Soft glass optical fiber splicing method
A technology of optical fiber fusion and soft glass, which is applied in the field of mid-infrared fiber lasers, can solve the problems of affecting fusion efficiency, reducing precision, and increasing fusion loss, so as to improve fusion efficiency, avoid excessive softening, and solve the effect of deliquescence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
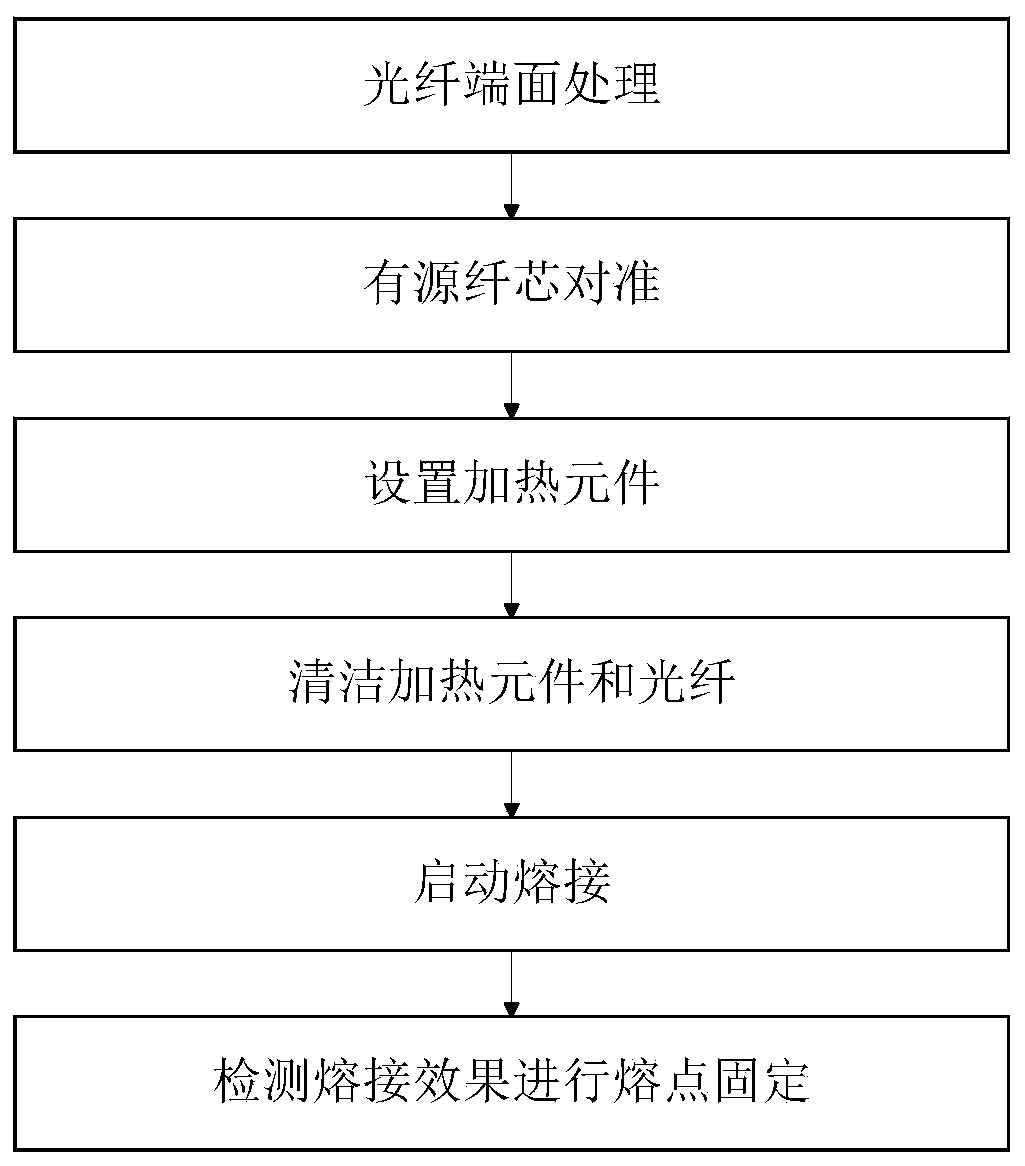
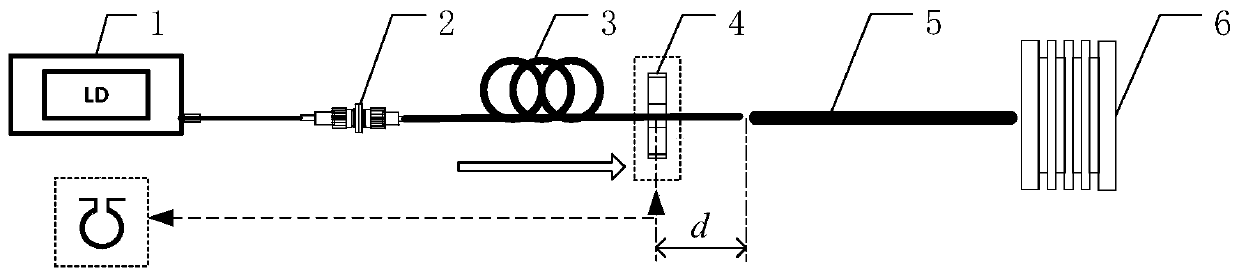
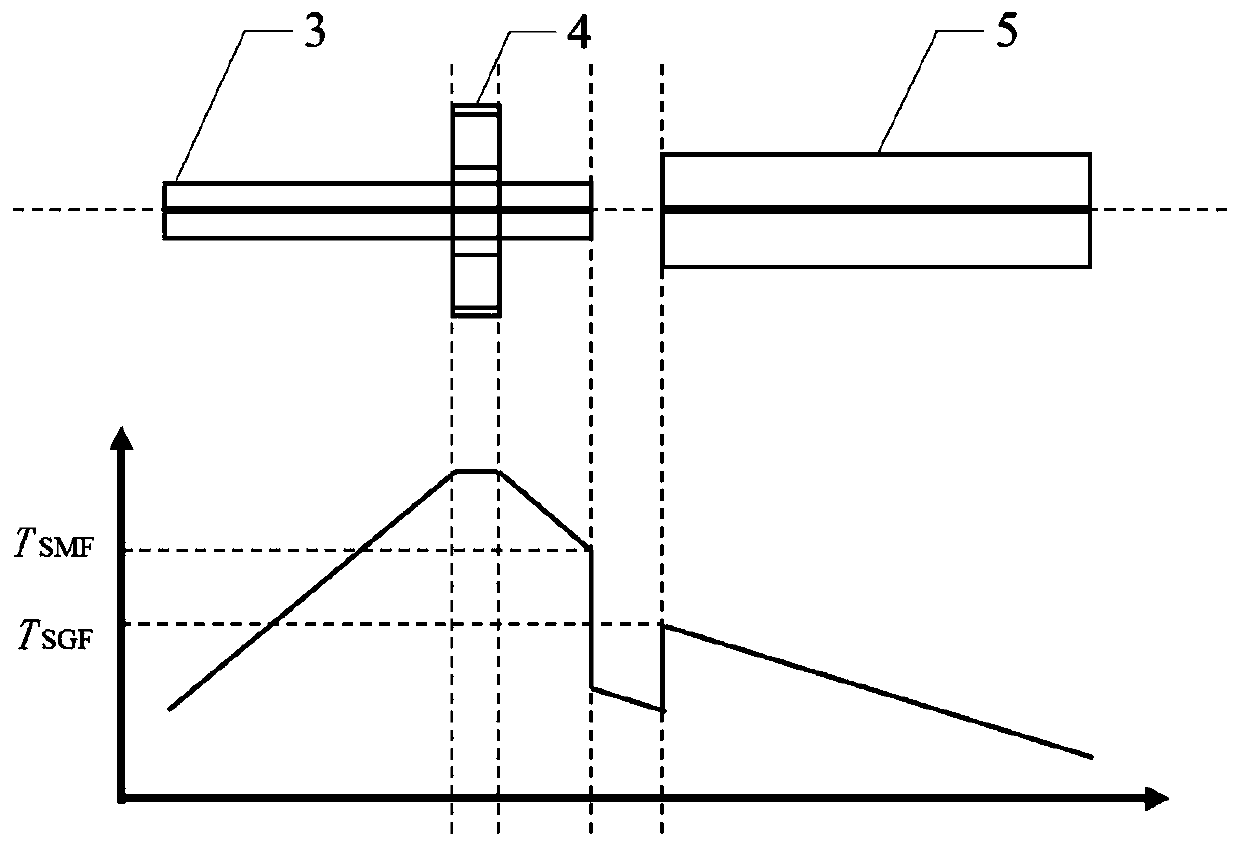
[0050] This embodiment takes the fusion splicing of soft glass optical fibers and single-mode silica optical fibers as an example, and uses the soft glass optical fiber fusion splicing method proposed by the present invention for fusion splicing. In this embodiment, a Vytran large-core fiber fusion splicer (GPX-3400) is used to realize the fusion splicing of soft glass optical fiber and single-mode silica optical fiber, wherein the soft glass optical fiber is a tellurate optical fiber with a core diameter of 12 μm and a cladding The diameter is 220 μm without coating; the core diameter of the single-mode silica fiber is 9 μm, the cladding diameter is 125 μm, and the coating diameter is 250 μm. In addition, because the fusion power required for soft glass fiber fusion is low, the fluctuation of room temperature will have a great impact on the setting of fusion parameters and the fusion effect. Therefore, in order to avoid the influence of room temperature changes, the room tempe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com