Non-local mean-guided partial volume correction method for PET images constrained by MR structural information
A non-local mean, partial volume technology, applied in the field of medical image processing, can solve the problems of Gibbs artifact, anatomical structure dependence, high level noise, etc., to improve accuracy and efficiency, improve accuracy, and improve PET images quality effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
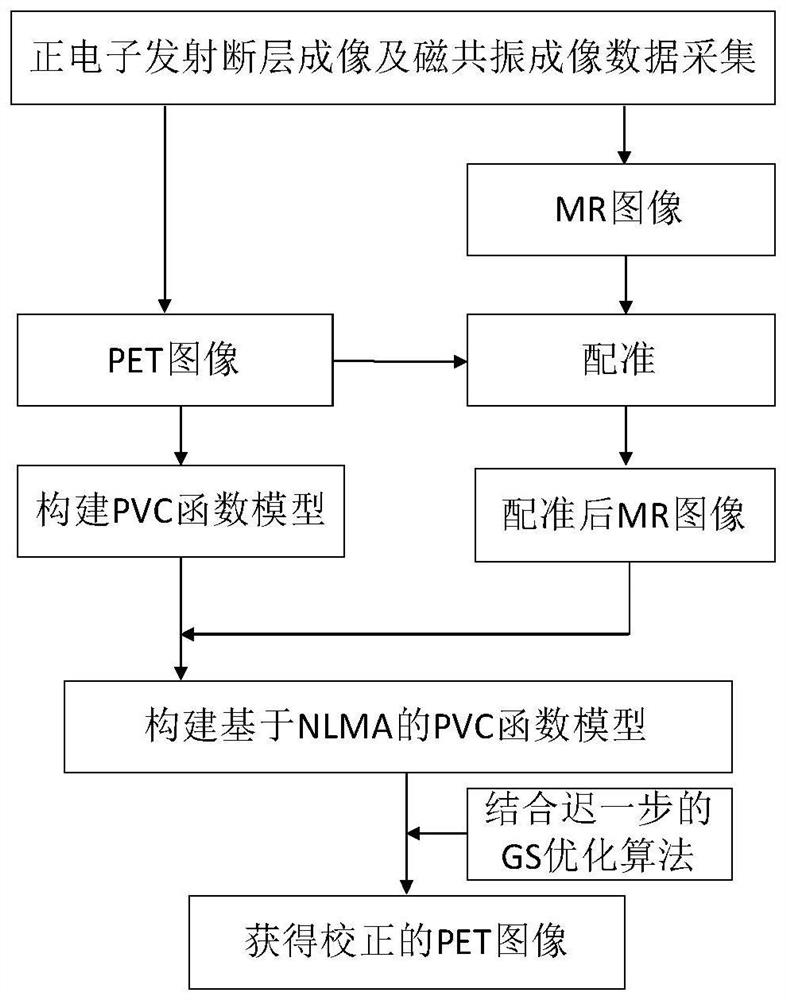
[0048] A non-local mean-guided partial volume correction method for PET images constrained by MR structural information, such as figure 1 As shown, the specific steps are:
[0049] Step (1) Synchronously collect PET and MR image data of the same object through PET equipment and MRI equipment respectively, obtain the PET image and MR image of the object synchronously, and obtain the system resolution of the detector in the PET imaging equipment at the same time;
[0050] Step (2) according to the PET image data that step (1) obtains, construct the model based on the partial volume correction of PET image under the PWLS framework;
[0051] Step (3) registering the MR image obtained in step (1) and the PET image;
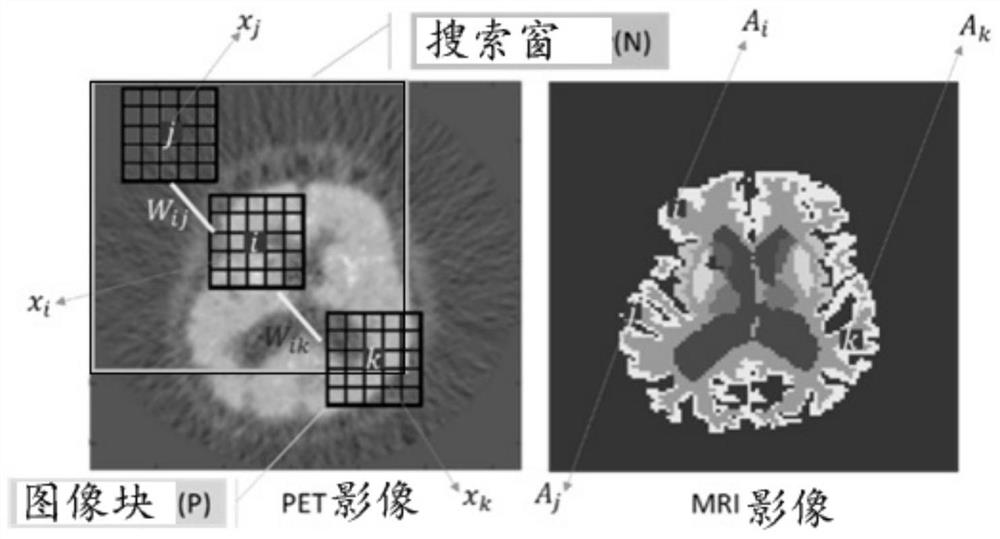
[0052] Step (4) introducing the non-local mean prior of MR image constraints into the PET partial volume correction model to construct a PET partial volume correction model based on NLMA;
[0053] In step (5), the objective function obtained in step (4) is iterativel...
Embodiment 2
[0081] A non-local mean-guided PET image partial volume correction method constrained by MR structure information, which is corrected according to the method described in Embodiment 1, the non-local mean-guided PET image partial volume correction method constrained by MR structure information.
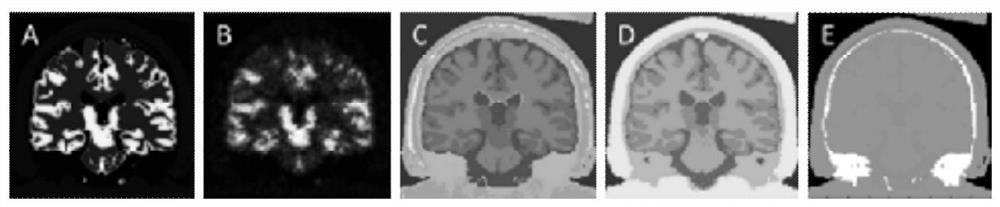
[0082] image 3 is the simulated image data used in the experiment in Example 2, which is obtained from real human body PET data, where image 3 (a) is the PET ideal image corresponding to the real object, the size is 128*128. image 3 (c) is the MR simulation image, which is divided into 6 different brain regions. image 3 (d) MR simulation image with segmentation error obtained with the SPM12 tool, also containing 6 different brain regions.
[0083] For the PET simulation image, the uncorrected PET image is obtained by MLEM iteration 240 times after attenuation correction, normalization correction, and photon count reduction in the projection domain, such as image 3 (b) shown. F...
Embodiment 3
[0089] A non-local mean-guided PET image partial volume correction method constrained by MR structure information, other features are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2, the difference is that the verification is performed according to Embodiment 2, and the method of the present invention is verified in order to verify the MR image segmentation deviation The influence of the two kinds of MR segmentation images is compared as the structure prior experiment, and the related results are as follows.
[0090] For PET simulation images, uncorrected PET images are obtained by attenuation correction, normalization correction, and photon count reduction in the projection domain, such as image 3 (b) shown. The RBV algorithm extends the GTM algorithm to pixels, is an algorithm based on MR segmentation, and is also a typical algorithm for partial volume correction using MR information. In this implementation 2, this method is selected for comparison with the method of the present inv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com