Inter-domain routing recovery method based on degree constraint minimum spanning tree
A recovery method and spanning tree technology, applied in the field of Internet security, to achieve the effect of easy backtracking and error correction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0042] Example: see figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Figure 6 and Figure 7 .
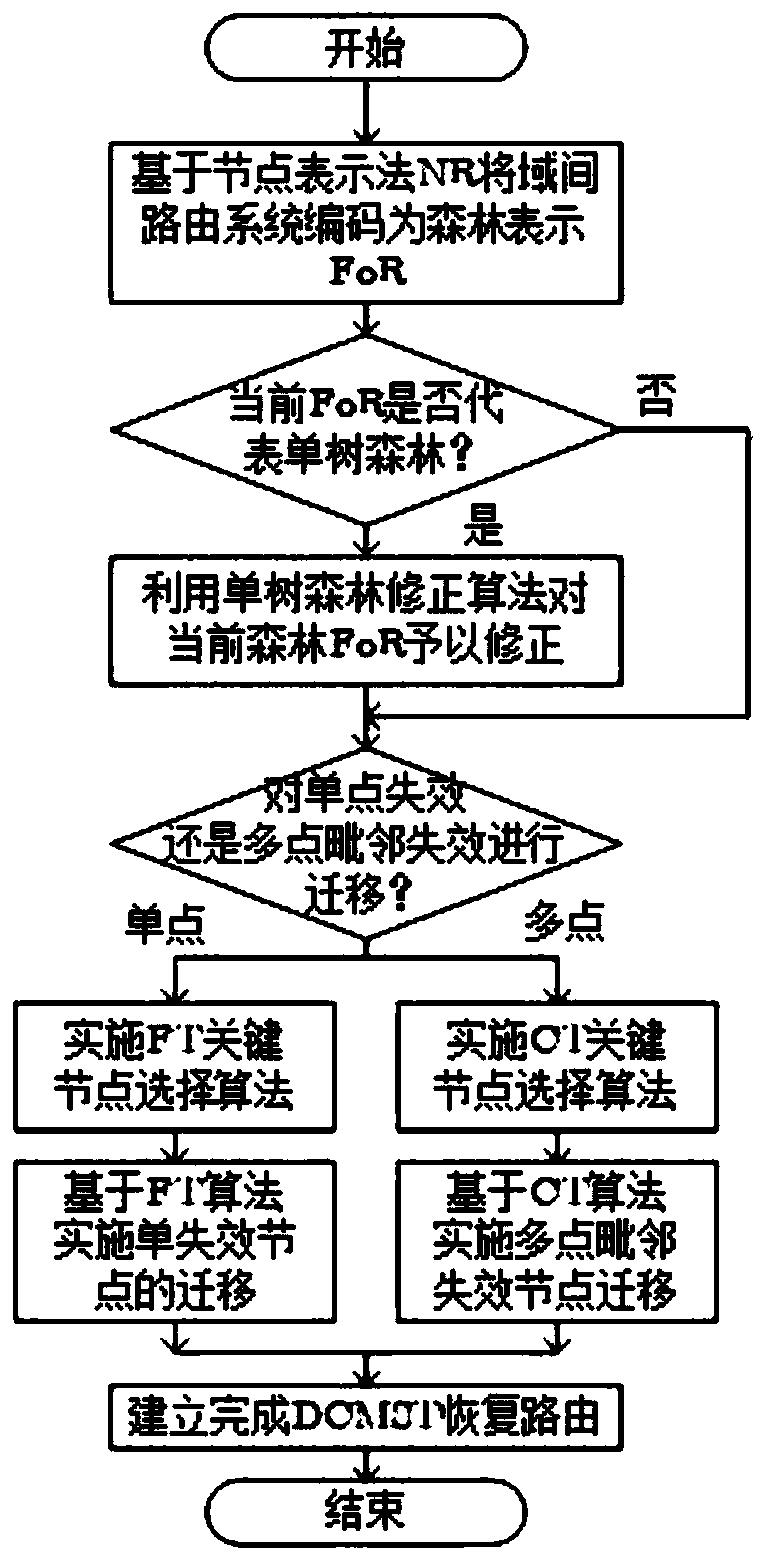
[0043] The inter-domain routing recovery method based on the degree-constrained minimum spanning tree expresses the inter-domain routing system after the BGP-LDoS attack as a spanning forest, using the basic migration algorithm, complex migration algorithm, single-tree forest correction algorithm, and FT key node selection algorithm Algorithms such as CT key node selection and other algorithms, construct inter-domain routing recovery topology based on degree-constrained minimum spanning tree under the condition of satisfying the established degree constraints. The steps are: Step 1. Establish a mathematical model of degree-constrained minimum spanning tree;
[0044] Step 2. Based on Node Representation (Node Representation, NR), encode the inter-domain routing system after being attacked by BGP-LDoS, and express it as Forest Representation (Forest Representation, Fo...
Embodiment 1
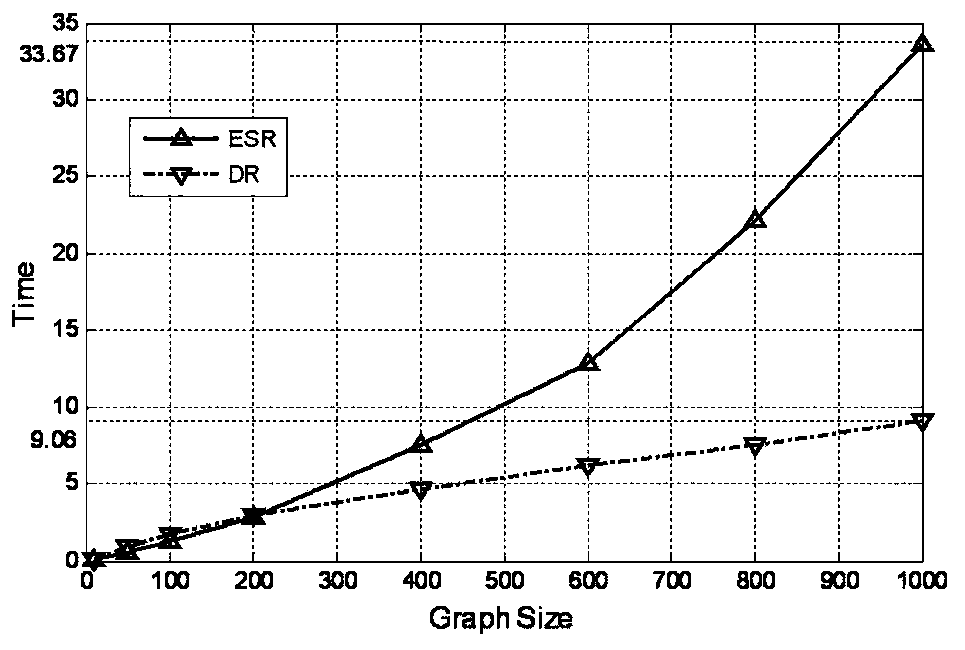
[0129] Using the BRITE topology generator, a random graph is generated based on the GLP model, which represents the AS-level simulation topology in the inter-domain routing system. In the regional inter-domain routing system established with small-scale multi-autonomous domain communities, the number of nodes in the random graph is set as 10, 50, 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, 1000.
[0130] Simulate the BGP-LDoS attack to attack the above random graph. For the surviving nodes and links, respectively use the DR algorithm proposed in this application and the classic ESR algorithm to generate DCMST as the recovery topology after the inter-domain routing system is attacked. The simulation environment is Windows 10, Intel i5 6200U, 16G memory. In order to effectively control the aggregation of nodes in the restored topology, the spanning tree node degree value range is limited to [3,6]; the average node degree of the random graph generated by the GLP model is 4.1. As a classic spanning...
Embodiment 2
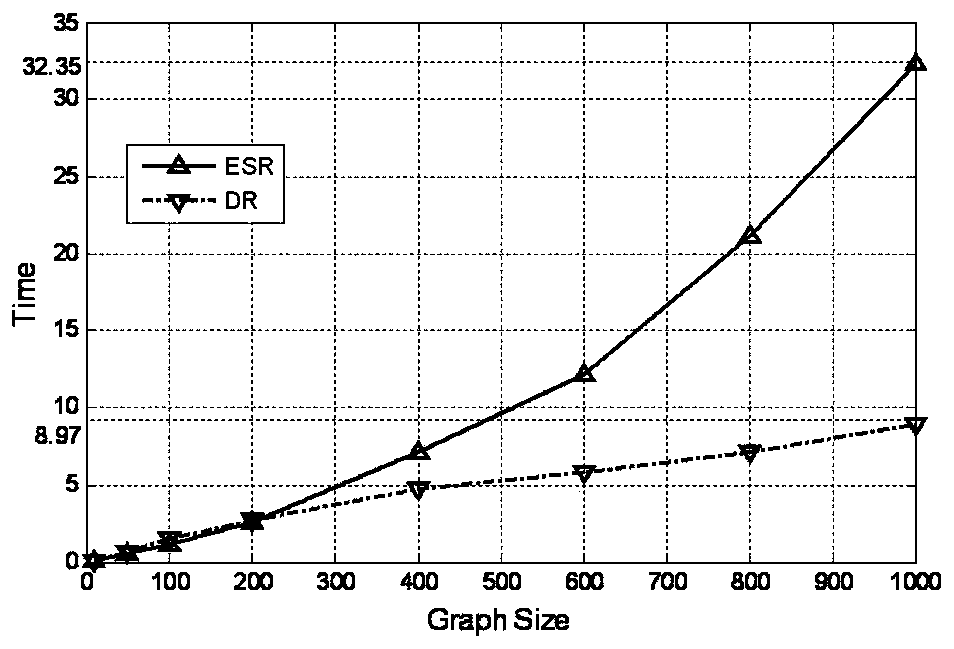
[0133] The real Internet AS-Level topology from CAIDA is used for simulation verification, and the sample topology is obtained from BGP_tables and WHOIS respectively. Both BGP_tables and WHOIS original data sets contain 30,000+ nodes. Considering that the actual Internet inter-domain routing recovery mechanism needs to be implemented within a certain range, the topologies covering the first 3000 AS nodes are respectively extracted from the two original data sets for simulation. Among them, the local topology obtained from BGP_tables is named B_tpl, and its average degree value is 2.51; the local topology obtained from WHOIS is named W_tpl, and its average degree value is 6.53.
[0134] Similar to Embodiment 1, BGP-LDoS is simulated to attack the B_tpl and W_tpl topologies, and for the surviving nodes and links, the DR algorithm proposed in this application and the classic ESR algorithm are used to generate DCMST as the recovery after the inter-domain routing system is attacked ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com