Improved split field time domain finite difference algorithm
A time domain finite difference and split field technology, applied in computing, complex mathematical operations, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as memory consumption and time consumption, and achieve the effect of reducing memory usage and fast computing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
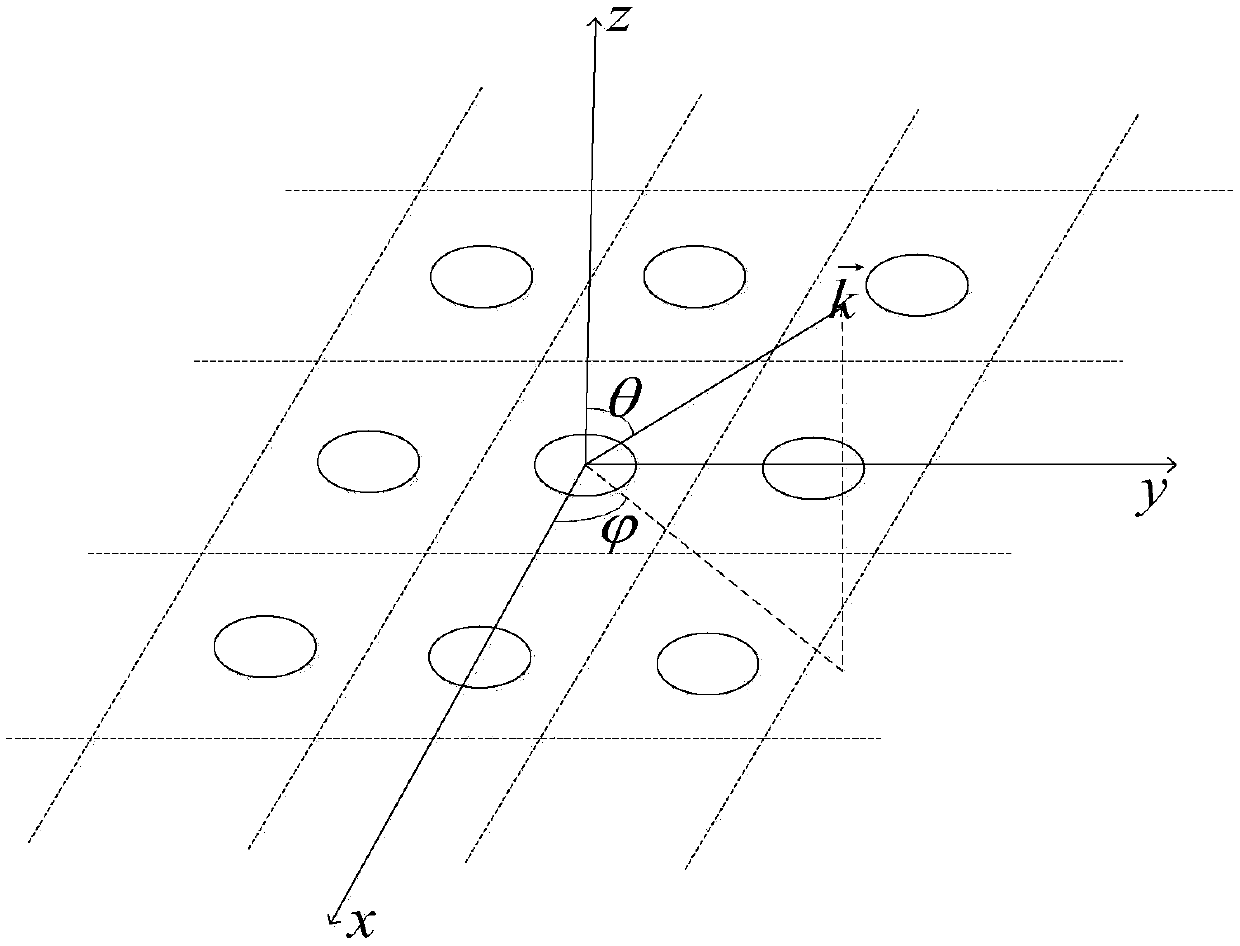
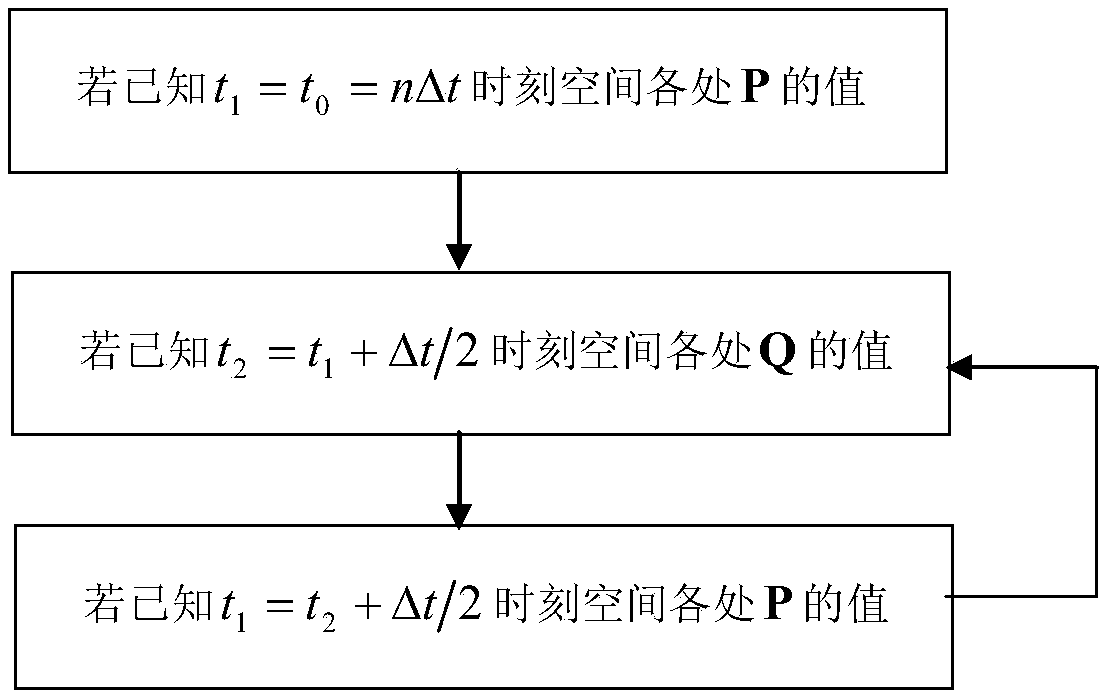
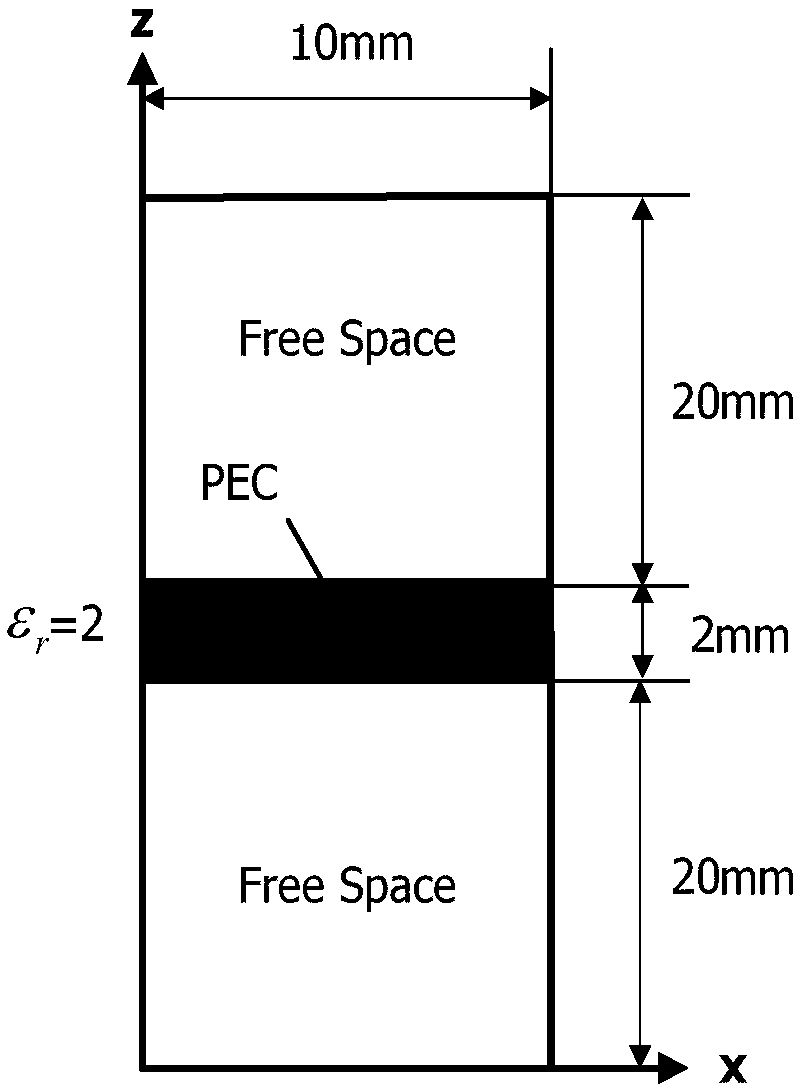
[0047] The frequency selective surface (FSS) is shown in Fig. 3(a) and Fig. 3(b). The dielectric parameter ε of the medium r = 2, a metal patch is placed in the middle, the incident wave is a modulated Gaussian pulse, the center frequency is 15GHz, and the calculation frequency range is 6-20GHz; the subdivision size of the Yee cell is △x=△y=△z=0.25mm, PML layer Set to 20 layers, the total number of grids is 40×40×106, and calculate the reflection coefficient when the incident angle of the plane wave deviates from the z-axis direction by 30°. Figure 4 The method proposed by the present invention is compared with the calculation results of the traditional split-field time-domain finite difference algorithm, and table 1 counts the calculation results of the method proposed by the present invention and the traditional split-field time-domain finite-difference algorithm under the same iteration time. Consumption time and memory comparison.
[0048] Table 1. Computational time an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com