Non-real-time data exchange method and system and computer equipment
A data exchange, non-real-time technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of high consumption and trouble of data exchange
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
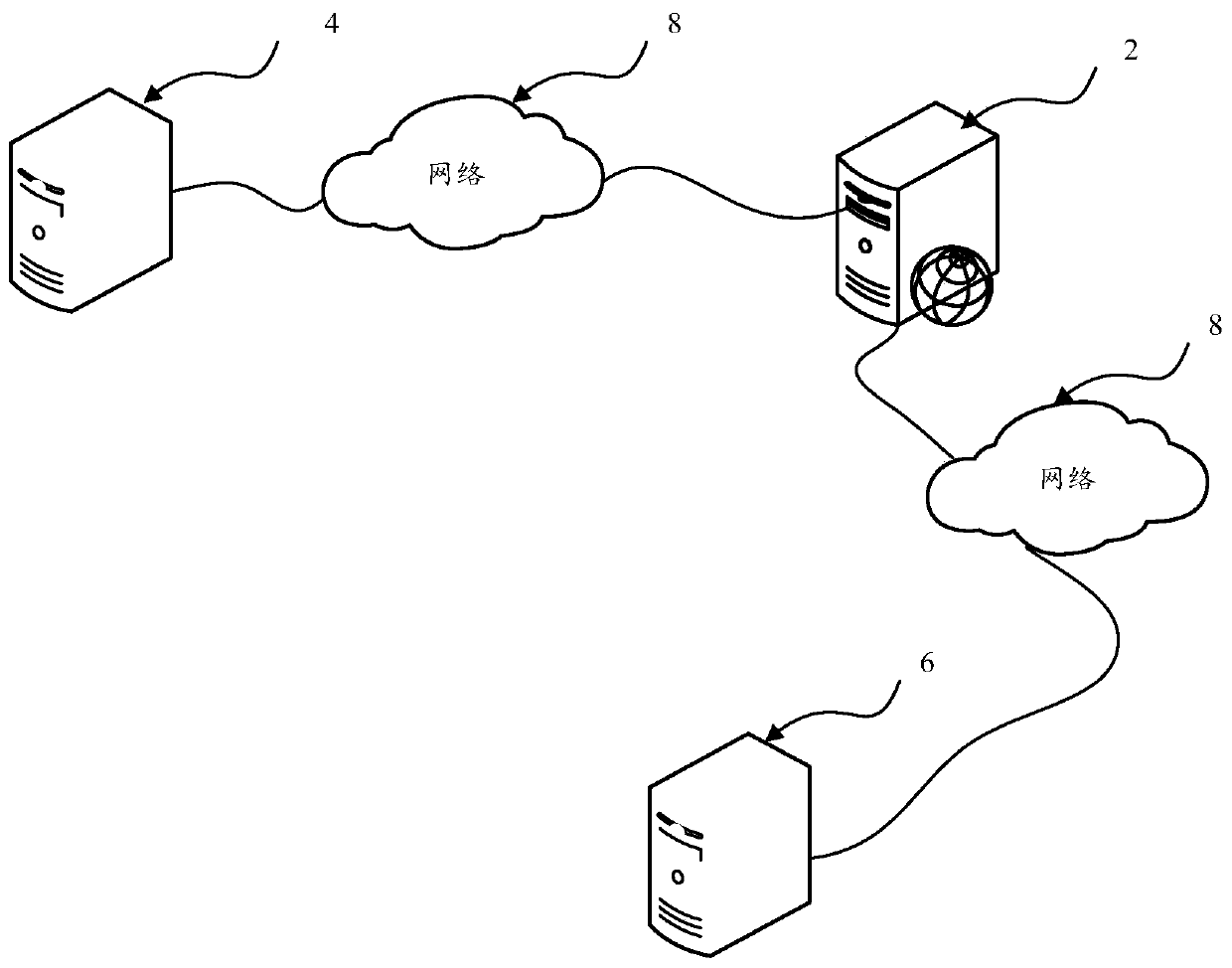
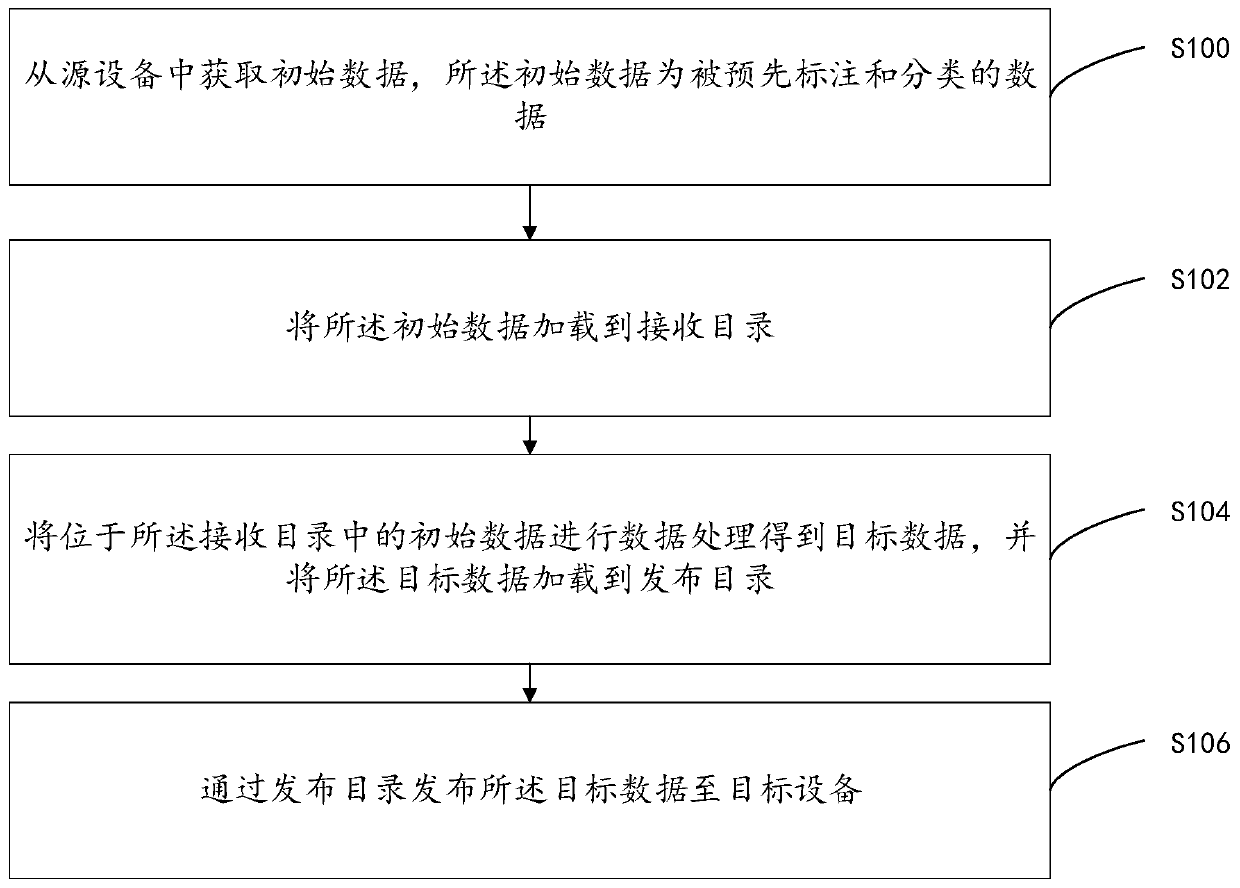
[0059] refer to figure 2 , shows a flow chart of the steps of the non-real-time data exchange method of the embodiment of the present invention. It can be understood that the flowchart in this method embodiment is not used to limit the sequence of execution steps. An exemplary description is given below taking the computer device 2 as the execution subject. details as follows.
[0060] Step S100, acquiring initial data from the source device 4, the initial data is pre-marked and classified data.
[0061] Exemplarily, the initial data may include auto insurance underwriting data, auto insurance claims data, personal accident data and reinsurance data.
[0062] Exemplarily, the initial data includes a signal file (.ok or .ok.ing), a system number, a batch number, and a list of batch files. Among them, the initial data of the same batch has data dependencies before and after; if the initial data has dependencies, it is divided into batch data, and the batch data can be seria...
Embodiment 2
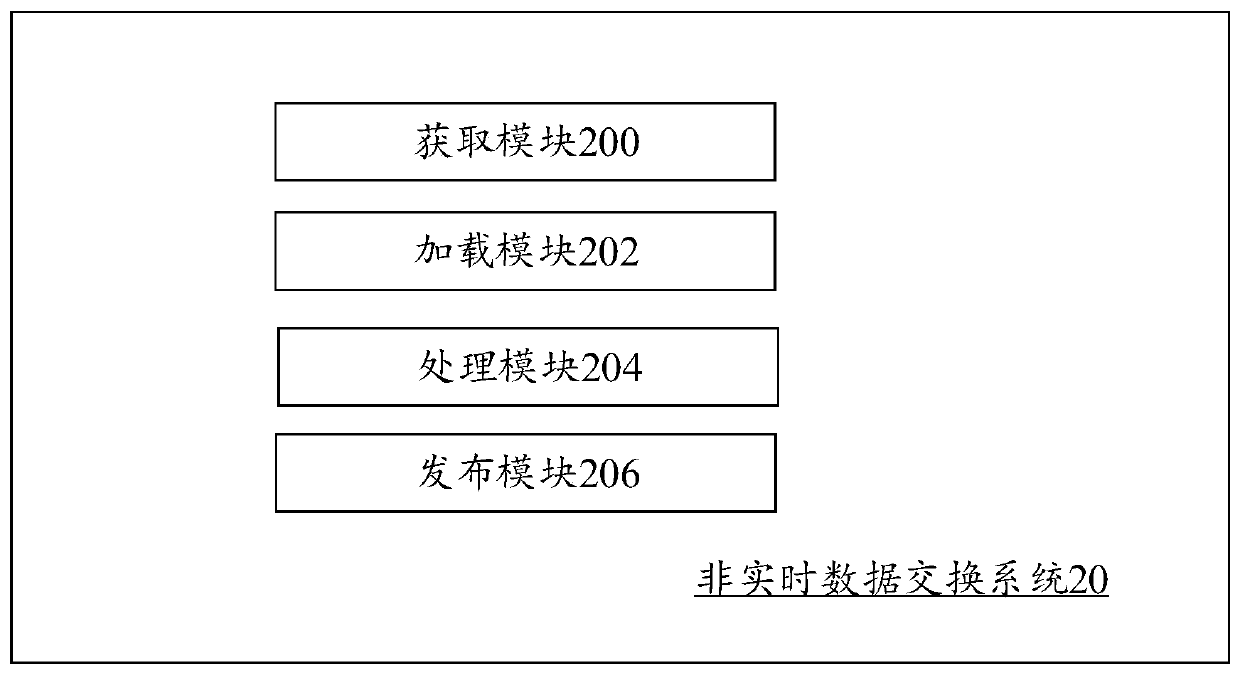
[0100] image 3It is a schematic diagram of program modules of Embodiment 2 of the non-real-time data exchange system of the present invention. The non-real-time data exchange system 20 may include or be divided into one or more program modules, one or more program modules are stored in a storage medium, and executed by one or more processors to complete the present invention, and may Realize the above-mentioned non-real-time data exchange method. The program module referred to in the embodiment of the present invention refers to a series of computer program instruction segments capable of completing specific functions, which is more suitable than the program itself to describe the execution process of the non-real-time data exchange system 20 in the storage medium. The following description will specifically introduce the functions of each program module of the present embodiment:
[0101] The acquisition module 200 is configured to acquire initial data from the source devi...
Embodiment 3
[0114] refer to Figure 4 , is a schematic diagram of the hardware architecture of the computer device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. In this embodiment, the computer device 2 is a device capable of automatically performing numerical calculation and / or information processing according to preset or stored instructions. The computer device 2 may be a rack server, a blade server, a tower server or a cabinet server (including an independent server, or a server cluster composed of multiple servers) and the like. As shown in the figure, the computer device 2 at least includes, but is not limited to, a memory 21 , a processor 22 , a network interface 23 , and a non-real-time data exchange system 20 that can communicate with each other through a system bus.
[0115] In this embodiment, the memory 21 includes at least one type of computer-readable storage medium, and the readable storage medium includes flash memory, hard disk, multimedia card, card-type memory (f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com