A2B7 type hydrogen storage alloy containing zirconium or titanium, negative electrode, battery and preparation method
A technology for hydrogen storage alloys and negative electrodes, which is applied in the direction of nickel storage batteries, battery electrodes, alkaline storage batteries, etc., can solve the problems of low L content of hydrogen storage alloys, improve service life, improve self-discharge characteristics and high-temperature discharge capabilities, and improve The effect of activation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0094] Preferably, the method for preparing the hydrogen storage alloy of the present invention includes: a melting step; an alloy flake or alloy ingot forming step; and a heat treatment step. A detailed description is given below.
[0095] will be composed to satisfy the RE x Gd y Ni z-a-b-c mn a al b m c Zr d Ti e The metal raw materials are placed in a vacuum environment for smelting to obtain smelted products. Wherein, each element and its mole fraction are as described above, and will not be repeated here. The relative vacuum degree of the vacuum environment is -0.01~-0.1MPa; preferably -0.02~-0.08MPa; more preferably -0.03~-0.06MPa. The melting temperature is 1200-1600°C, preferably 1300-1500°C, more preferably 1300-1400°C. Stop heating after the metal raw material in the furnace is completely melted, it takes about 10-60 minutes. Such smelting conditions are conducive to prolonging the service life, increasing the maximum discharge capacity and reducing self-...
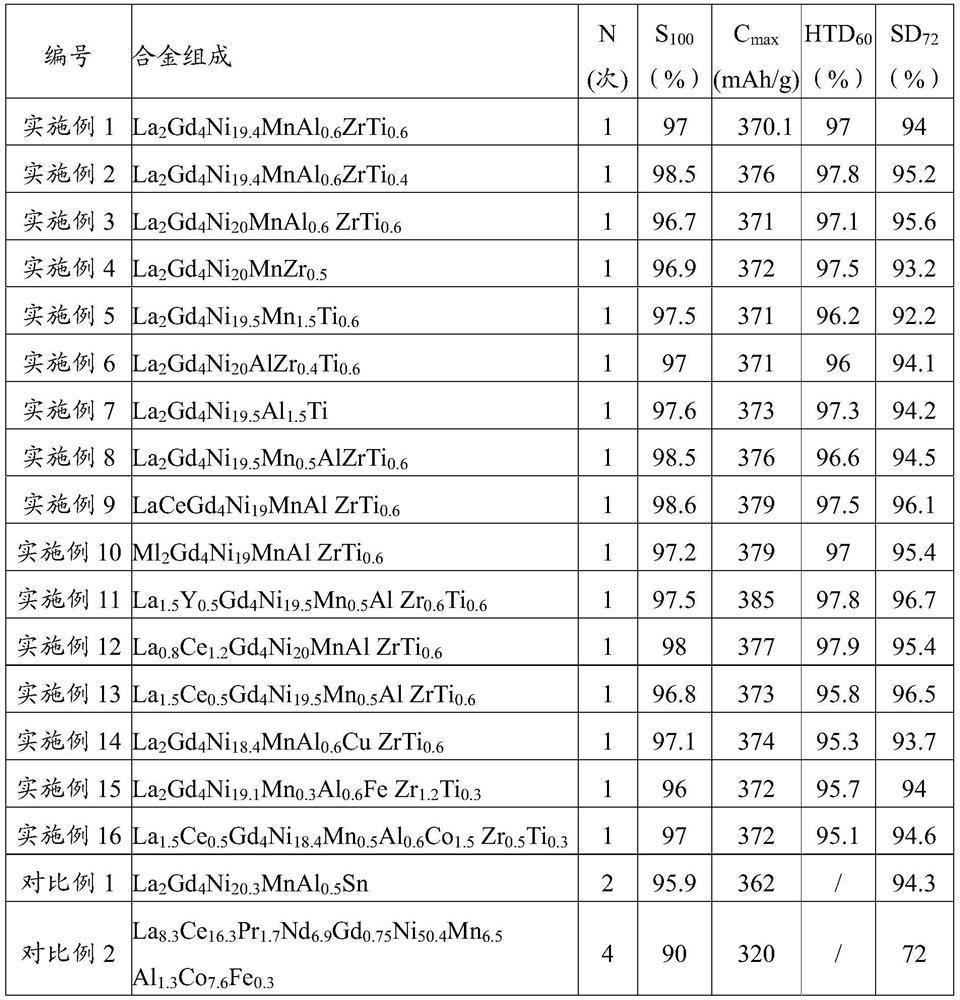
Embodiment 1
[0110] According to the formula in Table 1, prepare A according to the following steps 2 B 7 Type hydrogen storage alloy:
[0111] (1) Place the metal raw materials Ni, Mn, Al, Zr, Ti, La, Gd in the vacuum melting furnace from the bottom to the top in sequence, and then vacuumize the vacuum melting furnace to an absolute vacuum degree ≤ 5Pa, Fill with argon to a relative vacuum of -0.055MPa. The vacuum melting furnace is heated to 1400°C, and the metal raw material in the furnace is completely melted into a smelted product, and then the heat is kept for 3 minutes, and then the heating is stopped.
[0112] (2) Cast the smelted product onto a cooling copper roll, and quickly quench and spin it into an alloy sheet with a thickness of 0.3mm.
[0113] (3) Place the alloy sheet in a device filled with argon with a relative vacuum of -0.025MPa, heat treatment at 875°C for 16h, and obtain A 2 B 7 type hydrogen storage alloy.
Embodiment 2、3 and 8
[0115] According to the formula of table 1, prepare A according to the method for embodiment 1 2 B 7 type hydrogen storage alloy.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com