Method of correcting amplification deviation in amplicon sequencing
An amplicon and bias technology, which is used in biochemical equipment and methods, sequence analysis, and microbial determination/inspection. Problems such as increasing deviation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0131] Example 1: Multiplex PCR Amplification Bias Correction for Fetal Aneuploidy Detection
[0132] This article describes a computational method to correct for amplification bias and its application to noninvasive prenatal testing using cell-free maternal DNA to aid in the detection of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy. After correcting for amplification bias in 1855-plex PCR, fetal chromosomal aneuploidy can be detected in maternal blood with a fetal DNA fraction as low as 4%.
[0133] Amplification bias correction for amplicon sequencing was as follows:
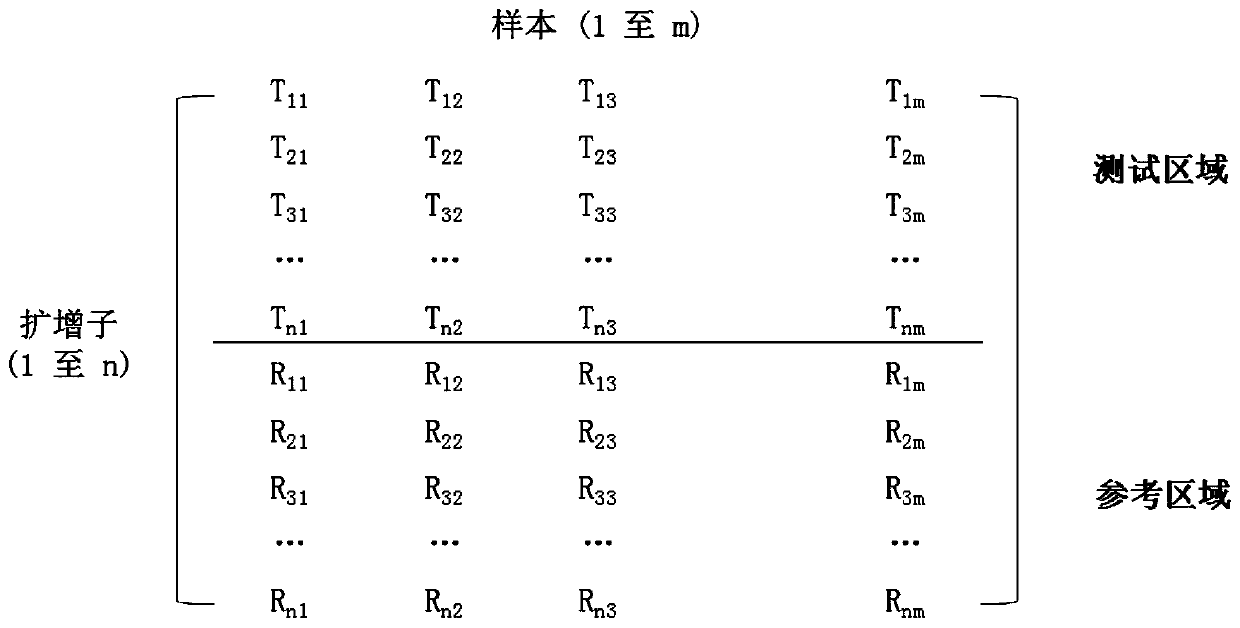
[0134] 1. If figure 1 As shown, the coverage of each amplicon is obtained for each sample tested, and then the data is entered into a matrix, with a single row representing a single amplicon and a single column representing a single sample.
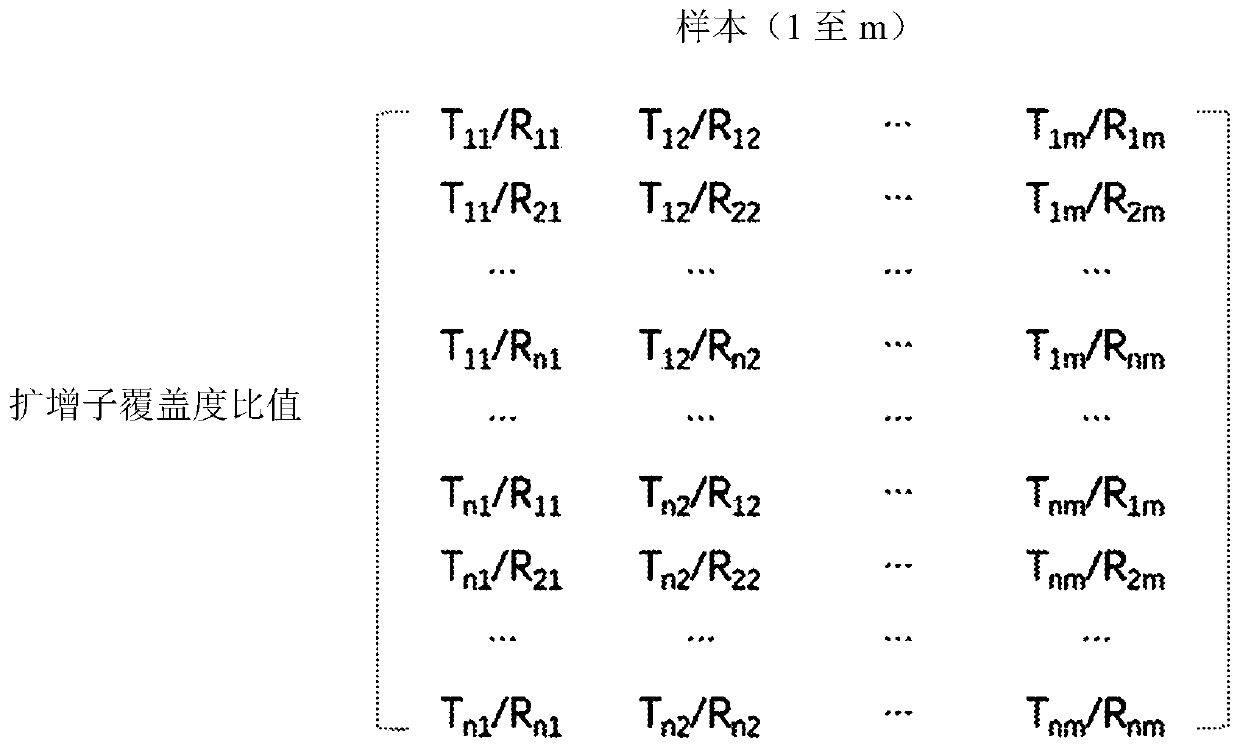
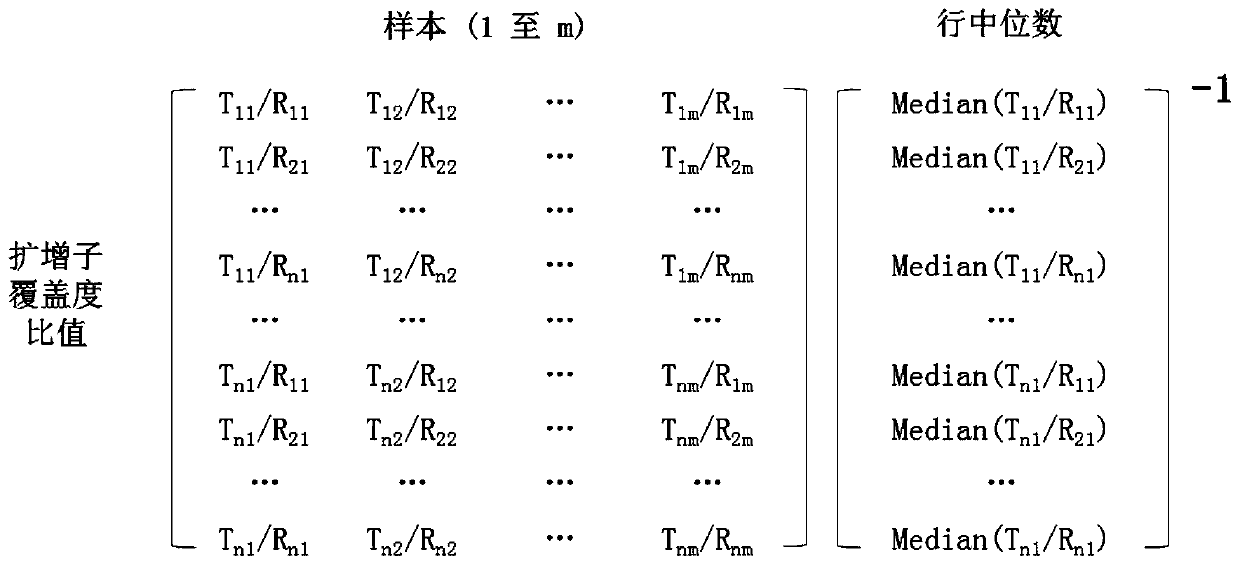
[0135] 2. Using the data matrix generated in step 1, generate an amplicon coverage ratio matrix by calculating the coverage ratios for each amplicon combination between the test genomi...
example 2
[0143] Example 2: Multiplex PCR Amplification Bias Correction for Pooled Plasma DNA Samples
[0144] 10 parts of plasma DNA samples were mixed together, and then equally divided into 10 parts for PCR amplification ( Figure 5 ). PCR bias was corrected as described in Example 1, and each data set was processed separately to obtain 10 separate sequencing results. Completing steps 1-4 of Example 1, and then calculating the difference in GC content of the amplicons between each T / R pair (T represents a site in the test region, R represents a site in the reference region), yields Diff amplicon GC, according to the Robust linear regression method to fit the logarithmic normalized amplicon coverage ratio (obtained in step 4 of Example 1) and Diff amplicon GC:
[0145] log(normalized coverage ratio)=β×Diff 扩增子GC +α+ε
[0146] where α is the intercept, β is the slope, and ε is the residual
[0147] As mentioned above, we obtained 10 experimental replicates from the same DNA source...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com