A near-ultraviolet LED using MOCVD technology and its preparation method
A near-ultraviolet, high-tech technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of electronic current leakage, low quantum efficiency and luminous efficiency of devices, and leakage, so as to improve crystal quality, improve polarization effect, reduce The effect of stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
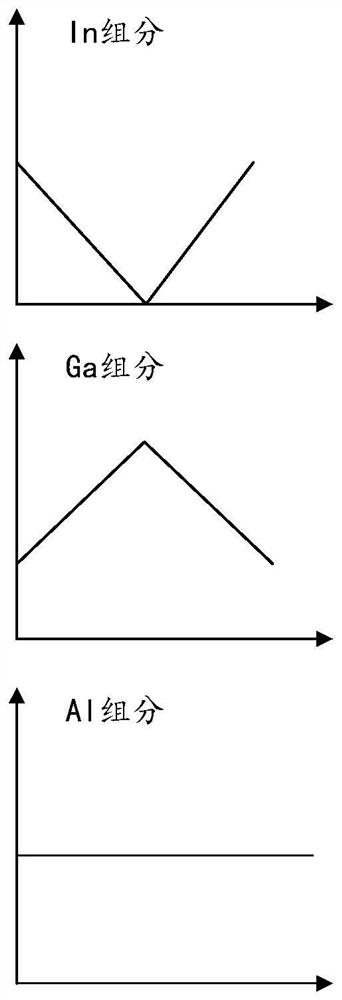
[0042] see figure 1 , this embodiment provides a near-ultraviolet LED 100 using MOCVD technology. The near-ultraviolet LED 100 includes a substrate 110 and a buffer layer 120, a high-temperature layer 130, and an n-type Al layer grown sequentially on the substrate 110. m Ga 1-m N layer 140, light emitting active region 150, p-type electron blocking layer 160, p-type Al n Ga 1-n N layer 170 and contact layer 180, wherein the material of the light emitting active region 150 includes In x Ga 1-x N and Al y Ga 1-y N, the material of the p-type electron blocking layer 160 includes Al y1 In x1 Ga 1-y1- x1 N, 0.001≤x<y≤1, y, m, n are all less than y1.
[0043] see figure 2 , along the growth direction of the p-type electron blocking layer 160, the Al composition value y1 remains unchanged, the In composition value x1 first decreases and then increases, and the Ga composition value 1-y1-x1 first increases and then decreases. Preferably, the In composition value x1 present...
no. 2 example
[0050] This embodiment provides a near-ultraviolet LED 100 using MOCVD technology, which is similar to the structure in the first embodiment, except that the lowest value x1 of the In composition in the p-type electron blocking layer 160 is greater than zero.
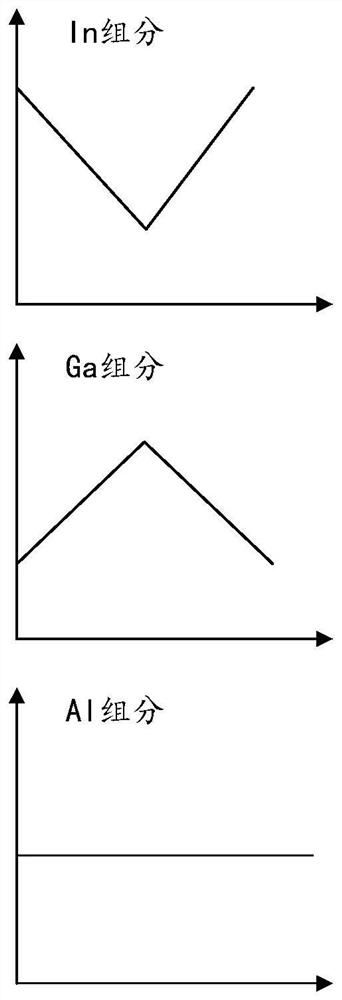
[0051] see image 3 , along the growth direction of the p-type electron blocking layer 160, the Al composition value y1 remains unchanged, the In composition value x1 presents a V-shaped gradual change, and the Ga composition value 1-y1-x1 presents an inverted V-shaped gradual change. Furthermore, the Ga composition value 1-y1-x1 is the highest at the position where the In composition value x1 is the lowest.
[0052] Wherein, the In composition value x1 is greater than zero at the lowest point, that is to say, the p-type electron blocking layer 160 is AlInGaN along the growth direction.
[0053] In addition, in the p-type electron blocking layer 160 , in the direction from the edge to the middle, the Mg doping concentr...
no. 3 example
[0058] see Figure 4 , this embodiment provides a method for preparing a near-ultraviolet LED 100 using MOCVD technology, which can be used to prepare the near-ultraviolet LED 100 in the first embodiment or the second embodiment. The preparation method of the near-ultraviolet LED 100 is mainly based on the MOCVD epitaxial growth technology, and specifically includes the following steps:
[0059] S1: see Figure 5 , on the substrate 110, the buffer layer 120, the high temperature layer 130, the n-type Al m Ga 1-m N layer 140 and light emitting active region 150 .
[0060] First, grow a GaN buffer layer 120 with a thickness of 1 micron to 3 microns on the PSS substrate 110 in a hydrogen atmosphere at a temperature of 800° C. to 1000° C. in the reaction chamber of the MOCVD epitaxial equipment.
[0061] Next, the temperature is increased to 1000° C.˜1150° C. to grow the high-temperature layer 130 with a thickness of 1 μm˜4 μm; the growth pressure is controlled between 100 mba...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com