Control method of expansion coefficient of light weight dense near zero expansion metal matrix composites
A composite material and near-zero expansion technology, which is applied in the field of lightweight near-zero-expansion composite materials, can solve problems such as easy damage, inability to change the temperature range of low thermal expansion coefficient, and inability to realize a wide range of thermal expansion coefficient, etc. The method is simple and easy to implement, and the effect of good mechanical properties and electrical and thermal conductivity characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
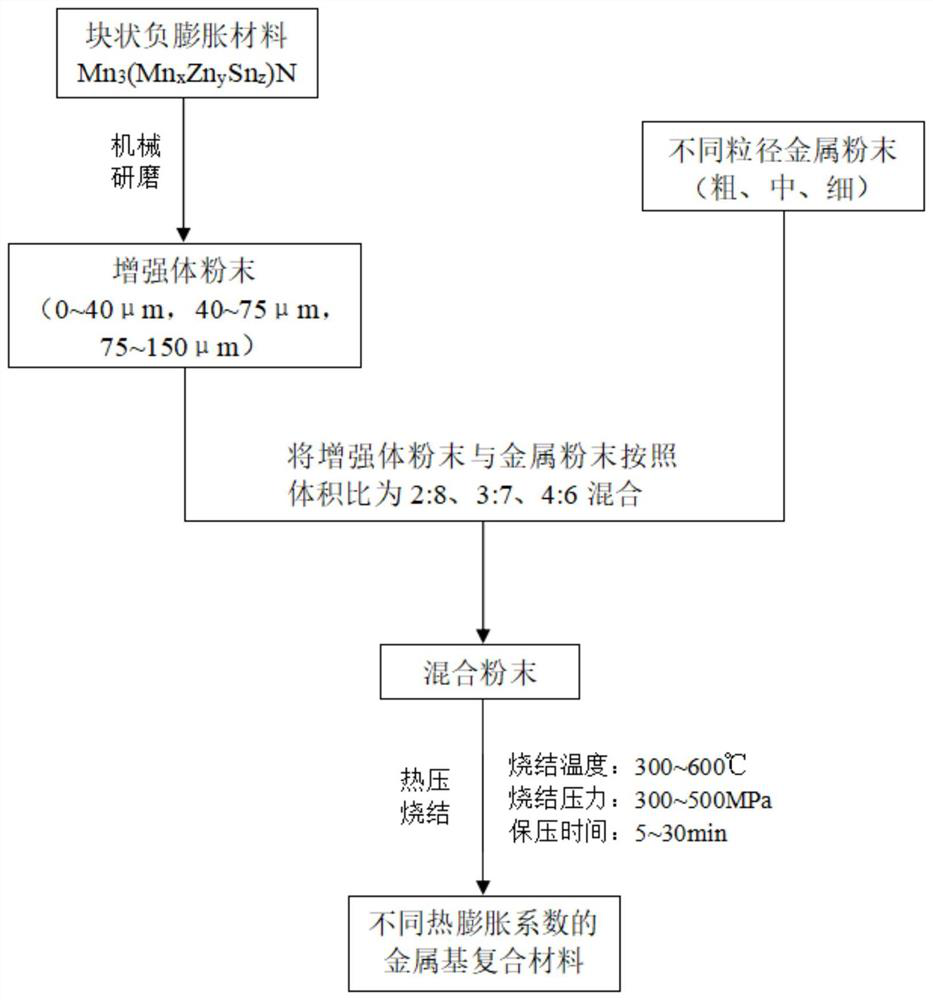
[0031] refer to figure 1 As shown, it is a flow chart of a method for regulating the expansion coefficient of a light-weight dense near-zero-expansion metal matrix composite material according to an embodiment of the present invention. The figure includes the following steps:
[0032] Negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 ) Preparation of N powder: the bulk negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N is ground with a vacuum ball mill, and sieved to obtain a powder of 75-150 μm, and set aside.
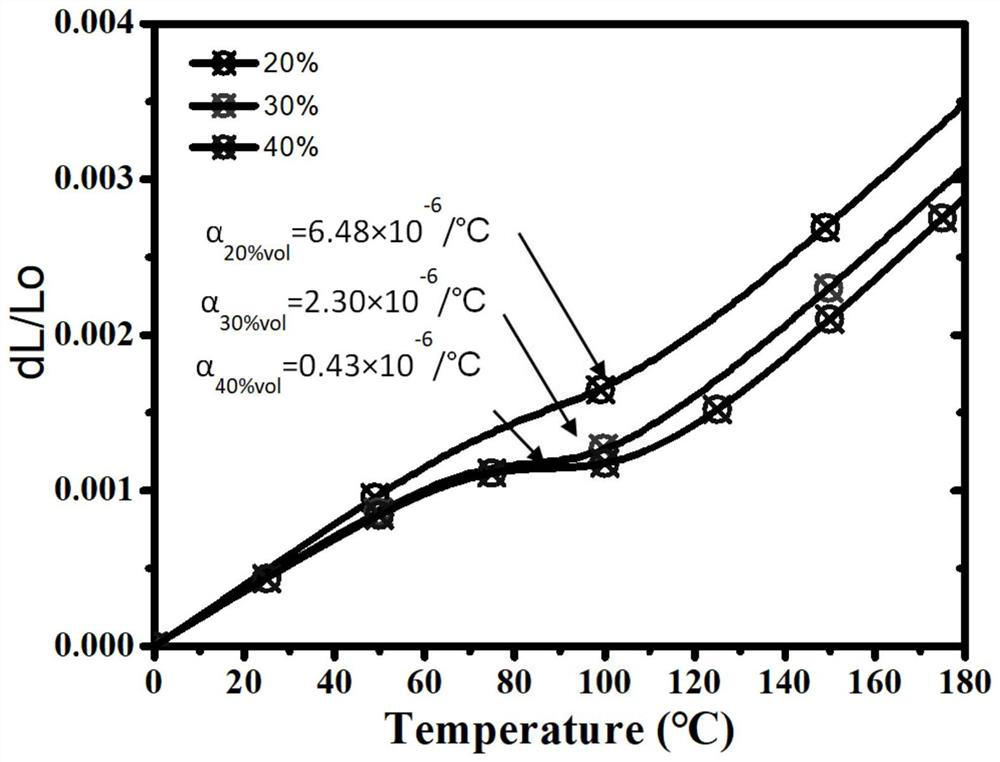
[0033] Then the prepared negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N powder and pure aluminum powder with a purity of 99.95% and a particle size of 25 μm are mixed according to the volume ratio of 2:8, 3:7, and 4:6 respectively. The mixing time is 30 hours, and the mixing speed is 150r / min. The first composite material mixed powder, the second composite material mixed powder and the third composite material mixed powder are respec...
Embodiment 2
[0038] refer to figure 1 As shown, it is a flow chart of a method for regulating the expansion coefficient of a light-weight dense near-zero-expansion metal matrix composite material according to an embodiment of the present invention. The figure includes the following steps:
[0039] Negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 ) Preparation of N powder: the bulk negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N is ground with a vacuum ball mill, and sieved to obtain a powder of 2-40 μm, and set aside.
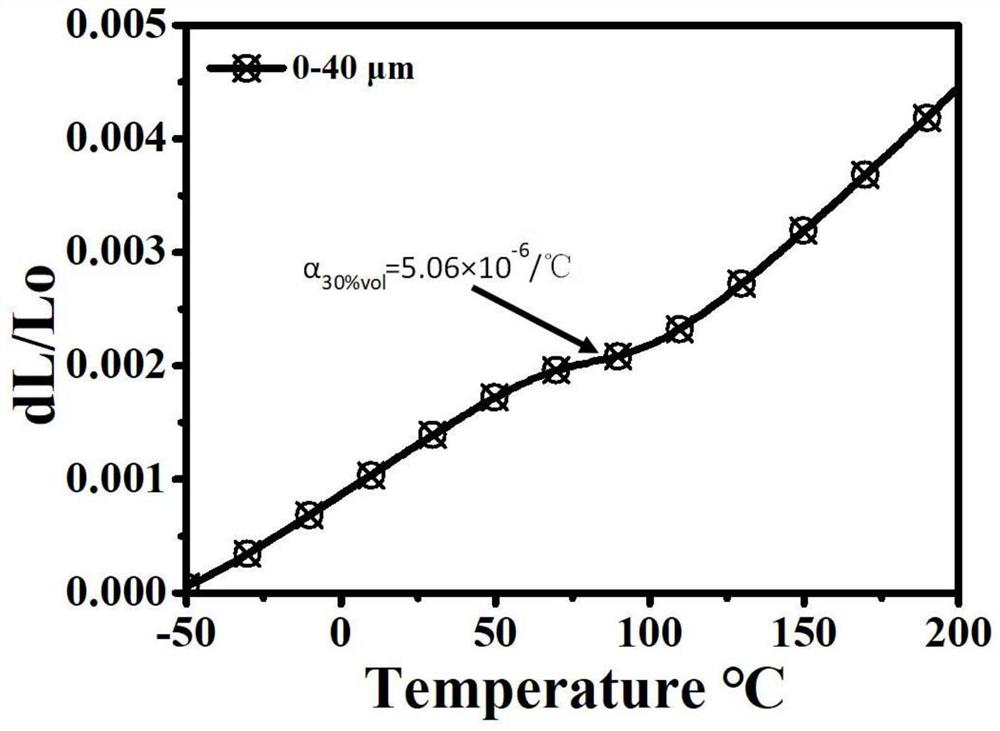
[0040] Then the prepared negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N powder and aluminum powder with a purity of 99.95% and a particle size of 25 μm were mixed according to a volume ratio of 3:7, the mixing time was 30 hours, and the mixing speed was 150 r / min to obtain a composite material mixing powder for later use.
[0041] Put the prepared composite material mixed powder into a vacuum hot-press sintering furnace for hot-press s...
Embodiment 3
[0044] refer to figure 1 As shown, it is a flow chart of a method for regulating the expansion coefficient of a light-weight dense near-zero-expansion metal matrix composite material according to an embodiment of the present invention. The figure includes the following steps:
[0045] Negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 ) Preparation of N powder: the bulk negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N is ground with a vacuum ball mill, and sieved to obtain a powder of 40-75 μm, and set aside.
[0046] Then the prepared negative expansion material Mn 3 (Mn 0.1 Zn 0.5 sn 0.4 )N powder and aluminum powder with a purity of 99.95% and a particle size of 25 μm were mixed according to a volume ratio of 3:7, the mixing time was 30 hours, and the mixing speed was 150 r / min to obtain a composite material mixing powder for later use.
[0047] Put the prepared composite material mixed powder into a vacuum hot-press sintering furnace for hot-press ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com