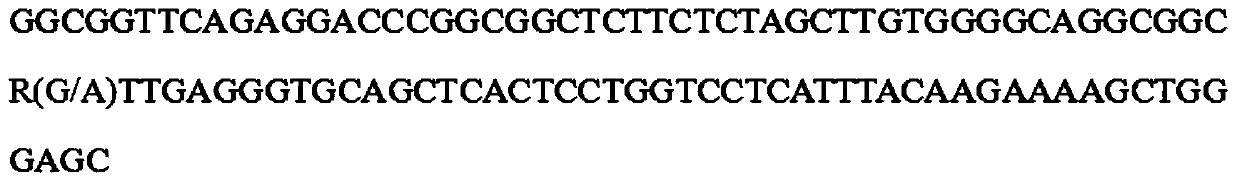SNP molecular marker related to pig fetal distance traits
A molecular marker and spacing technology, applied in recombinant DNA technology, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of small number of samples, difficult identification of major genes, single variety, etc., and achieve the effect of high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1: Genotyping and detection
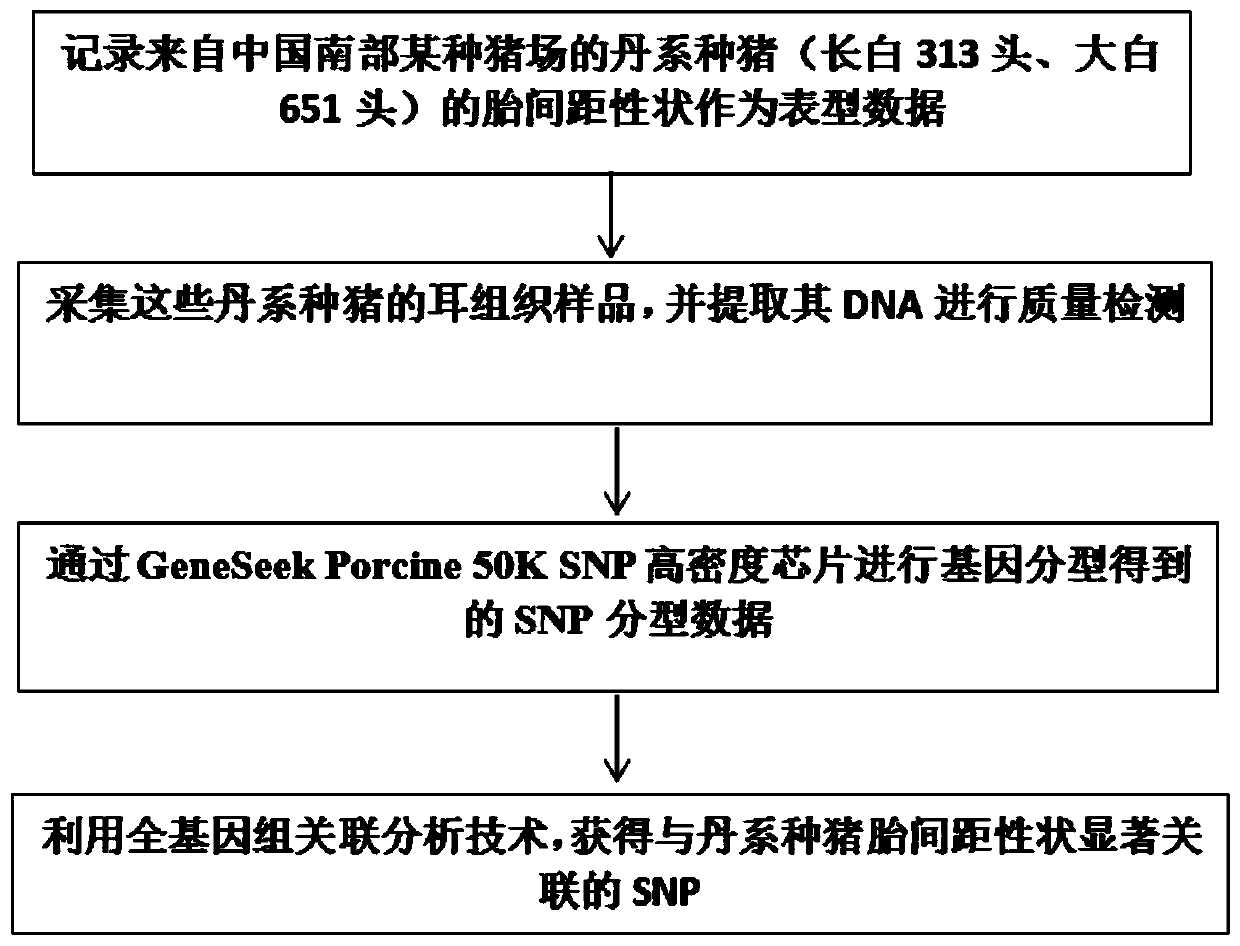
[0035](1) Genomic DNA was extracted and tested for quality by collecting Danish pig ear samples from a pig farm in southern China, and genotyping with GeneSeek Porcine 50K SNP high-density chip to obtain SNP typing data.
[0036] Use Plink1.9 software to convert the original data into VCF format, and then use this software to perform quality control on VCF format files: Specifically:
[0037] 1) maf 0.01: remove the SNP sites whose minimum allele frequency is less than 1%;
[0038] 2) geno 0.1: SNP sites whose genotype detection rate is less than 90% are eliminated;
[0039] 3) mind 0.1: Eliminate individuals whose genotype deletion rate is greater than 10%;
[0040] 4) hwe le-6: remove the SNP sites with Hardy-Weinberg balance test P value less than 10-6,
[0041] 5) Use beagle 4.1 software to fill in missing genotypes on the chip data after quality control, the command is as follows:
Embodiment 2
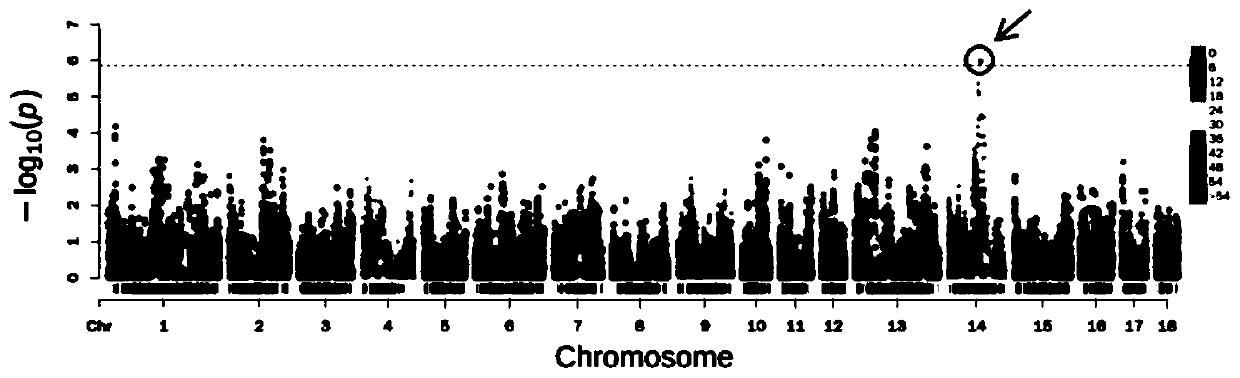
[0044] Embodiment 2: The method in the genome-wide association analysis of pig-fetal spacing traits
[0045] The phenotypes of Danish pigs' fetal spacing used in the association analysis with genotypes were from a certain pig farm in southern China, with a total of 964 individuals. Genome-wide association analysis (GWAS) was performed using the FarmCPU model in the MVP package under the R language. The specific model formula is as follows: y i = M i1 b 1 +M i2 b 2 +...+M it b t +S ij d j +e i (1) where y i is the trait observation value of the i-th individual; M i1 , M i2 ,...,M it is the genotype of t possible associated sites added to the model, and this part is empty during the first iteration; b 1 , b 2 ,...,b t is the corresponding effect value of the possible association sites added to the model; S ij is the genotype of the jth genetic marker of the i individual; d j is S ij The corresponding effect value of e i is the residual vector; y i = u i +e ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3: Application of rs328285068 molecular marker typing method in correlation analysis of pig-fetal spacing traits / correlation analysis between rs328285068 molecular marker (SWQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence table) and pig-fetal spacing traits:
[0052] Association analysis of the rs328285068 molecular marker and pig fetal spacing traits using a mixed linear model (MLM). The specific model is as follows:
[0053] the y ijklmn =μ+G i +HYS j +Breed+ID m +ε ijklmn
[0054] Among them, y ijklmn is the phenotypic value of the mth individual inter-fetal distance trait; μ is the group mean; G i is the genotype effect, HYS k is the joint effect of place of birth, year of birth and season of birth (fixed effect); Breed is the breed effect (fixed effect); ID m is the individual additive effect (random effect), ε ijklmno is the residual effect of the model, and the F test was used to analyze the significance of the inter-internal spacing traits among the three genotype ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com