Therapeutic medicine for fibrous disease
A technology for fibrotic diseases and drugs, applied in diseases, drug combinations, skin diseases, etc., can solve the problem that there is no radical treatment method for genetic diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
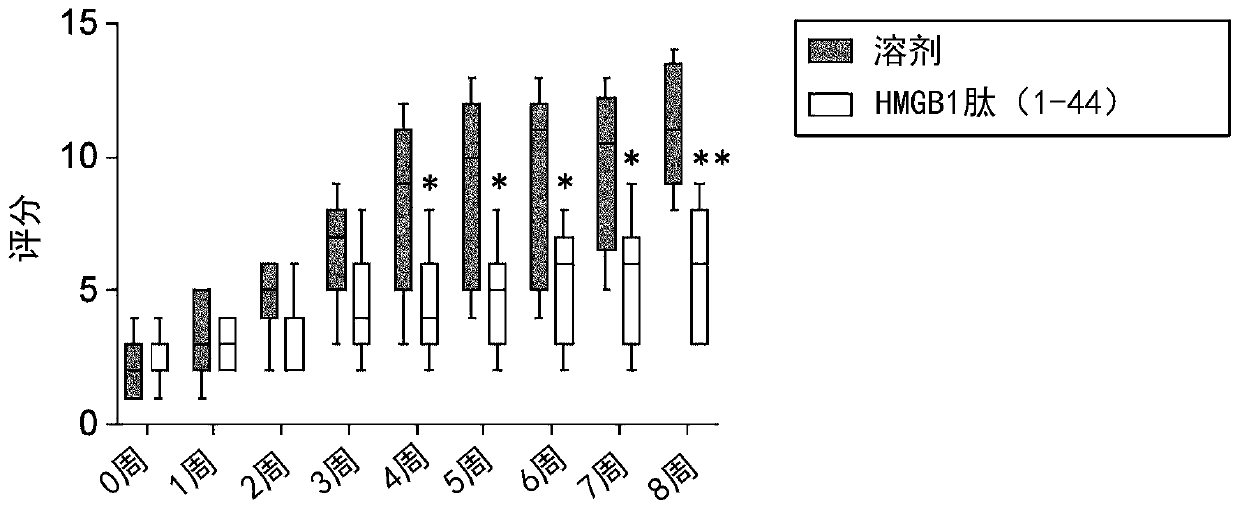
[0106] Inhibitory effect of HMGB1 peptide (1-44) on forelimb adhesions in a mouse model of epidermolysis bullosa (1) Materials and methods
[0107] i) animals
[0108] A mouse model of epidermolysis bullosa was obtained from Prof. Leena Bruckner-Tuderman at the University of Freiburg (Germany) with a homotype of mutant allele in the collagen type VII alpha1 (Col7a1) gene (Fritsch, et al., Col7a1 as described in J Clin Invest. 2008 May;118(5):1669-79 flNeo / flNeo mouse, hereinafter referred to as "129SV / colVII homo mouse" in this specification). The 15 mice (male) were acclimated in the rearing room for 2 weeks, and were divided into 2 groups according to the adhesion score described later so as to achieve the same degree, and the test substance was administered from the next day (age at the start of administration: 5 to 6 weeks of age). When the adhesion score was evaluated one week after the administration of the test substance, one mouse in the HMGB1 peptide (1-44)-admin...
Embodiment 2
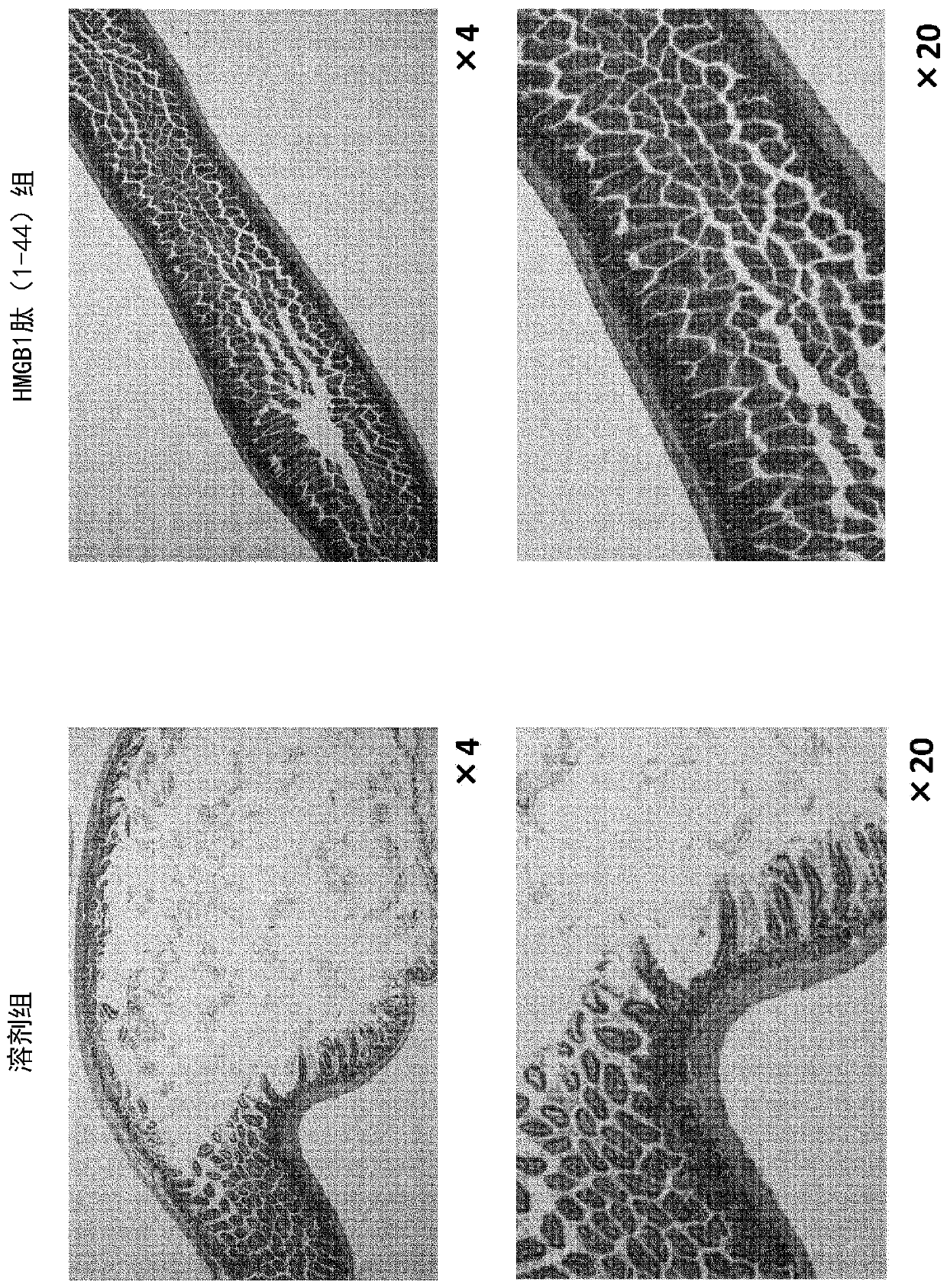
[0143] Inhibitory effect of HMGB1 peptide (1-44) on intestinal fibrosis and scarring in a mouse model of epidermolysis bullosa
[0144] (1) Materials and methods
[0145] i) animals
[0146] The 129SV / colVII homo mice (6 males) described in Example 1 were acclimated in the rearing room for 2 weeks, and divided into a solvent group (3 mice) and an HMGB1 peptide (1-44) administration group (3 mice), and then started. Administration of the test substance (age at the start of administration: 5 to 6 weeks of age).
[0147] ii) Test substance
[0148] As in Example 1, chemically synthesized HMGB1 peptide (1-44) was used as a test substance.
[0149] iii) Administration of test substance
[0150] A solvent (physiological saline, "Otsuka Raw Food Injection" manufactured by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) or HMGB1 peptide (1-44) (concentration: 0.2 mg / mL) was administered in a volume of 50 μL from the tail vein, respectively. The test substance was administered twice every week...
Embodiment 3
[0157] HMGB1 peptide (1-44) prolongs survival in a mouse model of epidermolysis bullosa
[0158] (1) Materials and methods
[0159] i) animals
[0160] The 129SV / colVII homo mice (male) described in Example 1 were acclimated in the rearing room for 2 weeks, and divided into the solvent group and the HMGB1 peptide (1-44) administration group, and the administration of the test substance was started (start of administration). Age: 5 to 6 weeks of age (weight 5 to 8 g).
[0161] ii) Test substance
[0162] As in Example 1, chemically synthesized HMGB1 peptide (1-44) was used as a test substance.
[0163] iii) Administration of test substance
[0164] The solvent (physiological saline, "Otsuka Raw Food Injection" manufactured by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) or HMGB1 peptide (1-44) (concentration: 0.2 mg / mL) was administered from the tail vein in a volume of 50 μL per one time. The test substance was administered twice every week from the next day of the grouping, and th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com