Dual-current bias type CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) pseudo resistor
A pseudo-resistance, dual-current technology, applied in the field of microelectronics, can solve problems such as poor stability, and achieve the effect of avoiding resistance changes and achieving good robustness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
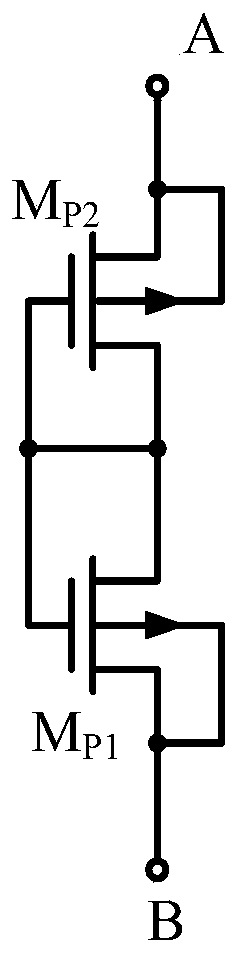
[0031] See figure 1 , figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the structure of a traditional pseudo-resistor, as shown in the figure, the traditional pseudo-resistor includes two PMOS field effect transistors M P1 and M P2 , the A terminal and the B terminal are respectively used as the two ends of the pseudo-resistor, and the connection method is shown in figure 1 , the small-signal equivalent resistance value of the traditional pseudo-resistor is deduced as follows.
[0032] Based on the EKV transistor model, the I-V relationship of the PMOS transistor is as follows:
[0033]
[0034] Among them, n p Indicates the subthreshold slope factor of the PMOS tube, μ P Indicates the hole mobility of the PMOS tube, V TH Indicates the threshold voltage of the PMOS tube, C ox Indicates the capacitance of the gate oxide layer of the PMOS transistor, W / L indicates the ratio of the channel width to the channel length of the PMOS transistor, V T Indicates temperature voltage, V BG I...
Embodiment 2
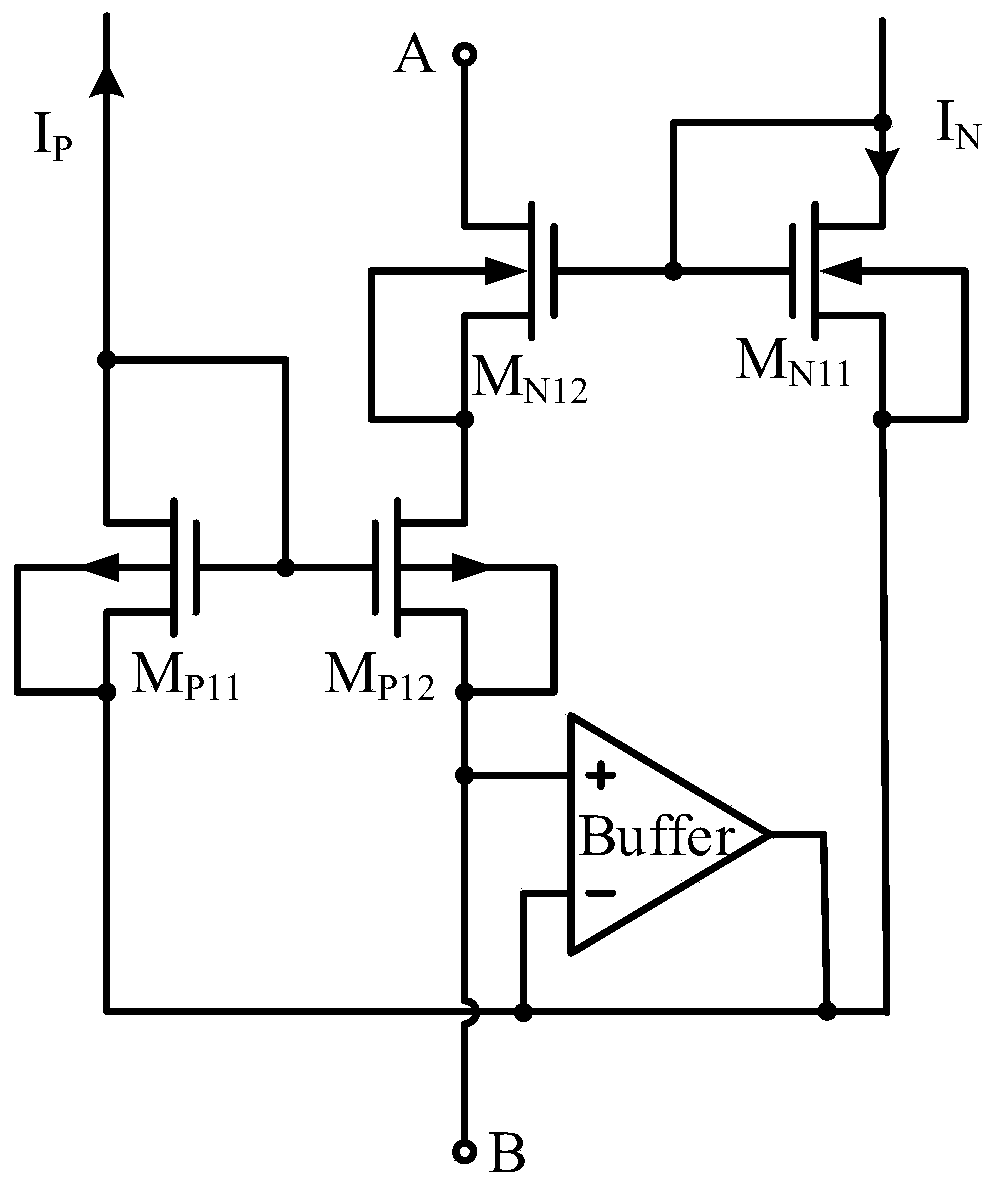
[0061] This embodiment provides a dual-current biased CMOS pseudo-resistor circuit, including a current source unit and a number of dual-current-biased CMOS pseudo-resistors in series as described in Embodiment 1, wherein the current source unit is coupled to The first PMOS transistor M connected to several CMOS pseudo-resistors connected in series with double current bias P11 The drain and the first NMOS transistor M N11 The drain is used to provide a bias current proportional to the absolute temperature; the adjacent series-connected double-current-biased CMOS pseudo-resistors share a buffer Buffer.
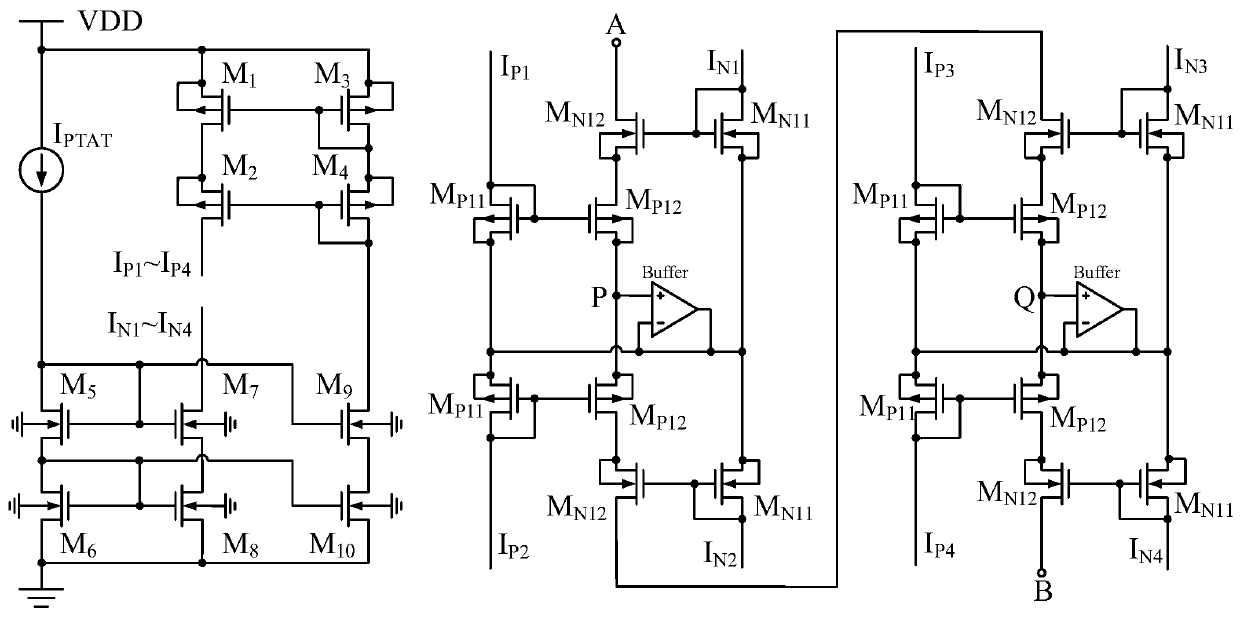
[0062] See image 3 , image 3 It is a schematic diagram of a dual current biased CMOS pseudo-resistor circuit provided by an embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, four CMOS pseudo-resistors with dual current bias are connected in series, and the current source unit includes a current source I PTAT , the first MOS tube M 1 , the second MOS tube M 2 , th...
Embodiment 3
[0071] This embodiment provides another double-current biased CMOS pseudo-resistor circuit. Compared with Embodiment 2, the dual-current-biased CMOS pseudo-resistor in this embodiment is connected in parallel, and the current source unit is the same as that in Embodiment 2. The structures are the same, and the drains of the first PMOS transistor and the drains of the first NMOS transistors of the plurality of double-current-biased CMOS pseudo-resistors connected in parallel are used to provide a bias current proportional to the absolute temperature.
[0072] See Figure 4 , Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of another dual current biased CMOS pseudo-resistor circuit provided by an embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, two dual-current biased CMOS pseudo-resistors are connected in parallel, and the second MOS transistor M 2 The drains are respectively connected to the first PMOS transistor M of two double current biased CMOS pseudo-resistors P11 The drain o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com