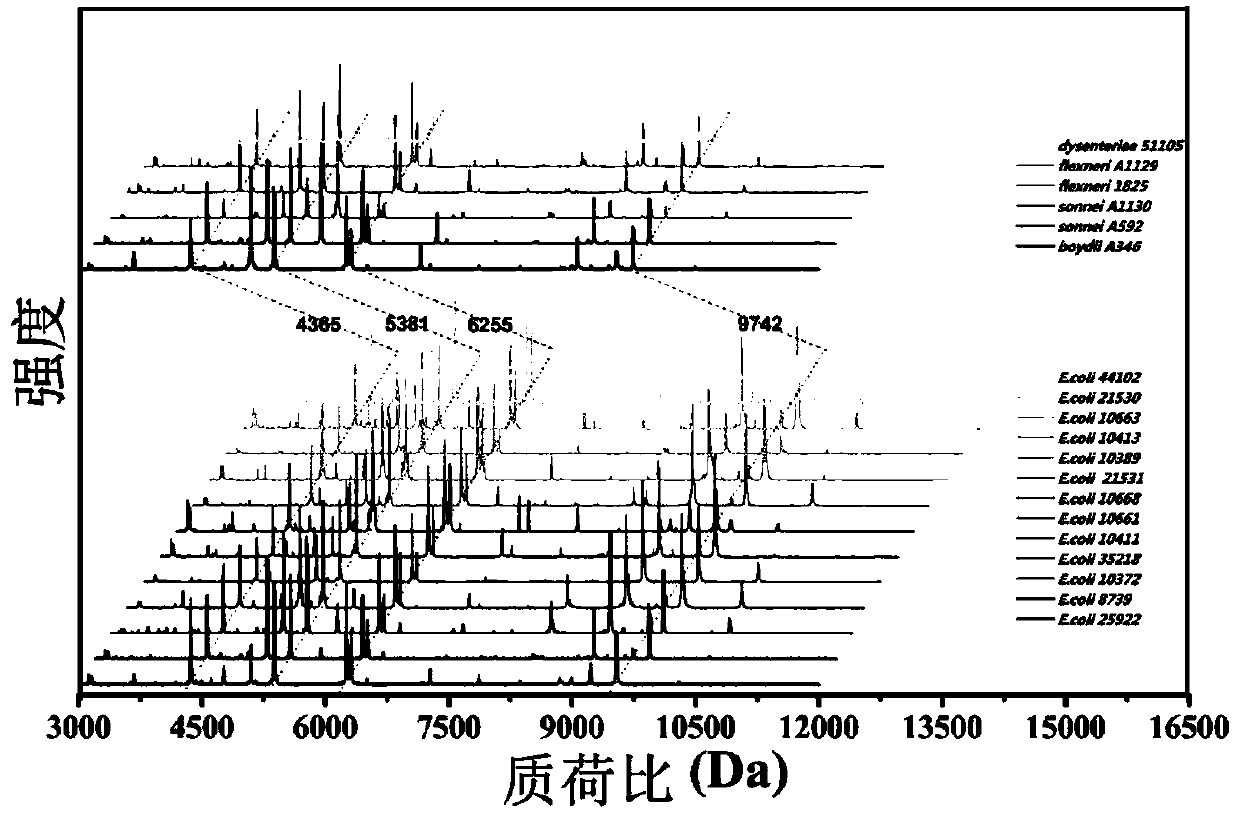
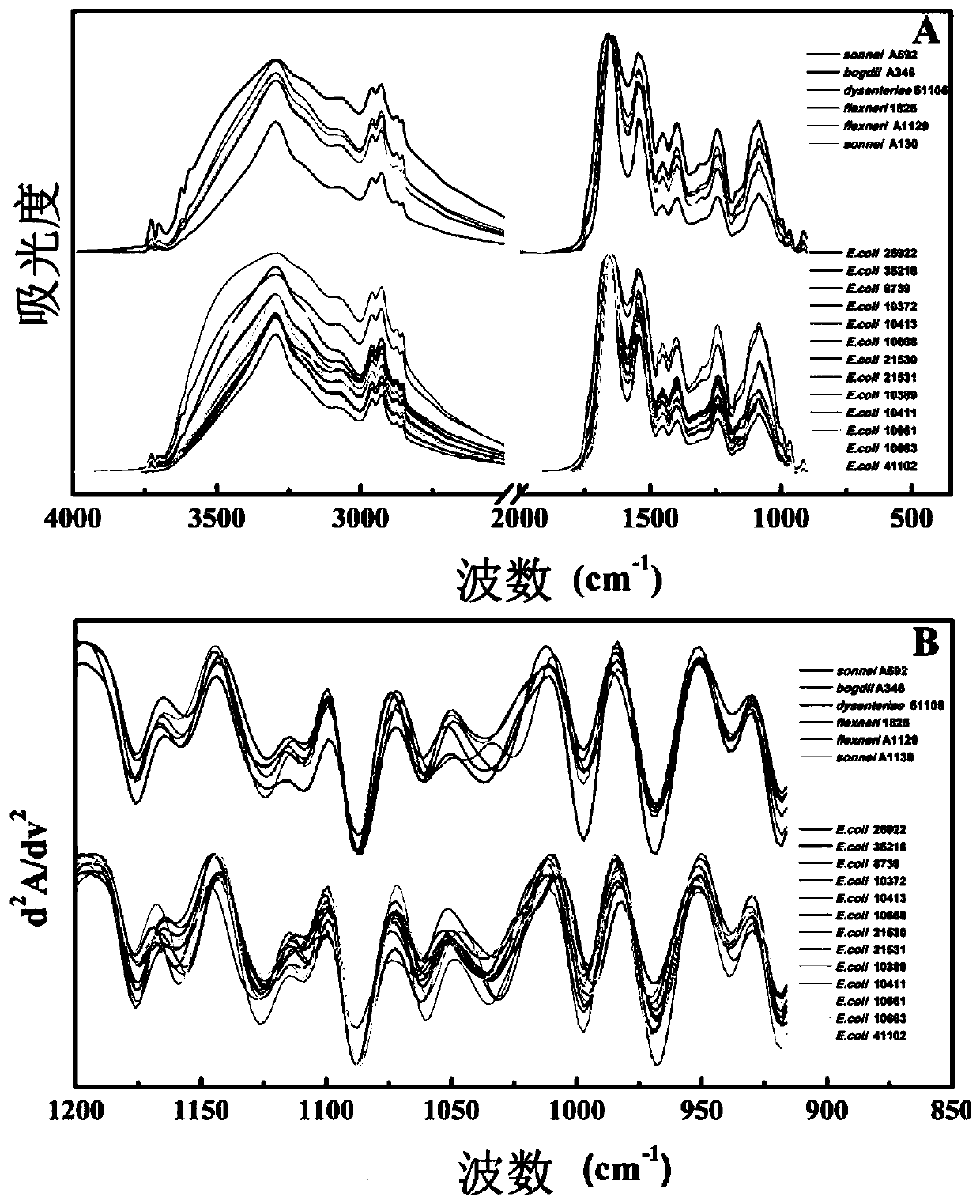
Microorganism identification and typing method in combination with mass spectrums and FTIR spectrums based on matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization flight time
A technology of time-of-flight mass spectrometry and matrix-assisted laser, applied in the field of microbial detection and analysis, can solve problems such as water interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Typing of Escherichia coli and Shigella (cultivation on tryptone soybean agar (TSA) solid medium)
[0036] 1. Collect microbial characteristic mass spectrum and infrared absorption spectrum respectively
[0037] 1) The strains frozen at -80°C were solid-cultured with TSA in a 37°C incubator for 14 hours for the subsequent collection of mass spectrometry and infrared spectrometry data. This bacterial culture method has no specificity, and only requires that it is suitable for bacterial growth and that the consistency of culture conditions should be ensured as much as possible throughout the identification process, so as to reduce the interference of unknown factors caused by different culture methods.
[0038] 2) For mass spectrometry, use an inoculation loop to pick an appropriate amount of bacteria on the solid medium and resuspend them in ethanol solution, and then use formic acid-acetonitrile extraction method (for general bacteria, direct coating method can ...
Embodiment 2
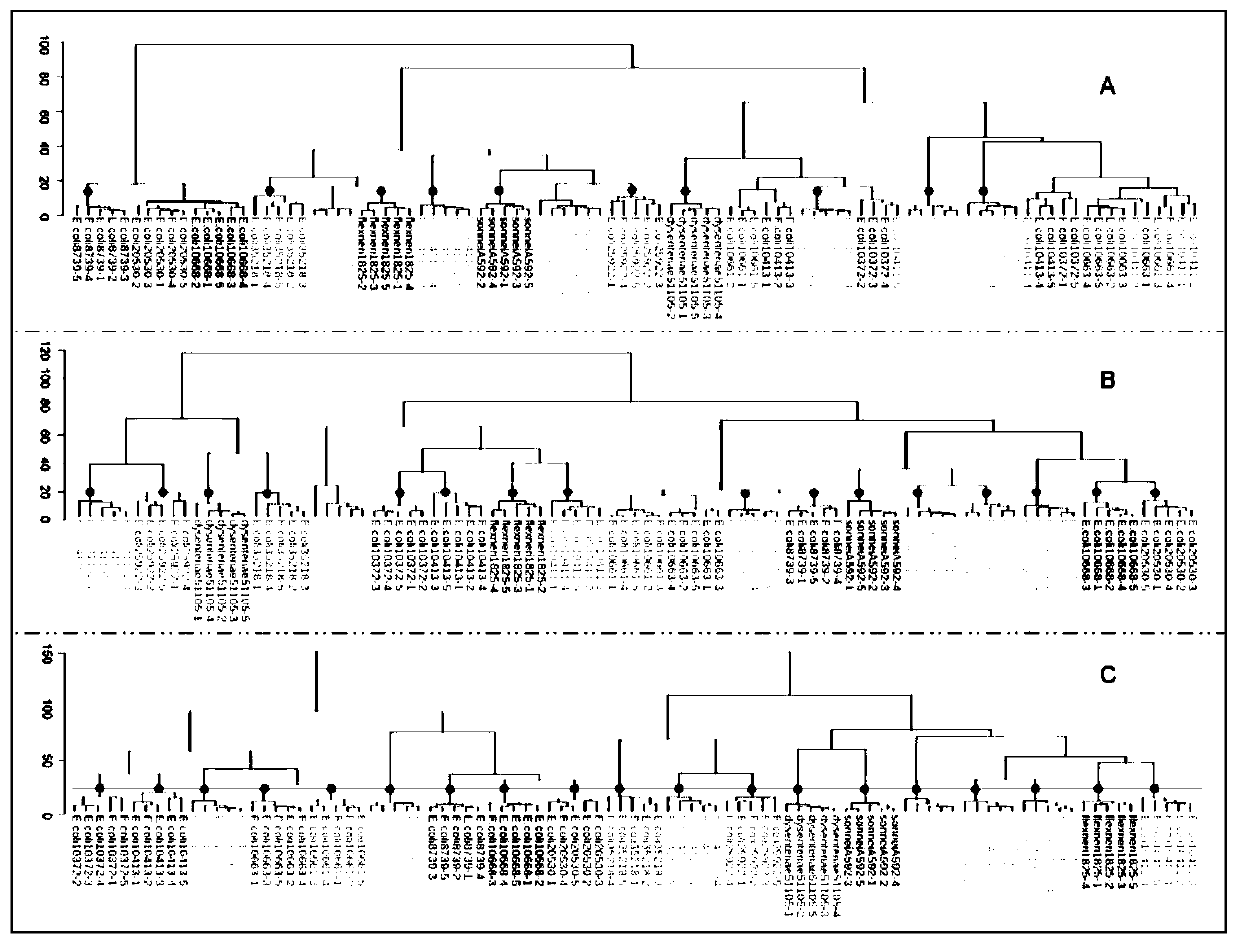
[0046] Types of Escherichia coli and Shigella (Cultivated on Columbia blood agar solid medium) (cluster analysis results see Figure 4 ) Figure 4 The green line in is the threshold line, and the red dots are the correctly clustered clusters. in Figure 4 A is the result of cluster analysis using MALDI-TOF data alone, a total of 19 strains, of which 9 strains are correctly clustered, and the clustering accuracy rate is 9 / 19; Figure 4 B is the result of cluster analysis using FTIR data alone, a total of 19 strains, of which 16 strains are correctly clustered, and the clustering accuracy rate is 17 / 19; Figure 4 C is the result of cluster analysis by fusion of MALDI-TOF and FTIR data. There are 19 strains in total, and 19 strains are correctly clustered, and the clustering accuracy rate is 100%. It shows that MALDI-TOF alone is used for typing Escherichia coli and Shigella, and its correct rate is low; FTIR is used alone for typing Escherichia coli and Shigella, and its typi...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Typing of Escherichia coli and Shigella (cultivated in LB broth liquid medium) (for cluster analysis results, see Figure 5 ) Figure 5 The green line in is the threshold line, and the red dots are the correctly clustered clusters. in Figure 5 A is the result of cluster analysis using MALDI-TOF data alone, a total of 19 strains, of which 9 strains are correctly clustered, and the clustering accuracy rate is 9 / 19; Figure 4 B is the result of cluster analysis using FTIR data alone, a total of 19 strains, of which 15 strains are correctly clustered, and the clustering accuracy rate is 1519; Figure 4 C is the result of cluster analysis by fusion of MALDI-TOF and FTIR data. There are 19 strains in total, and 19 strains are correctly clustered, and the clustering accuracy rate is 100%. It shows that MALDI-TOF alone is used for typing Escherichia coli and Shigella, and its correct rate is low; FTIR is used alone for typing Escherichia coli and Shigella, and its typing ac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com