Water circulation method and water circulation system for improving surface quality of hot-rolled strip steel
A technology of circulating water system and surface quality, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, workpiece surface treatment equipment, etc., can solve the problems of black and gray on the surface of strip steel, unable to meet production requirements, affecting product surface quality, etc. To achieve the effect of reducing suspended solids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
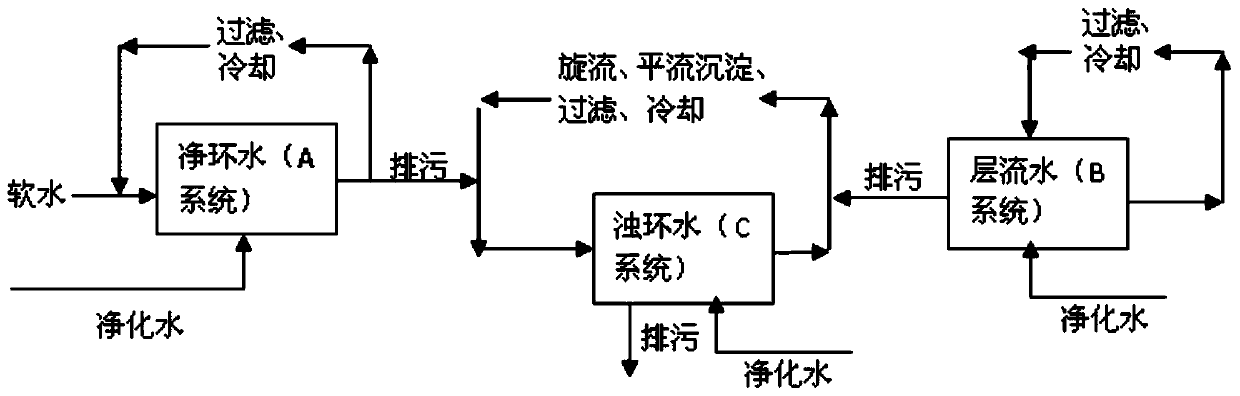
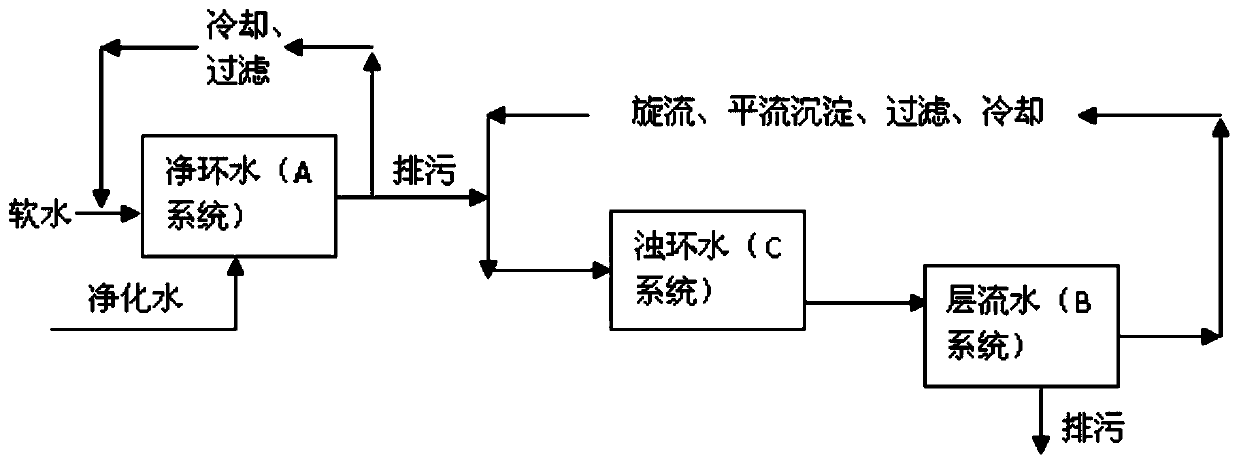
[0047] An embodiment of the present invention provides a water circulation method for improving the surface quality of hot-rolled strip steel, which is implemented based on an indirect cooling circulating water system, a laminar cooling circulating water system and a direct cooling circulating water system. The indirect cooling circulating water system, also known as the net ring water system (referred to as A system), mainly handles the cooling water of the furnace door and beam of the heating furnace, the cooling water of electrical equipment, hydraulic systems, air compressors, instruments and other equipment; laminar flow Cooling circulating water system, also known as laminar flow water system (referred to as B system), mainly handles laminar flow strip steel top spray, bottom spray cooling and side spray water; direct cooling circulating water system, also known as turbid ring water system (abbreviated as C system) , mainly deal with the roll cooling water of the roughing...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Based on the same inventive concept, an embodiment of the present invention provides a water circulation system for improving the surface quality of a hot-rolled strip, and the water circulation system is used to implement the water circulation method of the above-mentioned embodiment 1. see Figure 4 , the water circulation system comprises an indirect cooling circulating water system 100, a laminar cooling circulating water system 200, a direct cooling circulating water system 300 and a controller (not shown), wherein:
[0082] The indirect cooling circulating water system 100 includes a circulating pipeline 14 for circulating the indirect cooling circulating water for users 11 of the indirect cooling circulating water system 100, a replenishing water pipeline 15 for replenishing the indirect cooling circulating water, and a The blowdown pipeline 16 for blowdown of the indirect cooling circulating water. Wherein, a filtering device 12 for filtering the indirect cooli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com