Method for reducing degradation of complex ferrous iron under aerobic conditions
A ferrous and complexing technology, applied in the field of liquid-phase desulfurization and denitrification, can solve the problems of high operating cost and a large amount of waste liquid, and achieve the effect of saving cost, avoiding degradation and reducing cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
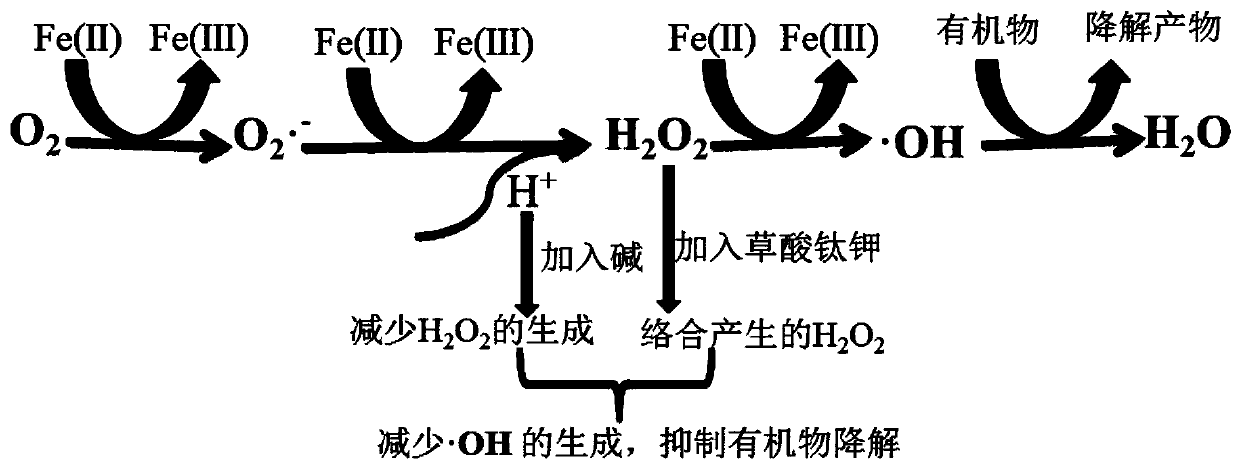
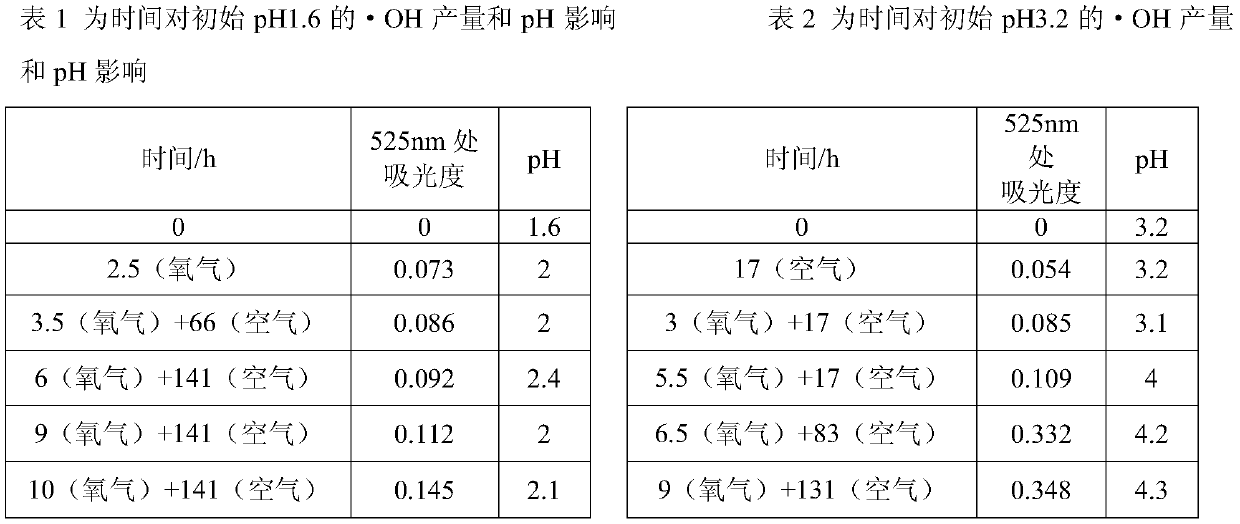
[0024] This embodiment provides a method for reducing the degradation of complexed ferrous iron under aerobic conditions, from which, the effect of initial pH on FeSO under aerobic conditions can be determined. 4 The influence of hydroxyl radical output in the aqueous solution, the steps are as follows:
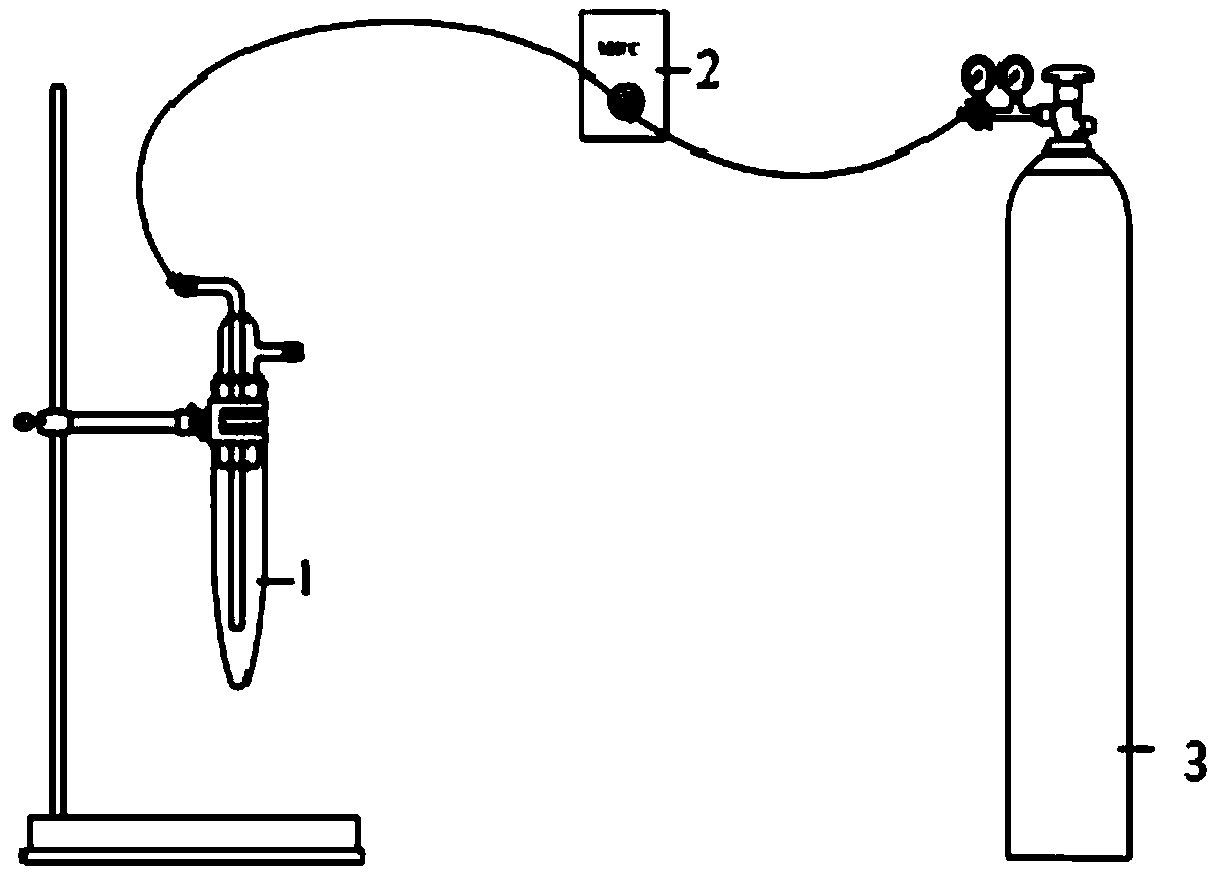
[0025] Weigh 0.02484g of salicylic acid, dissolve it with 2mL of absolute ethanol, dilute to a 100mL volumetric flask, mix well, and prepare a 1.8mmol / L salicylic acid solution. Weigh 0.1251g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was fixed to a 250mL volumetric flask and configured as 1.8mmol / L FeSO 4 solution. Take 4mL salicylic acid solution and 4mL FeSO 4 After the solution is mixed, adjust the pH of the solution with sulfuric acid or sodium hydroxide, and add ultrapure water to make it up to 10 mL, then put it into a bubbling tube, and inject oxygen into it for bubbling. Test the absorbance and pH at regular intervals, and determine the amount of hydroxyl radicals by measuring the absorban...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The present embodiment provides a method for reducing the degradation of complexed ferrous iron under aerobic conditions, from which, the impact of initial pH on the production of hydroxyl radicals in Fe(II)-EDTA aqueous solution under oxygen conditions can be determined, the steps are as follows:
[0032] Weigh 0.02484g of salicylic acid, dissolve it with 2mL of absolute ethanol, dilute to a 100mL volumetric flask, mix well, and prepare a 1.8mmol / L salicylic acid solution. Weigh 0.05004g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 0.06696g disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate were fixed to a 100mL volumetric flask, and configured as a 1.8mmol / L Fe-EDTA solution. After mixing 4mL salicylic acid solution and 4mL Fe-EDTA solution, adjust the pH of the solution with sulfuric acid or sodium hydroxide, add ultrapure water to make it 10mL, then put it into the bubbling tube, and let oxygen flow in for bubbling. Bubble; test absorbance and pH at regular intervals, determine the amount of hydroxyl ra...
Embodiment 3
[0037] This embodiment provides a method for reducing the degradation of complexed ferrous iron under aerobic conditions, from which, it can be determined that the intermediate product H 2 o 2 To the influence of the hydroxyl radical output in the Fe-EDTA aqueous solution under the condition of passing oxygen, the steps are as follows:
[0038] Take 4mL of 1.8mmol / L Fe(II)-EDTA solution with a pH of 4.4, add 4mL of 1.8mmol / L salicylic acid solution, and add ultrapure water to make the volume to 10mL, or take 1.8mmol / L with a pH of Add 4mL of 4.4 Fe-EDTA solution, add 4mL of 1.8mmol / L salicylic acid solution, and add 2mL of 0.1mol / L titanium potassium oxalate solution (3.54g constant volume 100mL), then put the two samples into the bubbler tube respectively, Bubble with oxygen supply gas. Test the absorbance and pH at regular intervals, and determine the amount of hydroxyl radicals by measuring the absorbance of hydroxybenzoic acid at 525nm. The greater the absorbance at 525n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com