method includes determining a streamline through each surface point on a segmented surface of the diffusion tensor field according to the principle diffusion direction field, determining an oriented texture intensity for the surface points from corresponding streamlines, determining a surface color for the surface points by combining the oriented texture intensity, a color determined from the principle diffusion direction field, and a value of fractional anisotropy field at the surface points, and visualizing the surface points by rendering the surface points having the corresponding surface colors.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
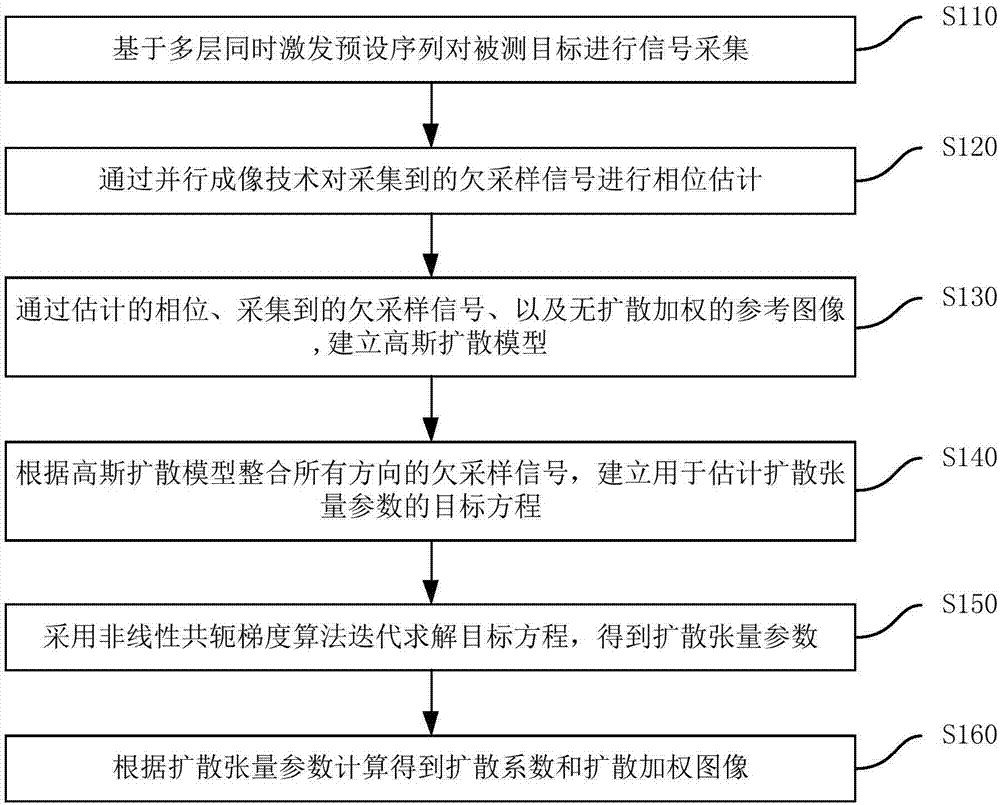
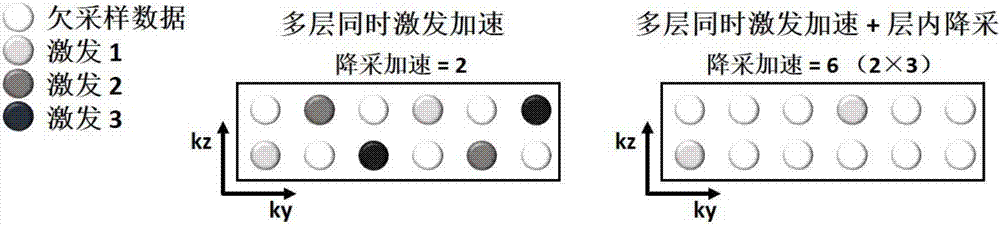
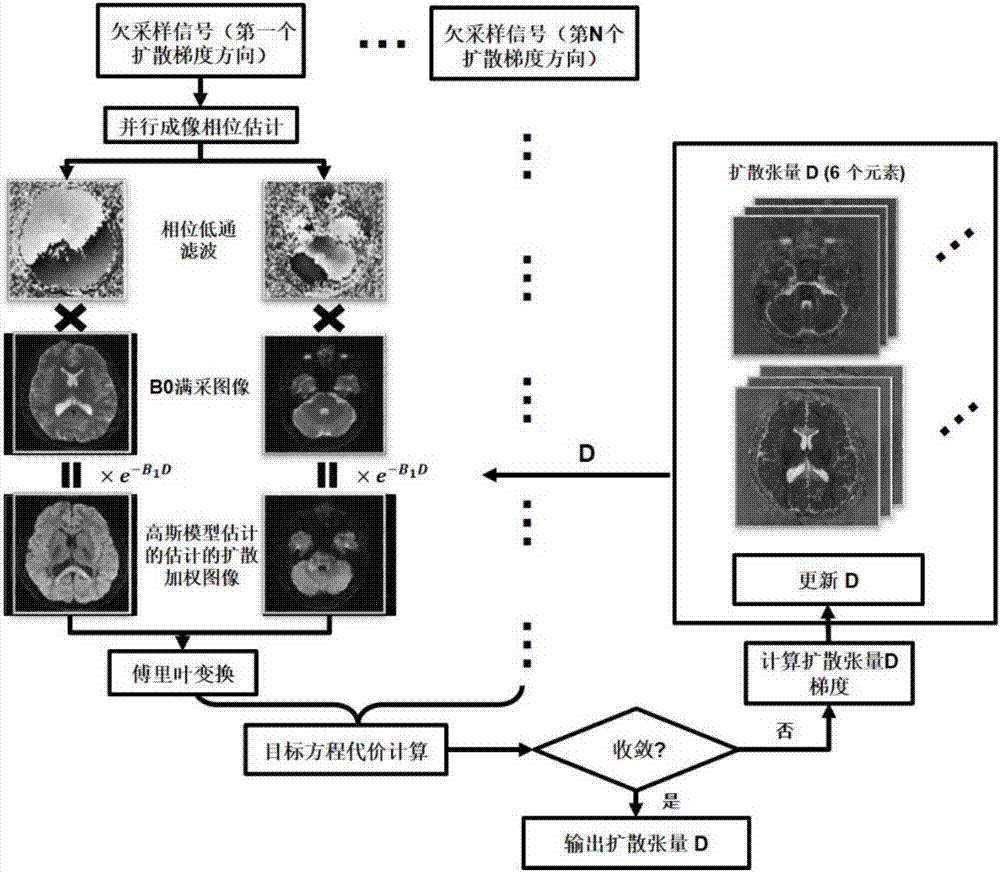
Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method for integration and reconstruction based on Gaussian model acting as instance
ActiveCN106997034AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsParallel imagingSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method for integration and reconstruction based on a Gaussian diffusion model acting as an instance. The method comprises the steps that signal acquisition is performed on a tested target based on multilayer simultaneously excited preset sequences; phase estimation is performed on the acquired under-sampled signals through a parallel imaging technology; the Gaussian diffusion model is established through the estimated phase, the acquired under-sampled signals and a reference image without diffusion weight; the under-sampled signals of all the directions are integrated according to the Gaussian diffusion model, and a target equation is established; the target equation is iteratively solved by using a nonlinear conjugate gradient algorithm so as to obtain a diffusion tensor parameter; and a diffusion coefficient and a diffusion weight image are calculated according to the diffusion tensor parameter. Therefore, high acceleration acquisition of magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging can be realized so that the acquisition time can be effectively reduced, the diffusion tensor parameter can be accurately estimated to obtain the diffusion image of high signal-to-noise ratio and high resolution, and the requirement of clinical application can be met.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
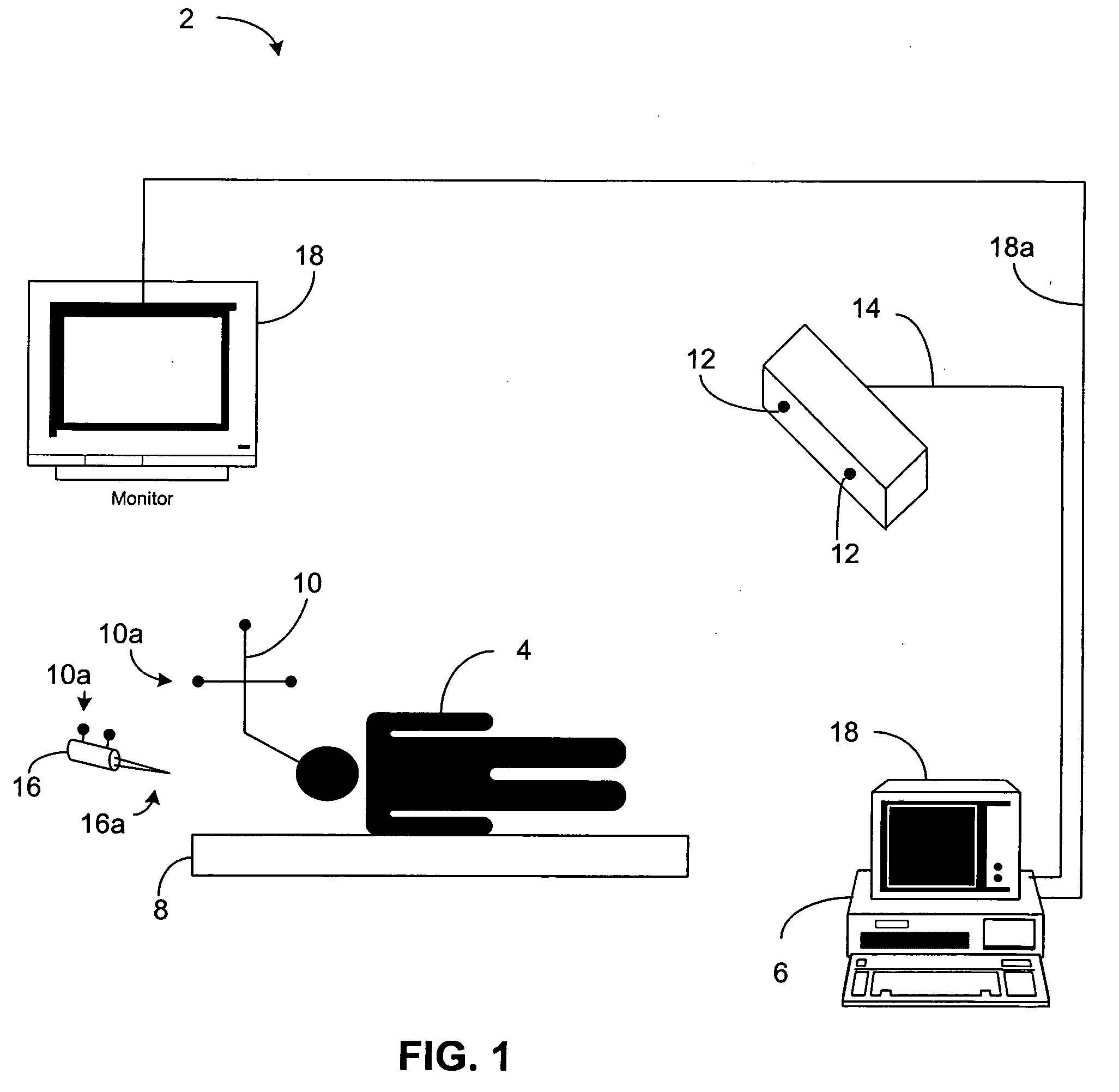
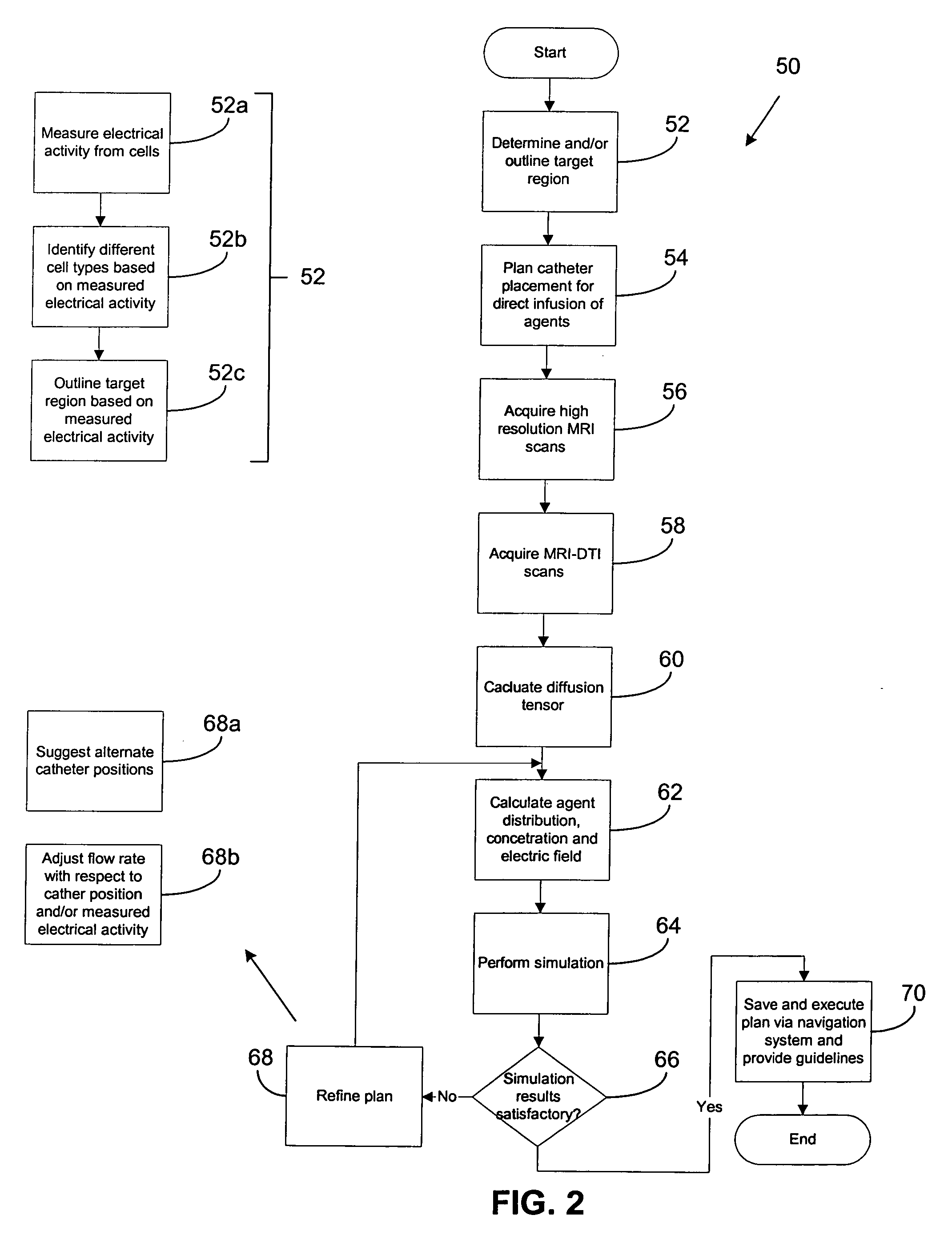
Targeted infusion of agents against Parkinson's disease
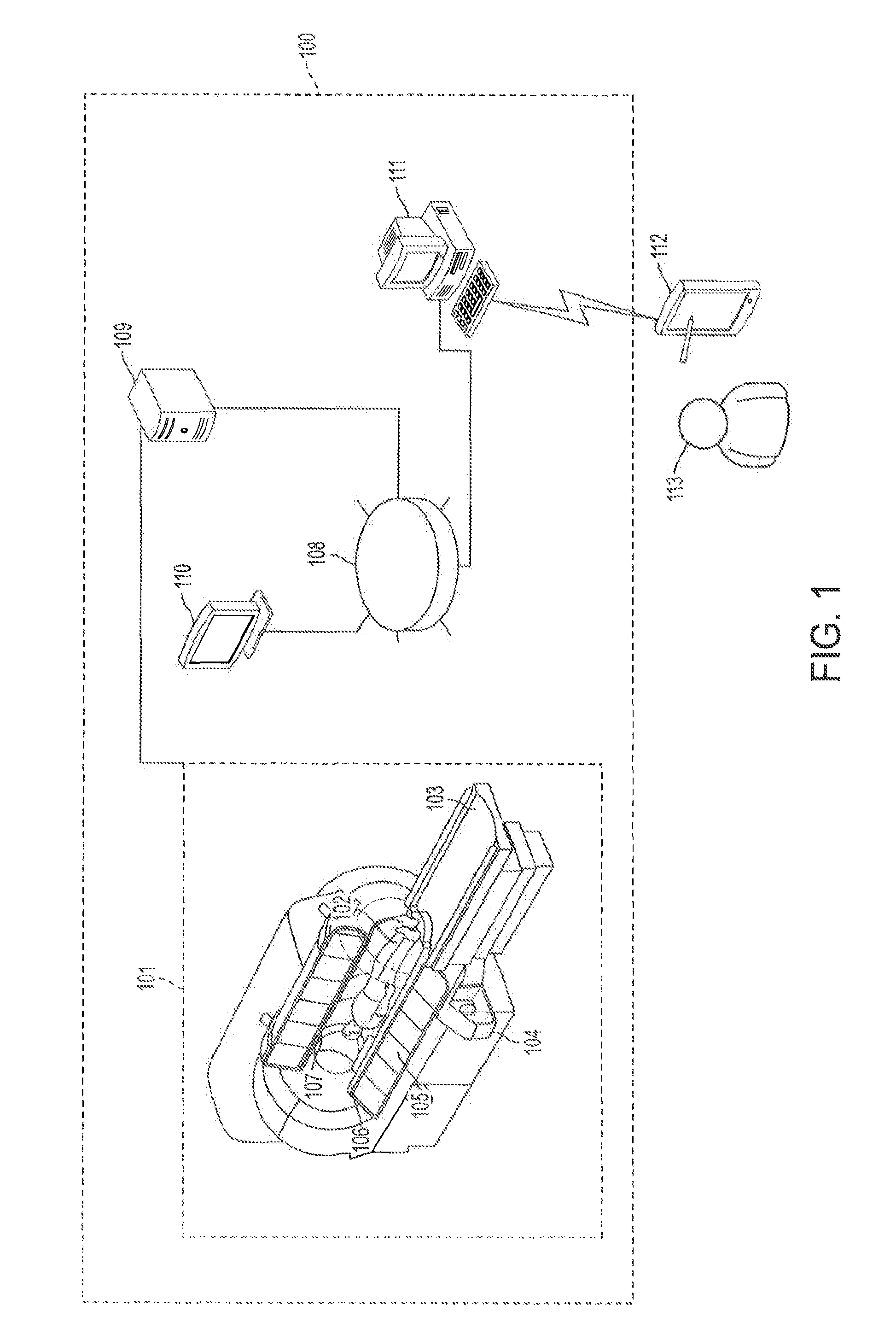
A system and method for treating Parkinson's disease by delivery of an agent within the brain. At least one image of a target region is acquired, and at least one magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging (MR-DTI) scan of the target region is acquired. A diffusion tensor is calculated from the at least one MR-DTI scan, and at least one of an agent distribution and an agent concentration from the images and the calculated diffusion tensor is calculated. Using at least one of the calculated diffusion tensor, the images, the calculated agent distribution, and the calculated agent concentration, the placement of a delivery instrument is planned to deliver the agent to the target region to achieve a desired agent concentration and / or agent distribution within the target region. Delivery of the agent can be coordinated with an applied electrical stimulation.
Owner:BRAINLAB
Brain function analysis apparatus
There is provided a method including, acquiring brain function data and diffusion tensor data (S10), calculating a connection degree between voxels adjacent to each other based on the diffusion tensor data (S30), constituting a data evaluation value based on the brain function data and the connection degree between the adjacent voxels (S40), subjecting the data evaluation value to nonparametric regression analysis (S50), and forming and displaying images based on results of the analysis (S60, S70).
Owner:TOKYO DENKI UNIVERSITY
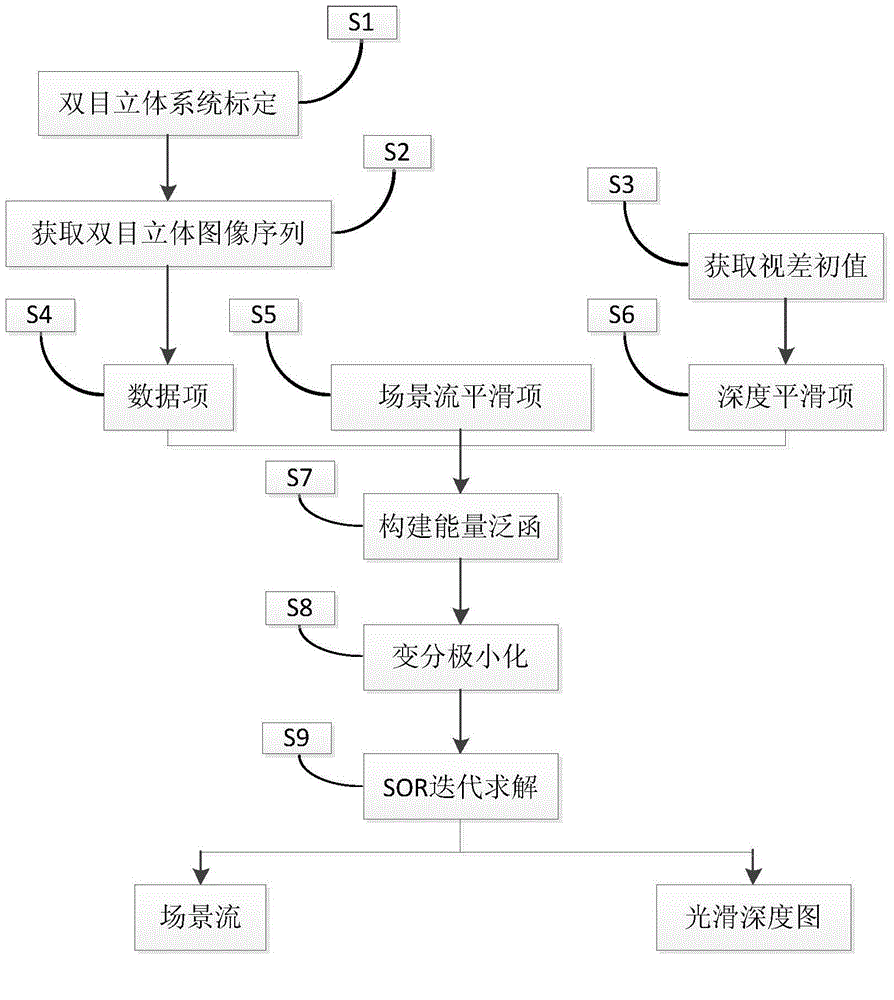
Method for estimating variational scene flow based on three-dimensional flow field regularization
ActiveCN104680544AAddresses a significant increase in estimation errorImprove robustnessImage analysisDiffusionDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for estimating variational scene flow based on three-dimensional flow field regularization. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing calibrated left and right video cameras to obtain left and right image sequences; performing regularization on a three-dimensional flow field and obtaining a scene flow data item; extending a two-dimensional optical flow smooth item to a three-dimensional space and obtaining a scene-flow-driven anisotropic scene flow smooth item; designing a diffusion tensor and performing intrinsic decomposition according to direction information, obtaining diffusion intensity in each direction, performing anisotropic smoothing, and obtaining a depth smooth item; combining the scene flow data item, the scene flow smooth item and the depth smooth item, and creating an energy functional; using a variational minimization method and obtaining a solution of an Euler equation corresponding to the energy functional; utilizing super-relaxation iteration to perform iterative solving on the Euler equation and obtaining the scene flow and depth information after optimization. The method has the advantages of high robustness and accurate scene flow.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
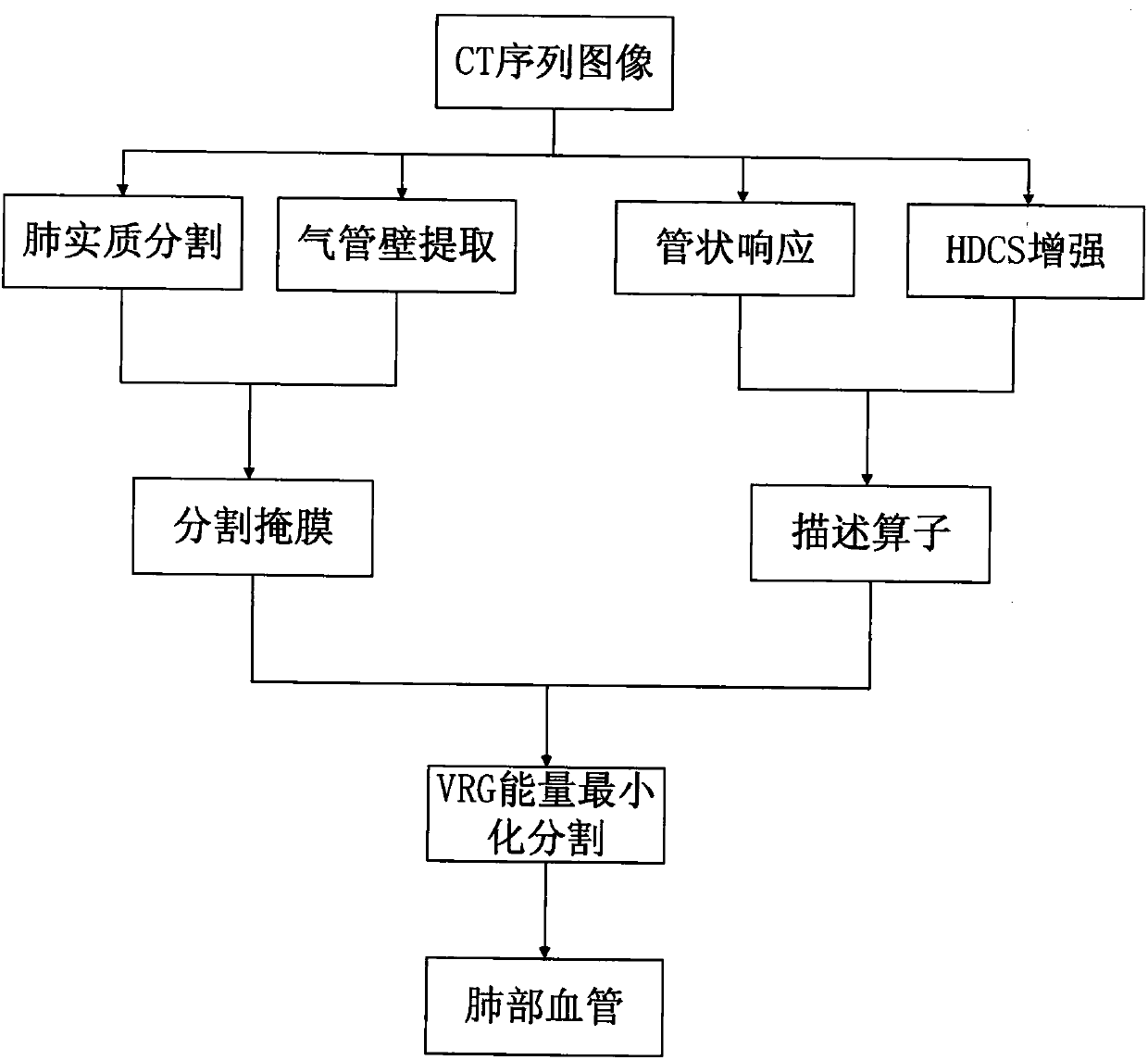
Pulmonary vascular tree segmentation method with tubular structure enhancement and energy function combined
InactiveCN108492300AStrong noise influenceReduce the impact of noiseImage enhancementImage analysisTracheal wallEnergy functional
The invention relates to a pulmonary vascular tree segmentation method with tubular structure enhancement and an energy function combined. A Pock function is used to calculate the response of a tubular structure, and a potential vascular region is thus detected; a tubular structure enhancement algorithm based on a diffusion tensor is then adopted to enhance the original image, influences on the original image by noise are reduced, and the vascular region is enhanced; and finally, a Pock function calculation result and an image enhancement result are combined to build a region description operator, and a minimum energy segmentation method VRG method is used to finely segment the pulmonary vessel. The segmentation result shows that while the method segments a main pulmonary vessel, a large amount of tiny vessels are also extracted, and the segmentation result is little influenced by the noise. The method is high in specificity, the sensitivity is strong, a vessel and a tracheal wall areacan be distinguished, and the segmentation result accuracy is further improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
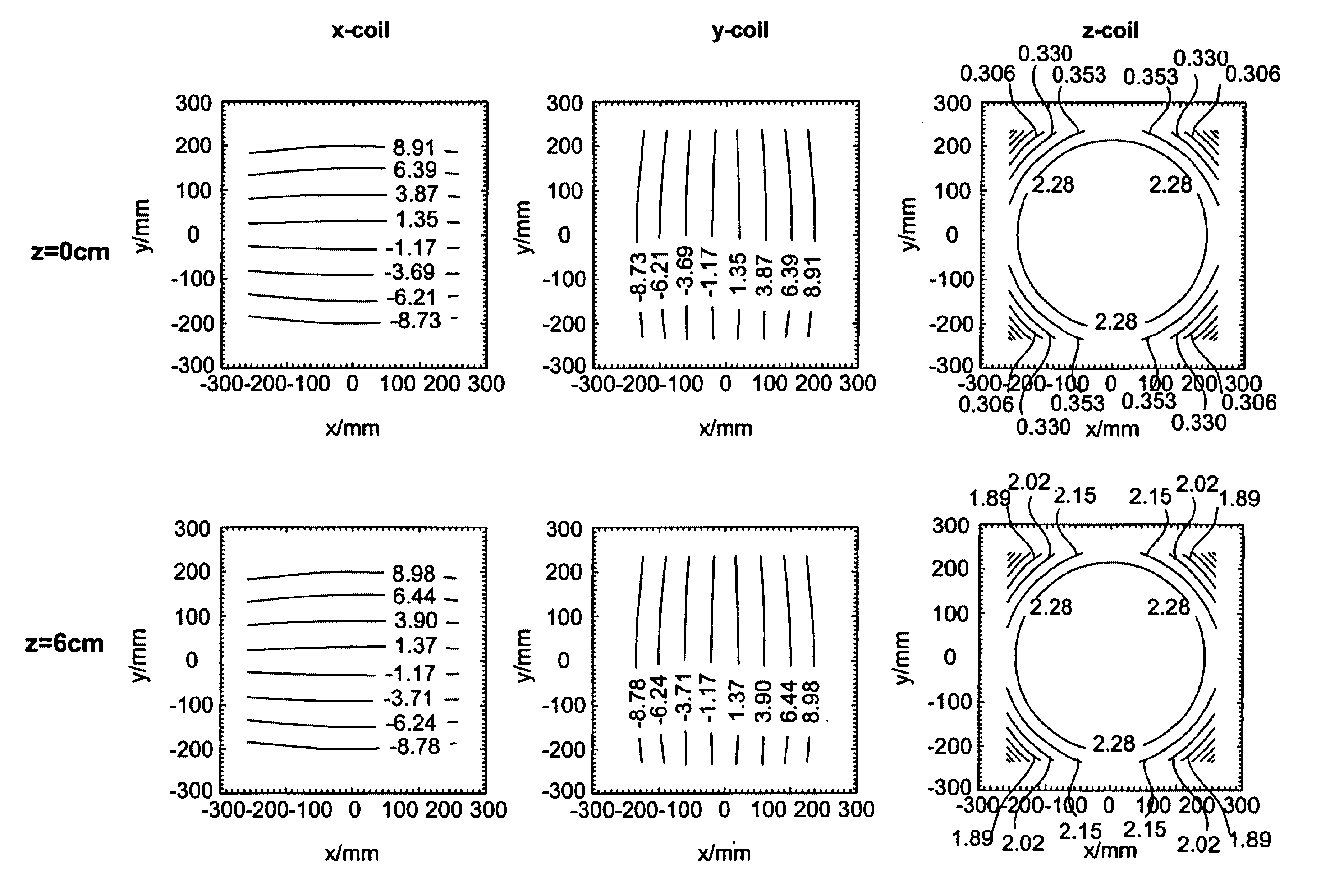
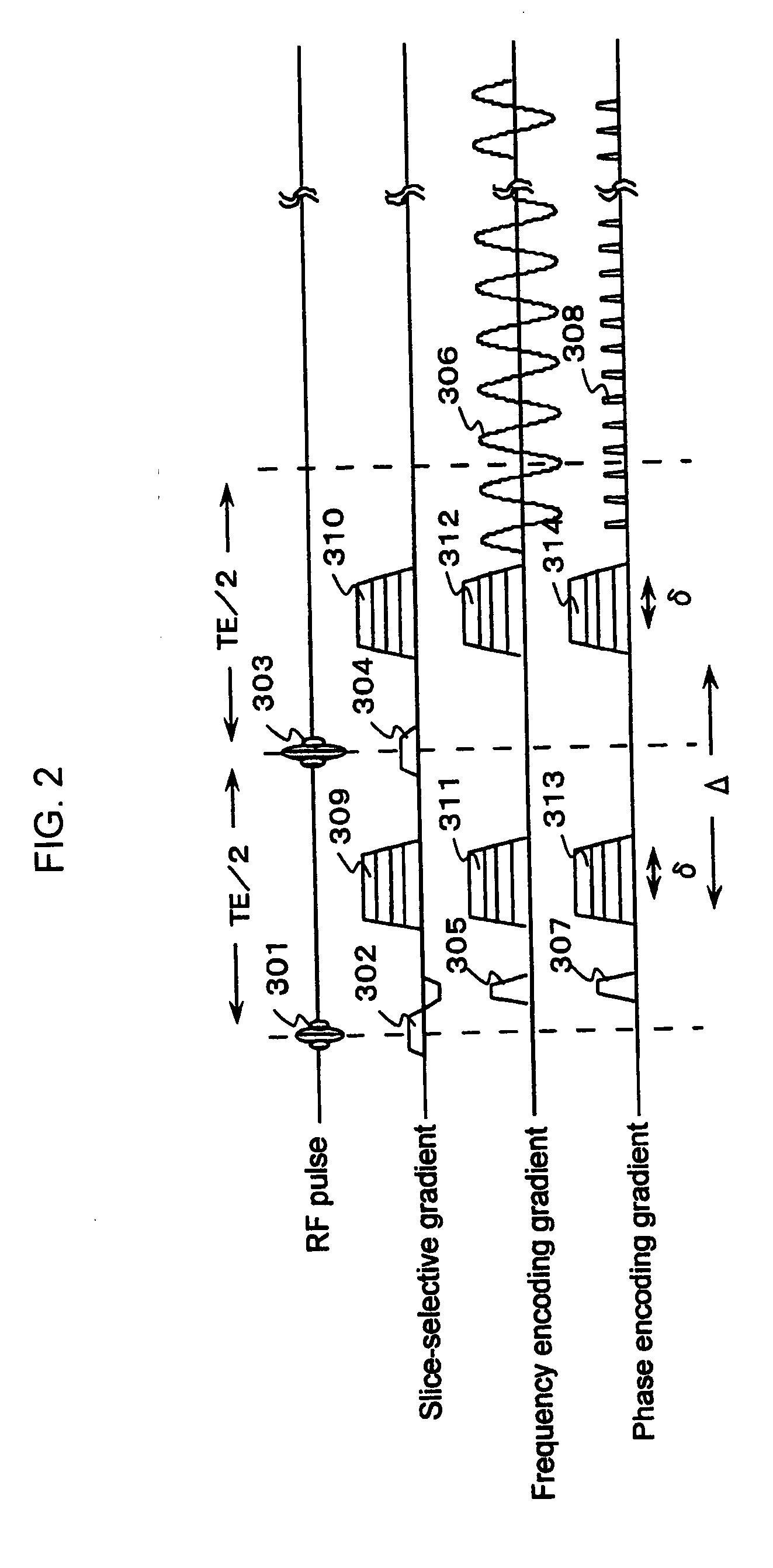
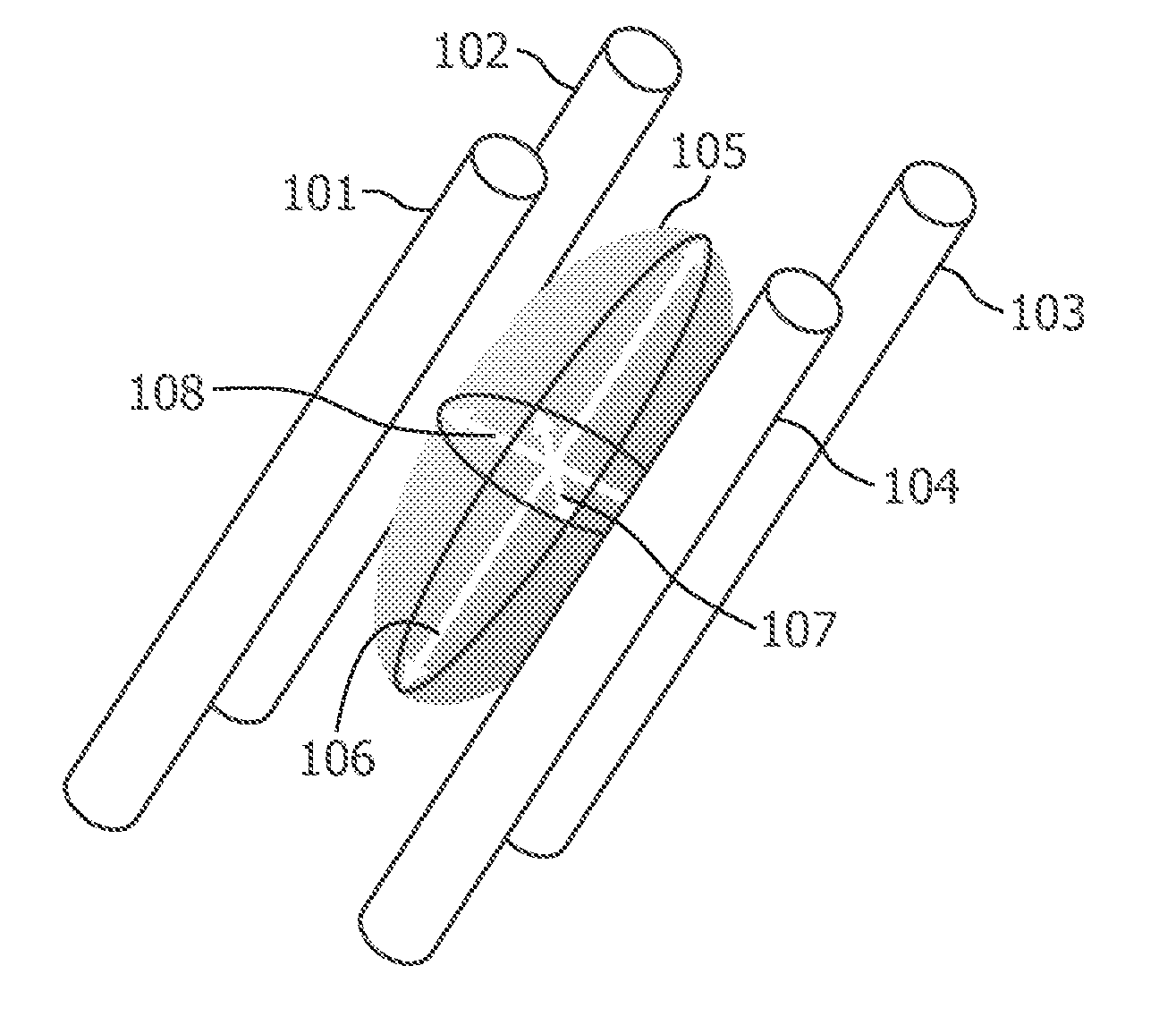
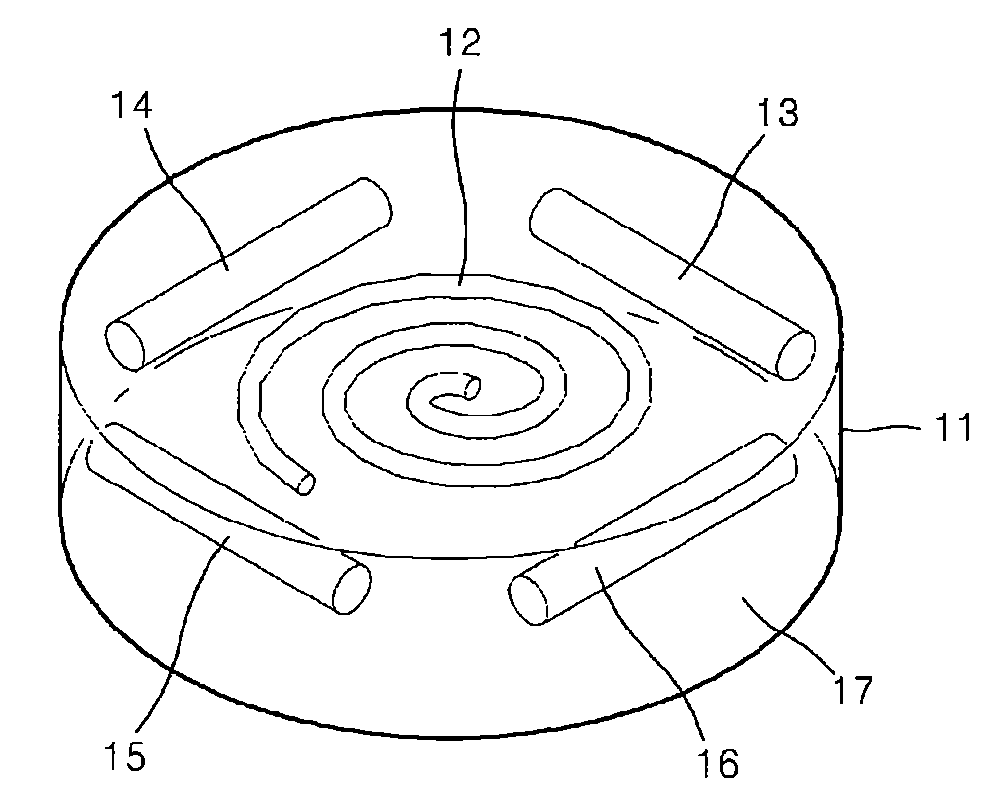
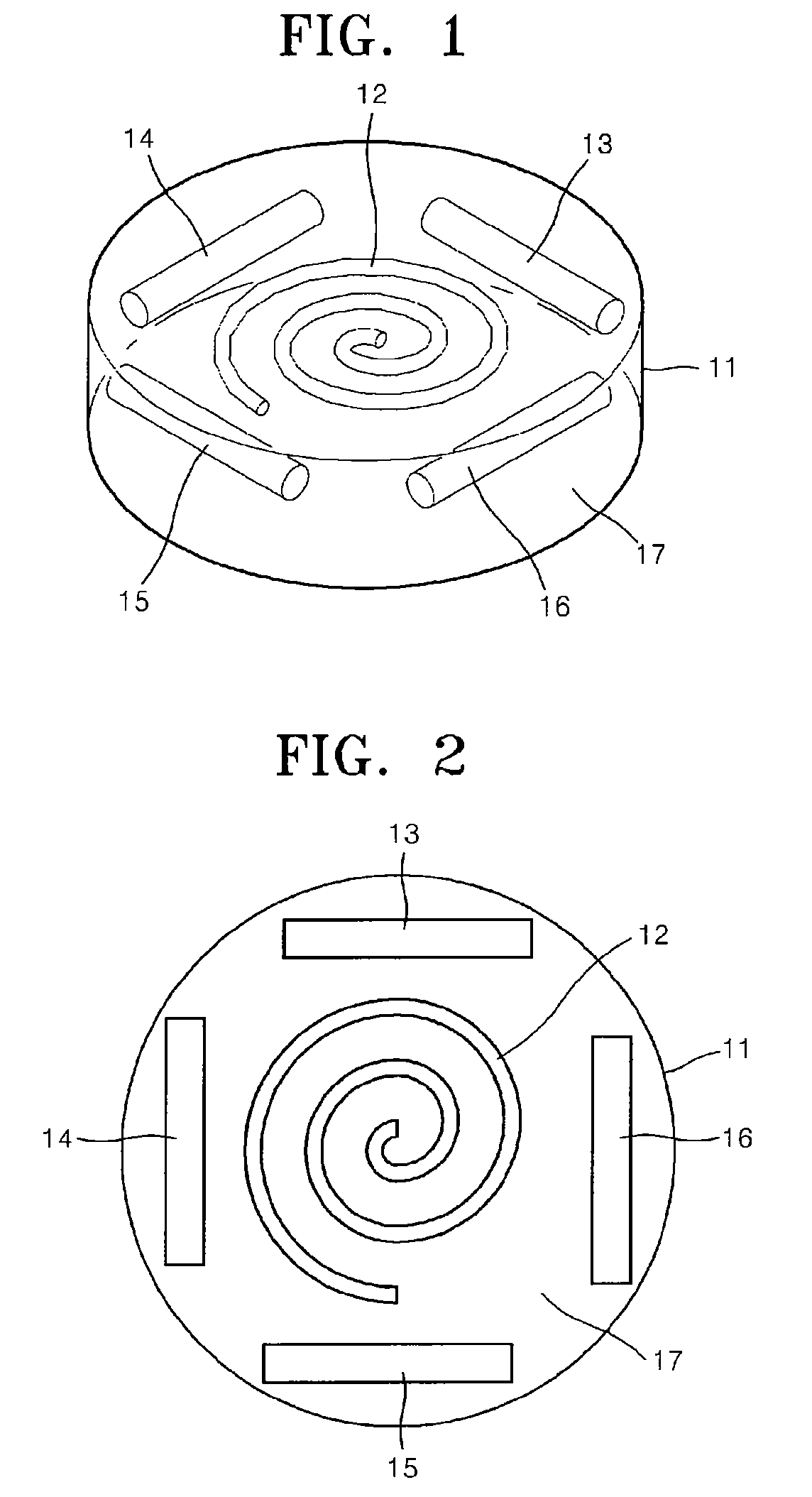
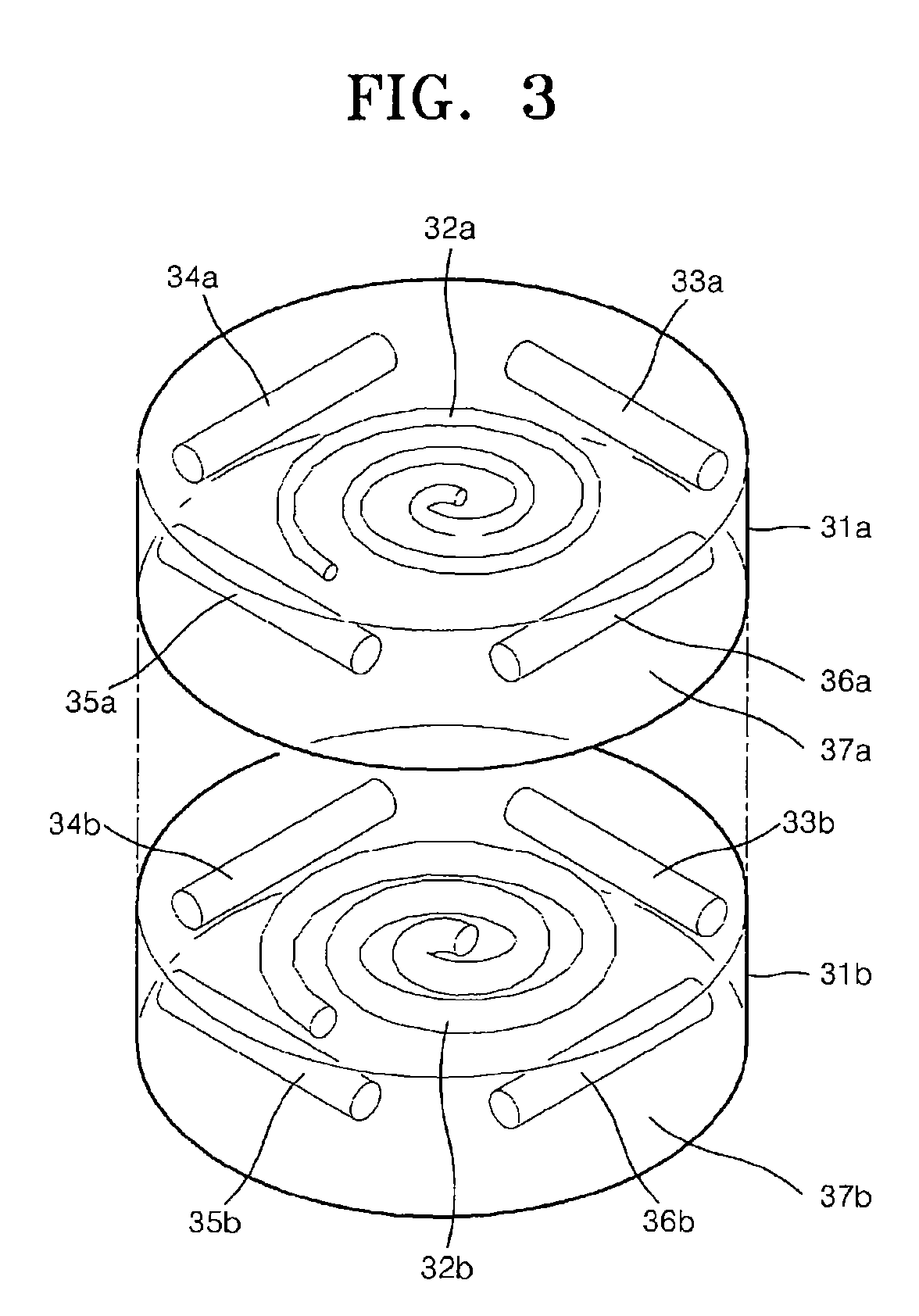
Phantom for diffusion tensor imaging
InactiveUS7667458B2Quality improvementMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiffusion AnisotropyDiffusion
A phantom for Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) to measure the main physical quantities of diffusion tensors, such as diffusion anisotrophy, a diffusion principal axis and a route of the diffusion principal axis, and to evaluate the accuracy of DTI are provided. The phantom for diffusion tensor imaging includes: an outer container providing a space; materials for diffusion measurement located in the space of the outer container and formed of bunches of microtubes; and materials for fixing located in the space of the outer container to fix the materials for diffusion measurement to a specific location.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com