Microfluidic Analysis Equipment
A device, analyte technology, applied in the direction of fluid controller, biochemical device and method, determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as the limitation of the degree to which the speed at which the droplet can move can be changed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0082] Apparatus suitable for sequencing polynucleotide DNA analytes according to the present invention will now be illustrated by the following figures and description.
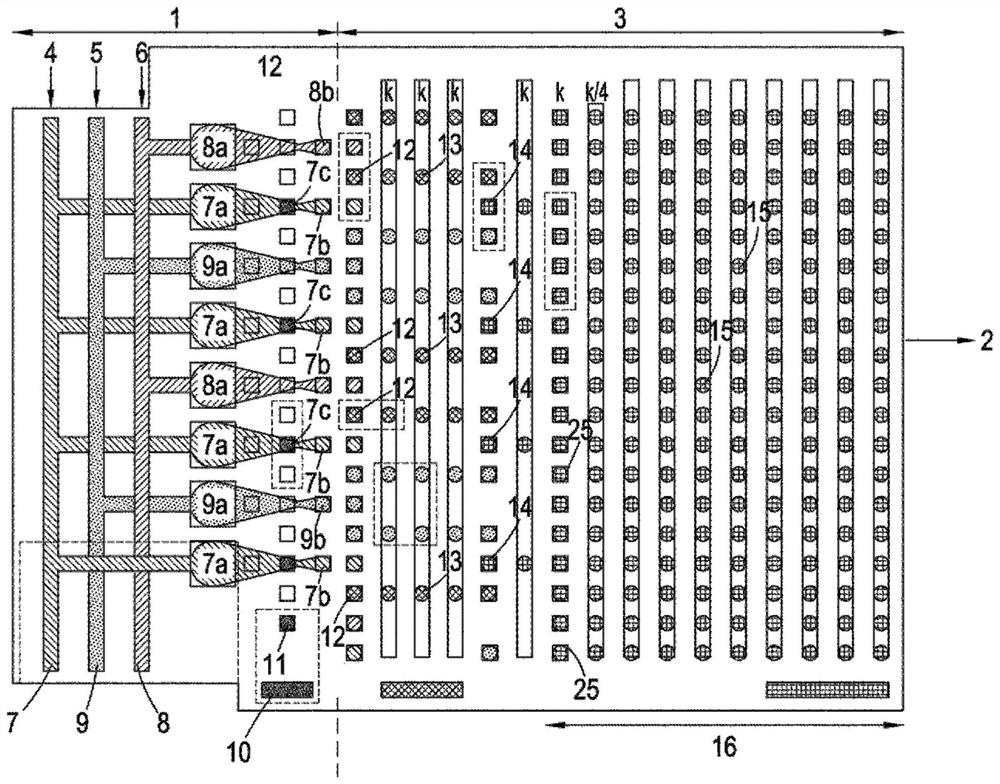
[0083] figure 1 A top view of a microfluidic substrate is shown comprising a droplet preparation area 1 and a droplet manipulation area 3 integrated into a single unit made of transparent plastic. in the substrate. 1 includes regions 7, 8, and 9 containing fluids attached to inlets 4, 5, and 6, which introduce pyrophosphate hydrolysis streams, inorganic pyrophosphatase streams, and various Detect the flow of chemicals and enzymes required to identify nucleoside triphosphates according to one of our earlier patent applications. These streams are then delivered to orifices 7a, 8a, and 9a, respectively, from which various droplets 7b, 8b, and 9b are produced (eg, using a drop-dispensing head or by cutting out of larger intermediate droplets). 10 is a reservoir containing paramagnetic polymer composite microb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com