Cutter for cutting gluteal muscle contracture fascia
A technique for shrinking tendons and gluteal muscles, applied in the direction of endoscopic cutting instruments and anatomical instruments, can solve the problems of no protective structure, easy mistakes, and easy handling, etc., to achieve convenient fascia thickness, fast and accurate cutting, and reduce damage effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
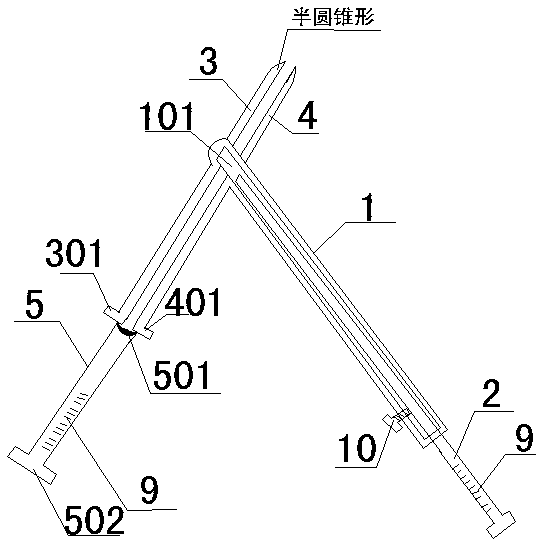
[0038] The invention relates to the field of surgical cutters, and discloses a cutter structure for cutting the contracture fascia of the gluteus muscle. Between the push knife 5.
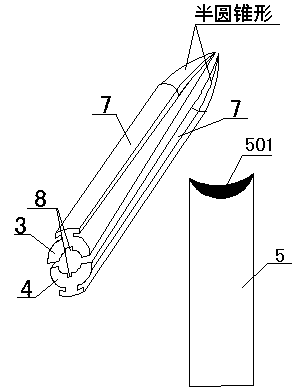
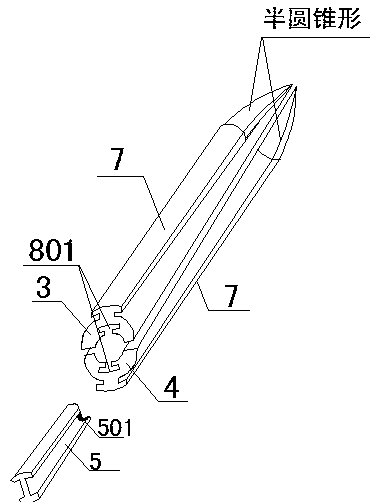
[0039] There are two clamping frames, respectively the first clamping frame 3 and the second clamping frame 4, both of which are semi-cylindrical tubular structures, and their front ends are semi-conical structures, and the two clamping frames are symmetrically arranged in a cylindrical shape. .
[0040] The adjustment column 1 is a cylindrical or ellipsoidal structure, and the inside of the adjustment column 1 is set to be hollow. A bar-shaped groove 101 is opened axially from the adjustment column 1 and runs through both sides. The height of the bar-shaped groove 101 is the same as that of the two clamping frames The diameters are the same, and the two symmetrically arranged clamping frames pass through the bar-shaped groove 101 on the adjustment column 1 .
[0041] An adjustment handle 2 is ar...
Embodiment approach 2
[0047] This embodiment is a further optimization of Embodiment 1. The specific optimization plan is: control the angle between the two symmetrically arranged clamping frames (the first clamping frame 3 and the second clamping frame 4) and the adjustment column 1 120-145 degrees. In this embodiment, the angle between the clamping frame and the adjustment column 1 is set to 120-145 degrees, so that the clamping frame enters the skin obliquely, and the fascia can be clamped without pressing the two clamping frames and the push knife 5, without It will cause damage to the skin and surrounding tissues, and the included angle is set at 120-145 degrees, which is convenient for doctors to hold and operate, simple and effective. Other operations in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment approach 3
[0049] This embodiment is a further optimization of Embodiment 1. The specific optimization plan is: the symmetrical positions of the inner walls of the tubes of the two clamping frames are respectively inwardly recessed to form a chute 8, and the lateral sides of the push knife 5 can be located in the chute 8 inside, see attached figure 2 . After the push knife 5 is slidably connected between the two holders, if no chute is provided on the inner walls of the two holders, the push knife 5 will rotate in the hollow inner wall formed by the two holders. After the rotation, The push knife 5 may not be right against the fascia, which affects the cutting efficiency and may cause damage to surrounding tissues. When the two sides of the push knife 5 are slidably connected in the chute 8, the push knife 5 will not rotate when it slides between the holders, so that no matter whether the push knife mechanism is pushed or pulled out, it is facing the fascia. Cutting tasks can be compl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com