Cutting method for improving utilization rate of monocrystalline silicon rod
A cutting method and monocrystalline silicon ingot technology, applied in fine working devices, stone processing equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the carbon footprint consumption of monocrystalline silicon wafers, increasing production costs, and consuming a large amount of electric energy, etc., to achieve Improve effective utilization, save processing costs, and save costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
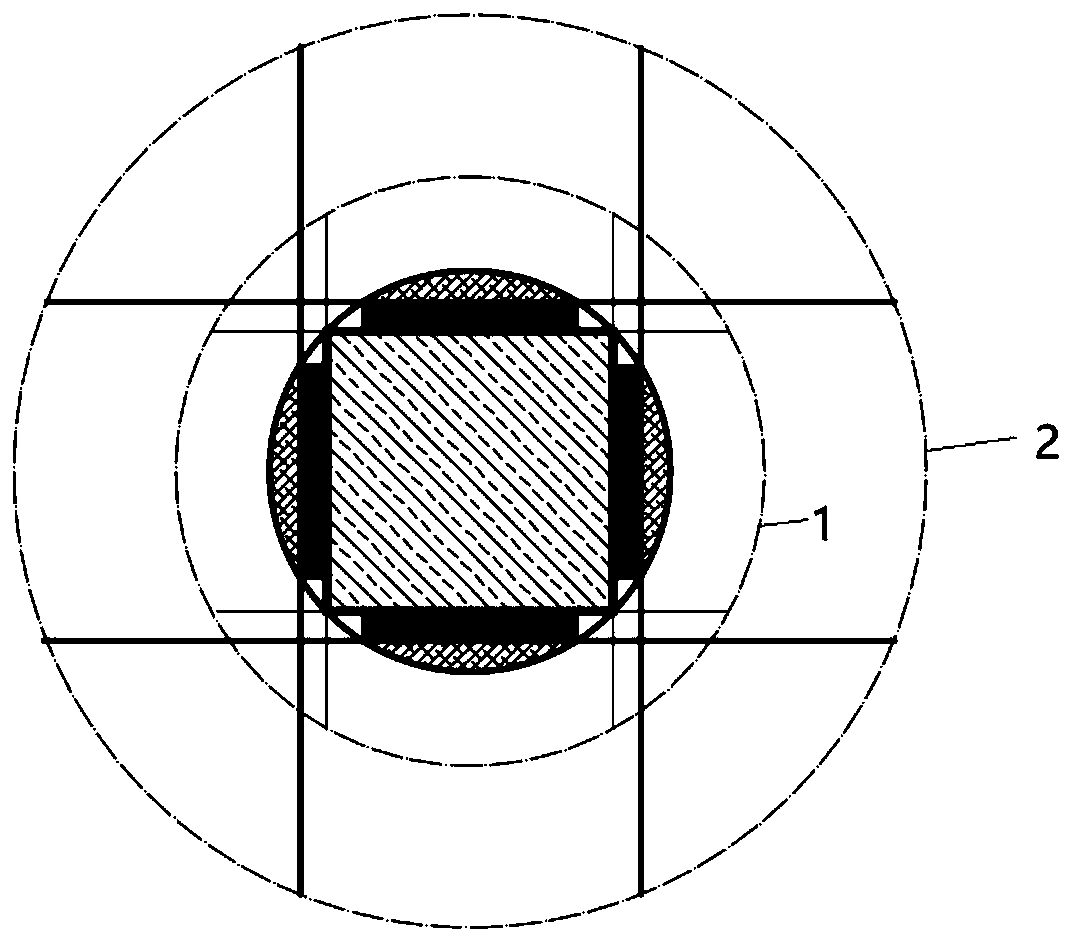
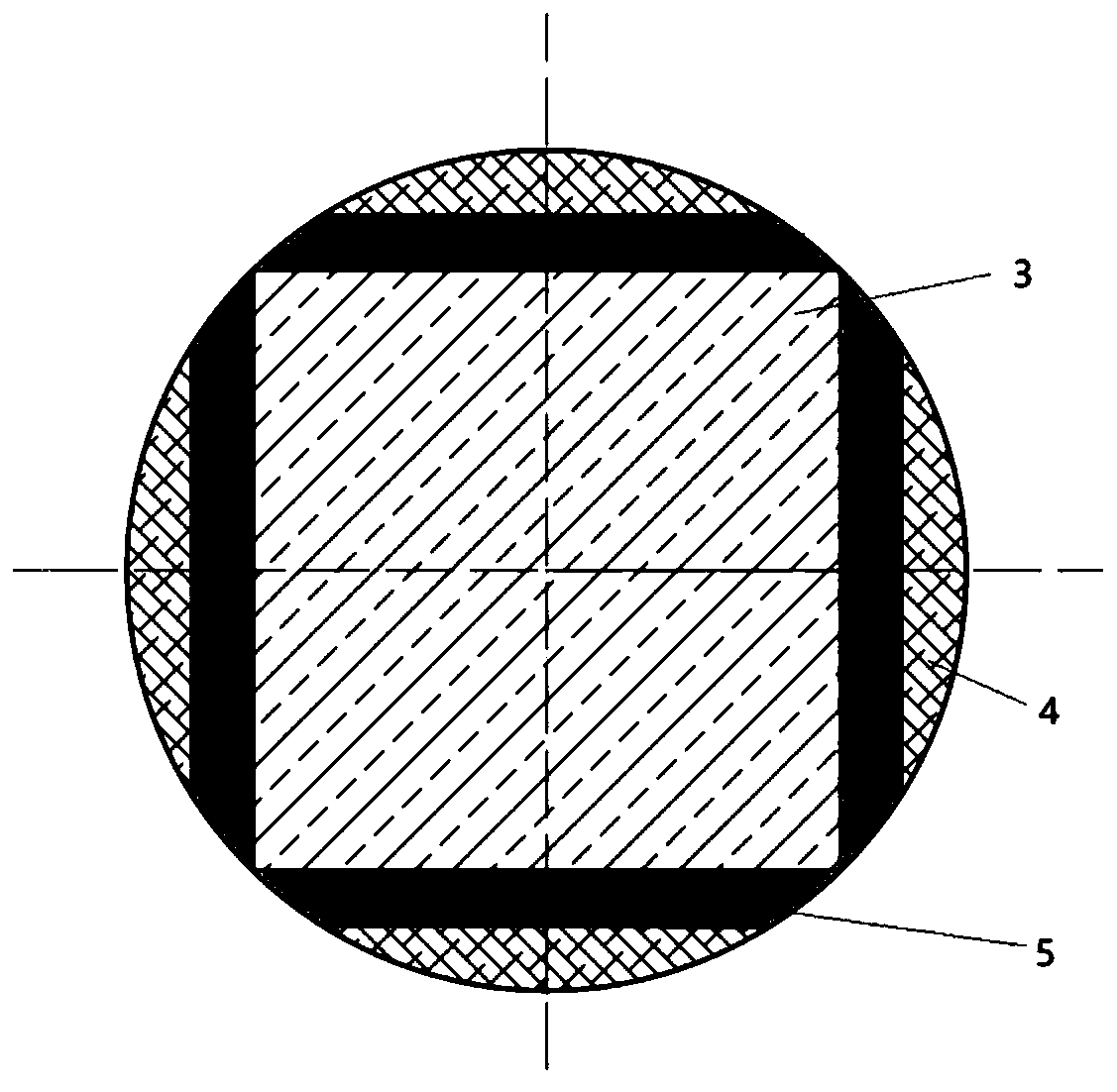
[0021] 1. Cut the truncated single crystal round bar with a length of 650mm and a diameter of 300mm, using the inner network cable 1 and the outer network cable 2 to cut a single crystal square bar 3 with a side length of 210mm, and produce four pieces of 20mm thick and 650mm long A single-crystal slab 5 with an arc and four arch-shaped single-crystal edges 4 with a thickness of about 25 mm.
[0022] 2. Bond a certain amount of monocrystalline slabs together with hydrosol, and use a diamond wire cutting machine to cut the two sides of the monocrystalline slabs in arcs to produce a rectangular parallelepiped silicon block with a side length of 158mm and a thickness of 20mm.
[0023] 3. Bond the cuboid silicon blocks together with water sol, cut them into squares with a size of 158mm, and use water sol to bond them to form a composite "square rod" with a length of 640-650mm.
[0024] 4. Put the square bar produced in step (3) on the surface after polishing, and slice it with a d...
Embodiment 2
[0027] 1. Cut the truncated single crystal round bar with a length of 650mm and a diameter of 300mm, using the inner network cable 1 and the outer network cable 2 to cut a single crystal square bar 3 with a side length of 210mm, and produce four pieces of 20mm thick and 650mm long A single-crystal slab 5 with an arc and four arch-shaped single-crystal edges 4 with a thickness of about 25 mm.
[0028] 2. Bond a certain amount of monocrystalline slabs together with hydrosol, and use a diamond wire cutting machine to cut the two sides of the monocrystalline slabs in arcs to produce a rectangular parallelepiped silicon block with a side length of 158mm and a thickness of 20mm.
[0029] 3. Cut the rectangular parallelepiped silicon block into 158mm in length and 20mm in thickness, and use it as seedlings for casting single crystal silicon, and lay it on the bottom of the crucible to induce the growth of quasi-single crystal crystals with a single crystal orientation.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com