Method for establishing transgenic system of high-sugar variety beet
A method of establishment and transgenic technology, which is applied in the field of establishment of the sugar beet transgenic system, can solve the problems of the reporting of the transgenic method and the unreported method of the sugar beet transgenic method, and achieve the effect of accelerating the transfer and improving the value of the ecological environment quickly and effectively
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Germination and growth of sugar beet seeds
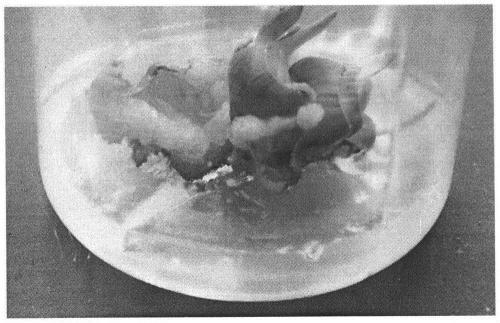
[0044] 1) Select 60 sugar beet seeds harvested in the same year, place them in a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask and add tap water to immerse them, culture them in a shaker at 37°C for 16 hours, wash them with running water for 24 hours, then sow them in a culture bottle containing moist gauze, and place them at 22°C , cultured in a culture room with a light duration of 16h / 8h, see figure 1 .
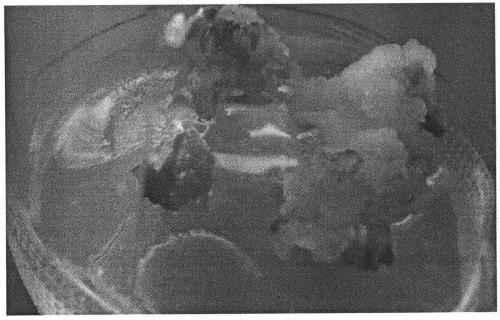
[0045] 2) When the beet seeds germinate small buds, start to record the number of days of growth, and it can be used for experiments when it grows for about 10 days.
[0046] See figure 2 .
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2: Transformation of transgenic sugar beets
[0048] a. Expanded culture of Agrobacterium
[0049] ① With LB solid and liquid medium containing kanamycin; the concentration of kanamycin used is 50mg / L;
[0050] ② In the workbench, use an inoculation loop to draw the preserved strain on the solid medium containing kanamycin, and culture it in the dark at 28°C for 48 hours;
[0051] ③ Take out the bacteria plate, pick a single colony with a sterilized yellow tip and place it in 20ml LB liquid medium containing kanamycin, shake the bacteria at 220rpm at 28°C for 24h;
[0052] ④ Pour the shaken bacterial solution into 200ml LB liquid medium containing kanamycin, shake at 28°C, 220rpm for 8-12h (note: volume ratio: V medium:V bacterial solution=100:1);
[0053] b. Agrobacterium-infected sugar beet
[0054] ① For the beet seedlings that have grown cotyledons, cut off a cotyledon and terminal bud with a scalpel, and put the cut beet upside down in a beaker;
[0055...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Implementation 3: GM sugar beet detection
[0067] 1. Fluorescence detection of young leaves of transgenic sugar beet
[0068] Fluorescence detection was carried out on the newly grown fresh leaves obtained in Example 2. The fluorescence detection steps were as follows: take fresh leaf dorsal epidermis tissue and place it on a glass slide, and drop sterile water to press it for fluorescence detection.
[0069] 2. PCR detection of transgenic sugar beets
[0070] The PCR method was used to detect the fresh leaves, and the primers were designed according to the GFP gene sequence carried on the carrier. The theoretical amplification product size was 516 bp, and the primer sequences were as follows:
[0071] Primer 1 (upstream primer): 5'-ATCCCGCCGGGAATGGTGATTACCGA
[0072] Primer 2 (downstream primer): 5'-GTCGTGCACCATCAGCACGTTATCGA
[0073] The total DNA of fresh sugar beet leaves was extracted by SDS method, and used as a template, under the guidance of primer 1 and pri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com