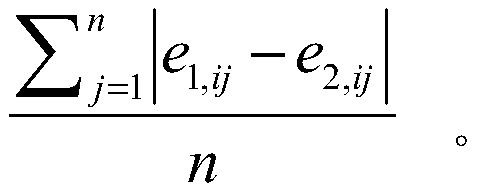Postmortem interval deduction method based on microbiome sequencing data and machine learning algorithms
A technology of death time and microbes, which is applied in the field of medical testing, can solve problems such as constraints, reducing the reliability of prediction results, and lack of versatility, so as to achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. The examples are only used to explain the present invention, rather than to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
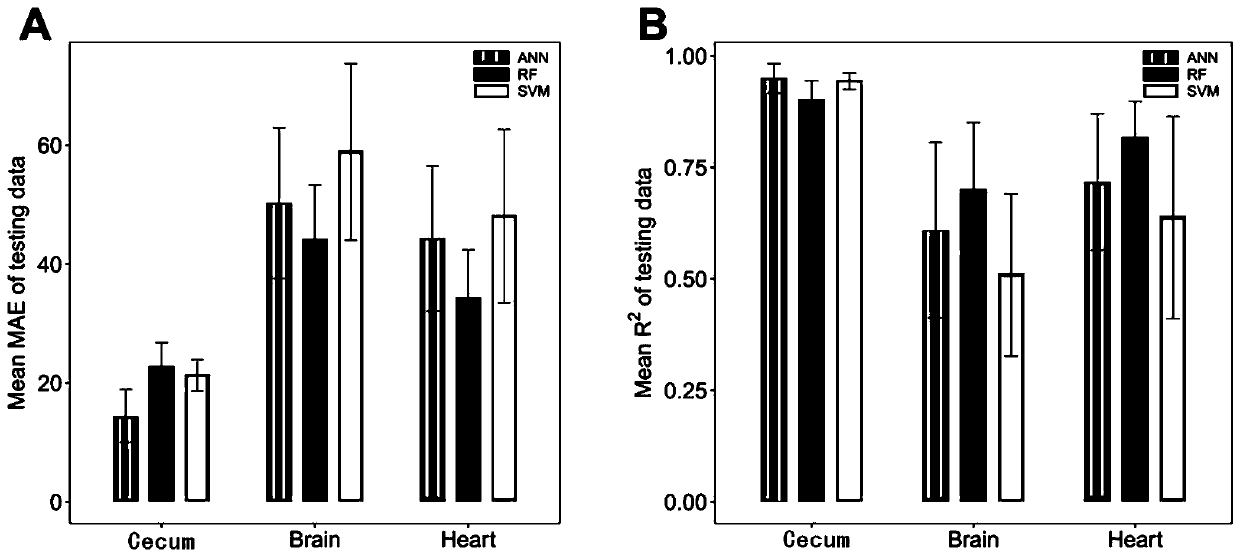
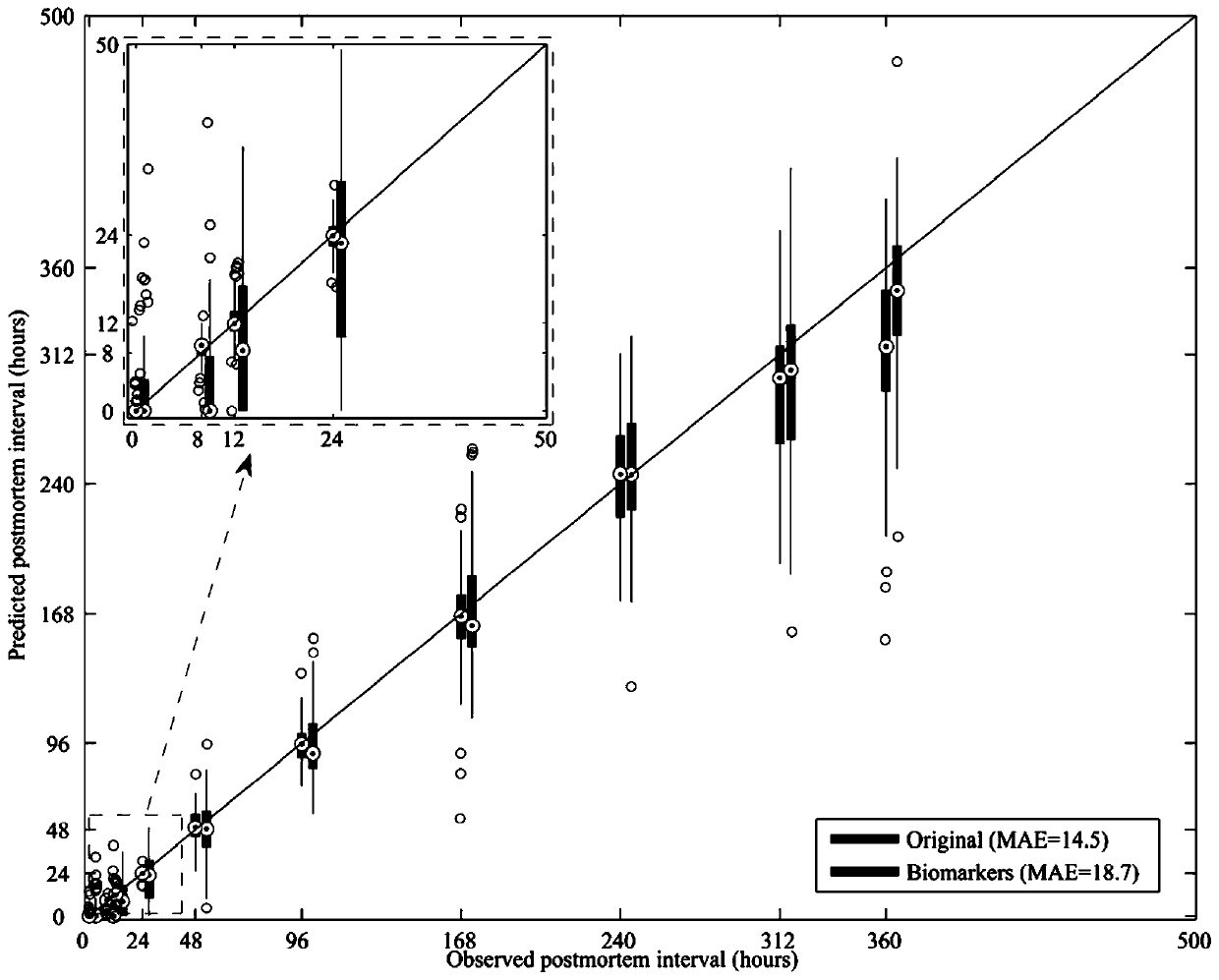
[0029] This example takes the prediction of the postmortem interval time of mice as an example, and specifically illustrates the method for estimating the time of death based on microbiome sequencing technology and machine learning algorithms. This method is also applicable to human or other mammal corpses.
[0030] 1. Sample DNA collection
[0031] Within 15 days after death of C57BL / 6 mice (n=8~24) (10 time points: 0 hour, 8 hours, 12 hours, 1 day, 2 days, 4 days, 7 days, 10 days, 13 days, and 15 days) of organ tissue samples (organ tissue types are specifically brain, heart or cecum) as a template, primers are designed for the 16S rDNA of microorganisms for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, and the amplifica...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap