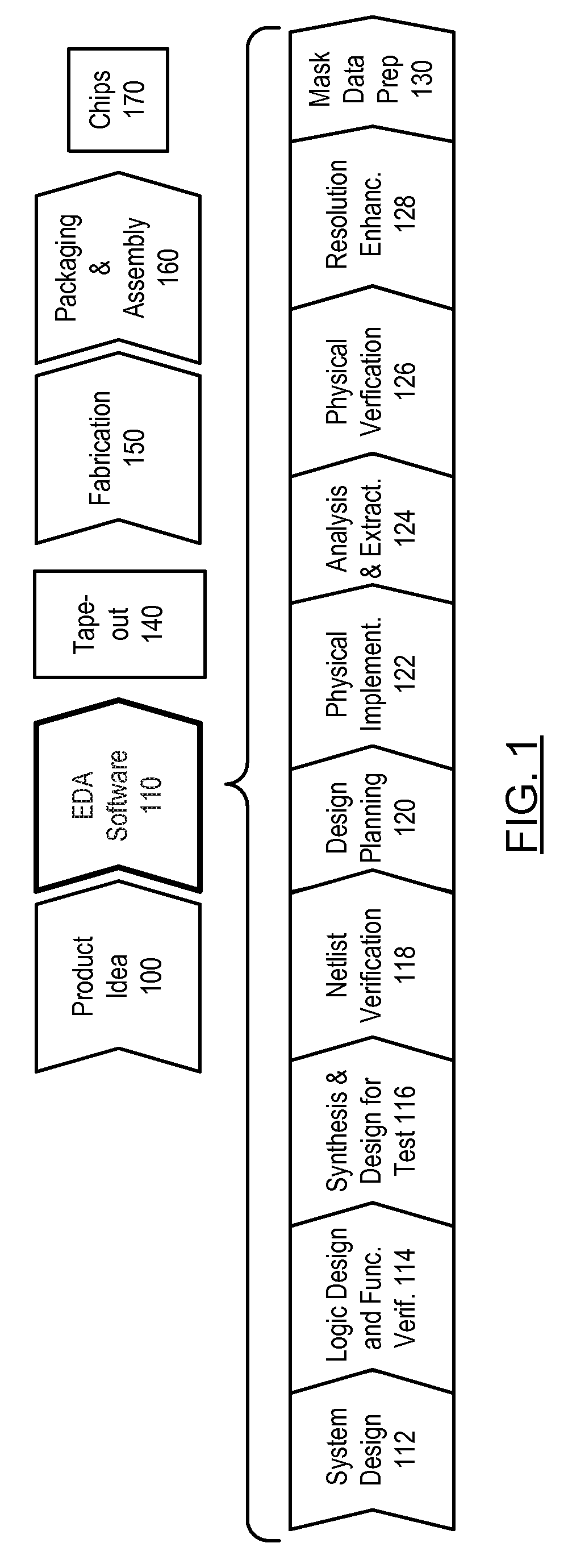
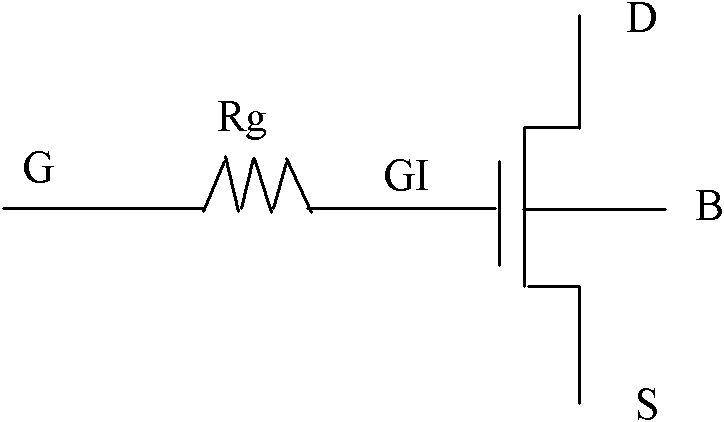Patents
Literature
88 results about "Transistor model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transistors are simple devices with complicated behavior. In order to ensure the reliable operation of circuits employing transistors, it is necessary to scientifically model the physical phenomena observed in their operation using transistor models. There exists a variety of different models that range in complexity and in purpose. Transistor models divide into two major groups: models for device design and models for circuit design.
Automated process monitoring and analysis system for semiconductor processing
InactiveUS6622059B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingError processingFeature parameter
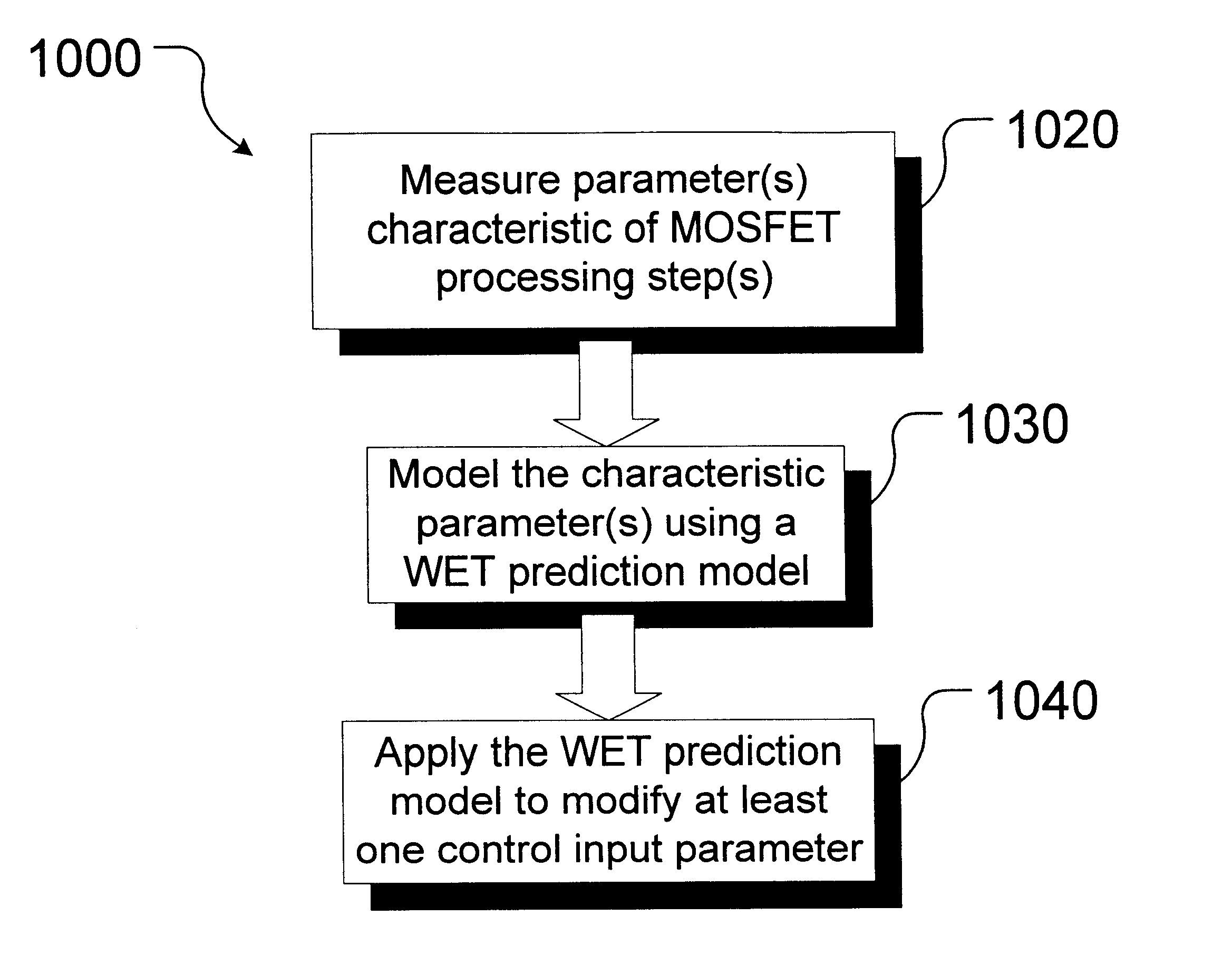
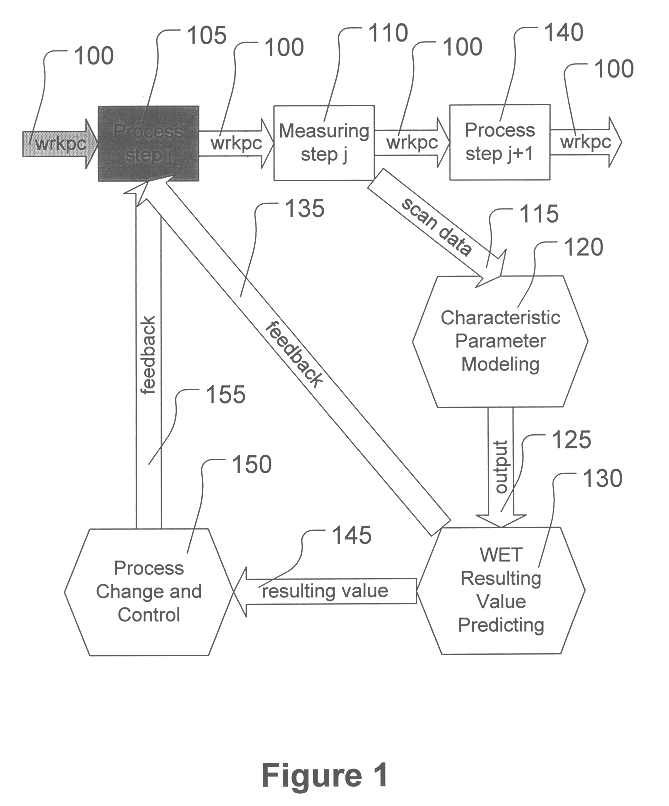
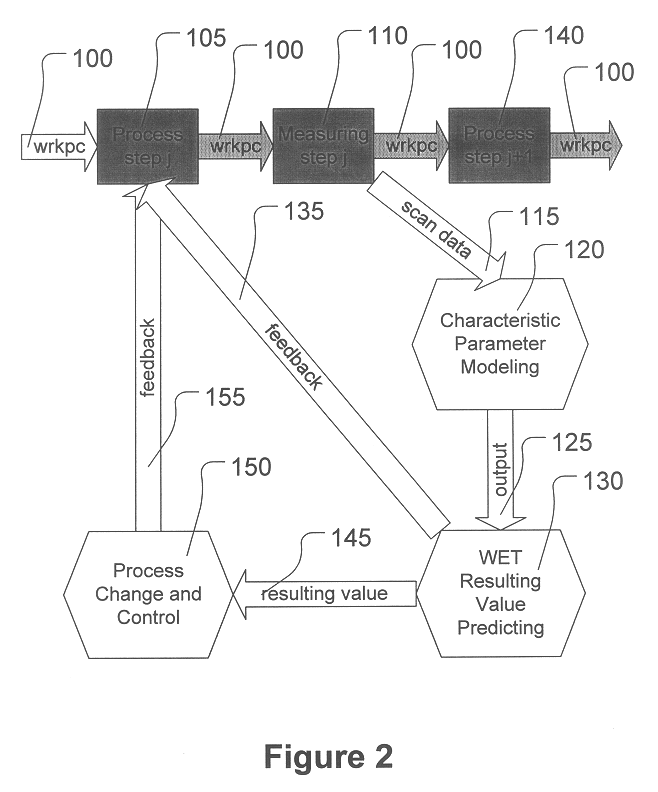
A method is provided for manufacturing, the method comprising processing a workpiece, measuring a parameter characteristic of the processing, and forming an output signal corresponding to the characteristic parameter measured by using the characteristic parameter measured as an input to a transistor model. The method also comprises predicting a wafer electrical test (WET) resulting value based on the output signal, detecting faulty processing based on the predicted WET resulting value, and correcting the faulty processing.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Circuit simulation method and circuit simulation apparatus
InactiveUS20060142987A1Improve accuracyHigh precision formingDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designEngineeringParameter dependent
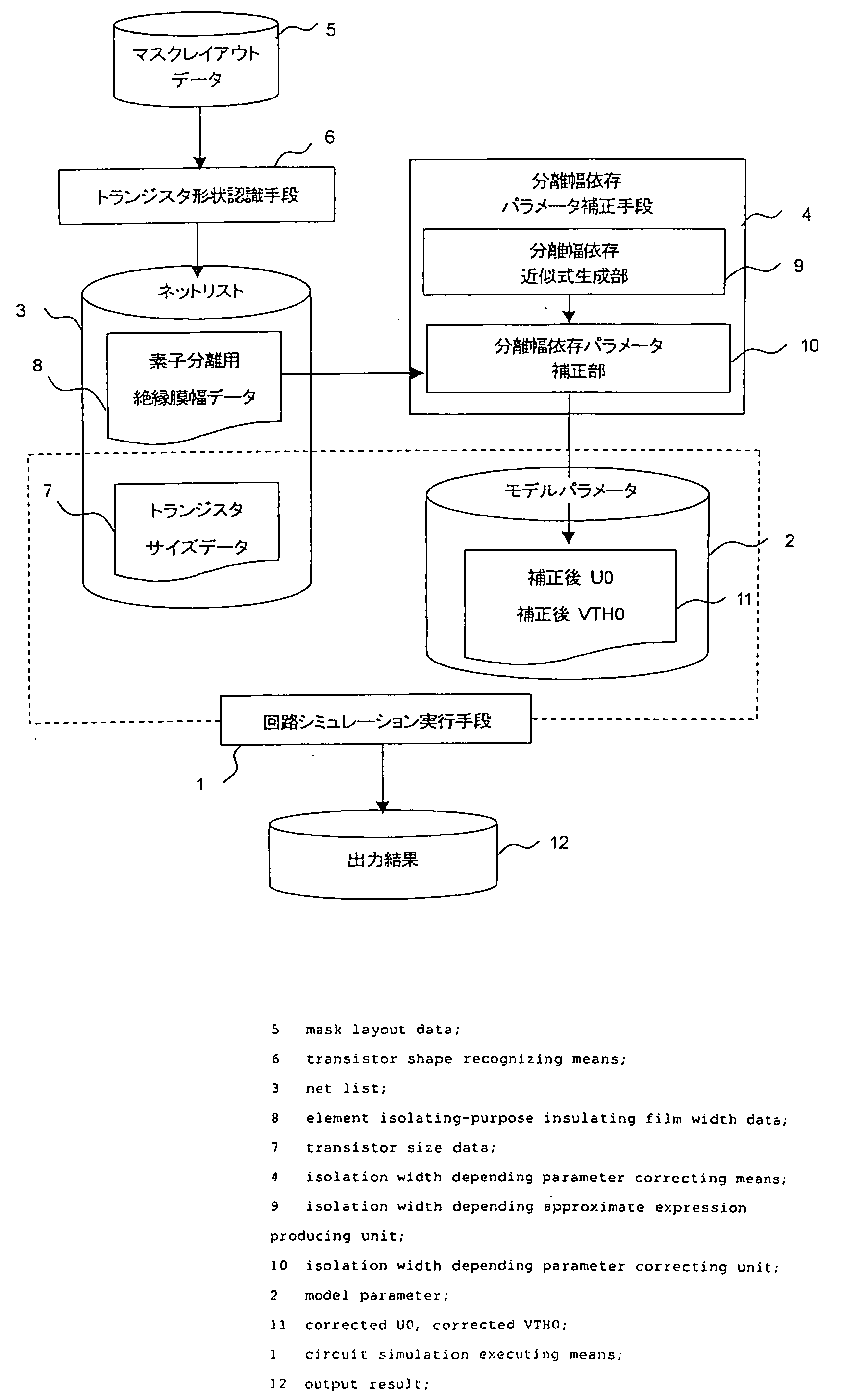
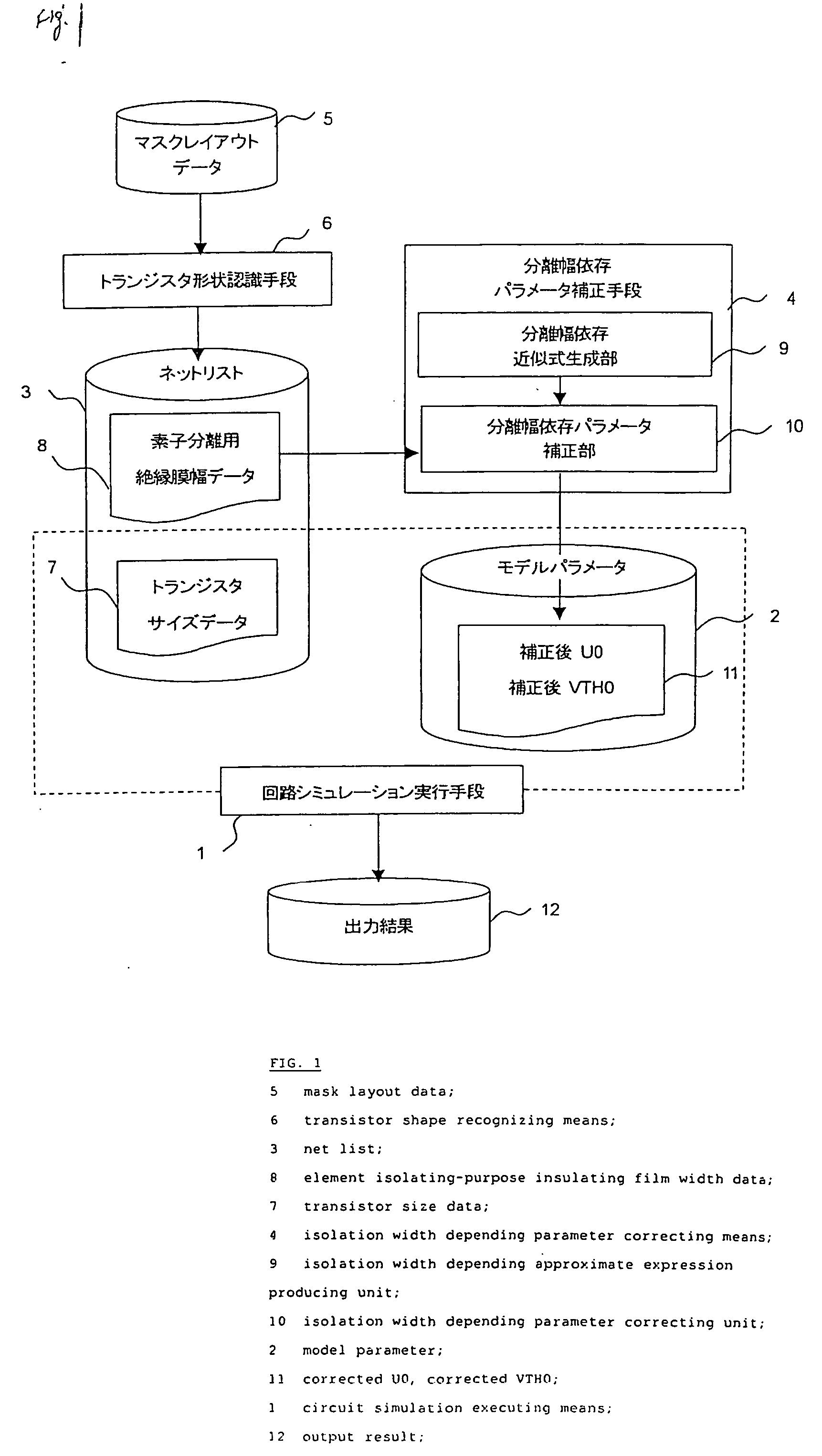
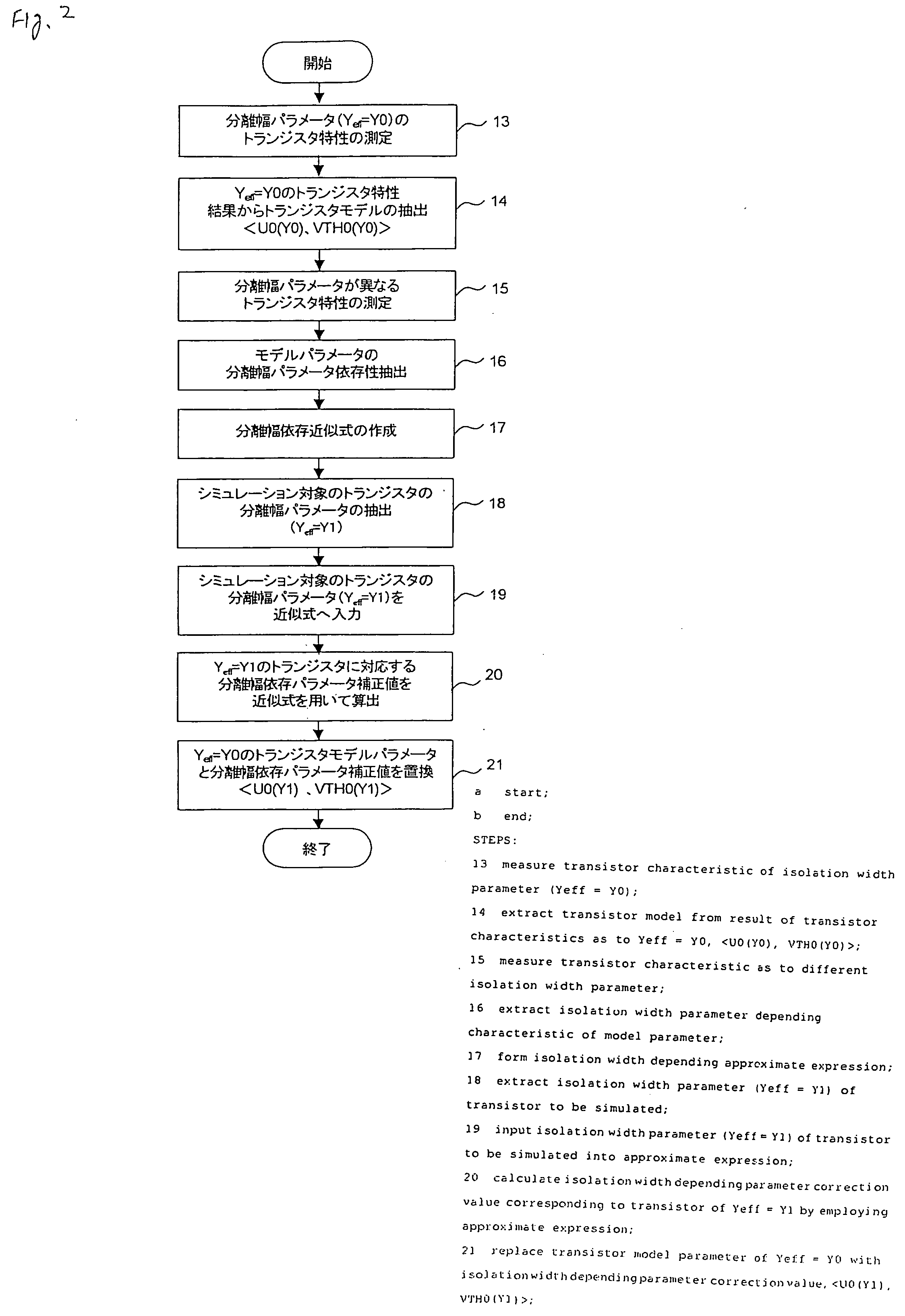
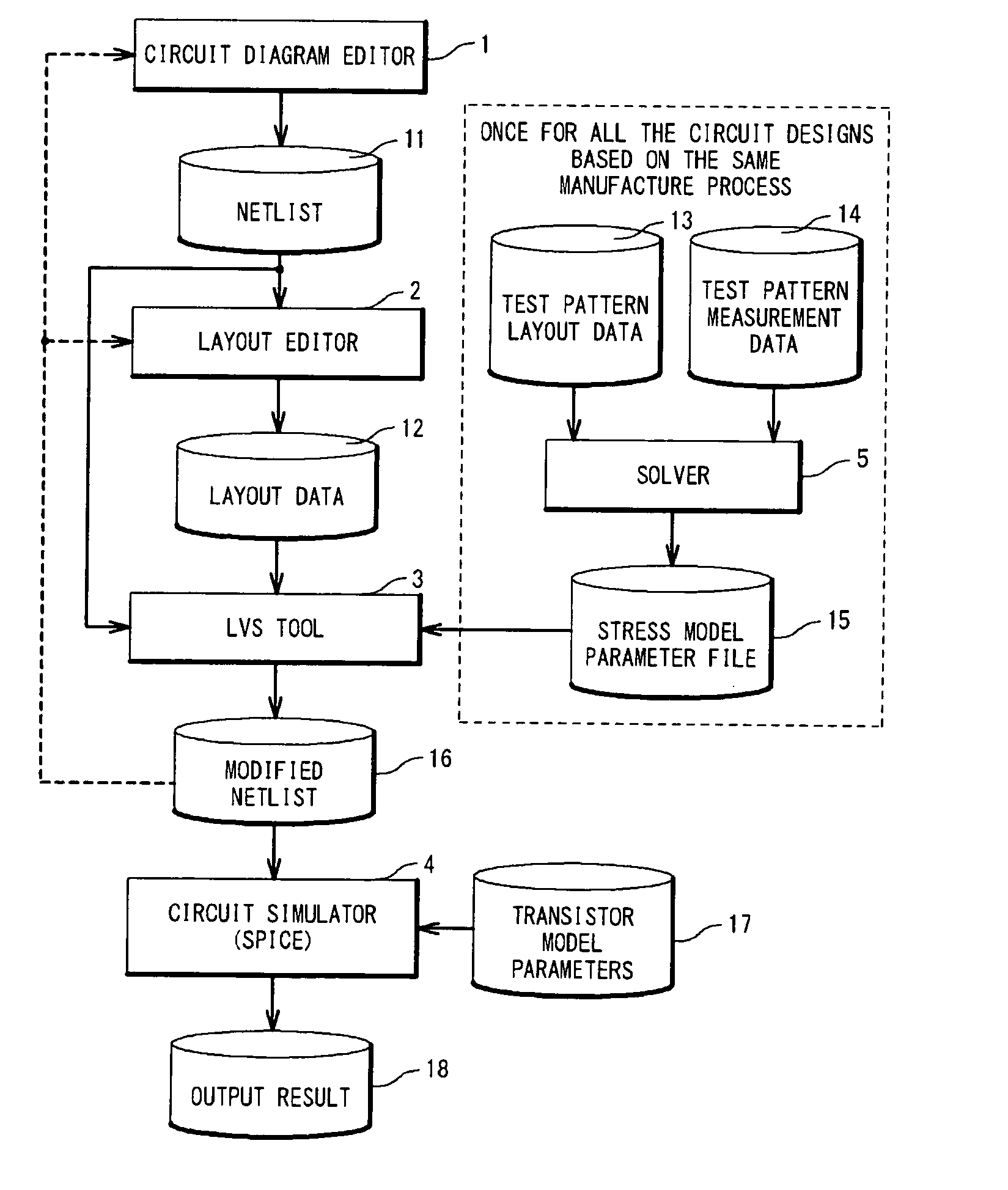
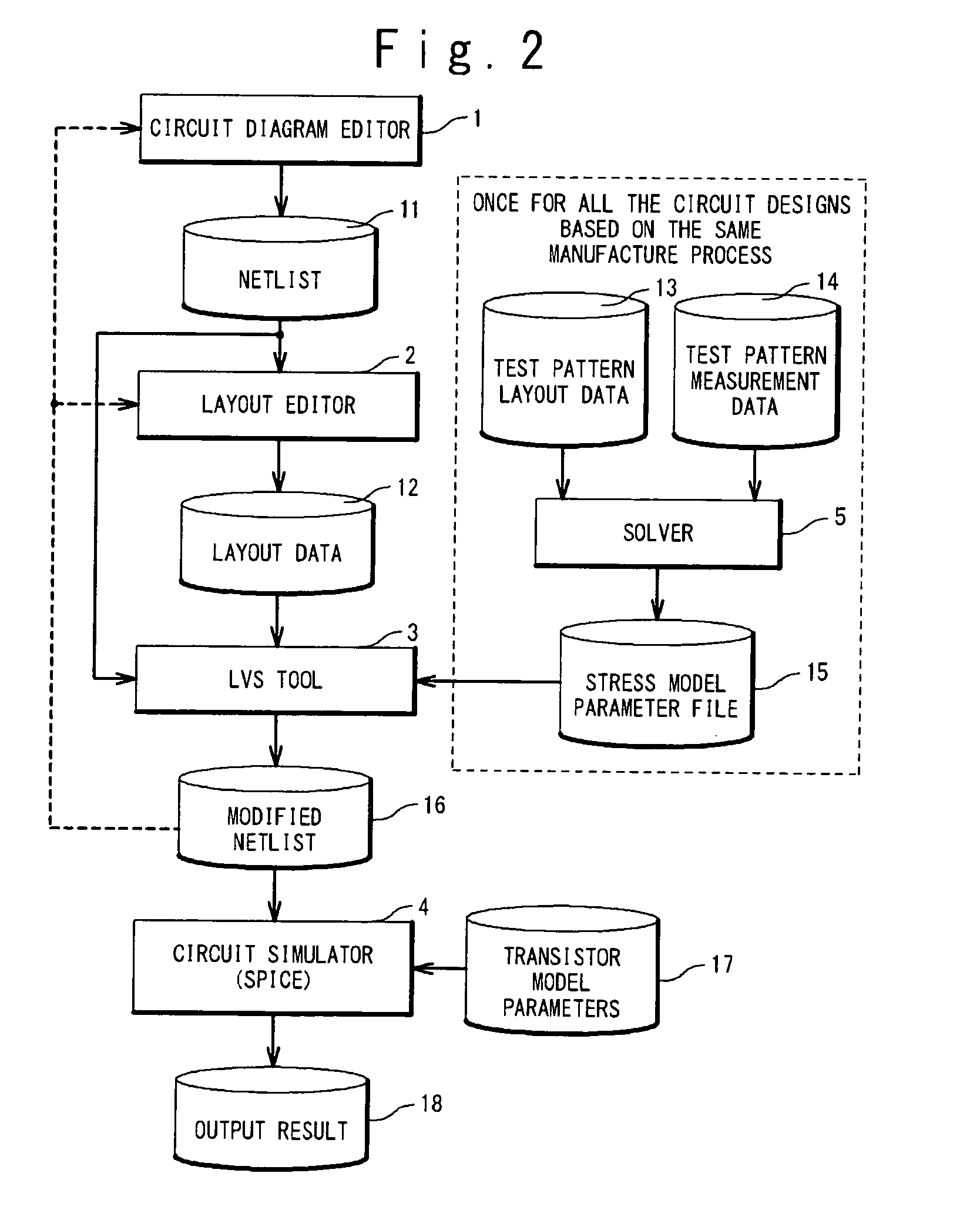
A circuit simulation apparatus and a modeling method are provided which are useful to design an integrated circuit in a very fine manner by forming a model of such a transistor that widths of element isolating-purpose insulating films are different from each other. In an isolation width depending parameter correcting means 4 of the present invention, an approximate expression of a parameter having an element isolating-purpose insulating film width depending characteristic is formed, and a value of a corrected parameter obtained by employing the formed approximate expression is replaced by a value of an original parameter, so that a transistor model of such a transistor is formed in which element isolating-purpose insulating film widths are different from each other. As a consequence, circuit simulation can be carried out in high precision by considering a change in transistor characteristics caused by a stress, which are approximated to actually measured data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
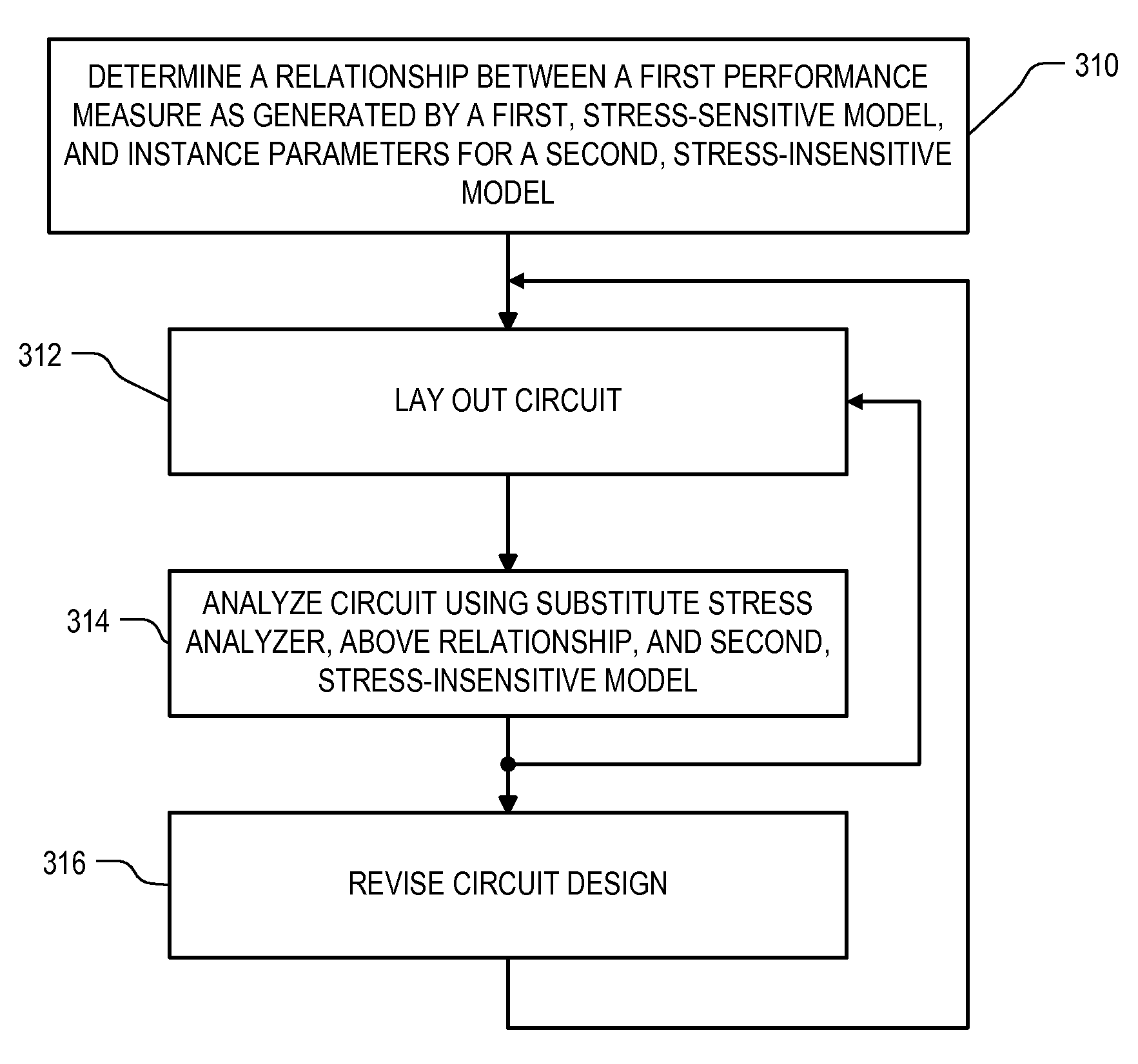
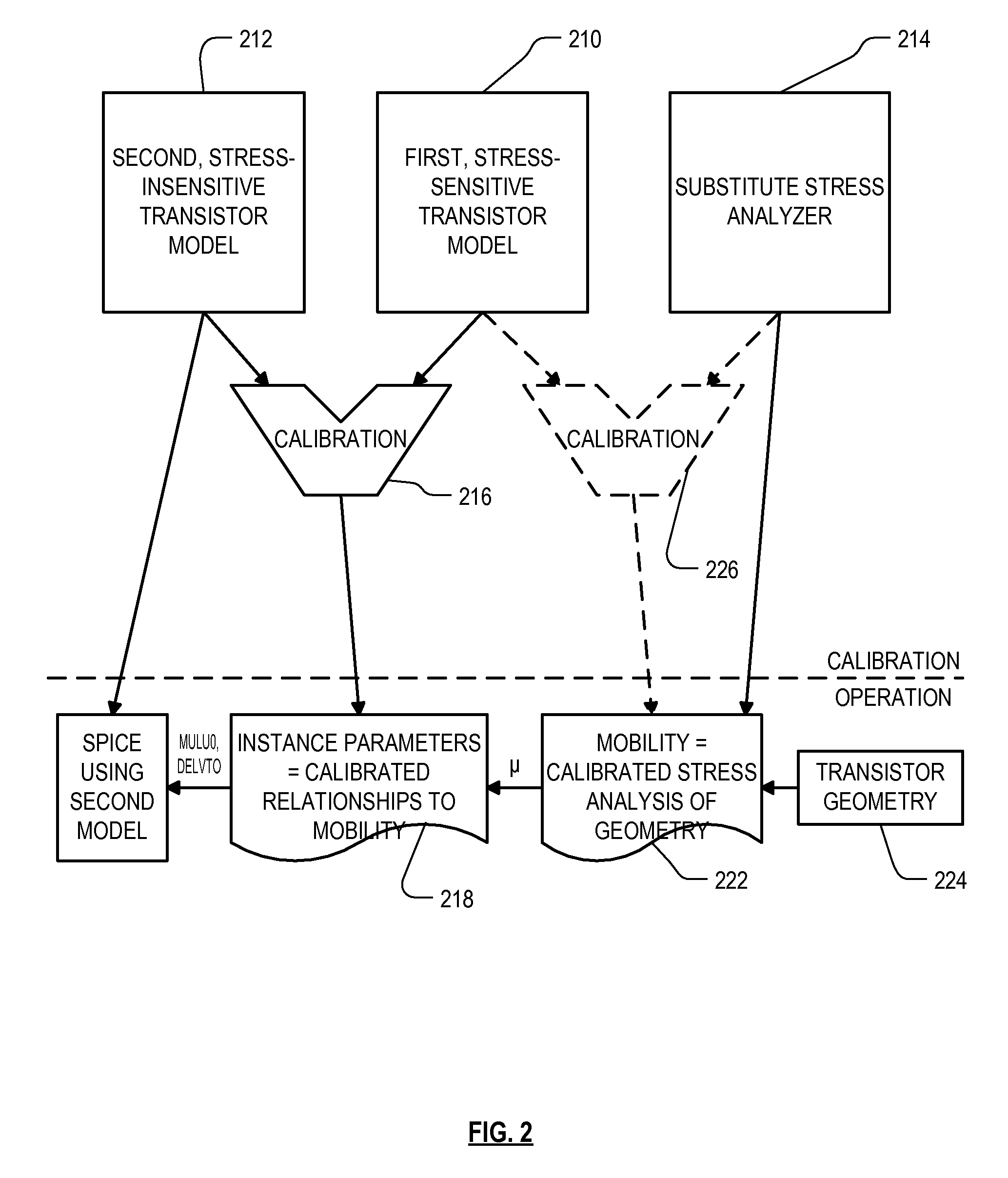
Method of correlating silicon stress to device instance parameters for circuit simulation
ActiveUS7542891B2Reduce the amount requiredRelieve pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty computer hardwareEngineeringSilicon
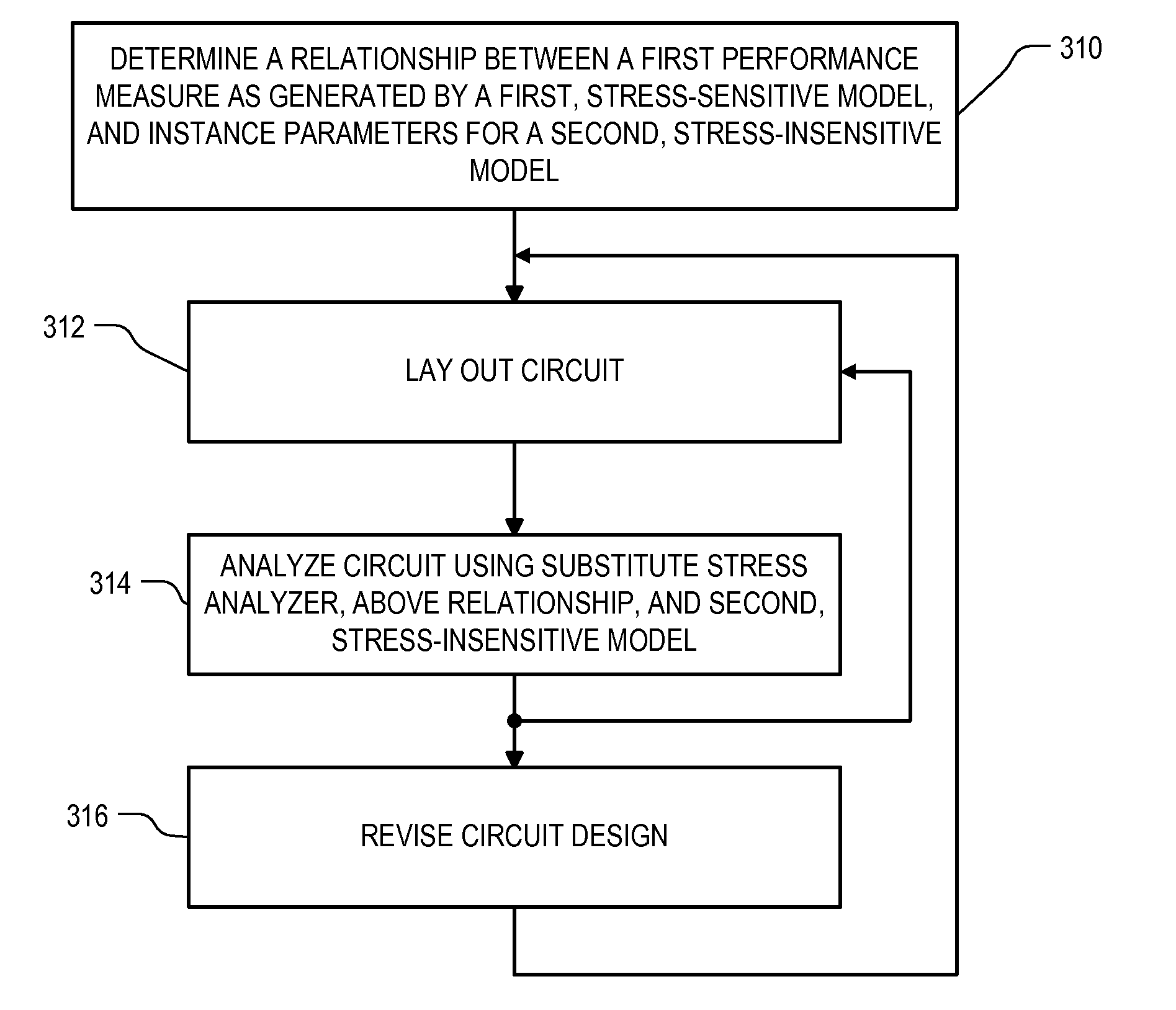
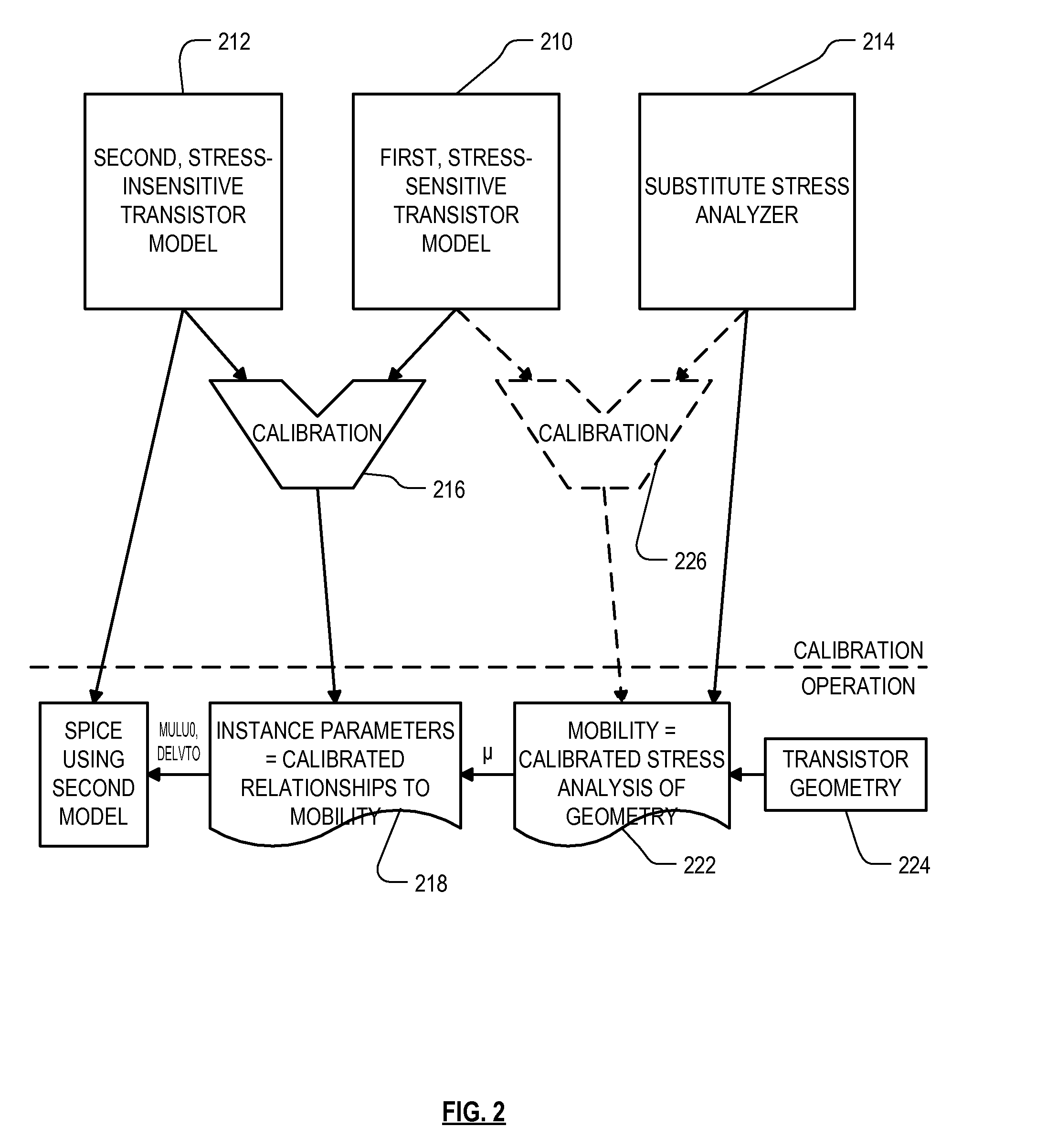
Roughly described, standard SPICE models can be modified by substituting a different stress analyzer to better model the stress adjusted characteristics of a transistor. A first, standard, stress-sensitive, transistor model is used to develop a mathematical relationship between the first transistor performance measure and one or more instance parameters that are available as inputs to a second, stress-insensitive, transistor model. The second transistor model may for example be the same as the first model, with its stress sensitivity disabled. Thereafter, a substitute stress analyzer can be used to determine a stress-adjusted value for the first performance measure, and the mathematical relationship can be used to convert that value into specific values for the one or more instance parameters. These values are then provided to the second transistor model for use in simulating the characteristics of the particular transistor during circuit simulation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
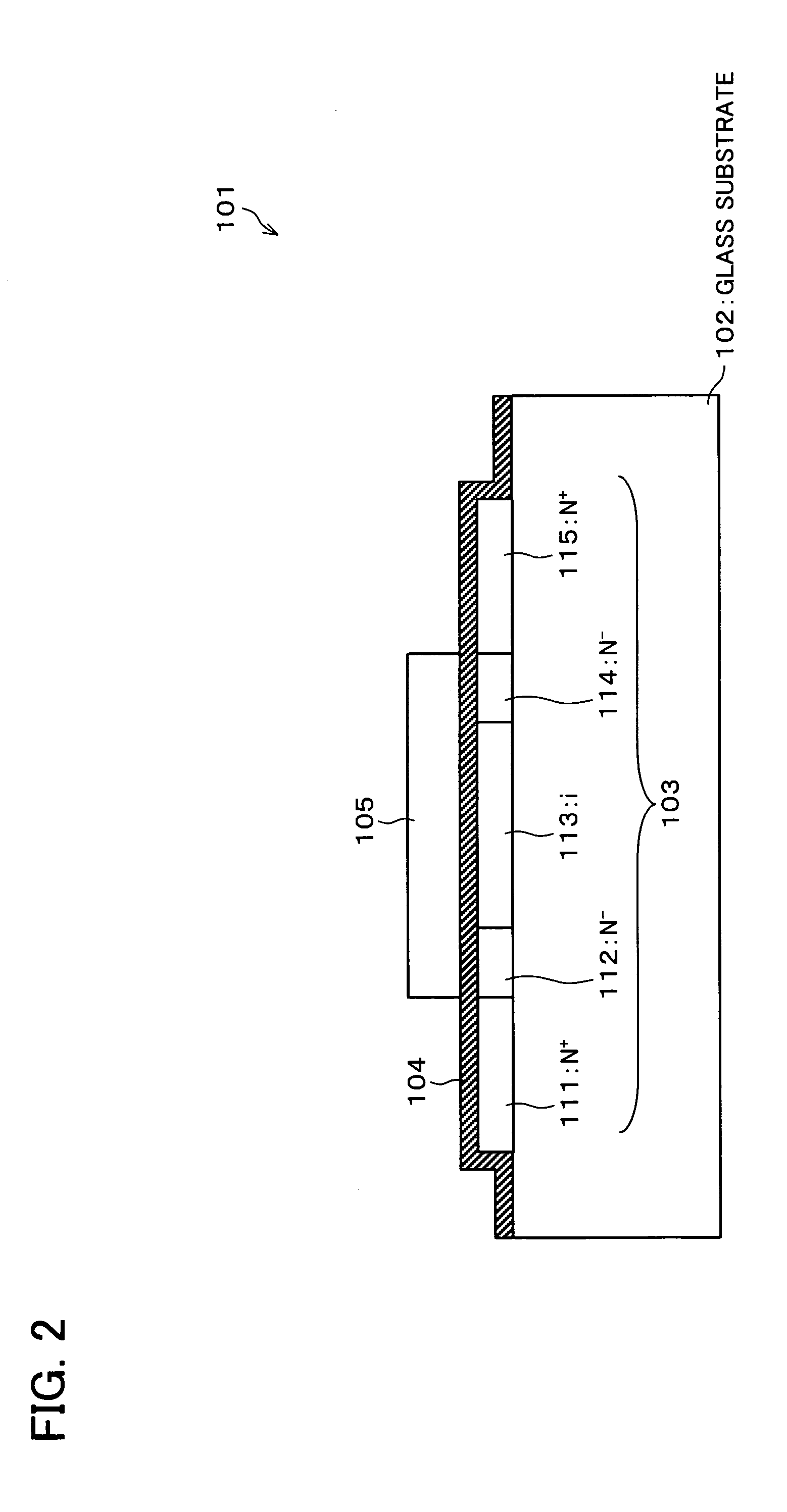
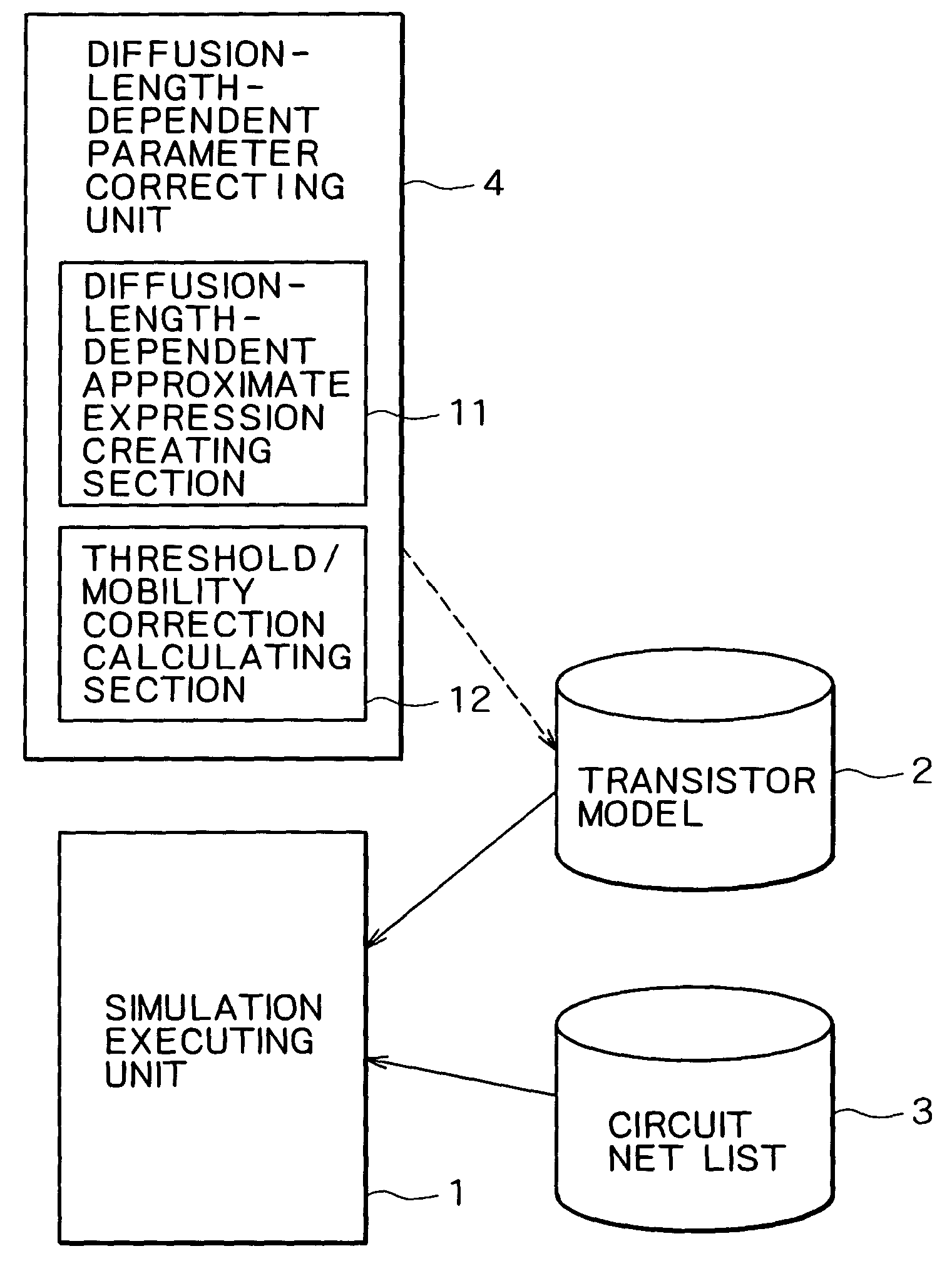
Circuit simulation apparatus incorporating diffusion length dependence of transistors and method for creating transistor model
InactiveUS20040059559A1Easy to createShort processTransistorDetecting faulty computer hardwareLength dependenceDrain current
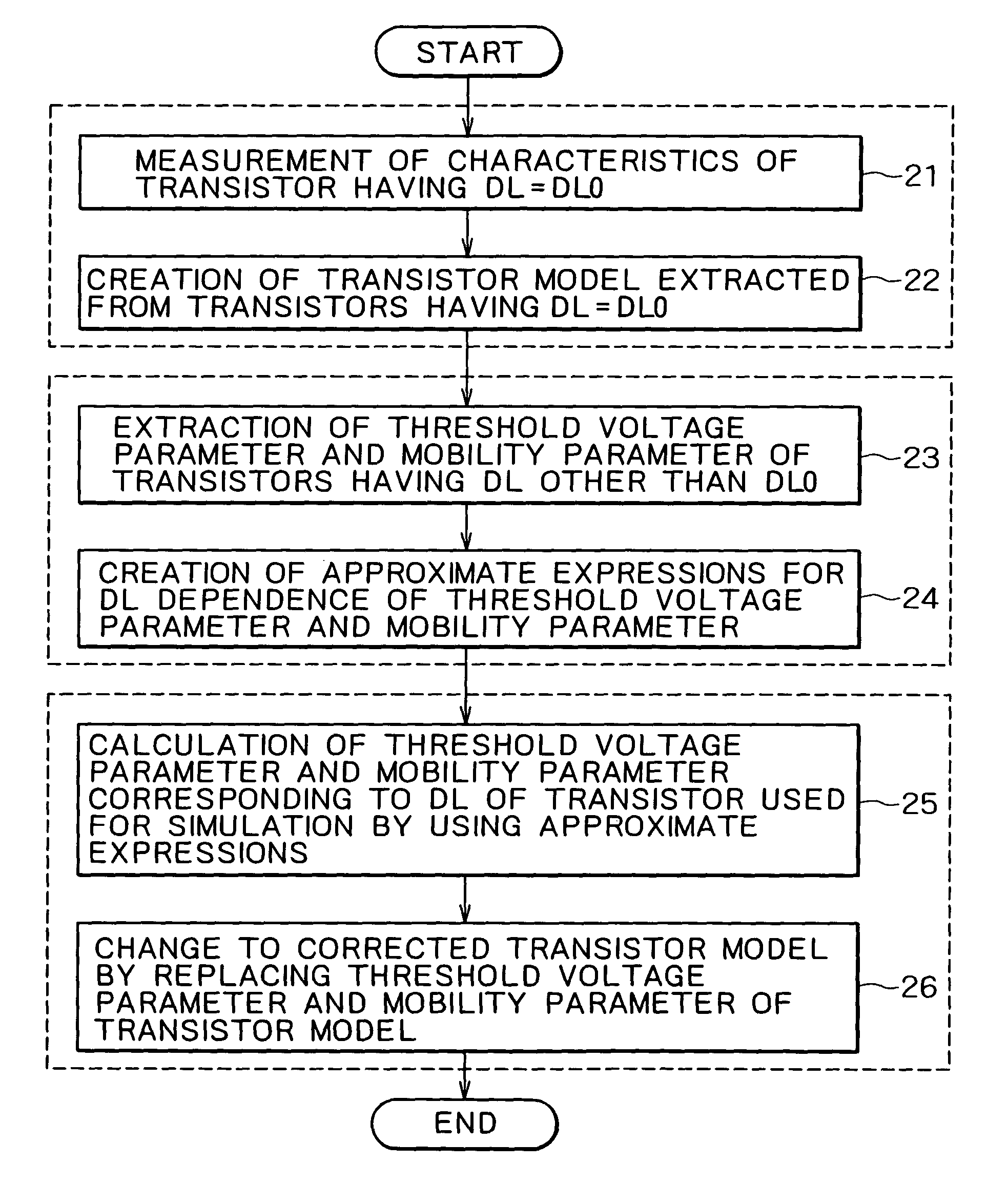
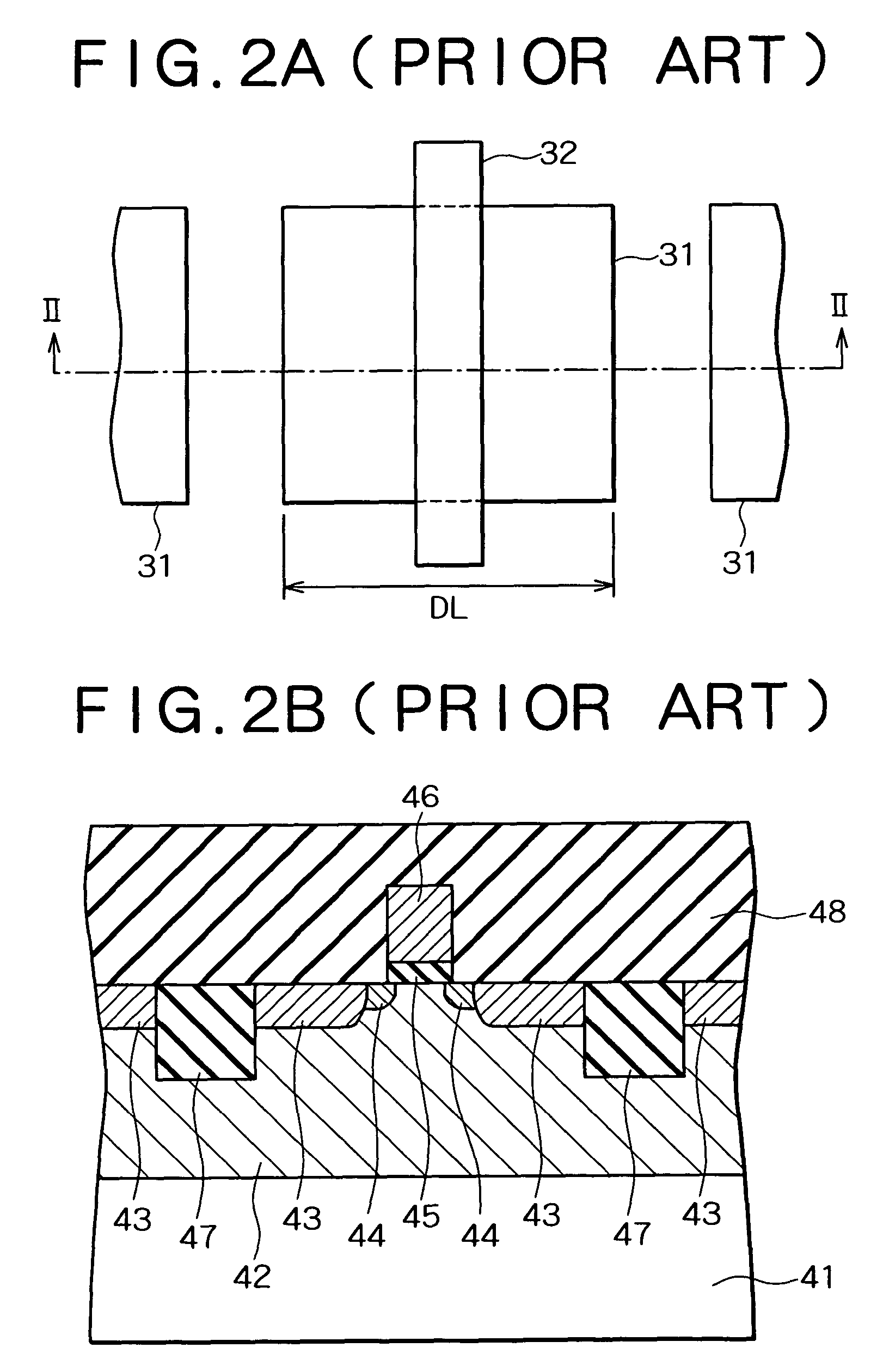
From the data of diffusion-length-dependent parameters extracted from the parameters of the transistor model of MOS transistors and from the parameters of transistors having various diffusion lengths, a diffusion-length-dependent parameter correcting unit creates approximate expressions of the diffusion length dependence of these parameters, and calculates parameter correction values to be used instead of original parameter values by using the created approximate expressions. Hence, the correction values can be used easily instead of the original parameter values, whereby a transistor model of MOS transistors having a different diffusion length DL can be created easily. Circuit simulation in consideration of the diffusion length dependence of the drain currents of MOS transistors can thus be carried out, whereby highly accurate simulation can be attained.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
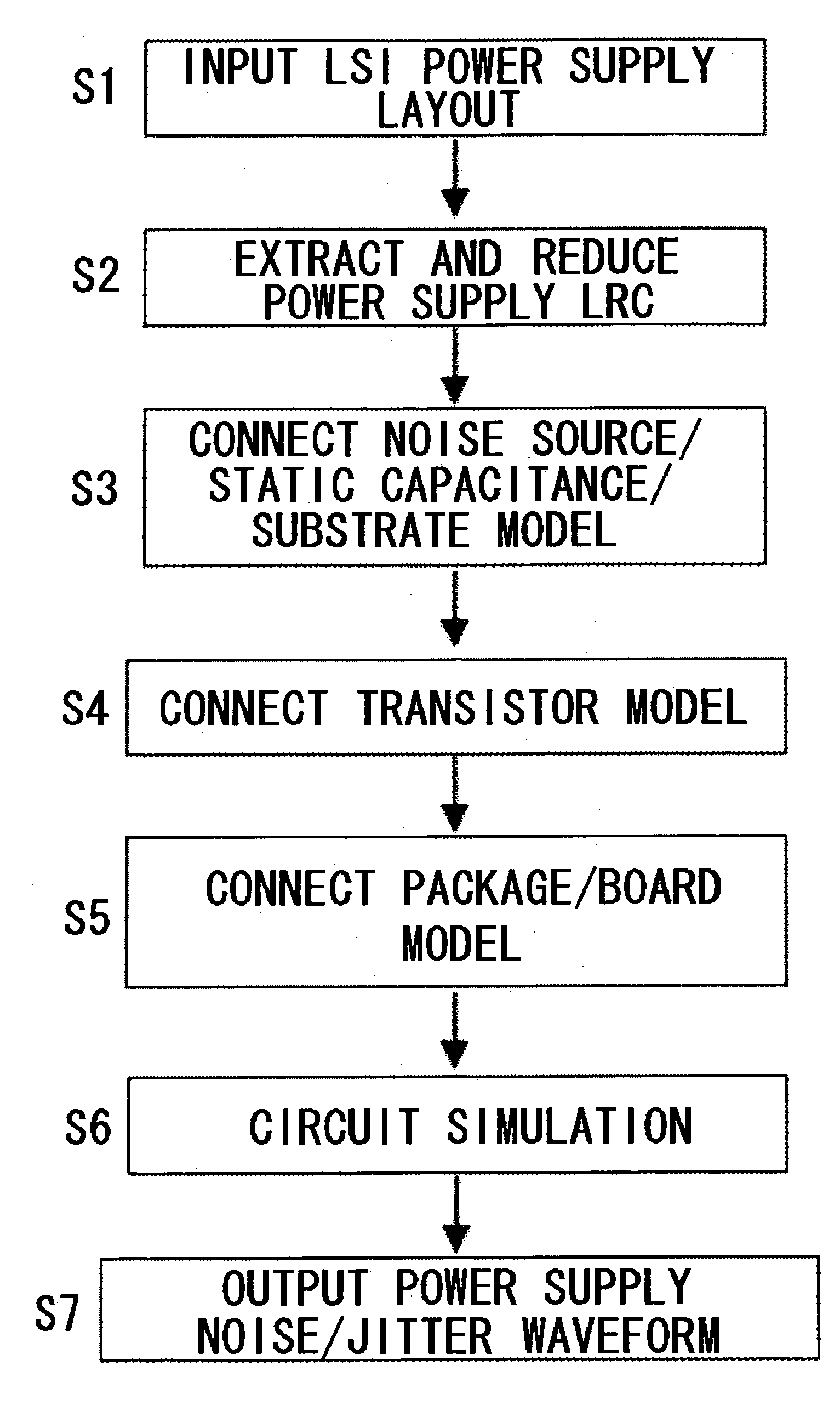
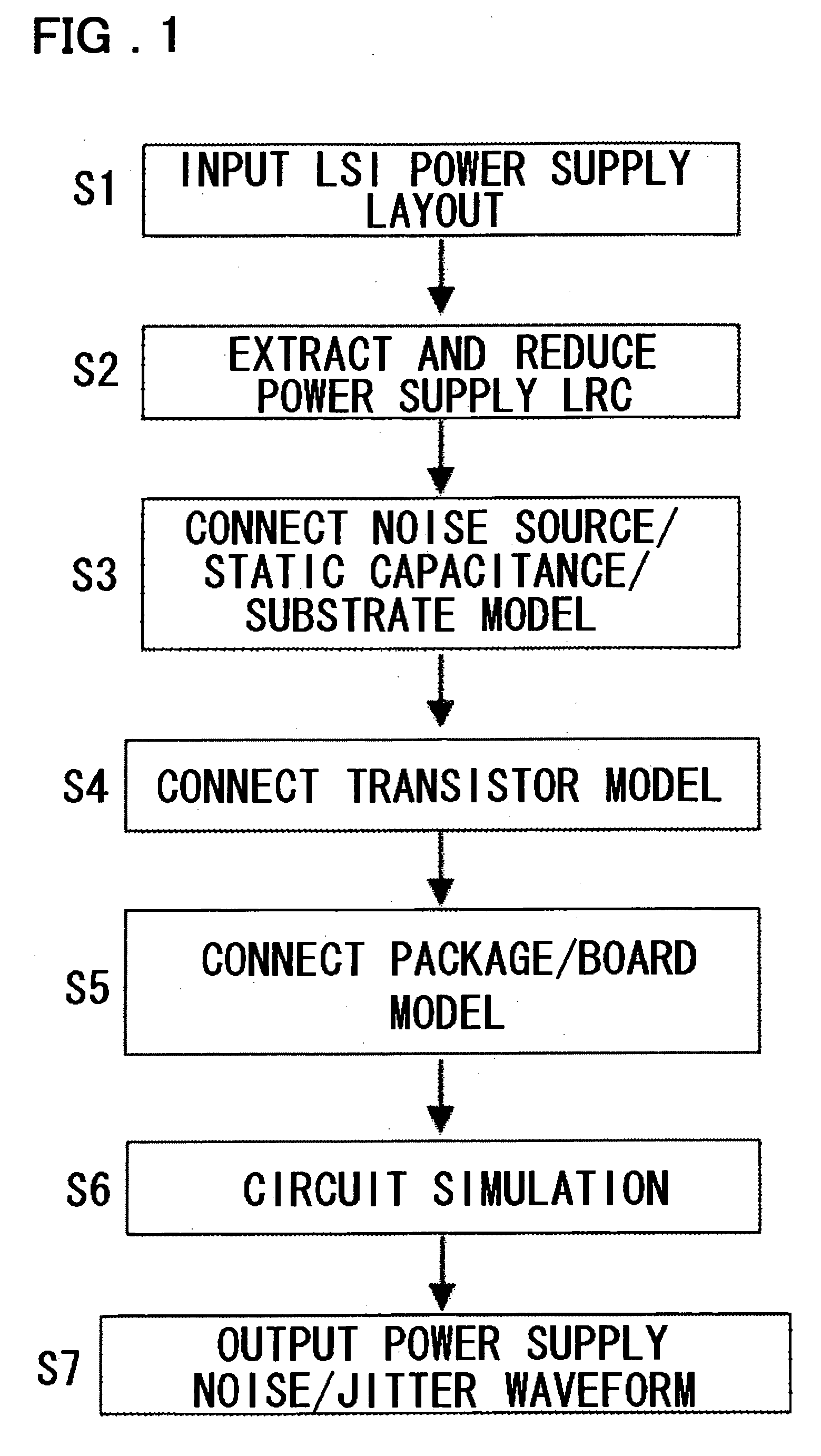
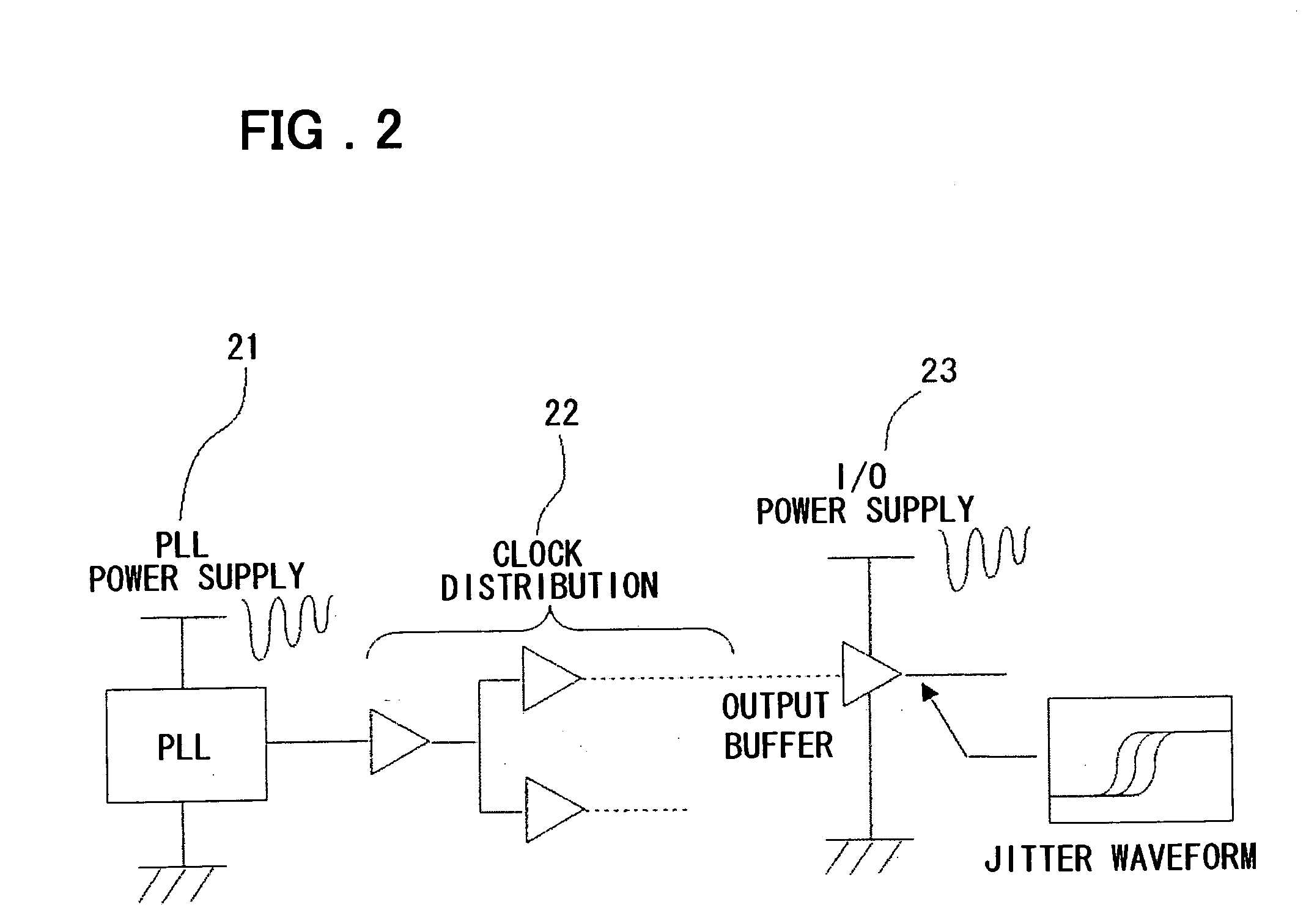
Method and apparatus for jitter analysis and program therefor
InactiveUS20060036980A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCapacitanceAnalysis data
A method, an apparatus and a program for comprehensively analyzing the power supply noise and consequent jitter for external output signals of the LSI in real time. From LSI layout designing data 601, the resistance, capacitance and inductance of the power supply interconnection are extracted to formulate a power supply LRC model 606. An analysis model formulating unit 812 connects a transistor model 610, a noise source model 607, a silicon substrate model 608 and a package / board (printed circuit board) model 611 to formulate a model for analysis of the power supply noise 813 and a model for jitter analysis 817. An analysis unit 814 acquires power supply noise waveform data 816 by first simulation and also acquires jitter analysis data 815 using power supply noise waveform data 816 by second simulation.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Method of correlating silicon stress to device instance parameters for circuit simulation
ActiveUS20090217217A1Reduce the amount requiredRelieve pressureDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputational physicsStatistical physics
Roughly described, standard SPICE models can be modified by substituting a different stress analyzer to better model the stress adjusted characteristics of a transistor. A first, standard, stress-sensitive, transistor model is used to develop a mathematical relationship between the first transistor performance measure and one or more instance parameters that are available as inputs to a second, stress-insensitive, transistor model. The second transistor model may for example be the same as the first model, with its stress sensitivity disabled. Thereafter, a substitute stress analyzer can be used to determine a stress-adjusted value for the first performance measure, and the mathematical relationship can be used to convert that value into specific values for the one or more instance parameters. These values are then provided to the second transistor model for use in simulating the characteristics of the particular transistor during circuit simulation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
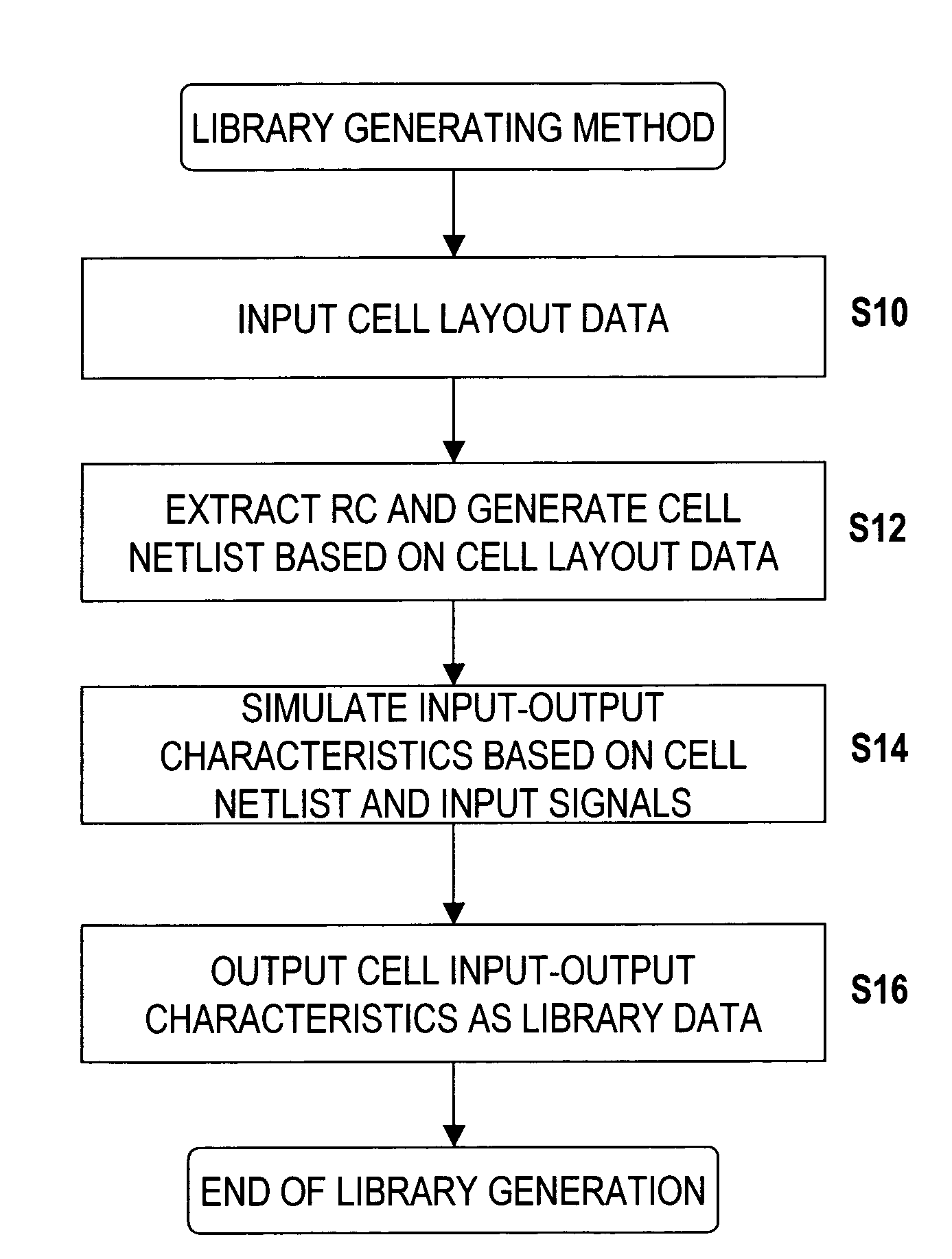
Method of generating cell library data for large scale integrated circuits
InactiveUS7320116B2Accurate representationAccurate extractionDetecting faulty computer hardwareRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceNetlist
A method of generating library data for a cell constructed of interconnected MOS transistors, includes a resistance extraction step which extracts source and drain resistances according to source and drain region surface areas by using a resistance calculating formula or referring to a resistance extraction reference file which, when the source and drain regions have a first surface area region, treats the source and drain resistances as resistance values depending on the surface areas, and when the source and drain regions have a second surface area region larger than the first surface area region, treats the source and drain resistances as fixed resistance values; and a simulation step which generates an input-output characteristic for the cell from a netlist containing a MOS transistor model that includes the extracted source resistances and drain resistances and connection information for the model, and from input signals.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
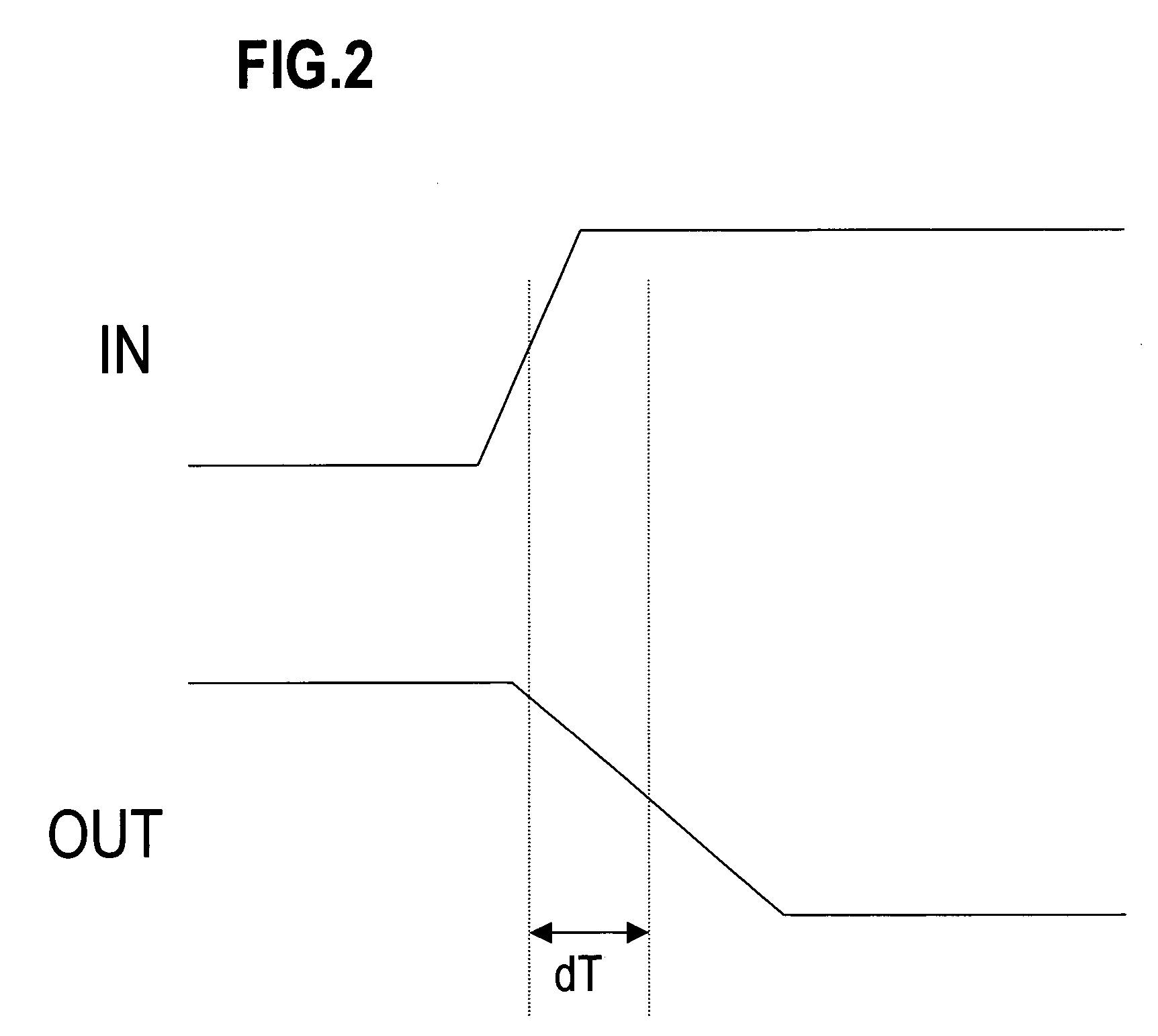
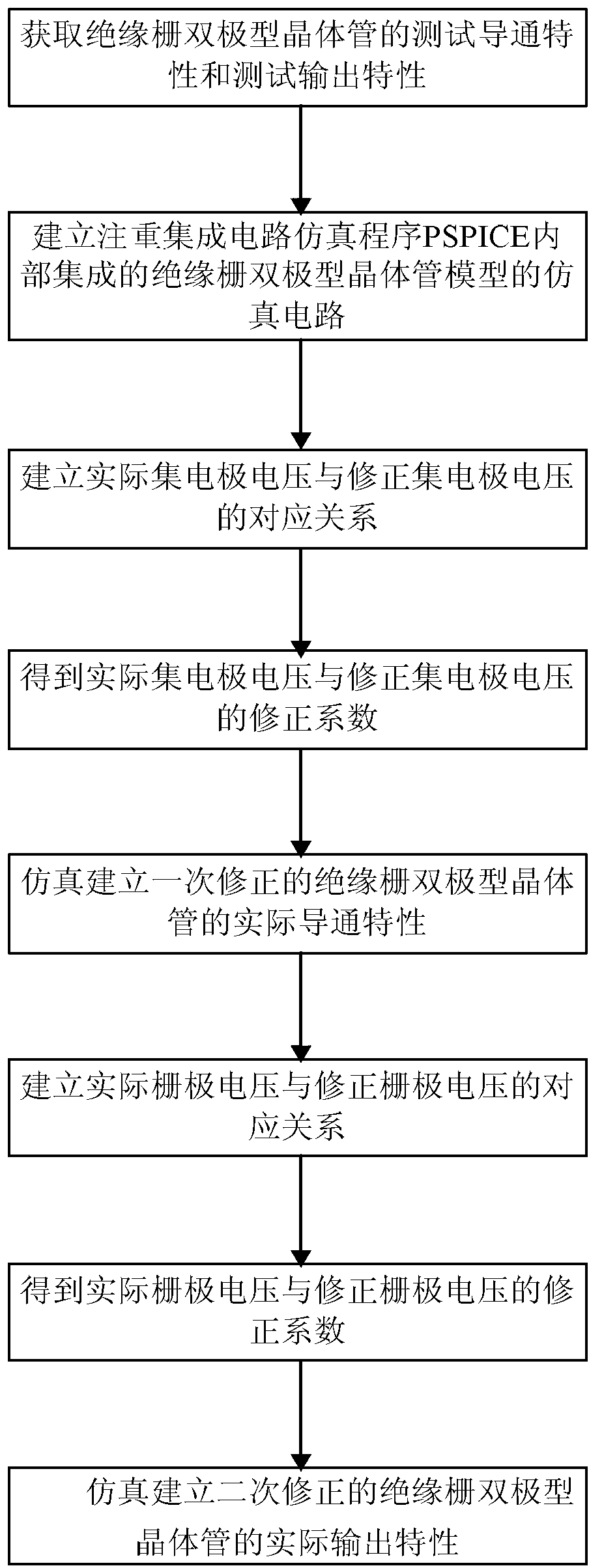
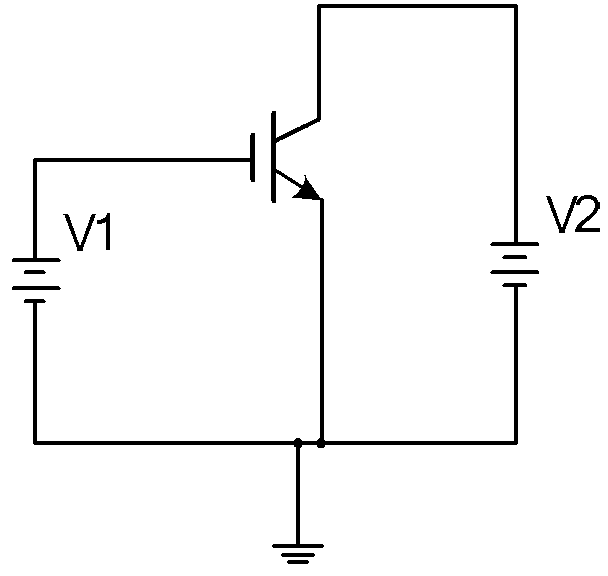
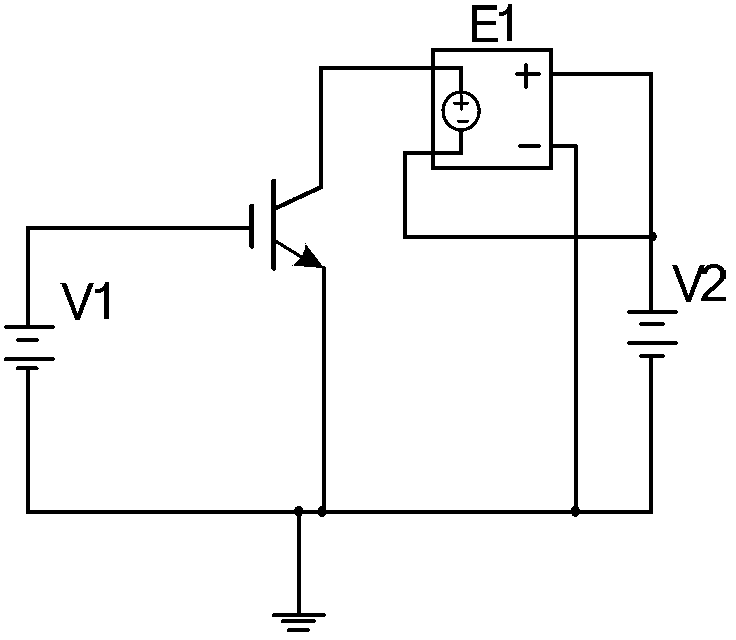
Simulated measurement method of current characteristics of insulated gate bipolar transistor
InactiveCN103105571ADifferent test conduction characteristicsCurrent characteristic fittingIndividual semiconductor device testingHemt circuitsComputational physics
The invention discloses a simulated measurement method of current characteristics of an insulated gate bipolar transistor. The simulated measurement method of the current characteristics of the insulated gate bipolar transistor includes the following steps of: step 10, obtaining test conduction characteristic and output characteristic of the insulated gate bipolar transistor, step 20, establishing a simulated circuit of an internal integrated model of an simulated program, step 30, establishing a corresponding relationship between an actual collector voltage and a corrected collector voltage, step 40, obtaining correction factors of the actual collector voltage and the corrected collector voltage, step 50, stimulatingly establishing a first-time corrected actual conduction characteristic, step 60, establishing a corresponding relationship between an actual grid voltage and a corrected grid voltage, step 70, obtaining correction factors of the actual grid voltage and the corrected grid voltage, and step 80, stimulatingly establishing a second-time corrected actual output characteristic. The simulated measurement method of the current characteristics of the insulated gate bipolar transistor solves the problem that current characteristics of insulated gate bipolar transistor integrated inside of a simulation program with intergraded circuit emphasis (PSPICE) are low in degree of accuracy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for modeling SPICE model of bipolar junction transistor
ActiveCN101201850AHigh simulationPromote resultsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringModel parameters
The invention discloses a modeling method of a SPICE model of a bipolar junction transistor, which comprises the steps that: firstly, the model parameter of a BJT transistor with emitter dimensioning is extracted and determined as initial model parameter, then based on the extracted model parameter, the parameter which has greater dependency on the emitter geometric dimensioning is adjusted according to the proportional relation of the emitter geometric dimensioning, and the adjusted new model parameter value is directly taken as the initial value of a transistor model to be molded with corresponding size, while the parameter which is unrelated with the emitter geometric dimensioning is directly taken as the initial value of the transistor model to be molded. According to the method provided by the invention, the SPICE model of the BJT transistor which has better fitness of the result of emulation and test and various sizes can be obtained in a short time.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Method and apparatus for circuit simulation in view of stress exerted on MOS transistor
InactiveUS20090089037A1Simulation is accurateComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsComputer science
A circuit simulation method includes: generating graphical data indicating dimensions of a subject MOS transistor; calculating a parameter correction amount based on said graphical data; correcting a given transistor model parameter in response to said parameter correction amount; and performing circuit simulation of a circuit that includes said subject MOS transistor by using said corrected transistor model parameter. The parameter correction amount is calculated based on said graphical data by using arithmetic equations. The arithmetic equations include at least one stress model equation expressing a stress exerted on a channel region of a model MOS transistor. The stress model equation is suitably defined to simulate the stress exerted on the channel region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
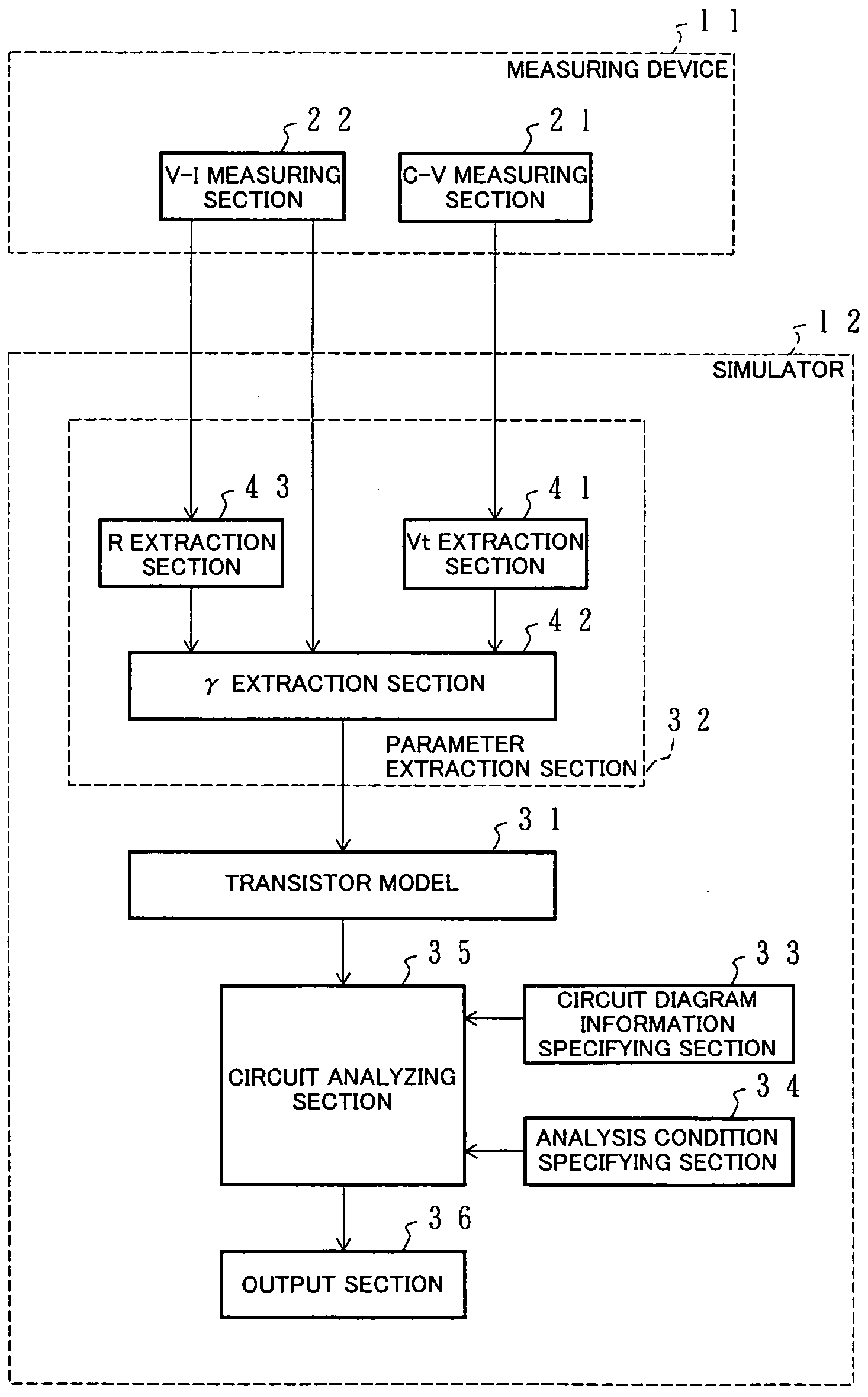
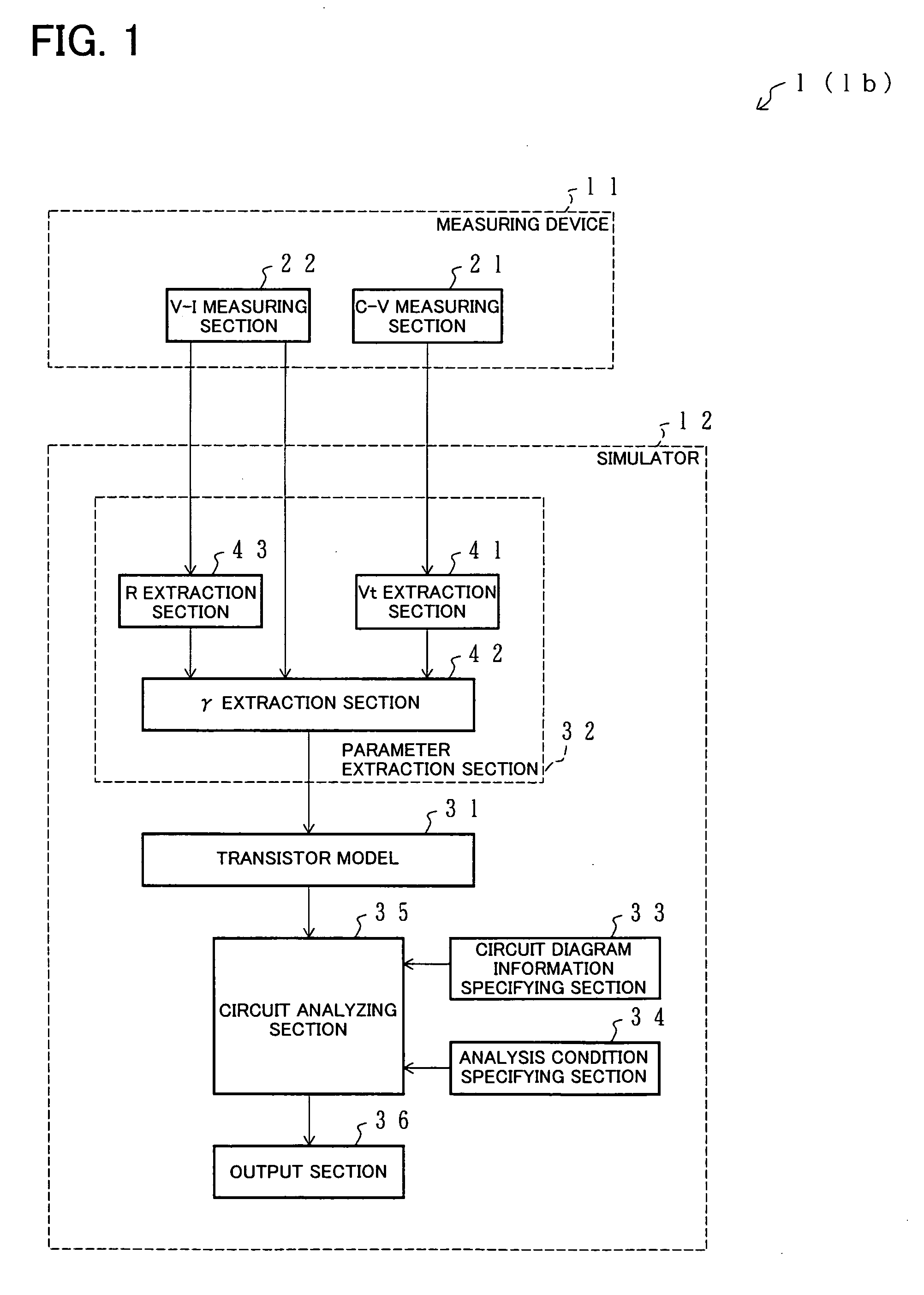
Simulator and parameter extraction device for transistor, simulator and parameter extraction method for transistor, and associated computer program and storage medium
InactiveUS20050015235A1Improve fitImprove accuracyTransistorAnalogue computers for electric apparatusCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A transistor model for a simulator simulates a resistance between a source region and a drain region with a model equation which has terms representing resistance values corresponding respectively to areas of mutually different impurity concentrations below a gate section in simulating characteristics of a transistor. At least two of the terms each having a threshold parameter indicating a voltage at which a semiconductor element composed of the associated region and regions adjacent to that region changes from an ON state to an OFF state. The threshold parameters of the terms being specified independently from each other. Thus, the characteristics of a transistor having a set of areas of mutually different impurity concentrations below a gate section, inclusive of subthreshold regions which are difficult to evaluate through actual measurement, can be simulated to high accuracy while preserving a good fit with a capacitance model.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Circuit simulation apparatus incorporating diffusion length dependence of transistors and method for creating transistor model
InactiveUS7222060B2Short processEasy to createTransistorDetecting faulty computer hardwareLength dependenceDrain current
From the data of diffusion-length-dependent parameters extracted from the parameters of the transistor model of MOS transistors and from the parameters of transistors having various diffusion lengths, a diffusion-length-dependent parameter correcting unit creates approximate expressions of the diffusion length dependence of these parameters, and calculates parameter correction values to be used instead of original parameter values by using the created approximate expressions. Hence, the correction values can be used easily instead of the original parameter values, whereby a transistor model of MOS transistors having a different diffusion length DL can be created easily. Circuit simulation in consideration of the diffusion length dependence of the drain currents of MOS transistors can thus be carried out, whereby highly accurate simulation can be attained.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Time sequence determining method and device of integrated circuit chip
The invention provides a time sequence determining method and device of an integrated circuit chip. The time sequence determining method includes subjecting a top module and at least two submodules of an integrated circuit chip to be designed to synthesization, overall arrangement and clock network design generation; extracting a boundary time sequence model according to the clock network of the submodules and the top module; if the boundary time sequence model meets the first time sequence conditions, designing wiring of the submodules and the top module; extracting an electric parameter model according to the wired submodules and the top module; if the electric parameter model meets the second time sequence condition, splicing the submodules and the top module and extracting a transistor model; if the transistor model meets the third time sequence condition, determining the time sequence of the integrated circuit chip. By the time sequence determining method and device, different time sequence models are extracted for different stages of integrated circuit chip design, and balance between speed and accuracy of the time sequence analysis is realized.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
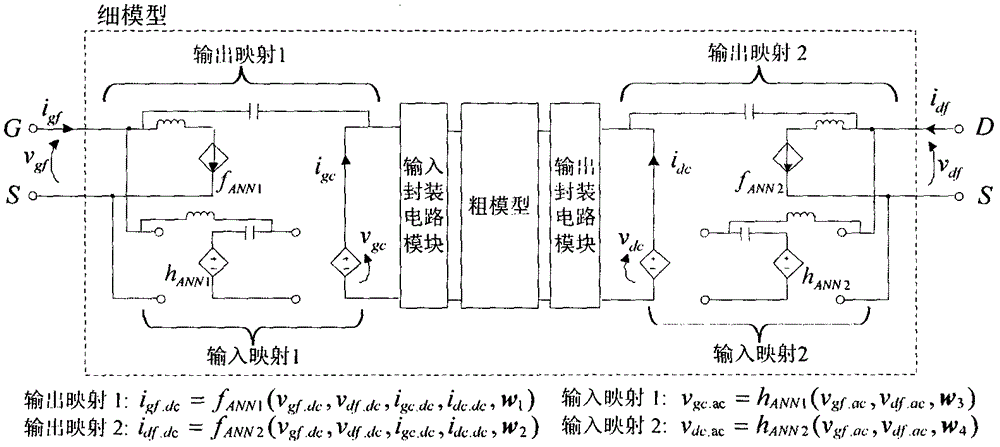
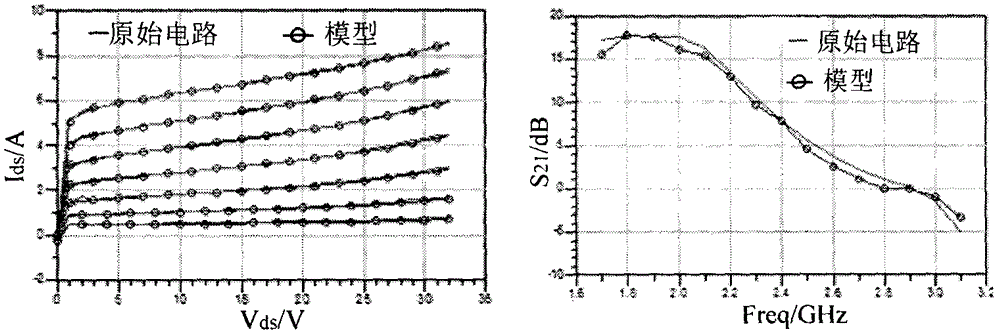
Neural network space mapping modeling method for power transistor
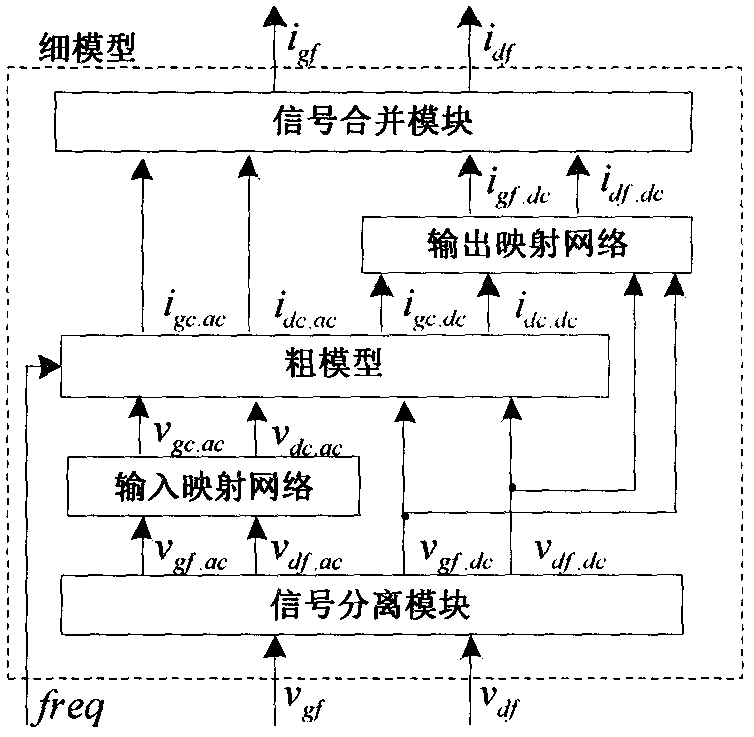
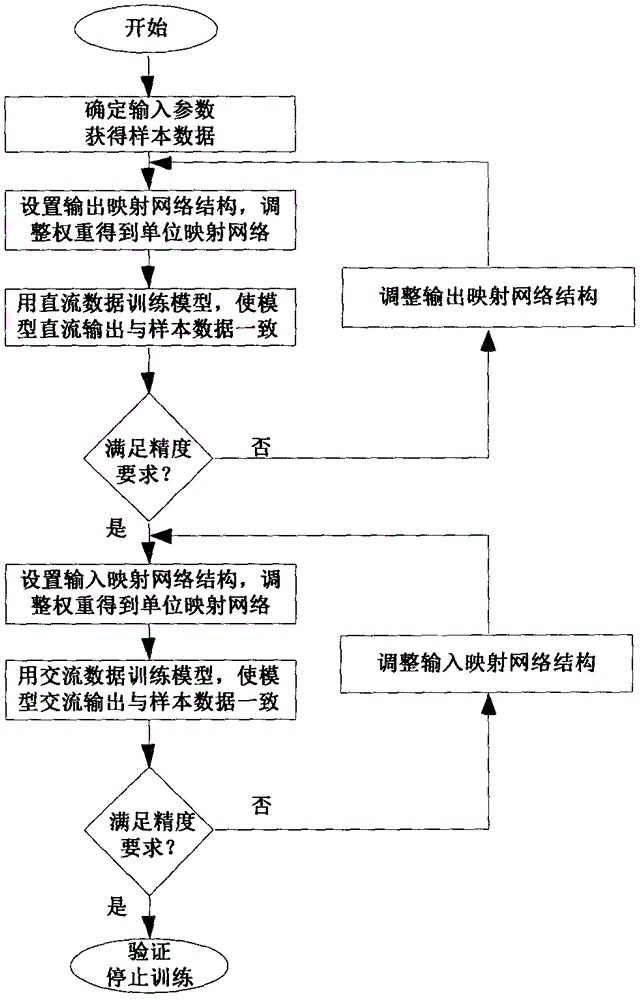
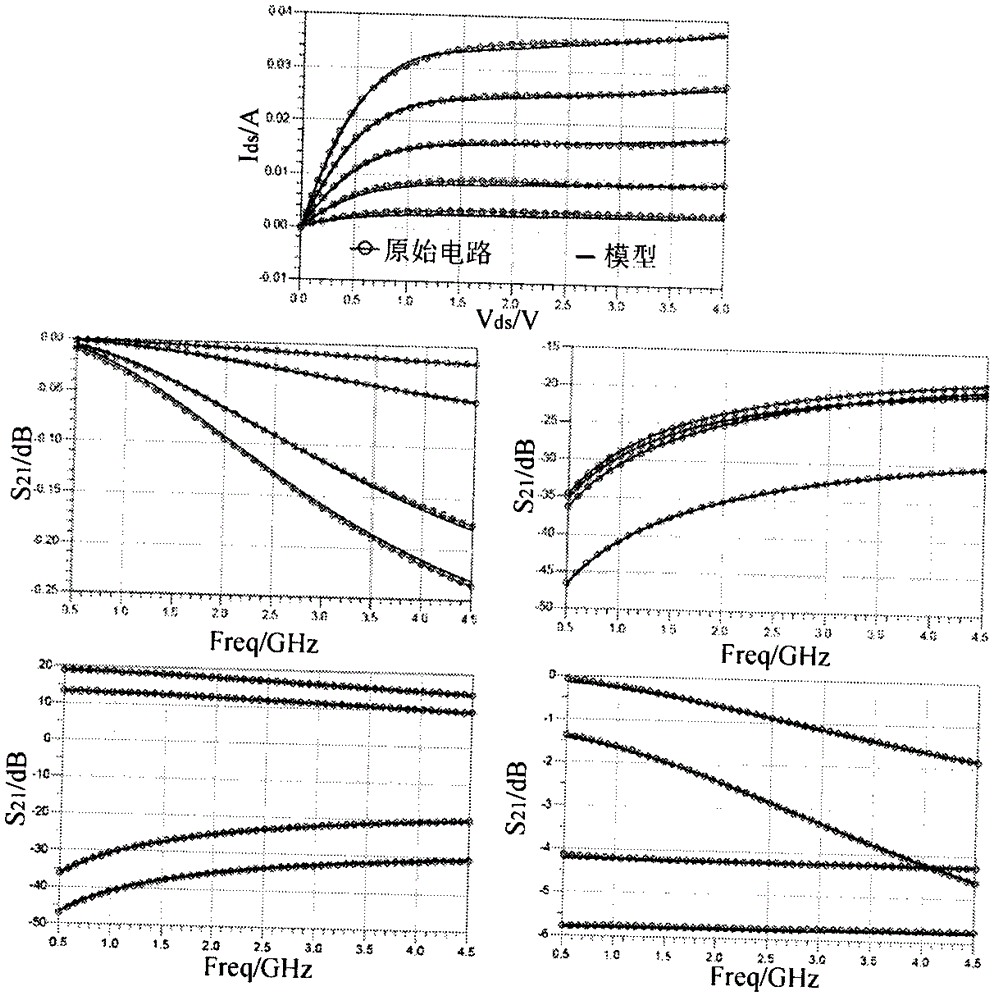
InactiveCN106777620ASimple structureReduce the number of iterationsNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsMicrowaveNerve network
The invention belongs to the field of modeling of microwave circuits and devices, and provides a neural network space mapping modeling method for a power transistor. According to the method, a direct current signal and an alternating current signal in an input / output signal of a power transistor model are separately processed, an output mapping network is used to adjust the direct current characteristic of the power transistor model, and an input mapping network is used to adjust the alternating current characteristic of the power transistor model. The method inherits the advantages of the conventional neural network space mapping method, the mutual interference of the parameters on the model performance is reduced, the repeated adjustment and optimization of the parameters is avoided, and the modelling period is shortened.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV +1
Method for modeling field effect transistor and circuit simulation method
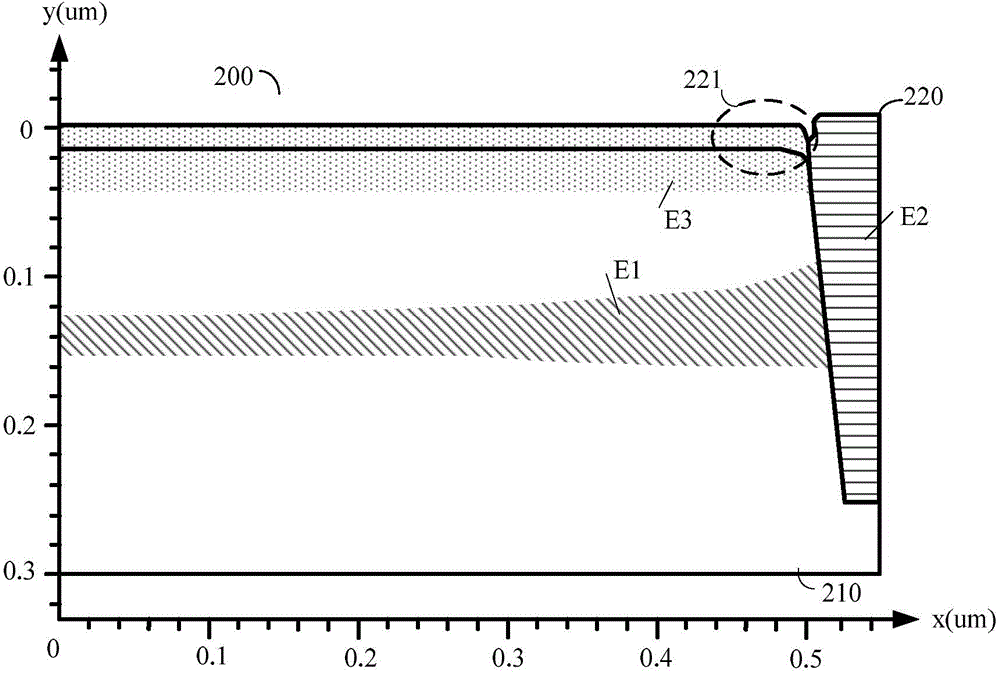
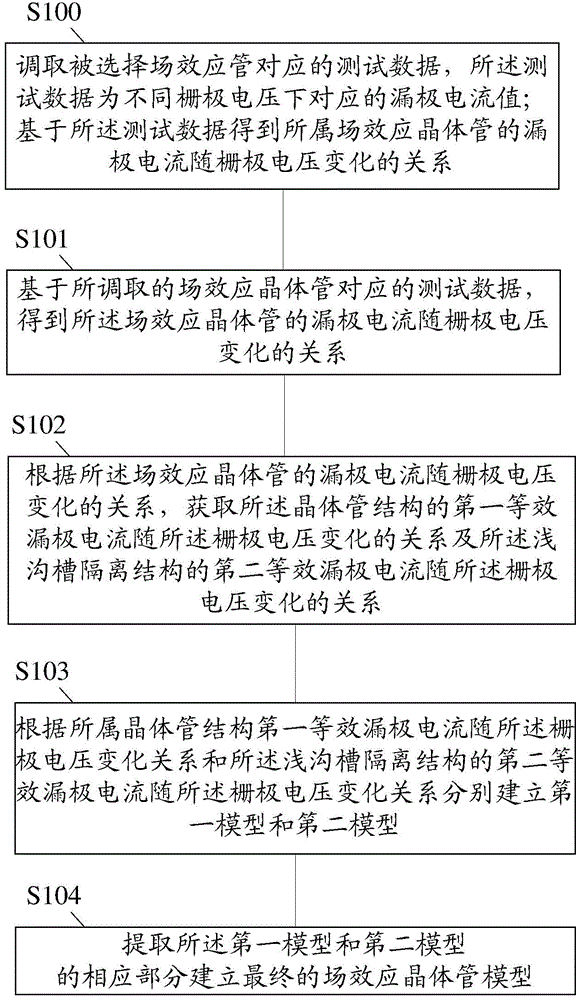
ActiveCN104657522AConform to the real characteristicsImprove scalabilitySpecial data processing applicationsPower flowEngineering
The invention relates to a method for modeling a field effect transistor and a circuit simulation method. The method for modeling the field effect transistor comprises the following steps: calling gate voltage recorded by the selected field effect transistor and the corresponding drain current thereof to obtain relation for change of the drain current of the field effect transistor with the gate voltage; acquiring the relation for the change of first equivalent drain current of the transistor structure with the gate voltage and the relation for change of second equivalent drain current of a shallow trench isolating structure with the gate voltage based on the relation for the change of the drain current of the field effect transistor with the gate voltage; establishing a field effect transistor model according to the relation for the change of the first equivalent drain current of the transistor structure with the gate voltage and the relation for the change of the second equivalent drain current of the shallow trench isolating structure with the gate voltage. The accurate field effect transistor model can be established to improve the precision of circuit simulation.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
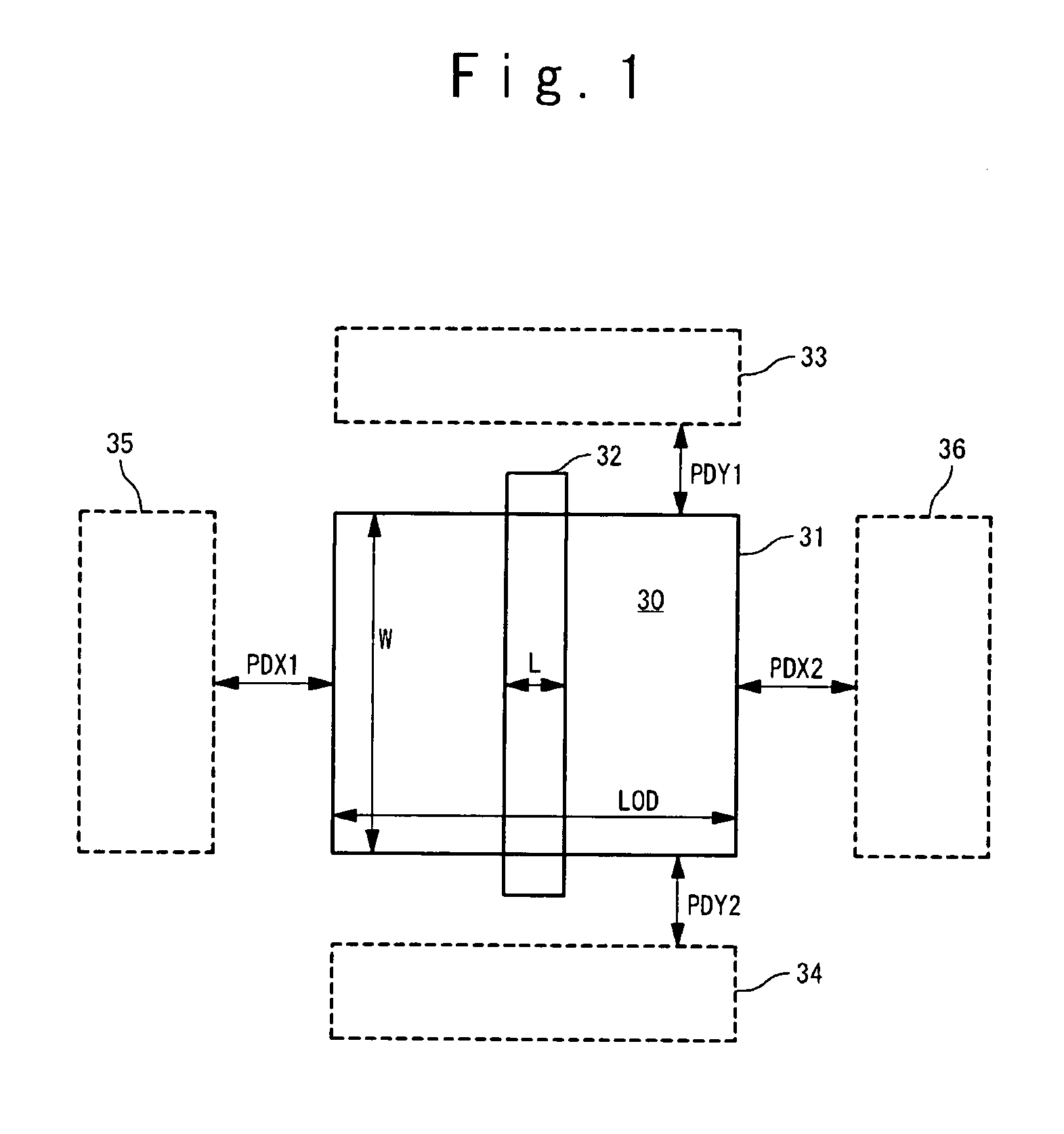
Circuit simulation based on gate spacing from adjacent mos transistors
InactiveCN101685478AHigh precisionComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsHemt circuitsSimulation based
A circuit simulation apparatus is provided with a parameter calculating tool (32) and a circuit simulator (31). The parameter calculating tool (32) is configured to extract gate spacings between gatesof a target MOS transistor and adjacent MOS transistors integrated in an integrated circuit from layout data of the integrated circuit, and to calculate a transistor model parameter corresponding toa threshold voltage of the target MOS transistor based on the extracted gate spacings. The circuit simulator (31) is configured to perform circuit simulation of the integrated circuit by using the calculated transistor model parameter.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
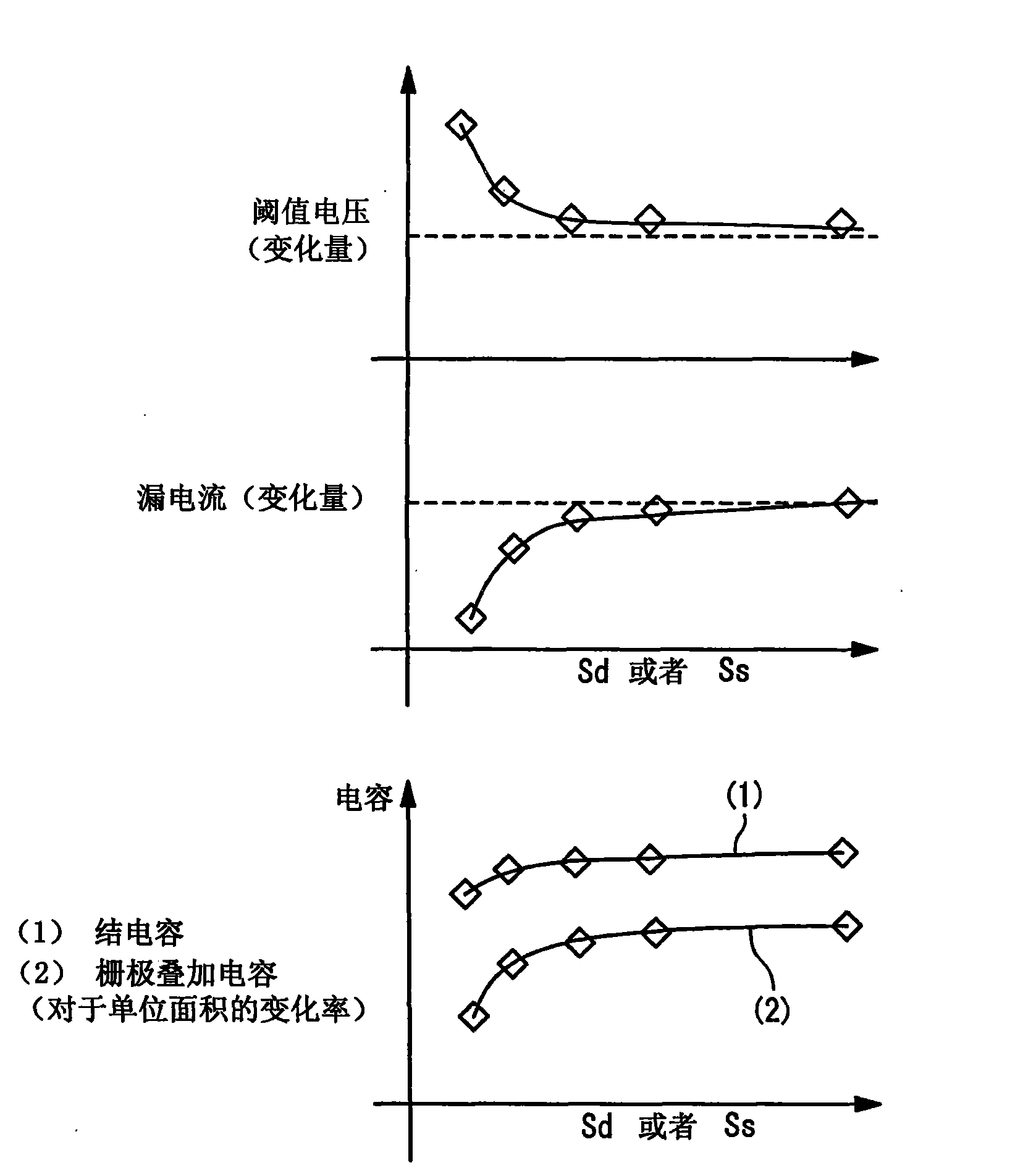
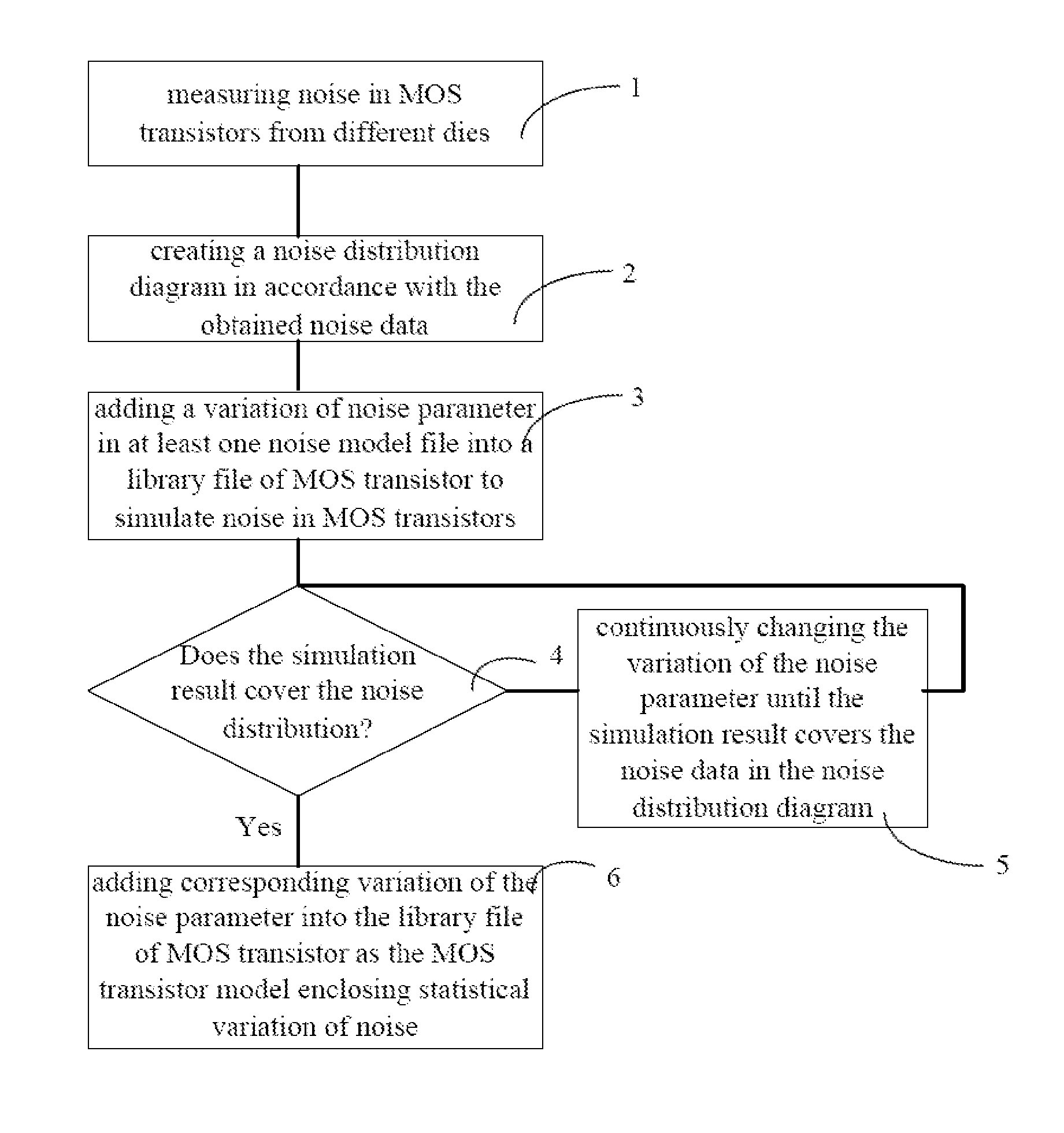
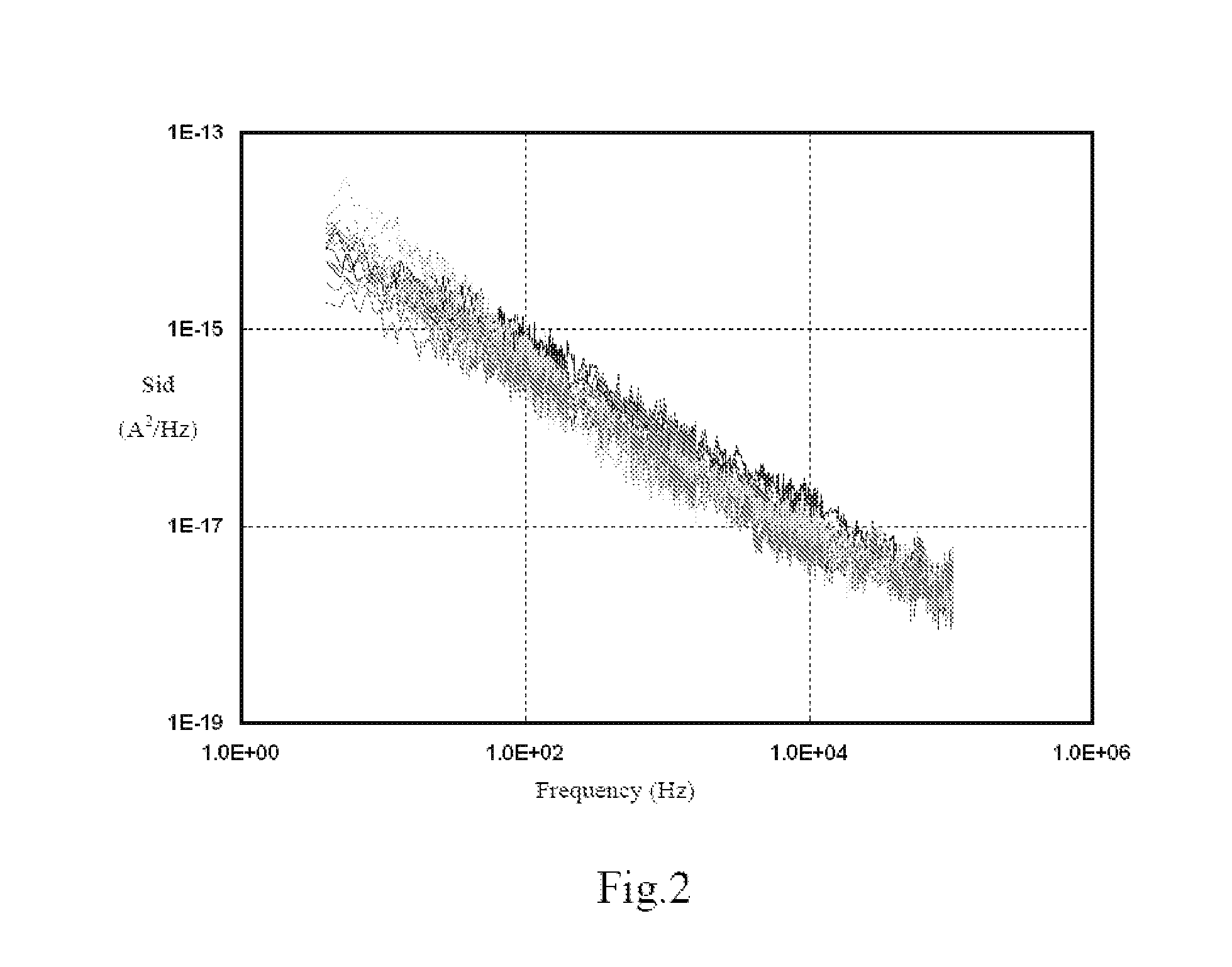
Method for Building MOS Transistor Model and Method for Verifying MOS Transistor Model
ActiveUS20080319721A1Not sufficientMore preciseAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationEngineeringDistribution diagram
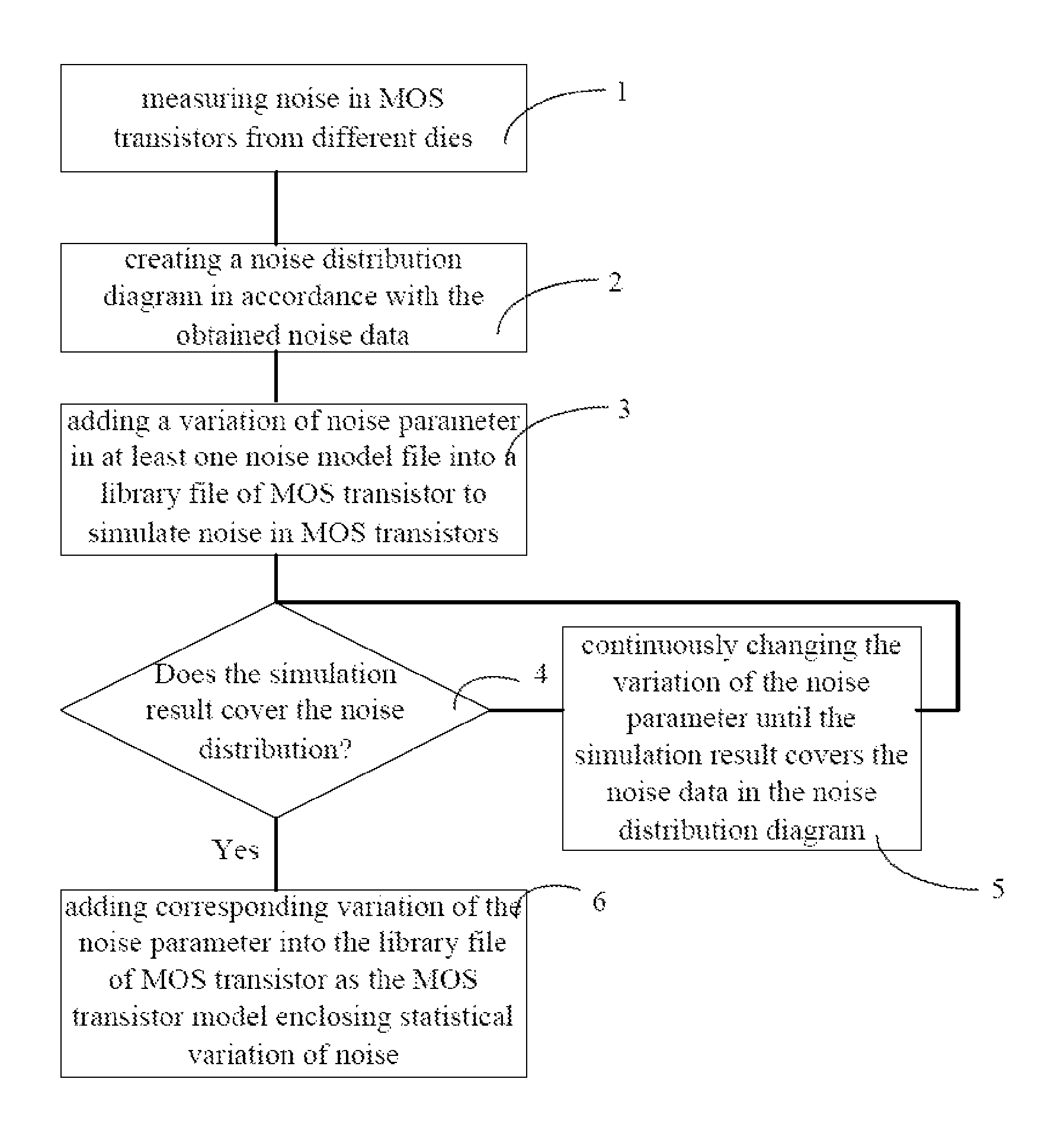
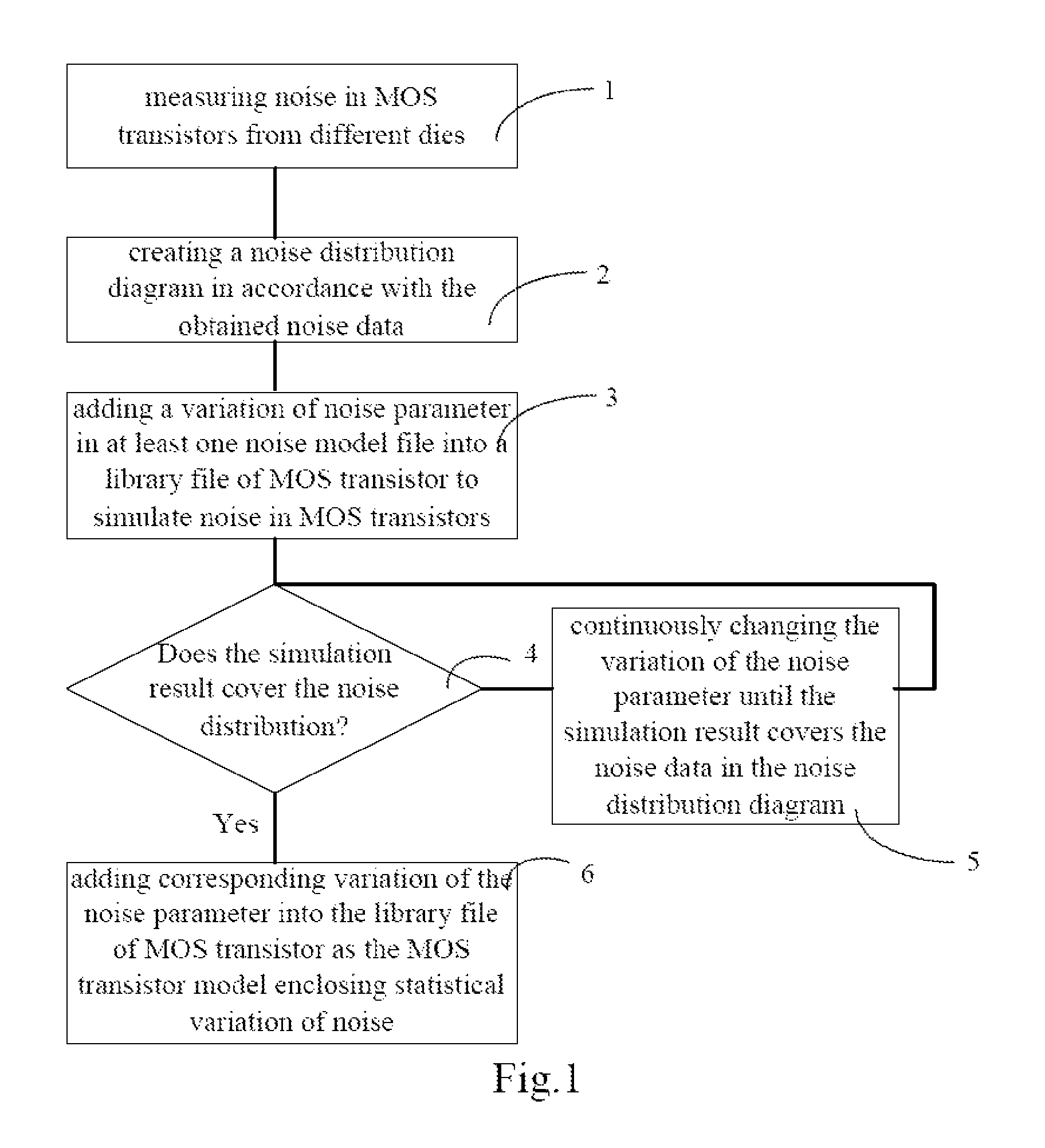
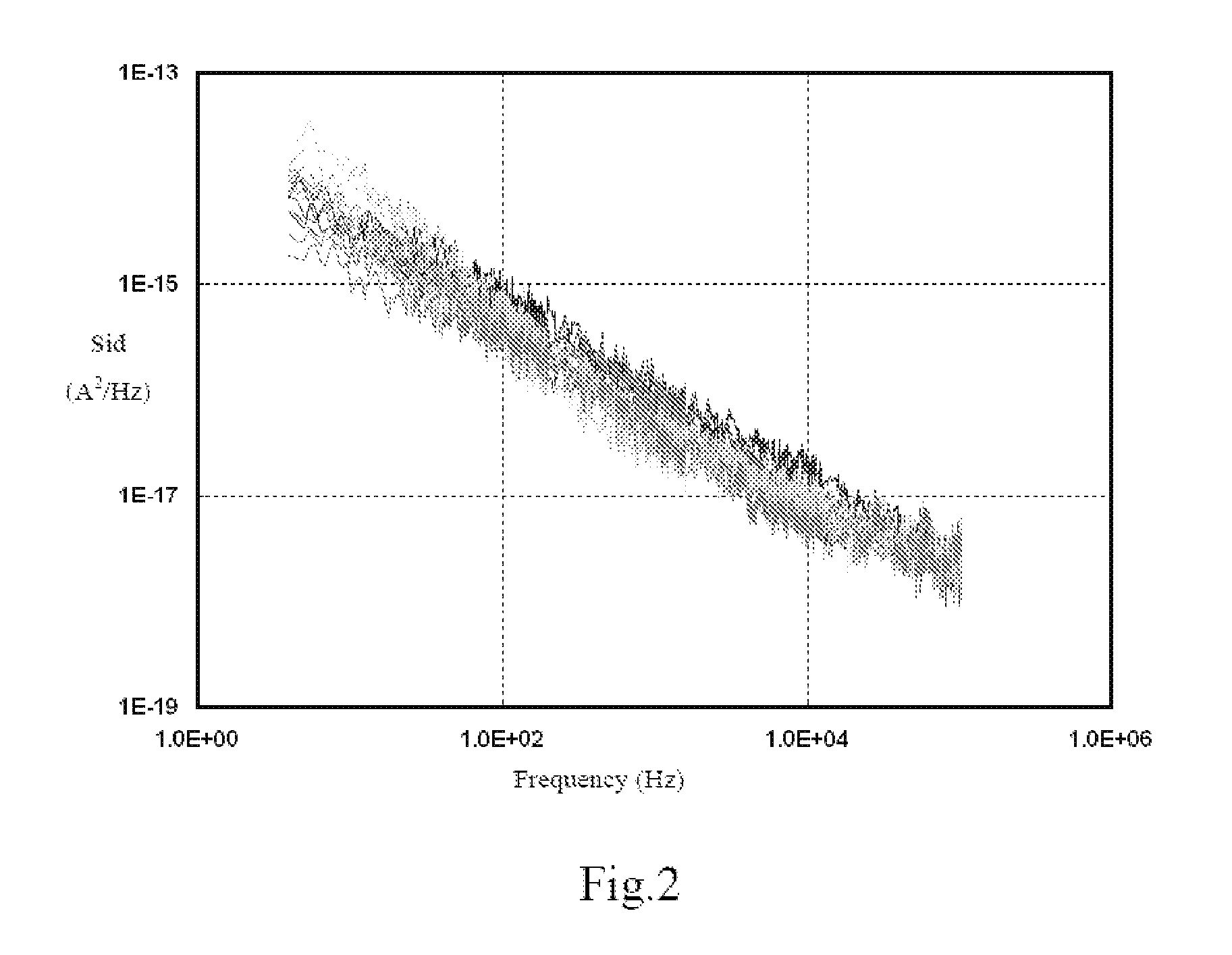
The present invention discloses a method for building an MOS transistor model enclosing statistical variation of noise, including: measuring noise in MOS transistors from different dies; creating a noise distribution diagram in accordance with the obtained noise data of the MOS transistors; adding a variation of noise parameter in at least one noise model file into a library file of MOS transistor to simulate noise in MOS transistors; if a simulation result does not cover the noise data in the noise distribution diagram, changing the variation of the noise parameter until the simulation result covers the noise data in the noise distribution diagram; if the simulation result covers the noise data in the noise distribution diagram, adding corresponding variation of the noise parameter into the library file of MOS transistor as the MOS transistor model enclosing statistical variation of noise. The model obtained by the present invention is more precise.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
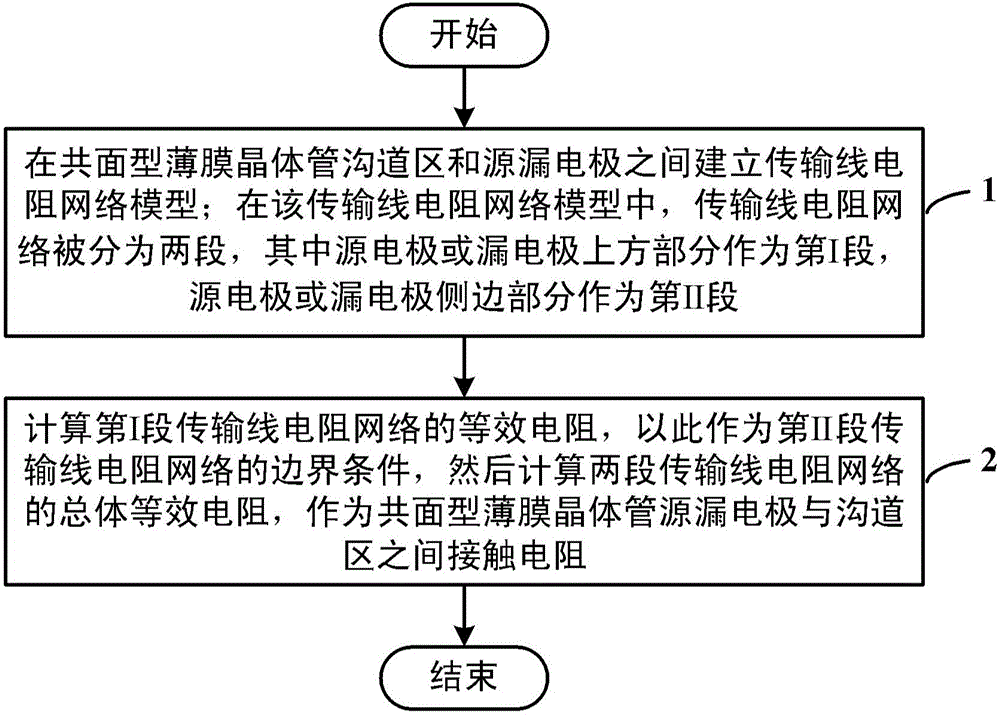
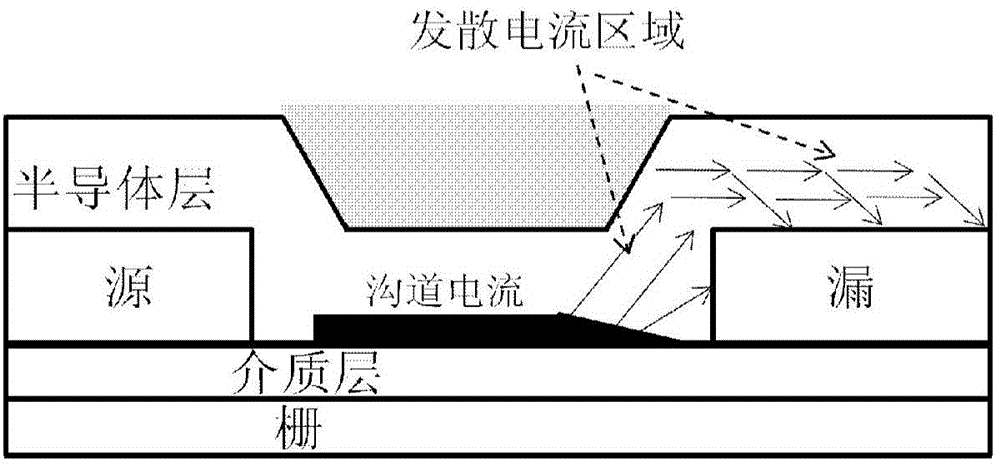
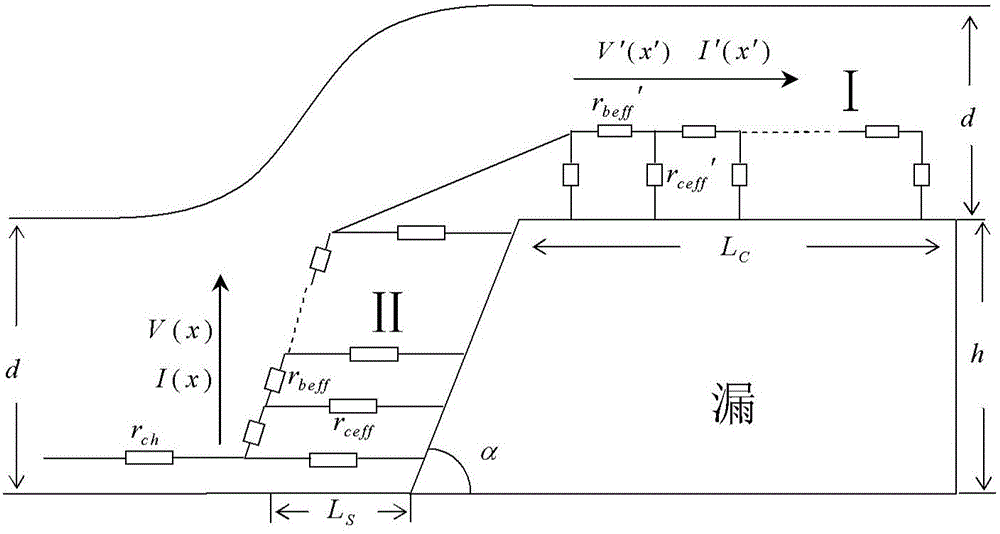
Method for obtaining coplane-type thin film transistor contact resistance
InactiveCN104156526AGet it quickly and accuratelySimple methodSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical resistance and conductanceNetwork model
The invention discloses a method for obtaining coplane-type thin film transistor contact resistance. The method comprises the steps that a transmission line resistance network model is built between a channel region, a source electrode or a drain electrode of a coplane-type thin film transistor; in the transmission line resistance network model, the transmission line resistance network is divided into two segments, the upper portion of the source electrode or the upper portion of the drain electrode is used as the first segment, and the side edge of the source electrode or the side edge of the drain electrode is used as the second segment; the equivalent resistance of the first segment of the transmission line resistance network is calculated and used as the boundary condition of the second segment of the transmission line resistance network, and then the total equivalent resistance of the two segments of the transmission line resistance network is calculated and used as the contact resistance between the source electrode or the drain electrode and the channel region of the coplane-type thin film transistor. By utilizing the method, the contact resistance of the coplane-type thin film transistor can be obtained through precise fitting calculation, and the method is suitable for modeling research of the thin film transistor. The method is reasonable in theory, accurate in result, easy to implement and beneficial to building the complete thin film transistor model.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
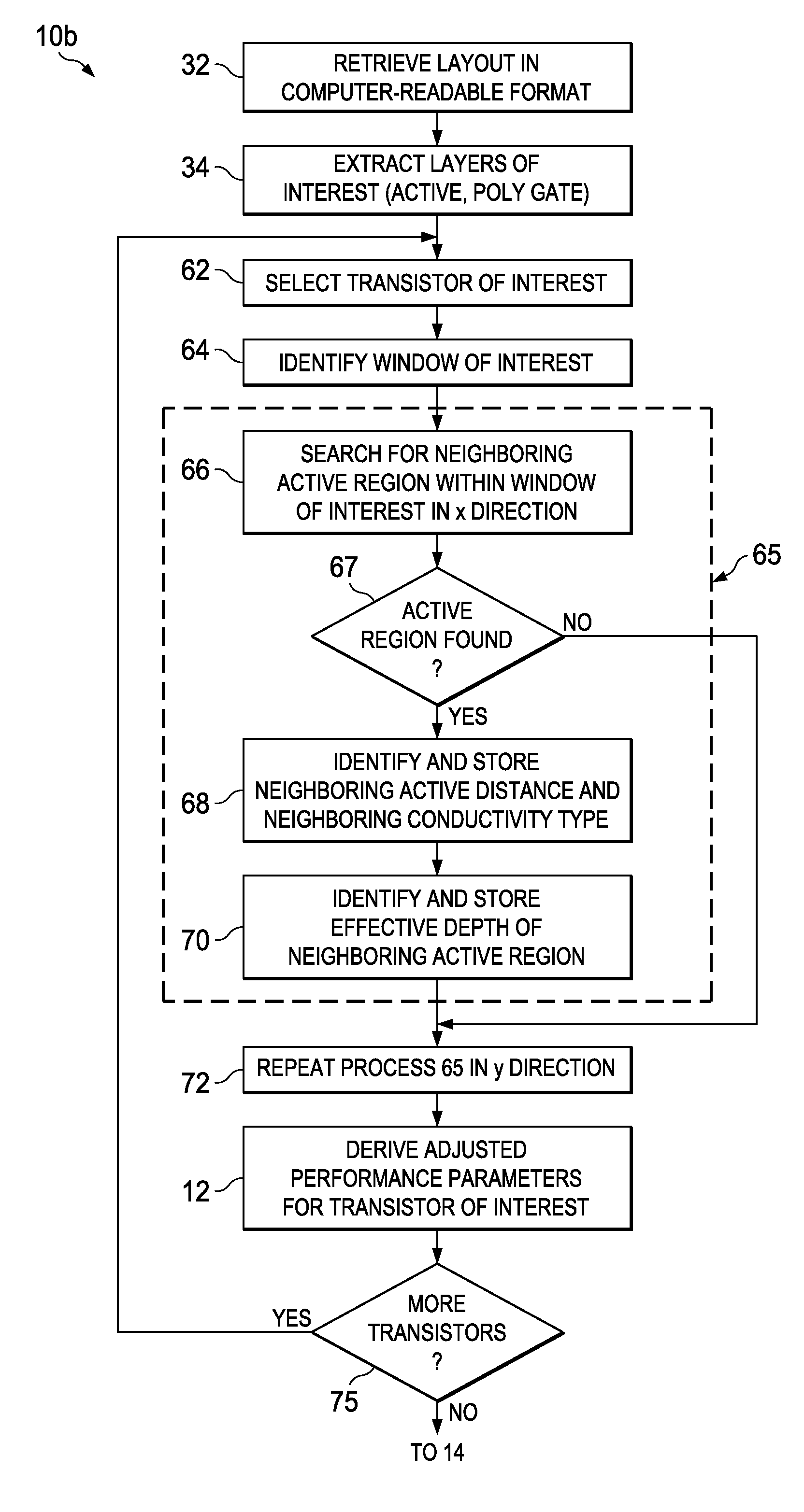
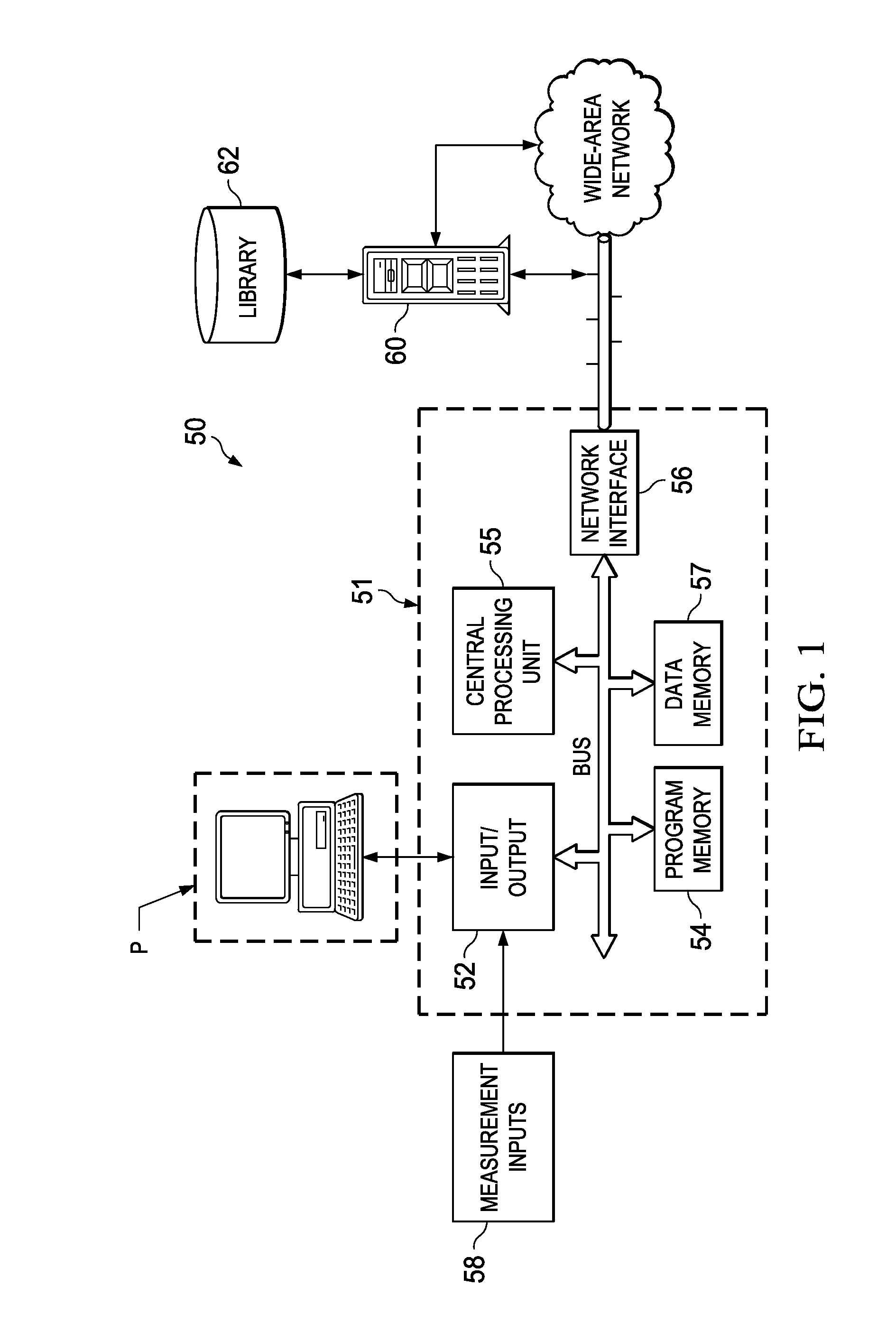
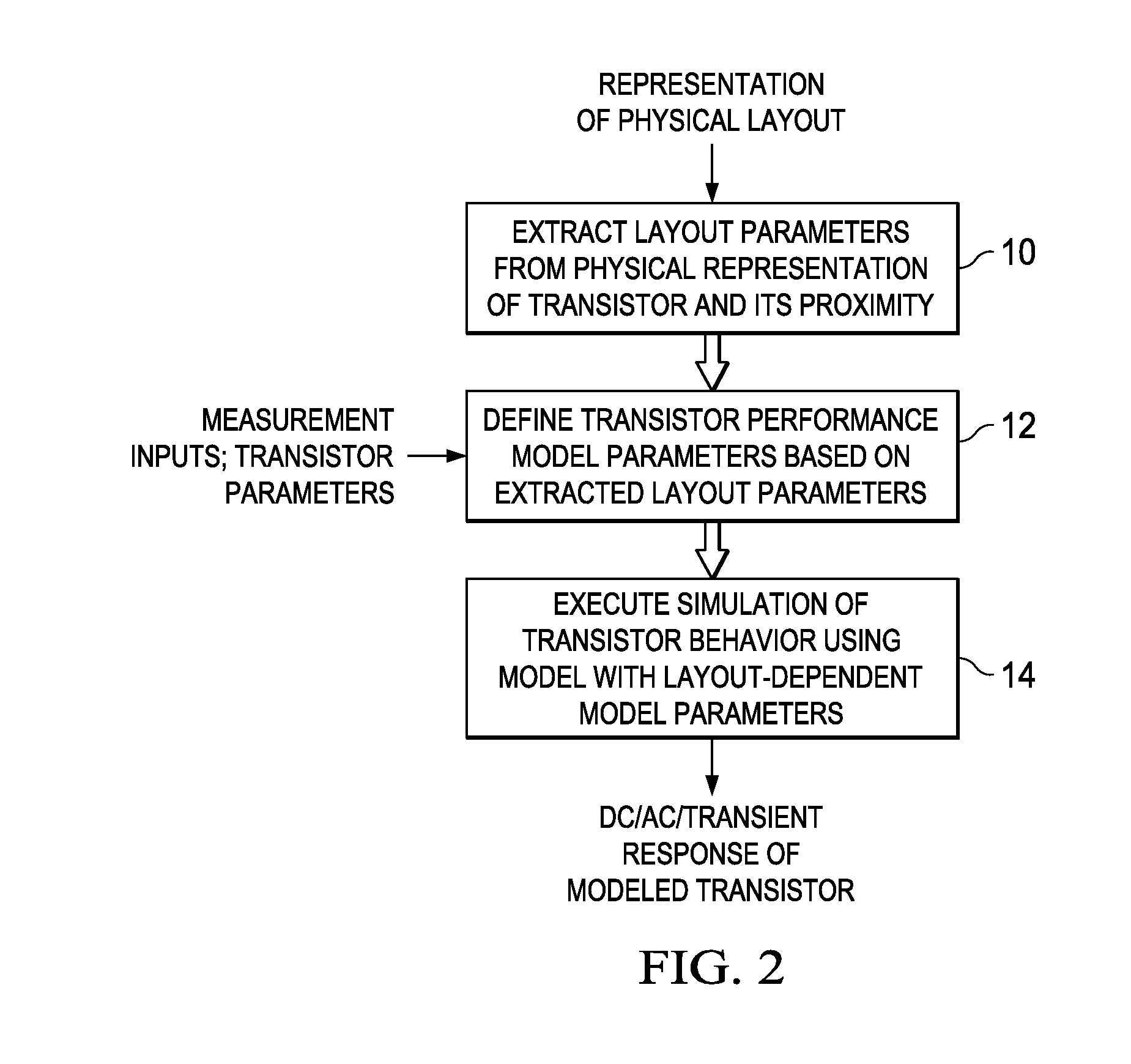
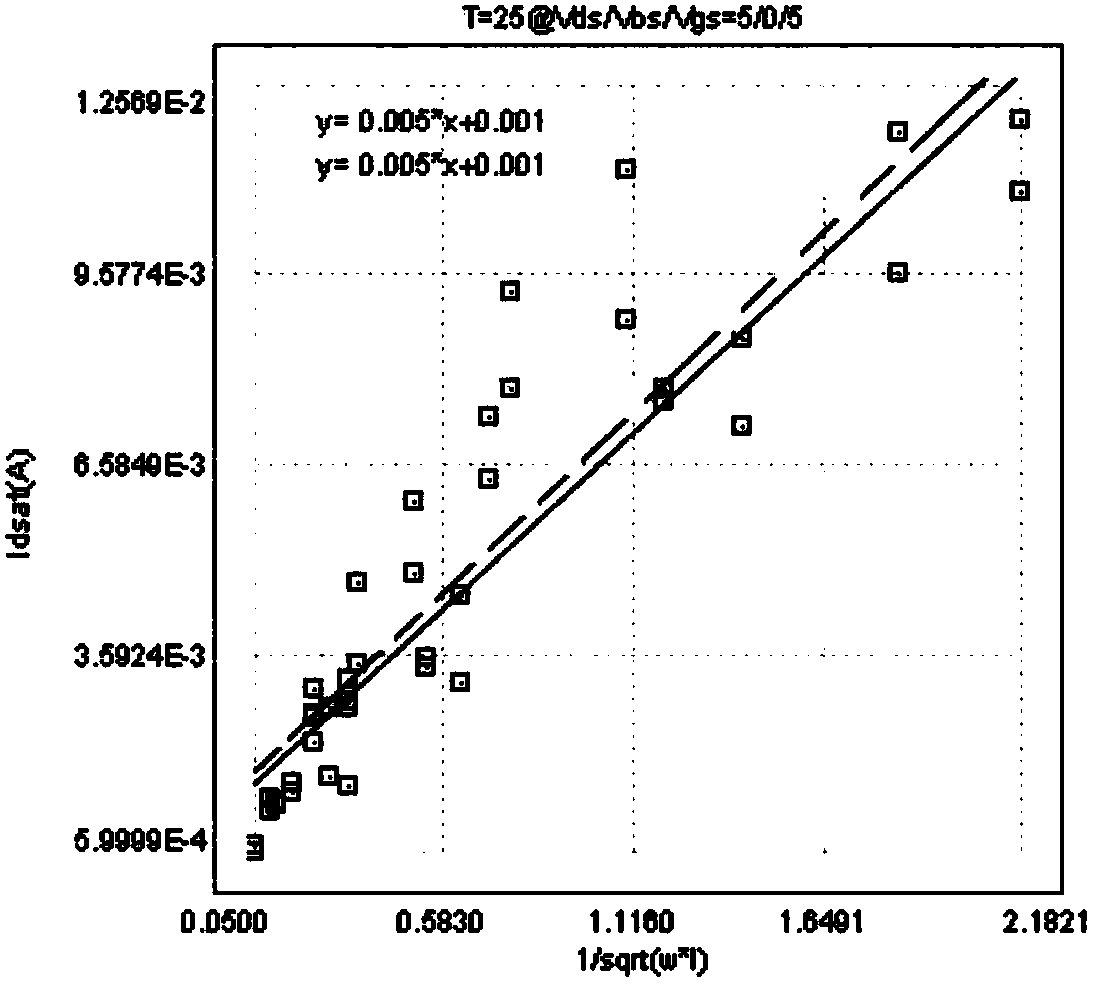
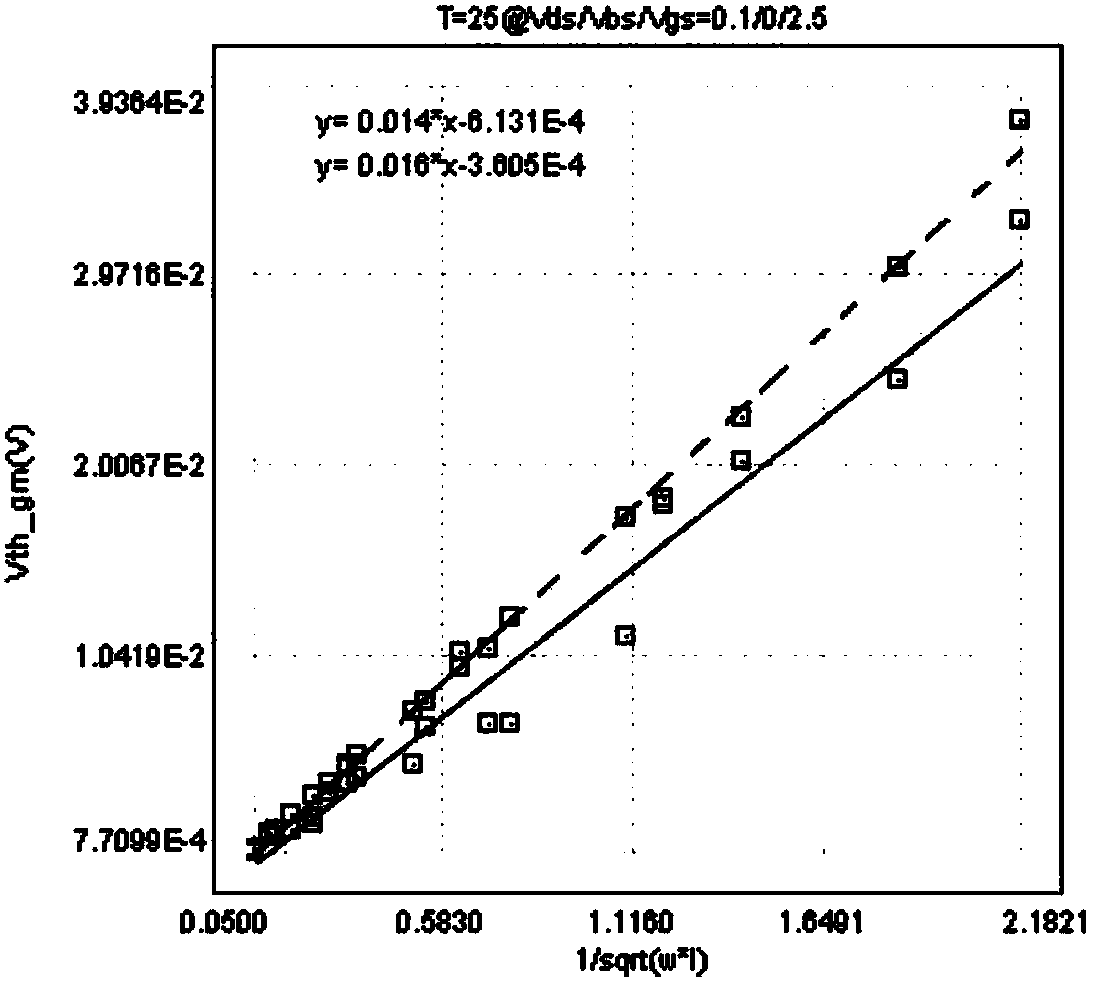
Automated Extraction of Size-Dependent Layout Parameters for Transistor Models
InactiveUS20120143569A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringIntegrated circuit layout
A system and method for determining transistor model parameters that account for layout-dependent features in the transistor being modeled, and also in neighboring devices in the same integrated circuit. A computer-readable expression of the integrated circuit layout is retrieved, and active and gate layers in that expression extracted. For a transistor being modeled, its active regions are analyzed to determine whether these regions have a complex shape. Model parameters are derived based on volume effects of the complex shaped active regions. Neighboring active regions that affect parameters of the transistor being modeled are also identified and their effective depth determined. Strain effects due to complex shaped active regions and neighboring elements are thus included in the transistor model.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
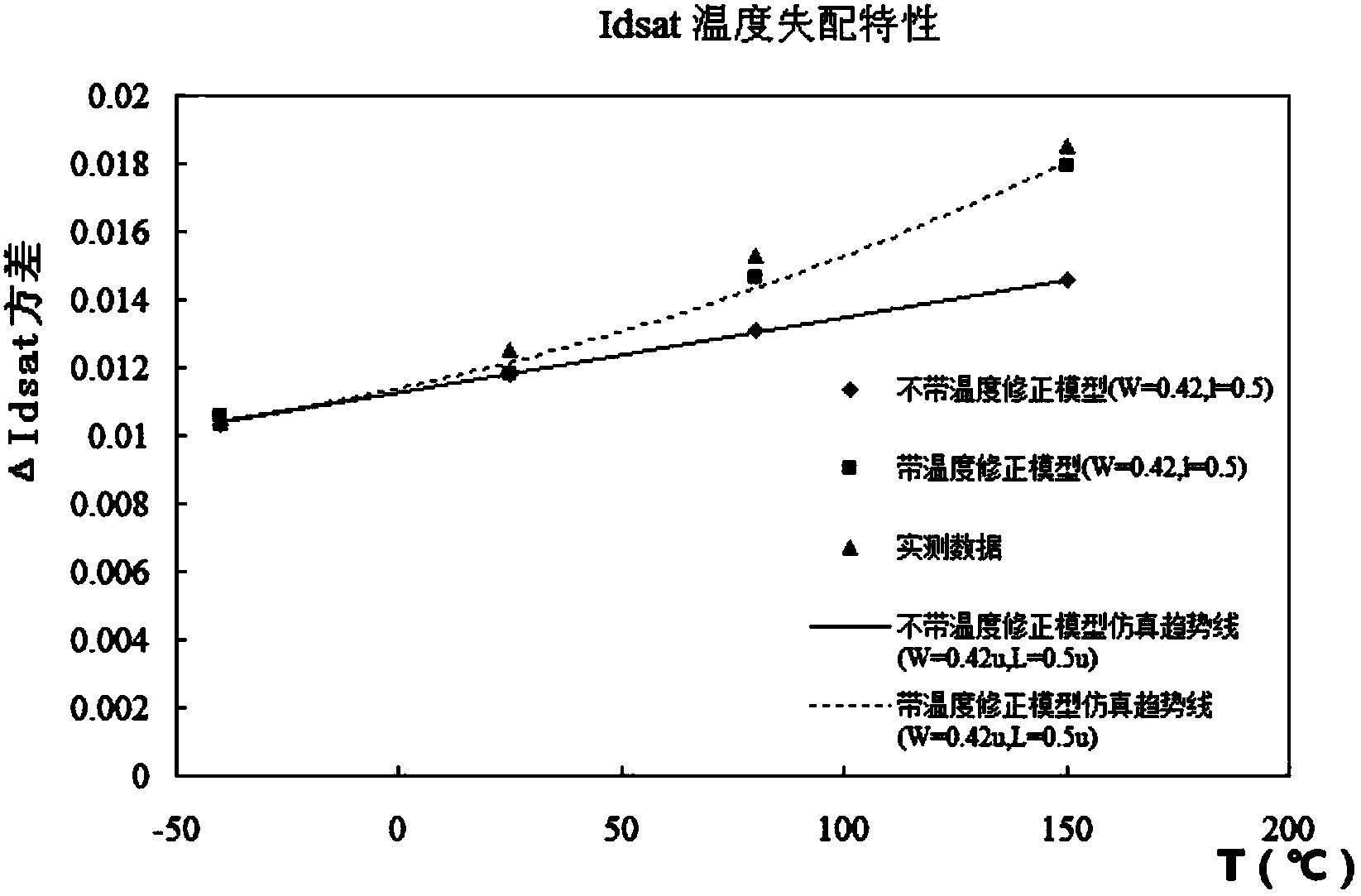
Transistor model capable of describing high temperature and low temperature mismatching characteristics and simulation method
The invention discloses a transistor model capable of describing high temperature and low temperature mismatching characteristics and a simulation method. The changing trends, along with temperature, of the transistor mismatching characteristics are analyzed on a plurality of temperature conditions respectively, a threshold voltage parameter and a migration rate parameter are selected, extra temperature correction formulas and extra temperature correction coefficients are added respectively on the basis of original correction formulas in a mismatching macro-model, fitting is conducted on the correction coefficients by the utilization of the mismatching trends, along with high and low temperature changes, of the transistor so as to enable the mismatching model to be capable of well reflecting the electrical characteristic mismatching characteristics, and high-quality reference is provided for a circuit designer.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
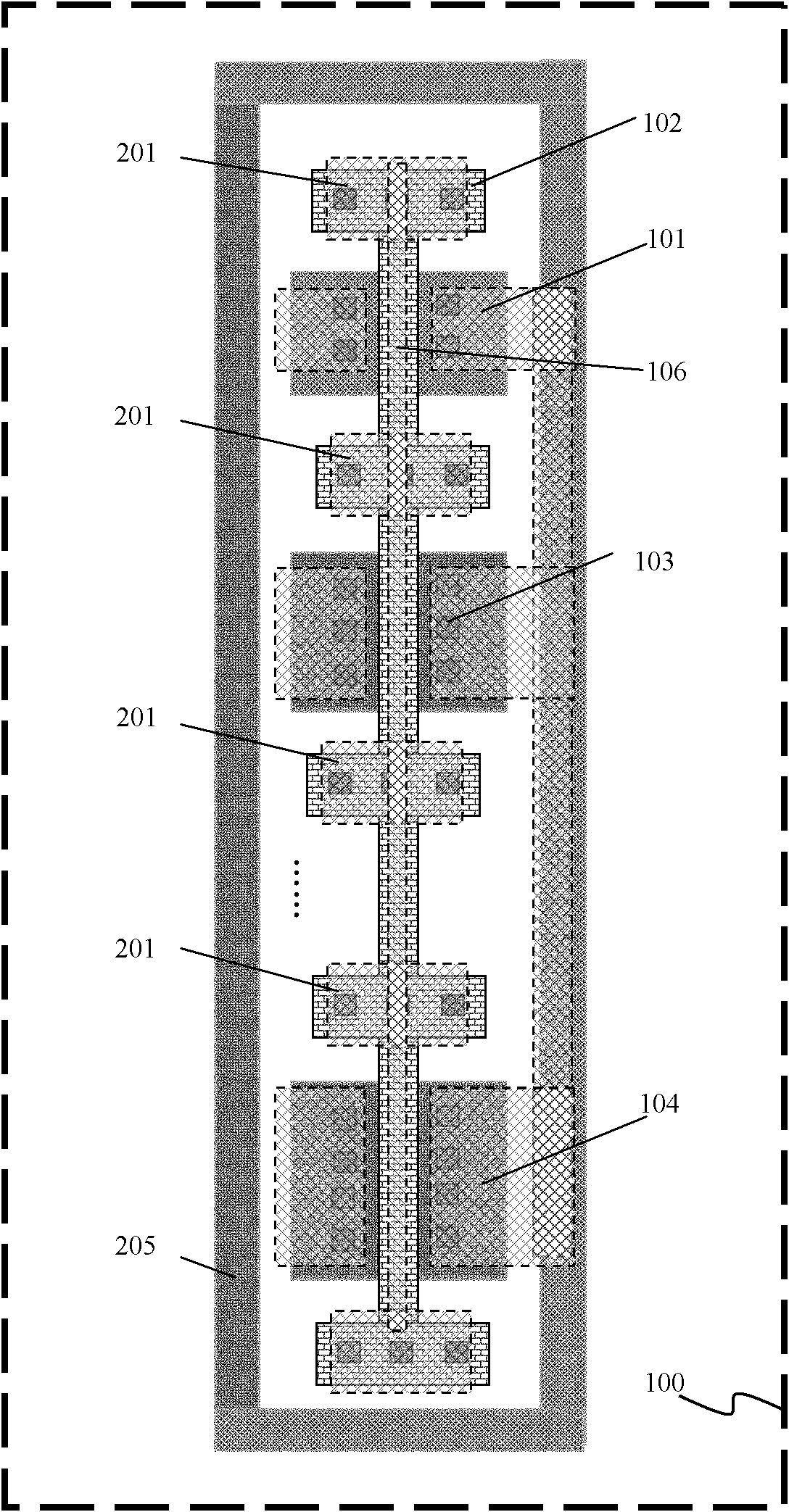
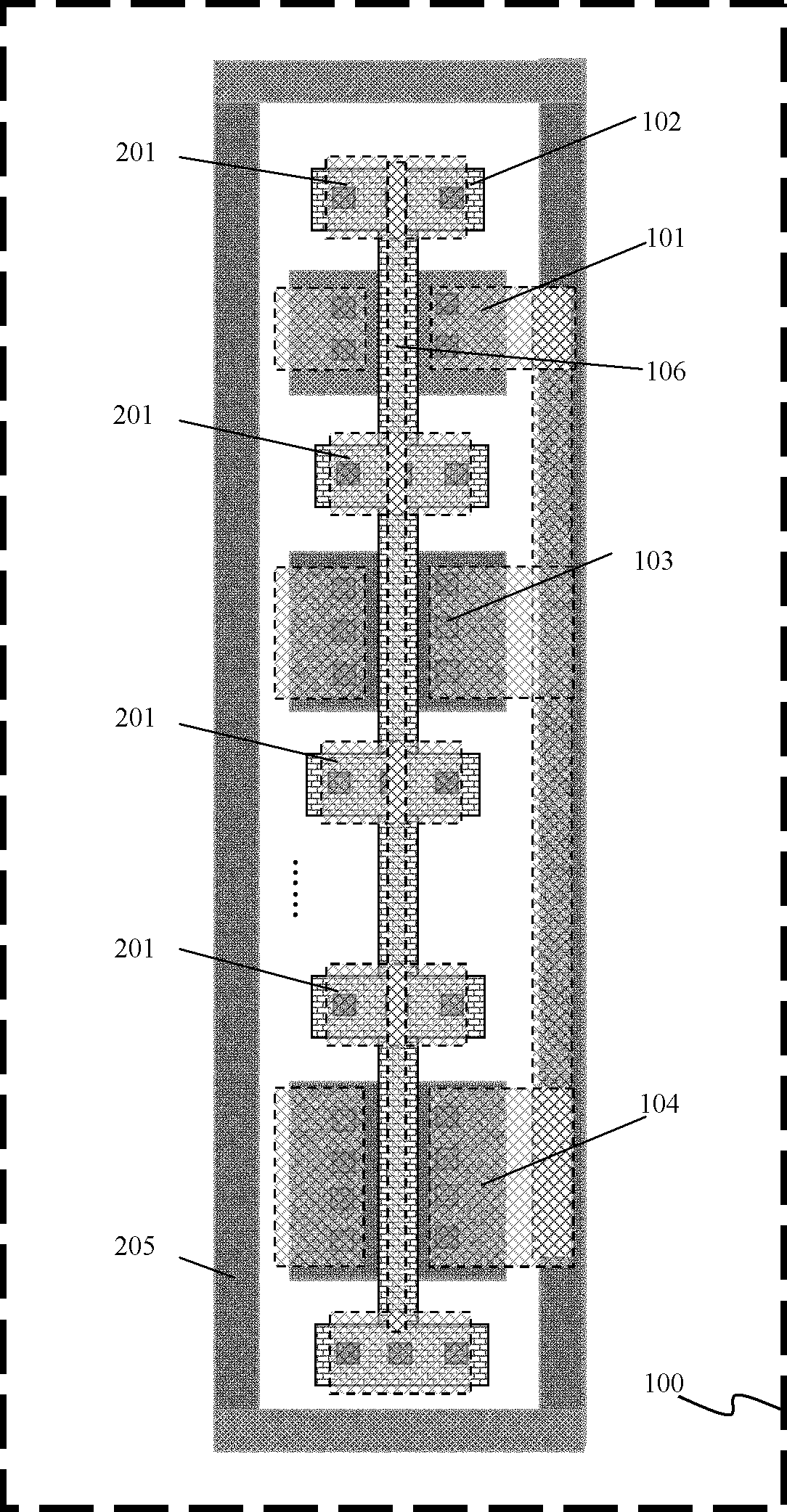
Grid resistor test structure for MOS transistor
ActiveCN102693959ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringChannel width
The invention discloses a grid resistor test structure for a metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) transistor. The test structure includes m groups of MOS transistors; each group of the MOS transistors comprises n MOS transistors with various channel widths, wherein the MOS transistors in the same group have the identical channel length and different groups of MOS transistors have different channel lengths; and all the MOS transistors have the same type. According to the grid resistor test structure of MOS transistors, all coefficients in a resistance element Rg functional expression in an MOS transistor model can be visually obtained with consideration of the influence of a grid resistor on MOS transistor characteristics.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
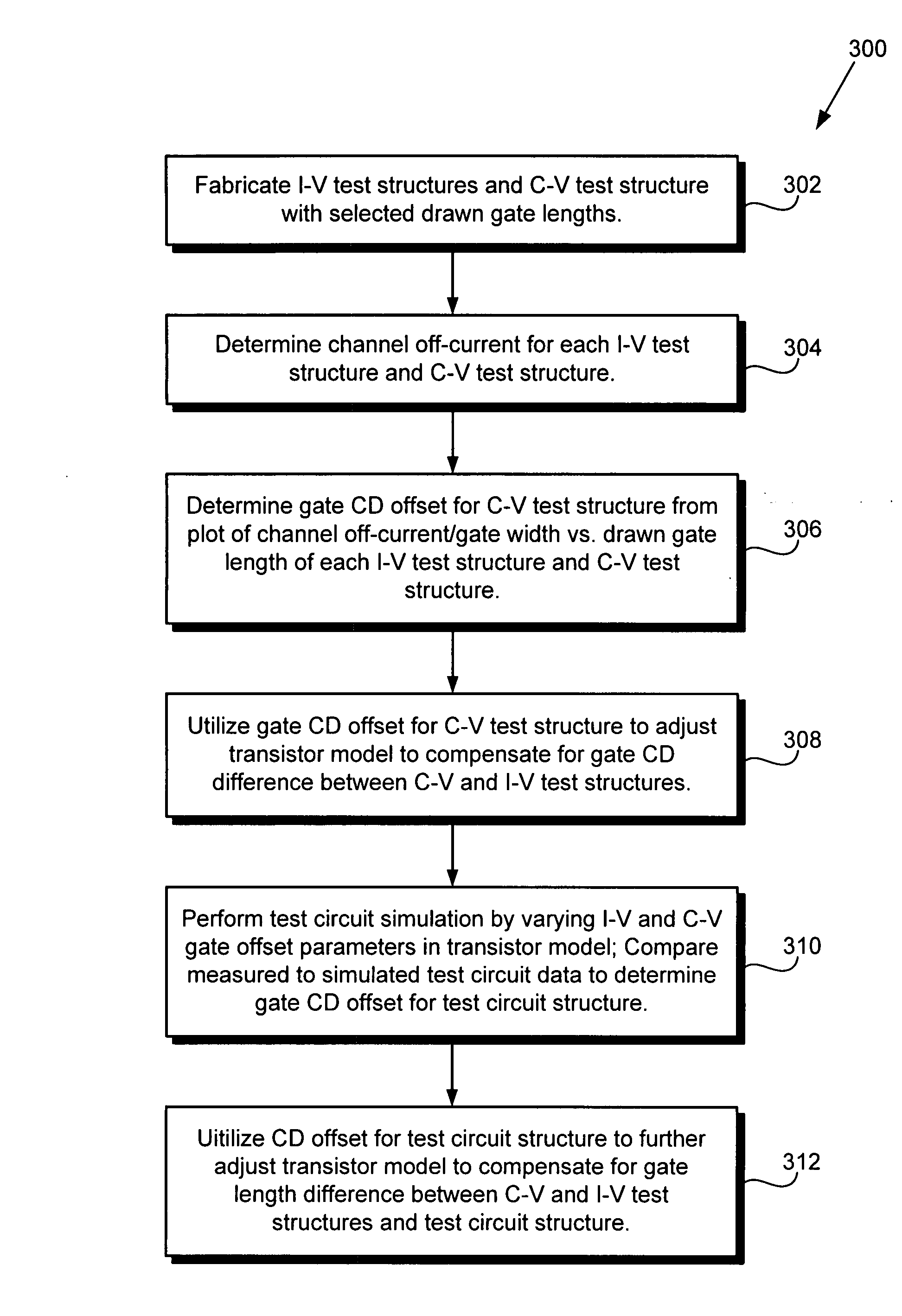
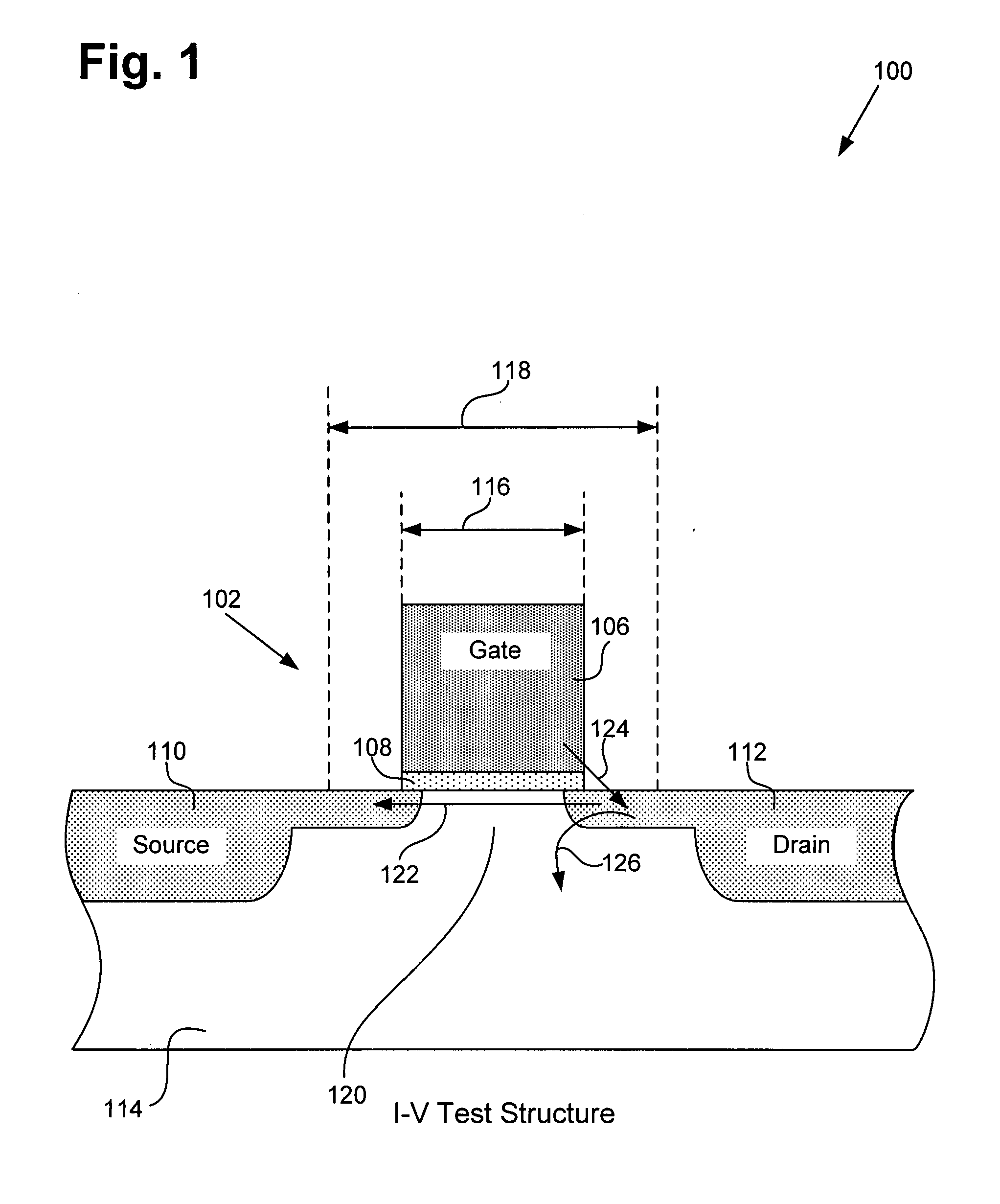
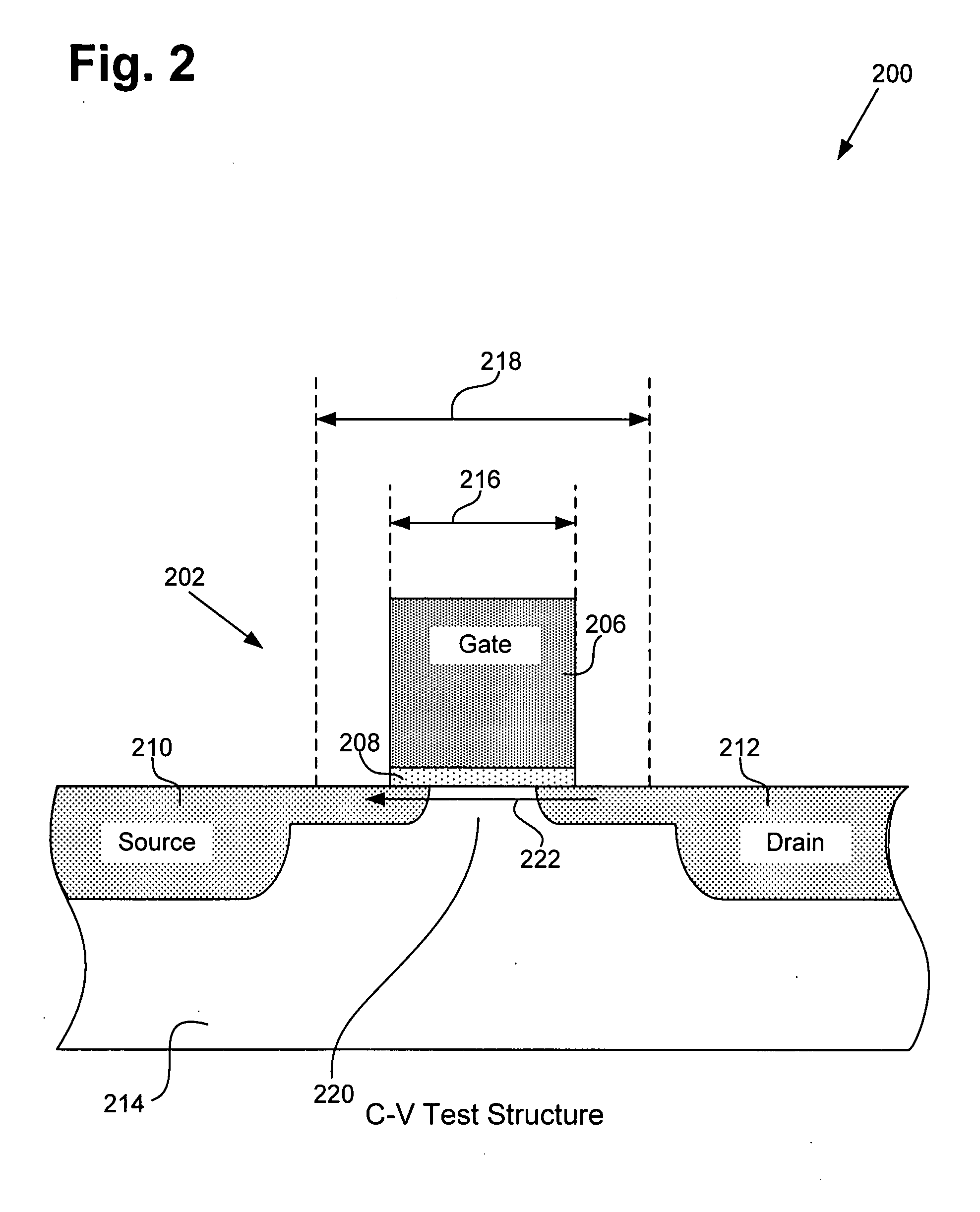
Method for adjusting a transistor model for increased circuit simulation accuracy
ActiveUS20080286887A1Increased circuit simulation accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectrical current
According to one exemplary embodiment, a method for adjusting a transistor model for increased circuit simulation accuracy includes determining a first gate CD offset by matching a C-V test structure having a normalized channel current to an I-V test structure having the normalized channel current. The method further includes utilizing the first gate CD offset to adjust the transistor model for increased circuit simulation. The method also includes determining a second gate CD offset by varying I-V and C-V gate length parameters in the transistor model to cause simulated data from a test circuit to be approximately equal to measured data from the test circuit. The method further includes utilizing the second gate CD offset to adjust the transistor model.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
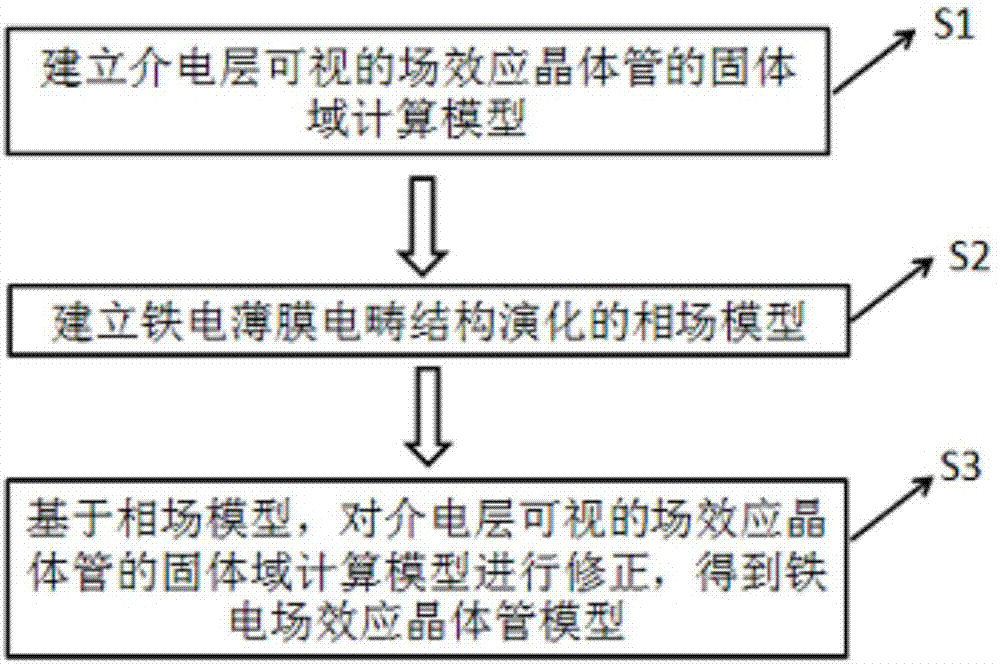
Building method and system for ferroelectric field effect transistor model
ActiveCN107423463AAvoid failureSimulation is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsCharge carrierElement modeling
The invention relates to a building method and system for a ferroelectric field effect transistor model, and belongs to the technical field of finite element modeling. The method comprises the steps of building a solid domain calculation model of a field effect transistor with a visible dielectric layer; building a phase field model of an electric domain of a ferroelectric film; and based on the phase field model, performing correction on the solid domain calculation model to obtain the ferroelectric field effect transistor model. Therefore, the electric domain evolution process of the dielectric layer under the action of an electric field can be accurately simulated and the domain structure and the domain switching condition of the dielectric layer can be observed; and moreover, the reflection of the macro-performance of the transistor and the potential distribution and carrier concentration distribution conditions under different domain structures can be simulated.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Simulation method for transistor unsuitable for existing model
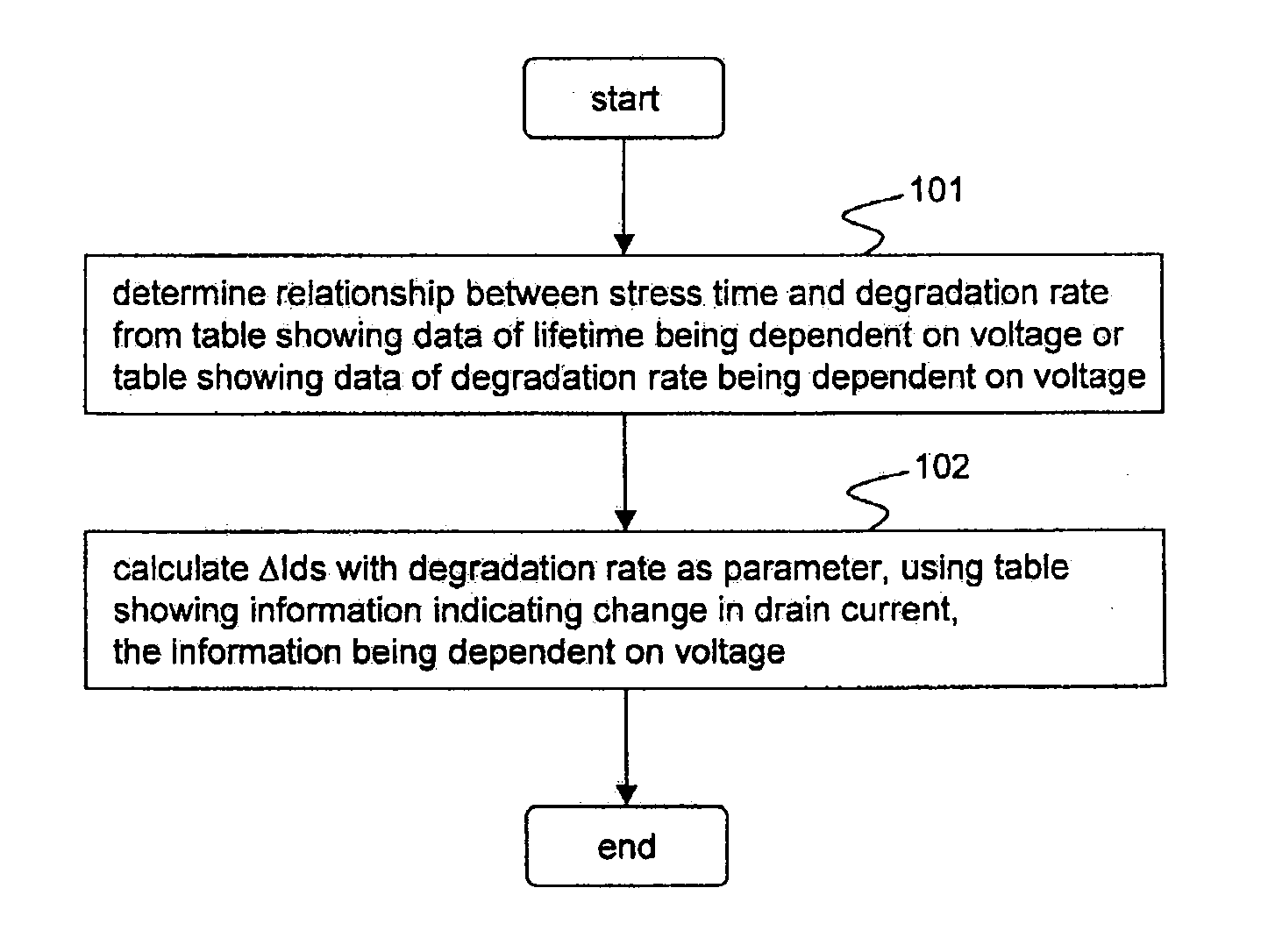
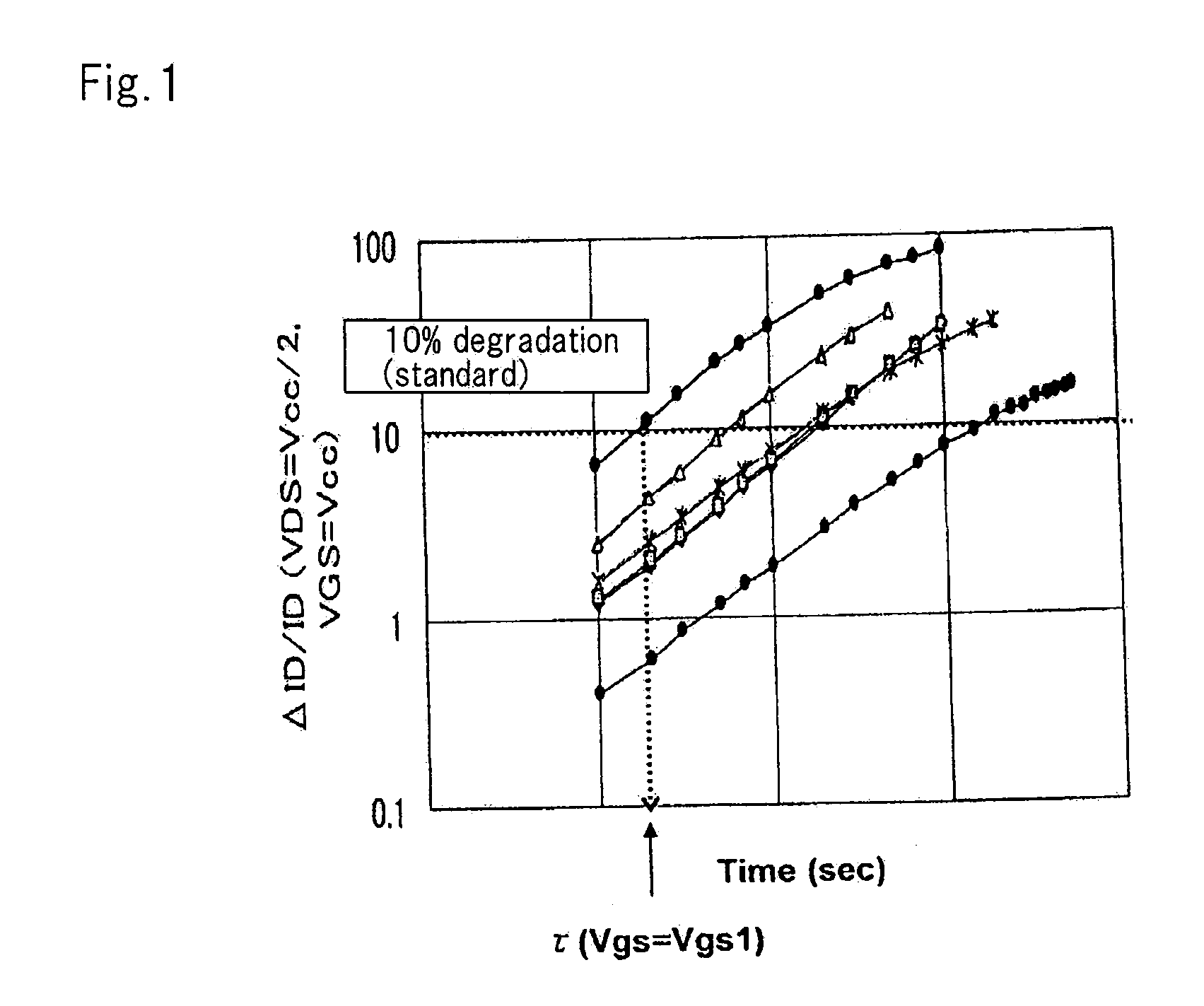
ActiveUS20100114543A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationSimulationStress time
A simulation method includes determining a relationship between stress time and a degradation rate of drain current on a basis of a table in which data of a lifetime of a transistor, or the degradation rate of the transistor, is written, and calculating an amount of change in drain current accordance with the degradation rate, using a table in which information indicating a change in the drain current, being dependent on voltage, is written, based on actually measured data of drain current of the transistor after degradation, drain current in an initial state of a particular transistor model, and the relationship between stress time and the degradation rate of drain current.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
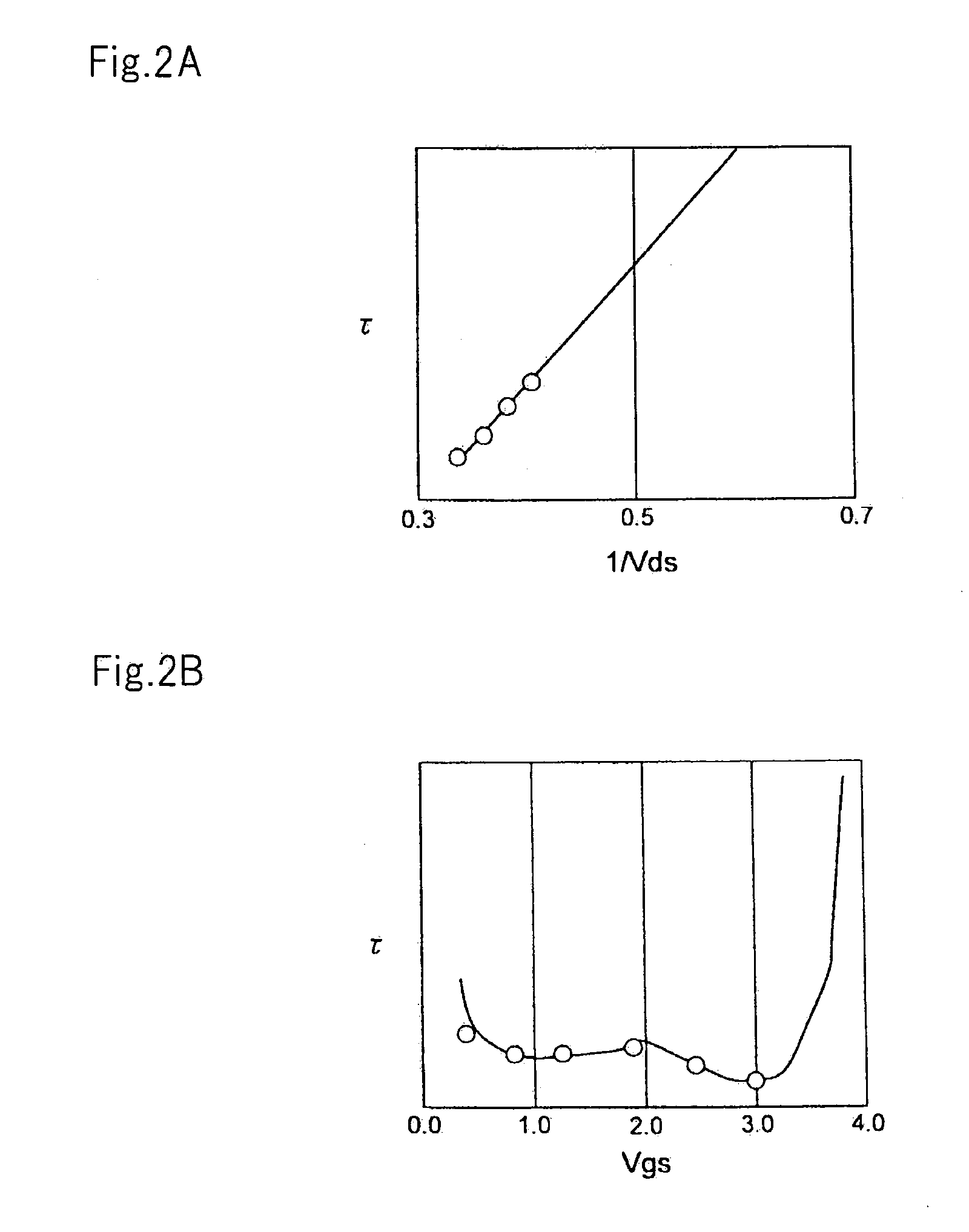
Method and device for evaluating electric performances of an fdsoi transistor
ActiveUS20110050253A1Accurate detectionTesting dielectric strengthResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceElectricity
A method for evaluating the electric performances of an FDSOI transistor, including the steps of:measuring the capacitance and / or the conductance of the FDSOI transistor, by applying a rear voltage VBG>0 or VBG<0 on the substrate of the transistor, depending on a front voltage VFG applied on the gate of the transistor,calculating the theoretical values of the capacitance and / or the conductance of a transistor modeled by an electric circuit equivalent to the FDSOI transistor, for different selected theoretical values of defect densities Dit1, Dit2 at the dielectric-semiconductor interfaces of the modeled transistor,determining the real values of Dit1, Dit2 at the corresponding interfaces of the FDSOI transistor by a comparison between the measured values of the capacitance and / or the conductance of the FDSOI transistor and the calculated theoretical values of the capacitance and / or the conductance of the modeled transistor.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Field effect transistor model parameter correction method taking shallow trench isolation into account
InactiveCN102955883AAccurate descriptionStrong physical propertiesSpecial data processing applicationsMOSFETModel parameters
The invention relates to a field effect transistor model parameter correction method taking shallow trench isolation into account and belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit design. The method comprises the steps that a parasitic parameter extraction tool is adopted to extract STI (shallow trench isolation) structural parameters from an input layout; the stress in the trench of an MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor), along the length direction and the width direction of the trench is calculated according to the STI structural parameters; and the MOSFET model parameter corrections are obtained through the stress calculation, including electron mobility correction, hole mobility correction, N-MOSFET threshold voltage correction and P-MOSFET threshold voltage correction, electron saturation speed correction and hole saturation speed correction. The field effect transistor model parameter correction method taking shallow trench isolation into account can improve the reliability of circuit simulation and increase the success rate of integrated circuit design.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Neural network space mapping modeling method for packaged transistors
InactiveCN106777621ASimple structureFeatures accurately reflectCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsCommunications systemNerve network
The invention provides a neural network space mapping modeling method for packaged transistors. Building of accurate packaged transistor models is of vital importance on improving the precision of wireless communication system circuits. The neural network space mapping modeling method aims to overcome the shortcomings of requirements on internal structure information and high computational complexity of existing modeling methods for packaged transistors. The neural network space mapping modeling method for the packaged transistors includes dividing each packaged transistor model into an input packaged circuit module, a nonlinear circuit module and an output packaged circuit module; respectively constructing structures of the input packaged circuit modules, the nonlinear circuit modules and the output packaged circuit modules. The neural network space mapping modeling method has the advantages that characteristics of the packaged transistors can be accurately reflected by trained models, the neural network space mapping modeling method is high in simulation speed, the design cycle can be greatly shortened, and large-scale circuits can be possibly further designed.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV +1
Circuit simulation based on gate spacing from adjacent MOS transistors
InactiveUS20100082308A1Accurate estimateImprove accuracyComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designSimulation basedHemt circuits
A circuit simulation apparatus is provided with a parameter calculating tool and a circuit simulator. The parameter calculating tool is configured to extract gate spacings between gates of a target MOS transistor and adjacent MOS transistors integrated in an integrated circuit from layout data of the integrated circuit, and to calculate a transistor model parameter corresponding to a threshold voltage of the target MOS transistor based on the extracted gate spacings. The circuit simulator is configured to perform circuit simulation of the integrated circuit by using the calculated transistor model parameter.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for building MOS transistor model and method for verifying MOS transistor model
ActiveUS7885799B2More precise.Accurate methodAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationEngineeringDistribution diagram
The present invention discloses a method for building an MOS transistor model enclosing statistical variation of noise, including: measuring noise in MOS transistors from different dies; creating a noise distribution diagram in accordance with the obtained noise data of the MOS transistors; adding a variation of noise parameter in at least one noise model file into a library file of MOS transistor to simulate noise in MOS transistors; if a simulation result does not cover the noise data in the noise distribution diagram, changing the variation of the noise parameter until the simulation result covers the noise data in the noise distribution diagram; if the simulation result covers the noise data in the noise distribution diagram, adding corresponding variation of the noise parameter into the library file of MOS transistor as the MOS transistor model enclosing statistical variation of noise. The model obtained by the present invention is more precise.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
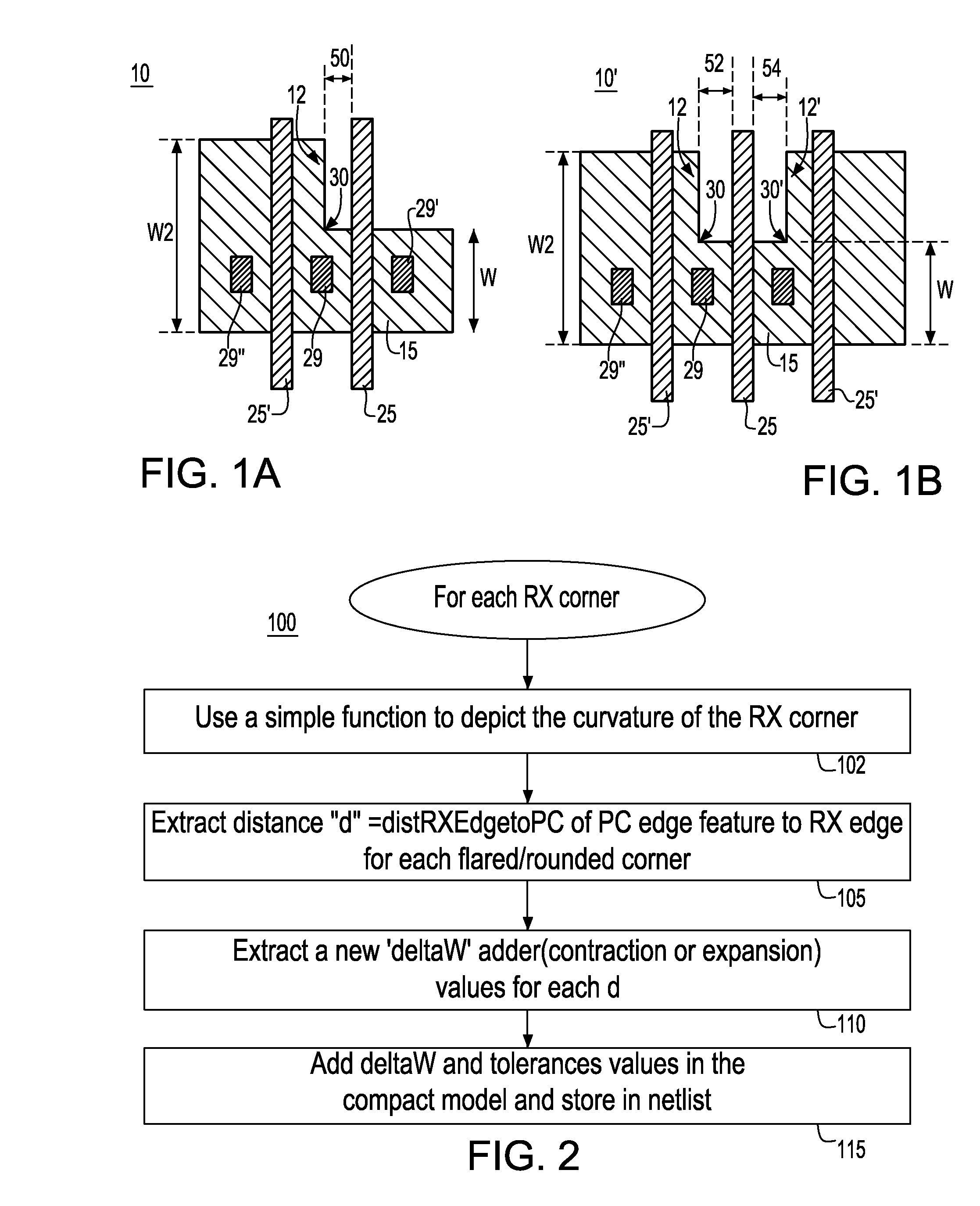
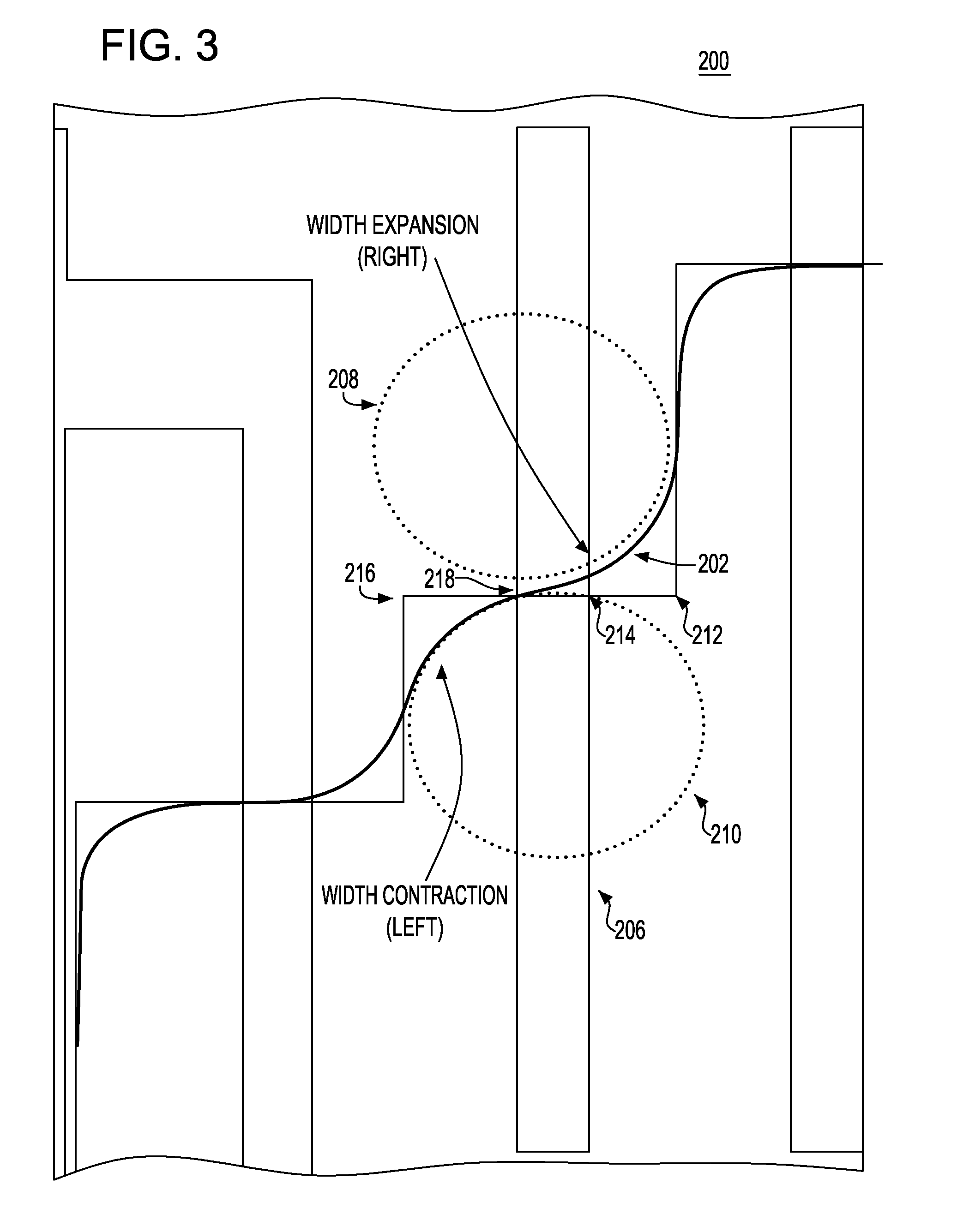
Methodology for improving device performance prediction from effects of active area corner rounding
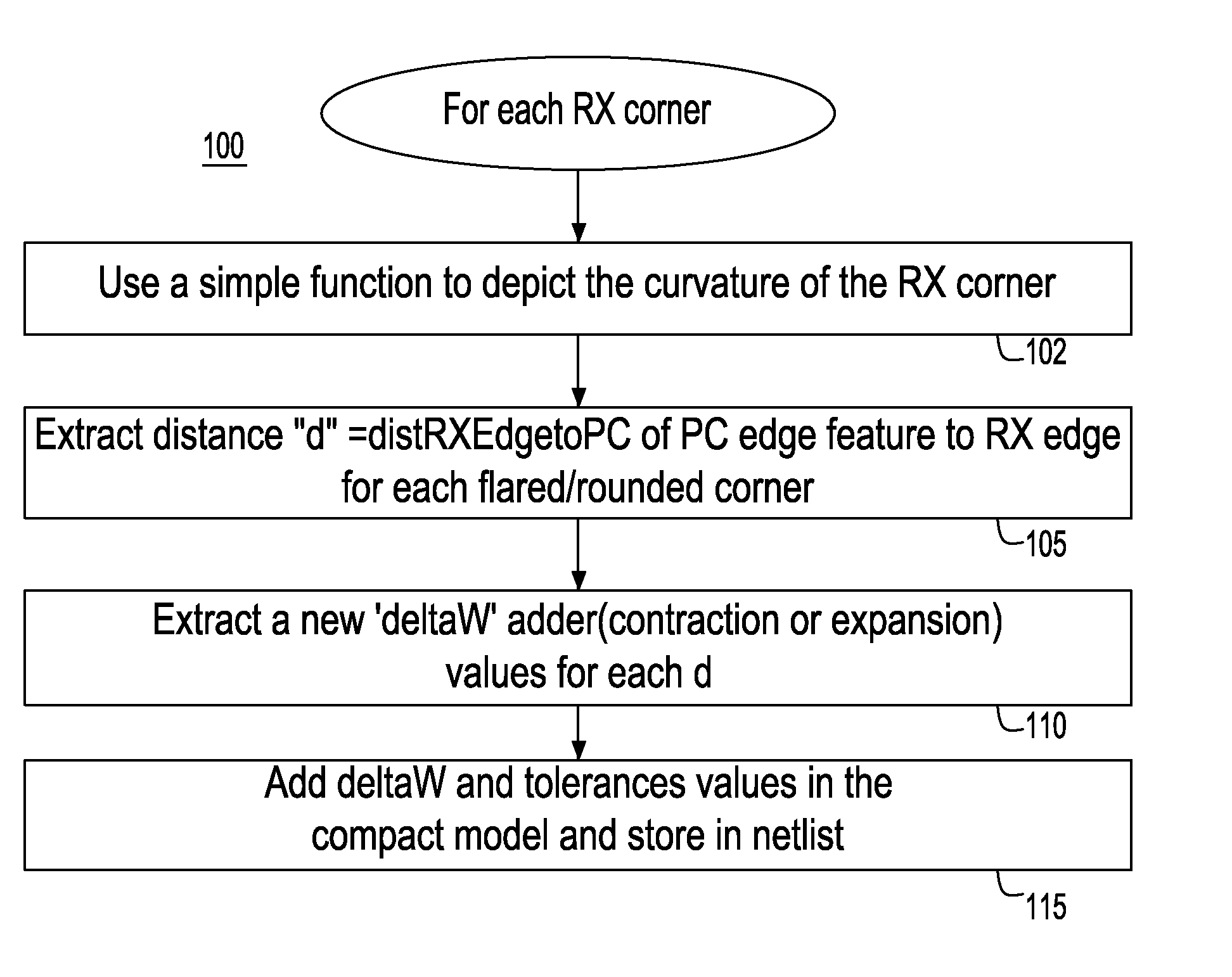
InactiveUS20090178012A1Shrinking and increase of size of deviceAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDetecting faulty computer hardwareNetlistPhotolithography
A system and method for modeling a semiconductor transistor device structure having a conductive line feature of a designed length connected to a gate of a transistor device in a circuit to be modeled, the transistor including an active device (RX) area over which the gate is formed and over which the conductive line feature extends. The method includes providing an analytical model representation including a function for modeling a lithographic flare effect impacting the active device area width; and, from the modeling function, relating an effective change in active device area width (deltaW adder) as a function of a distance from a defined edge of the RX area. Then, transistor model parameter values in a transistor compact model for the device are updated to include deltaW adder values to be added to a built-in deltaW value. A netlist used in a simulation includes the deltaW adder values to more accurately describe the characteristics of the transistor device being modeled including modeling of lithographic corner rounding effect on transistor device parametrics.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com