Method for specific regulation and control on activity of nuclease
A technology of nuclease activity and specificity, applied in the field of DNA sequence detection, can solve the problems of interfering with the normal operation of the enzyme-nucleic acid probe system, unclear nuclease distribution mechanism, and reduced detection efficiency, so as to achieve stable detection efficiency and retention The main activity and the effect of improving detection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
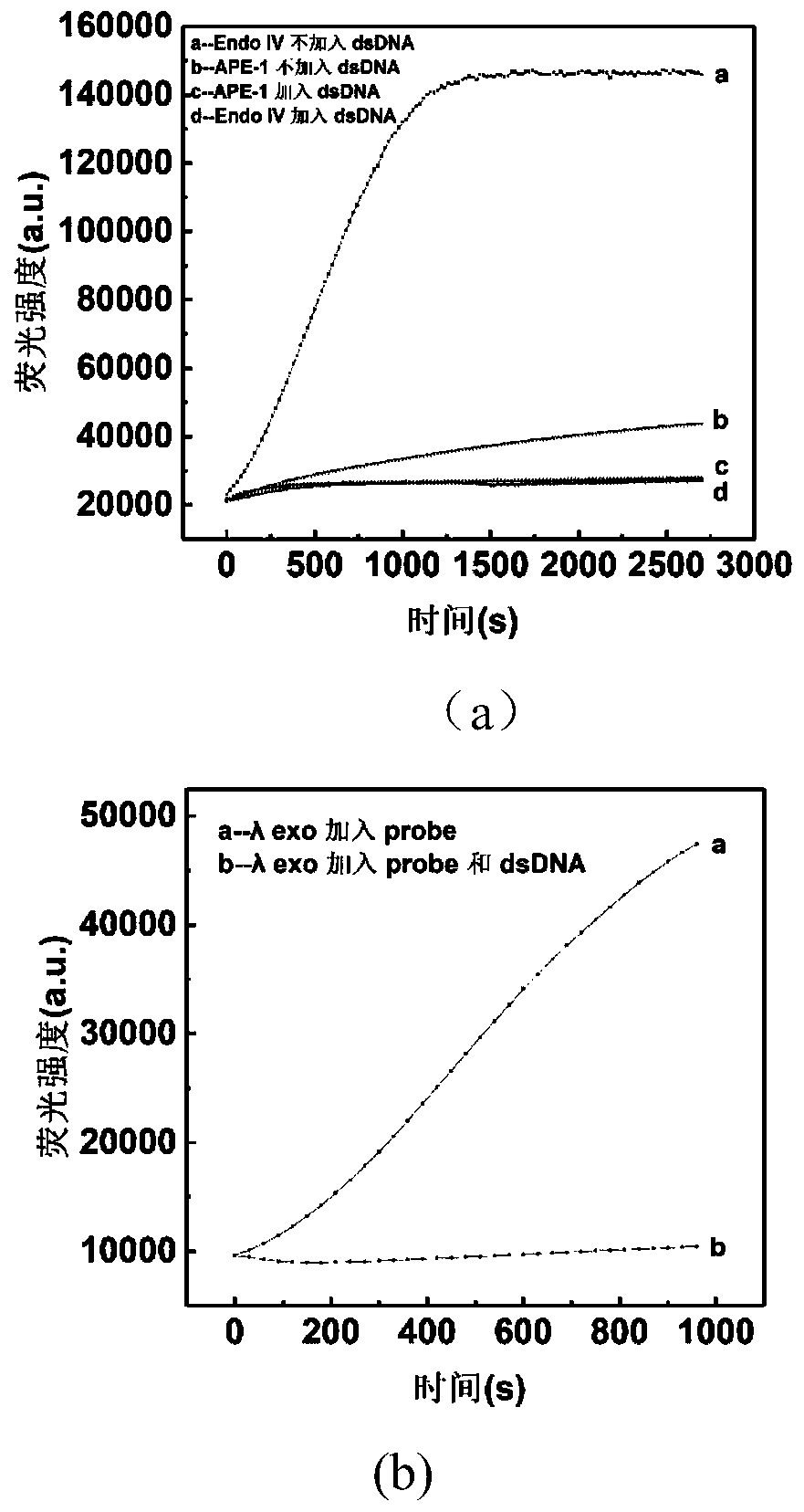
[0064] Embodiment 1: Check the inhibitory effect of double-stranded DNA on nuclease side activity
[0065] In this example, a kit containing only Endo IV / APE1 / lambda exo, single-stranded probe, buffer, and H 2 Add double-stranded DNA irrelevant to the reaction system to the system of O to test whether double-stranded DNA can inhibit nuclease from cutting single-stranded probes. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0066] 1. Design the reaction system and synthesize the oligonucleotide chain.
[0067] The reaction system includes nuclease, probe, buffer, H 2 O and double-stranded DNA. The sequences of primers and probes are listed in Table 1.
[0068] Table 1, check the inhibitory effect of double-stranded DNA on nuclease side activity
[0069]
[0070] 2. Configure the reaction system
[0071] Add 100nM probe, 5uL ThermoPol buffer (10×), 0.1 unit EndoIV or 2 units APE-1 or 2 units lambda exo to 400uL enzyme labeling strip, and make up to 50uL total volu...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Embodiment 2: Guiding chain improves the existing detection technology.
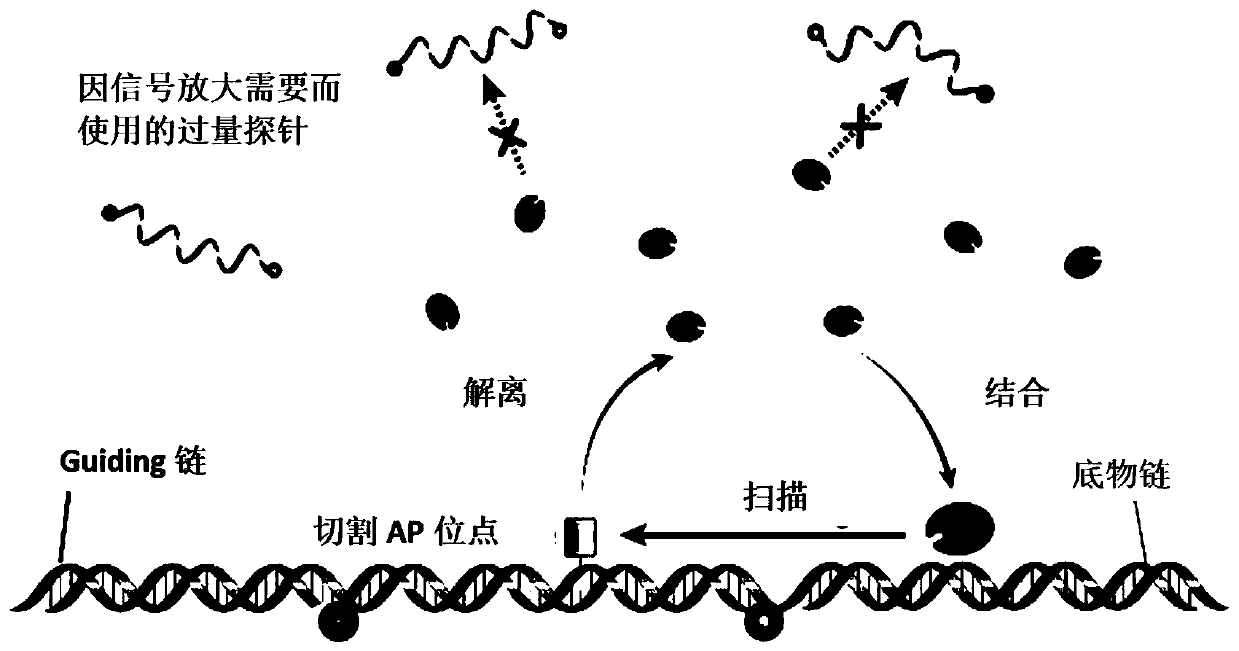
[0077] In this example, the Guiding chain was added to the nucleic acid detection system participated by Endo IV, and the improvement of the detection performance by the Guiding chain was tested. For detection principle see figure 1 , the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0078] 1. Design the reaction system and synthesize the oligonucleotide chain.
[0079] The target is the EGFR-L858R mutation. Based on the DNA sequence of the mutation, design the substrate chain (MT, WT), probe, blocker and corresponding Guiding required for the nucleic acid detection system involved in Endo IV chain. The sequences of primers and probes are listed in Table 2. The schematic diagram of the probe system is shown in figure 1 .
[0080] Table 2, Guiding Chain Improvements to Existing Detection Techniques
[0081]
[0082] 2. Configure the reaction system
[0083] In 400uL enzyme labeling s...
Embodiment 3
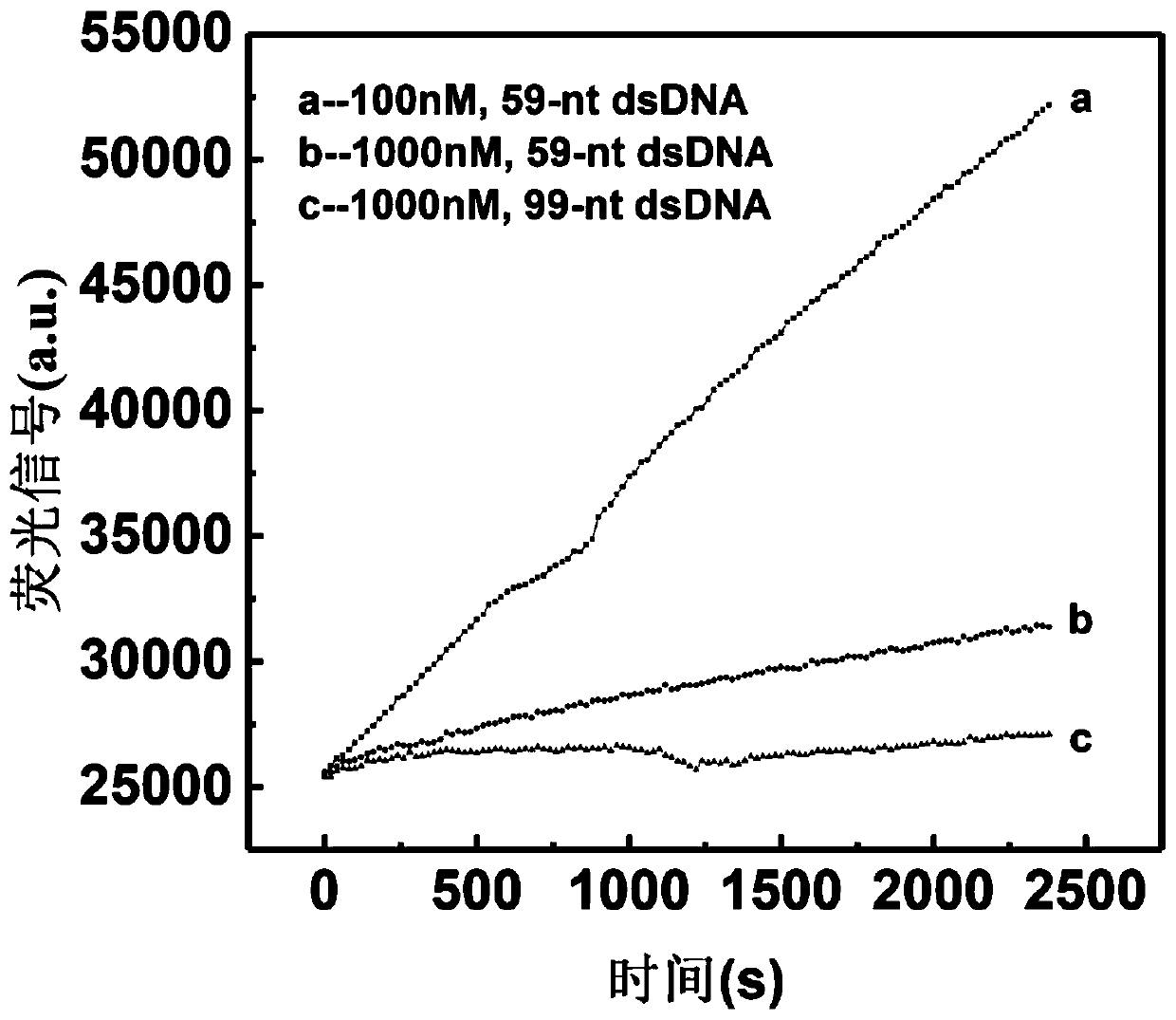
[0088] Example 3: Detection of low-abundance mutations
[0089] In this embodiment, the system to be tested is a mixed system of wild chain and mutant chain, and a series of different mutation ratios are set to detect the lowest possible mutation ratio. For detection principle see figure 1 , the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0090] 1. Design the reaction system and synthesize the oligonucleotide chain.
[0091] The target is the EGFR-L858R mutation. According to the DNA sequence of the mutation, design the substrate strands (MT, WT), probes, blockers and corresponding Guiding required for the nucleic acid detection system involved in Endo IV chain. The sequences of primers and probes are listed in Table 2. The schematic diagram of the probe system is shown in figure 1 .
[0092] 2. Configure the reaction system
[0093] 50μL reaction system of mutants with different proportions: probe amount: 1000nM; mutation ratio: 100%, 10%, 1%, 0.5%, 0.1%, 0.01%, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com