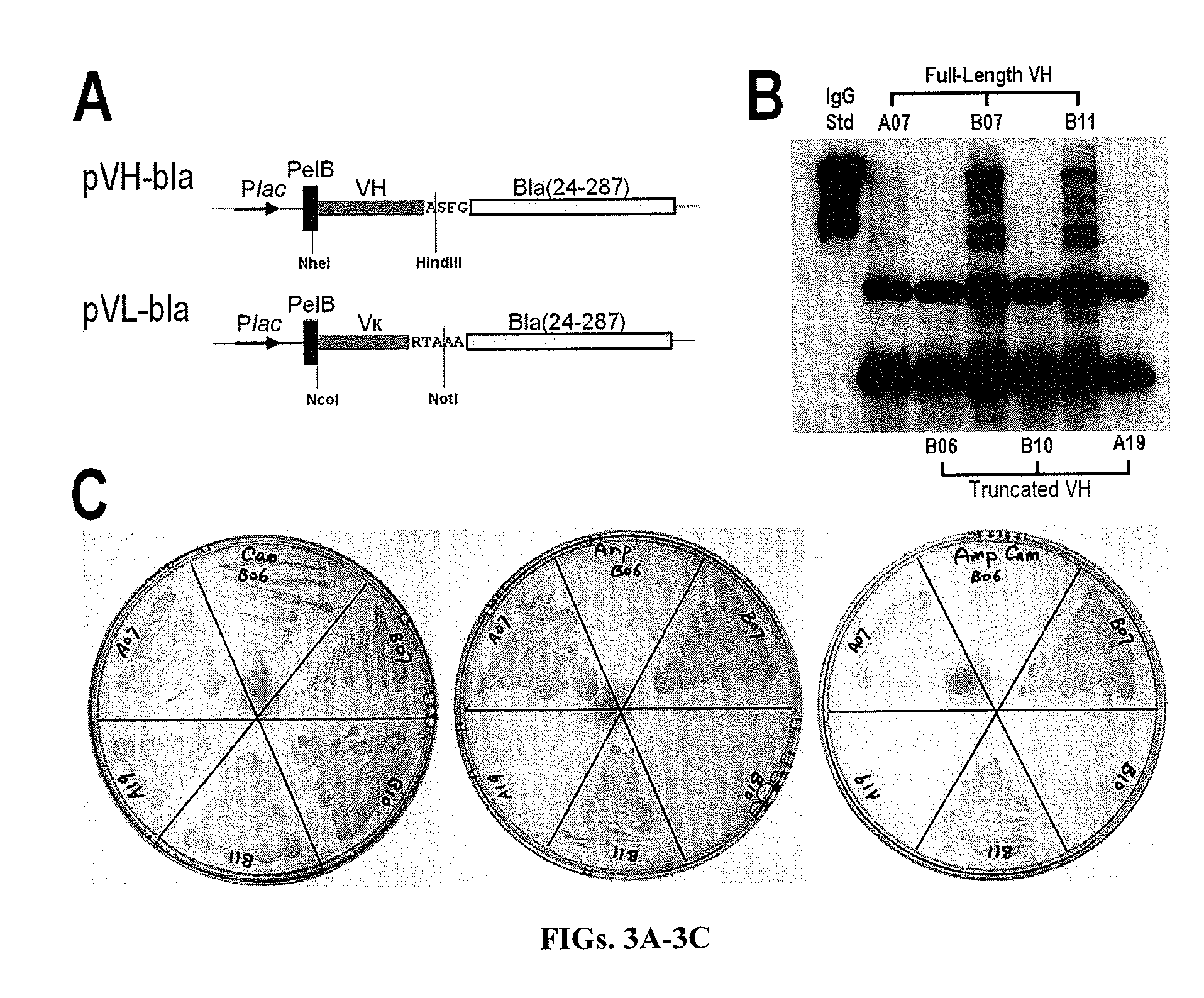
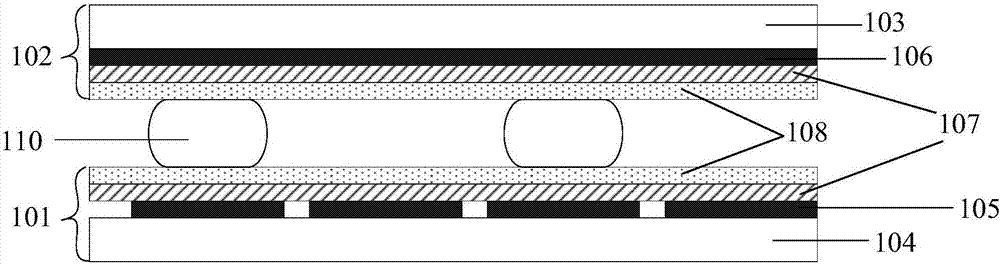
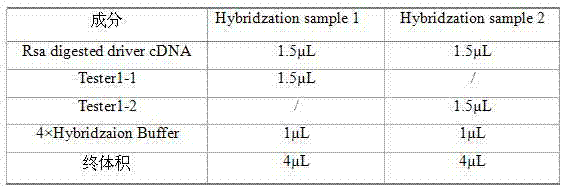
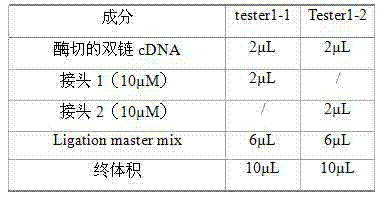
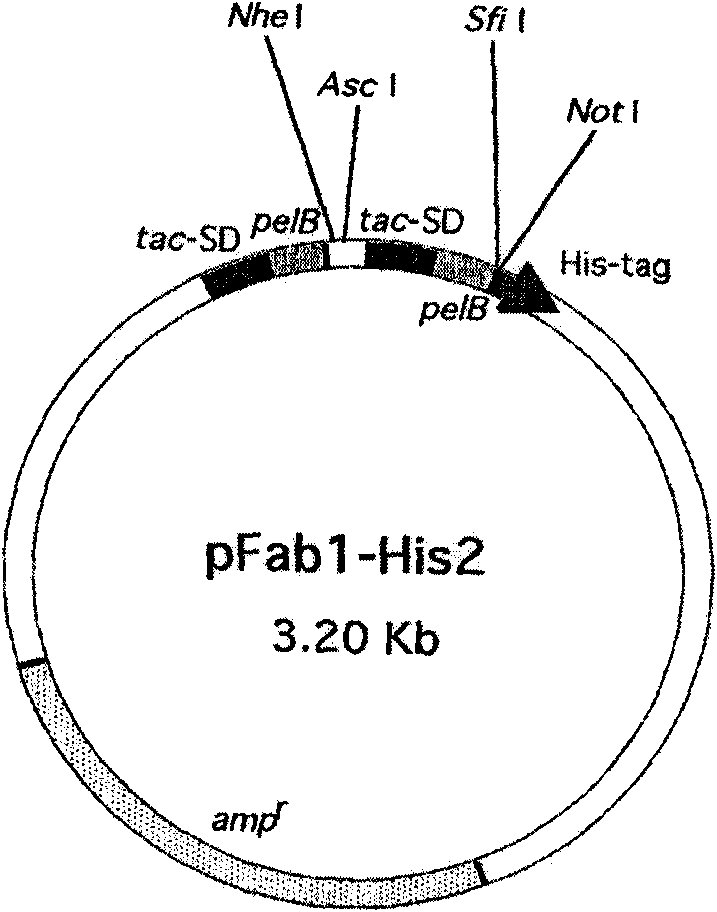
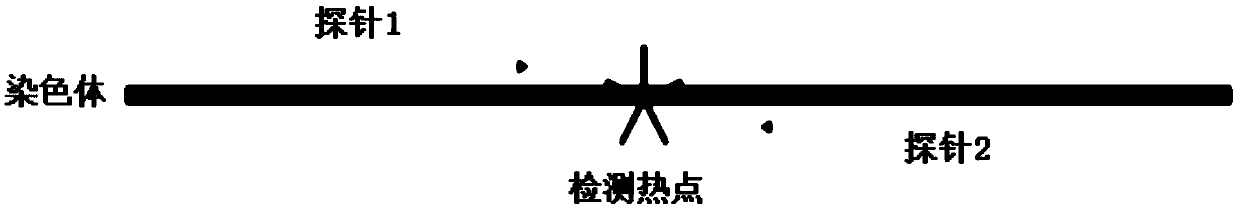
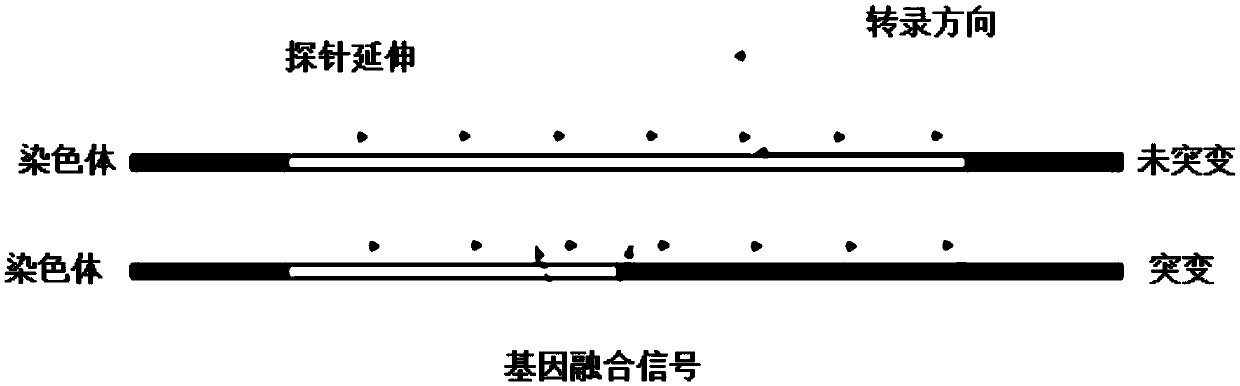
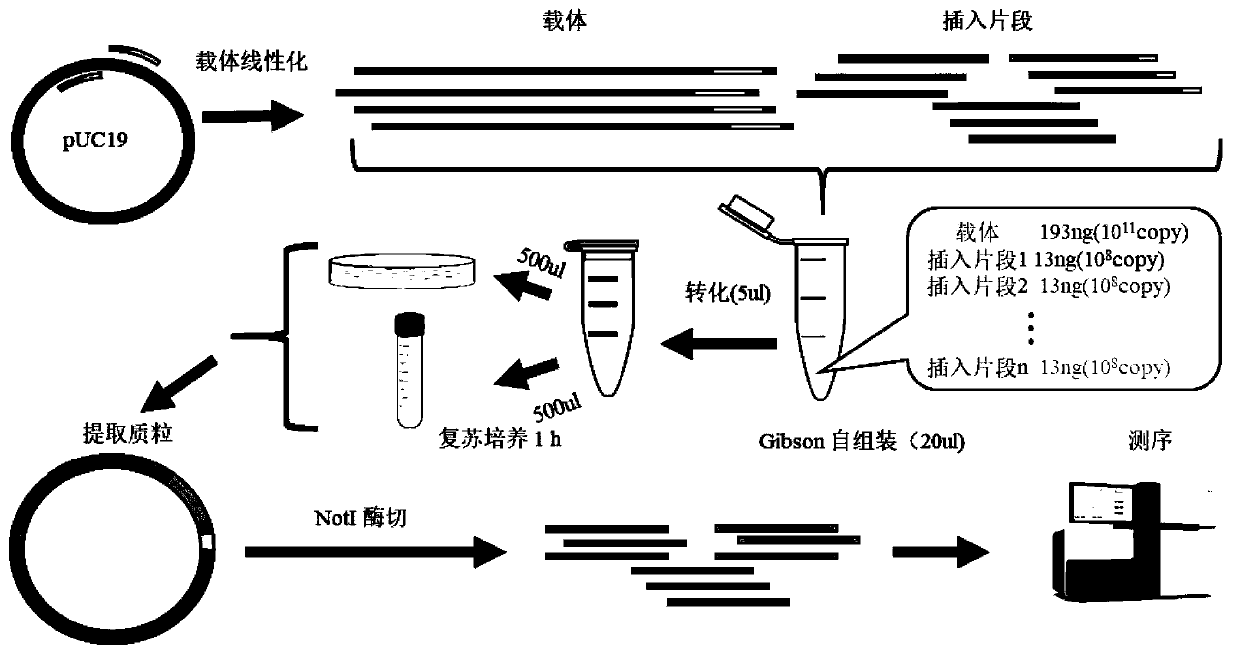
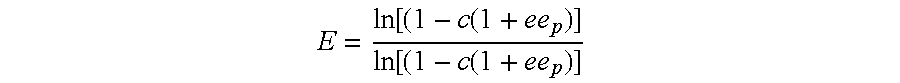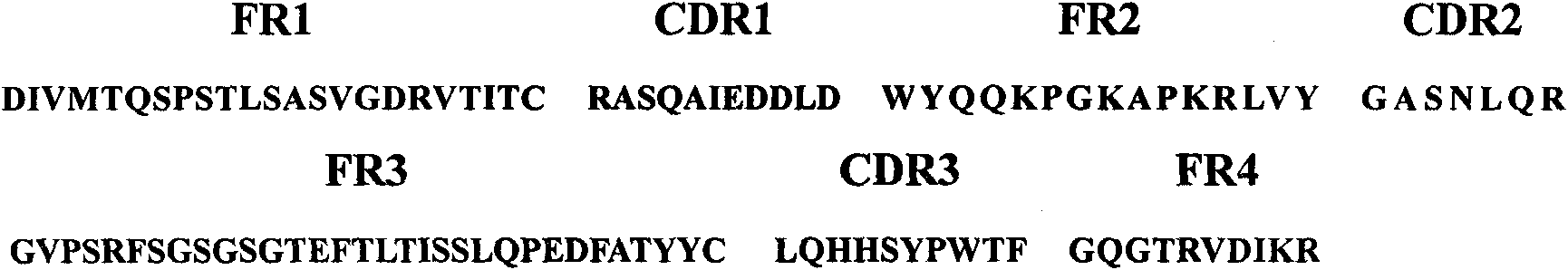Patents
Literature
142 results about "Genetic library" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any well-defined collection of genetic material used to identify unknown nucleic acids; classically, a collection of expressed cDNA clones representing the genome of a particular organism, used to identify newly purified genes or mRNAs by hybridization.
Methods for measuring relative amounts of nucleic acids in a complex mixture and retrieval of specific sequences therefrom
InactiveUS20020172965A1Poor enrichmentMultiplicative improvement in overall enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesCDNA libraryNucleic acid sequencing
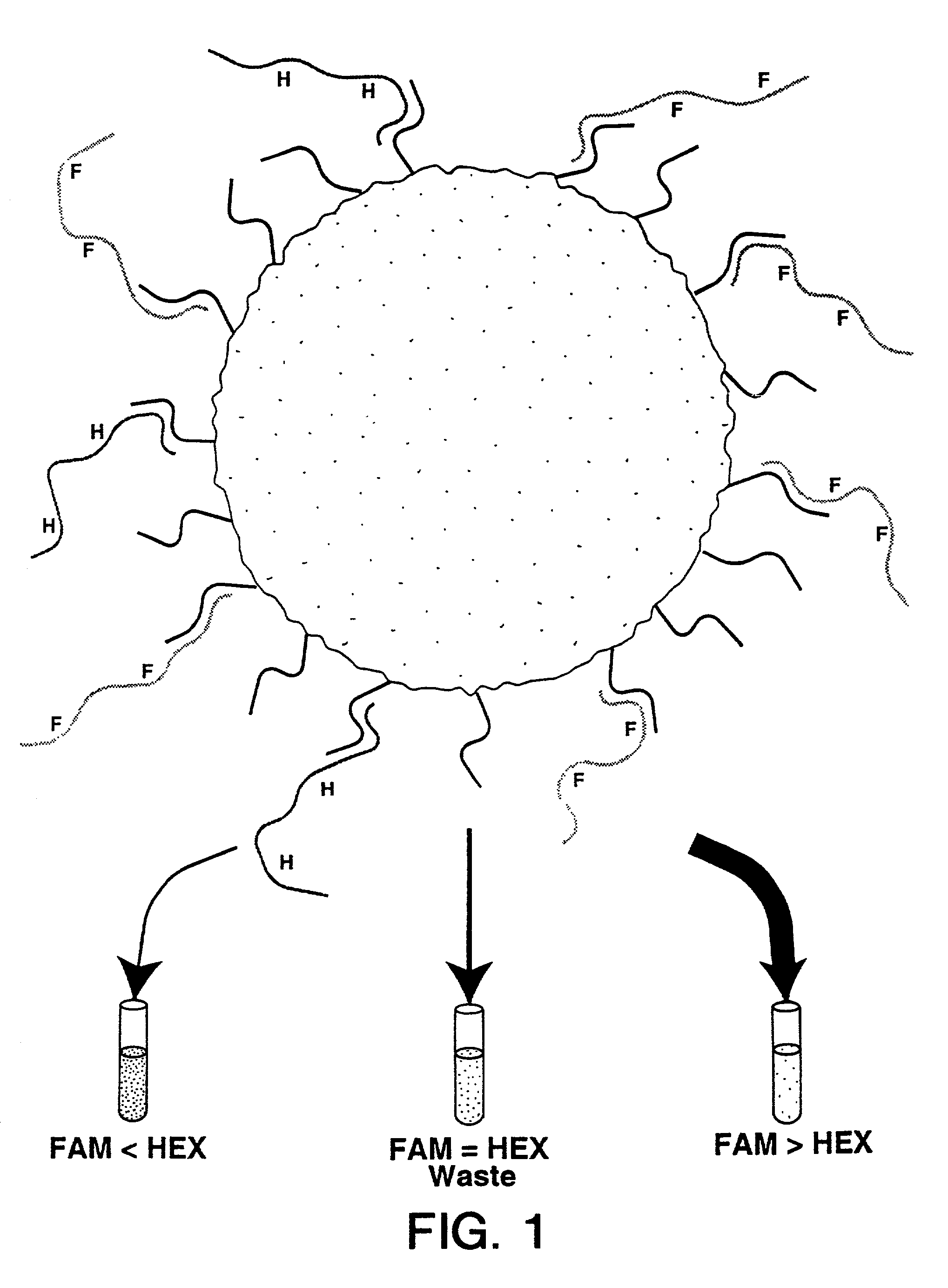
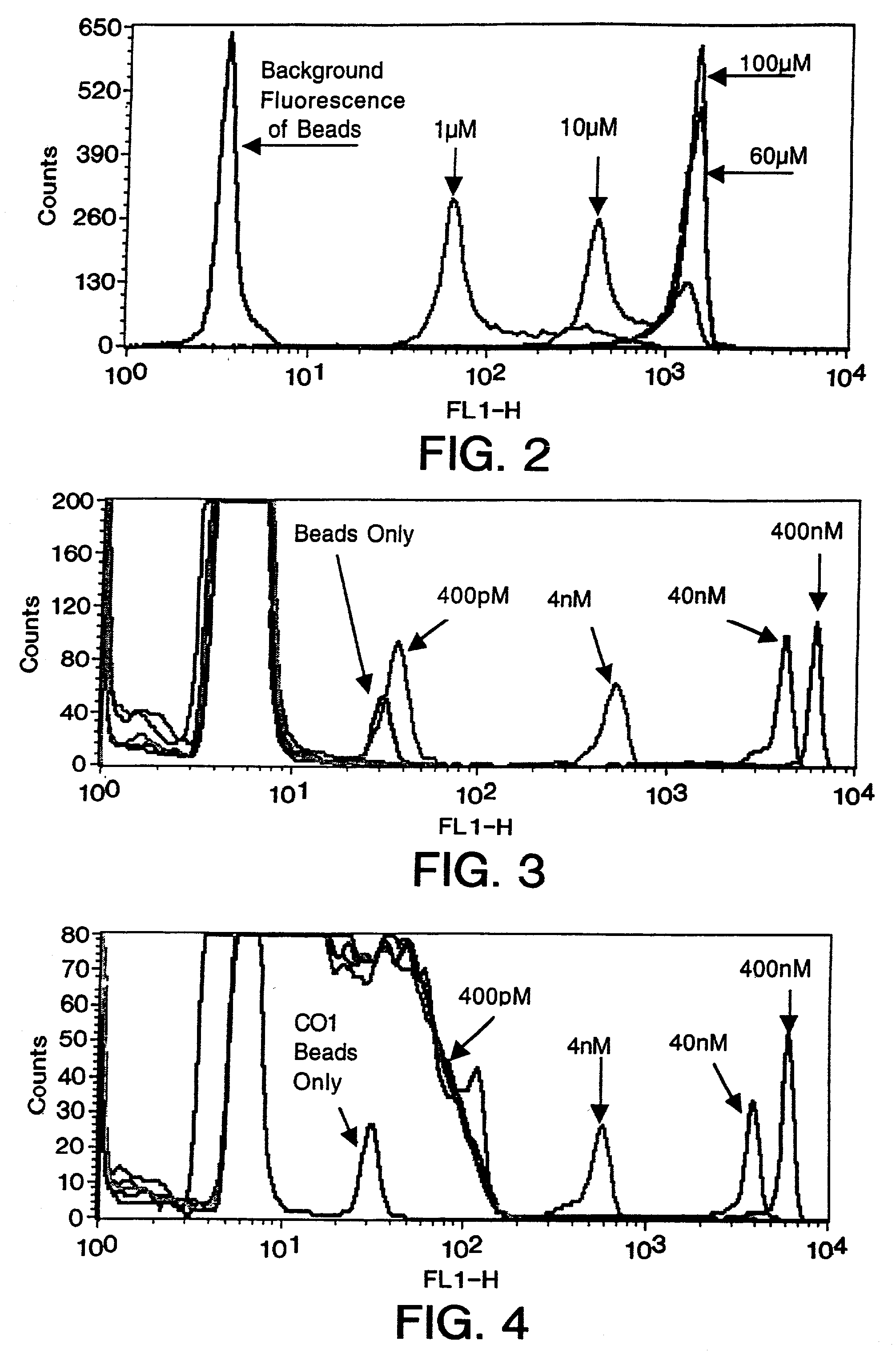
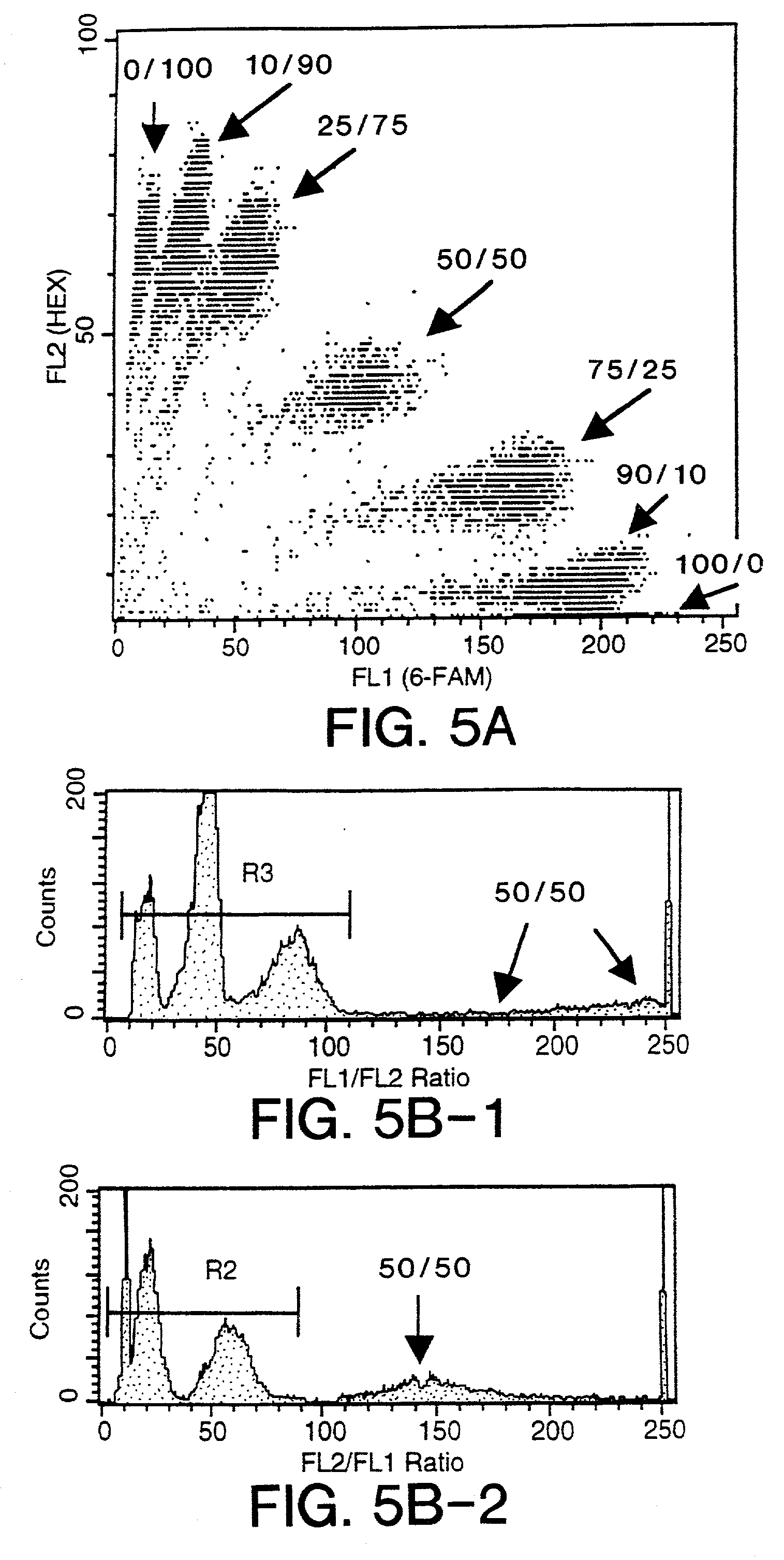
The present invention relates to a method for the comparative assessment of the level of specific nucleic acid sequences in samples derived from different sources. More specifically, the invention relates to a method using oligonucleotides covalently linked to a solid support, such as beads, to isolate specific labeled nucleic acid sequences from complex mixtures. The methods disclosed allow quantitative comparisons of the amount of nucleic acid of defined sequence in a plurality of different samples of nucleic acid, e.g., from different cells or tissues or from genetic libraries. Nucleic acids from the samples are labeled in such a fashion that the signals can be distinguished and compared following hybridization to the oligonucleotides on the beads. According to the invention, the solid supports with the hybridized nucleic acid may be retrieved, and the target nucleic acid eluted and analyzed. Furthermore, the invention provides a method for tagging individual clones from a cDNA library such that they can be identified uniquely and retrieved by hybridization to specific beads.
Owner:DELTAGEN PROTEOMICS
Combinatorial screening of mixed populations of organisms
InactiveUS7018793B1Quick filterLess immunogenicSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganismGenus
Provided is a method of screening gene libraries derived from a mixed population of organisms for a bioactivity or biomolecule of interest. The mixed population of organisms can be a cultured population or an uncultured population from, for example, the environment. Also provided are methods of screening isolates or enriched populations of organisms, which isolates include a population that is spatially, temporally, or hierarchical, for example, of a particular species, genus, family, or class of organisms. Identified clones containing a biomolecule or bioactivity of interest can be further variegated or the DNA contained in the clone can be variegated to create novel biomolecules or bioactivities of interest.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Non-treatment-purpose method for screening mutation of pathogenic genes relevant with hypertrophic cardiac myopathy
ActiveCN105695606AThe method is simple and fastLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMyopathy
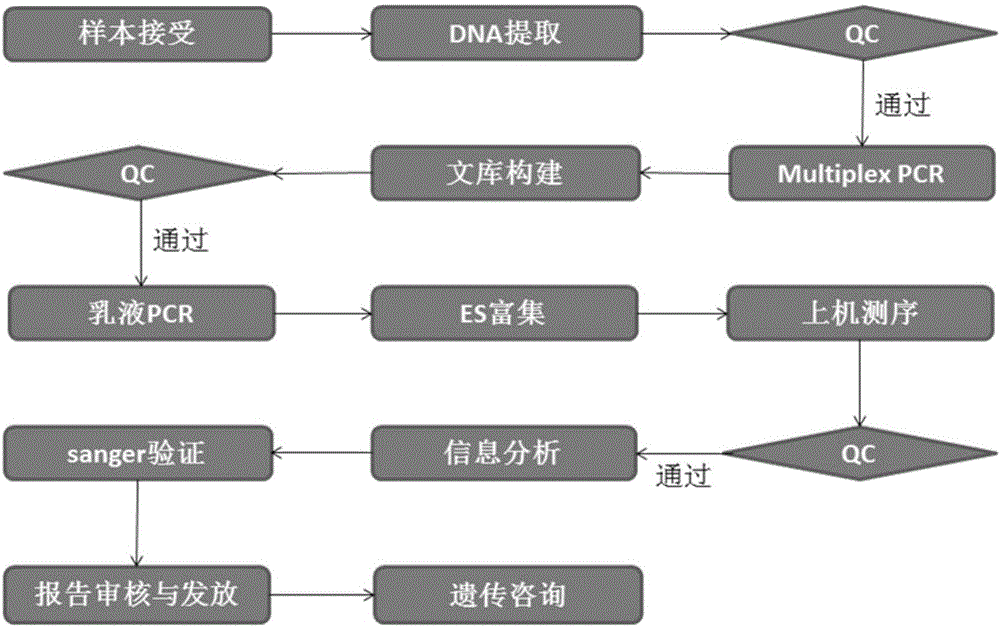
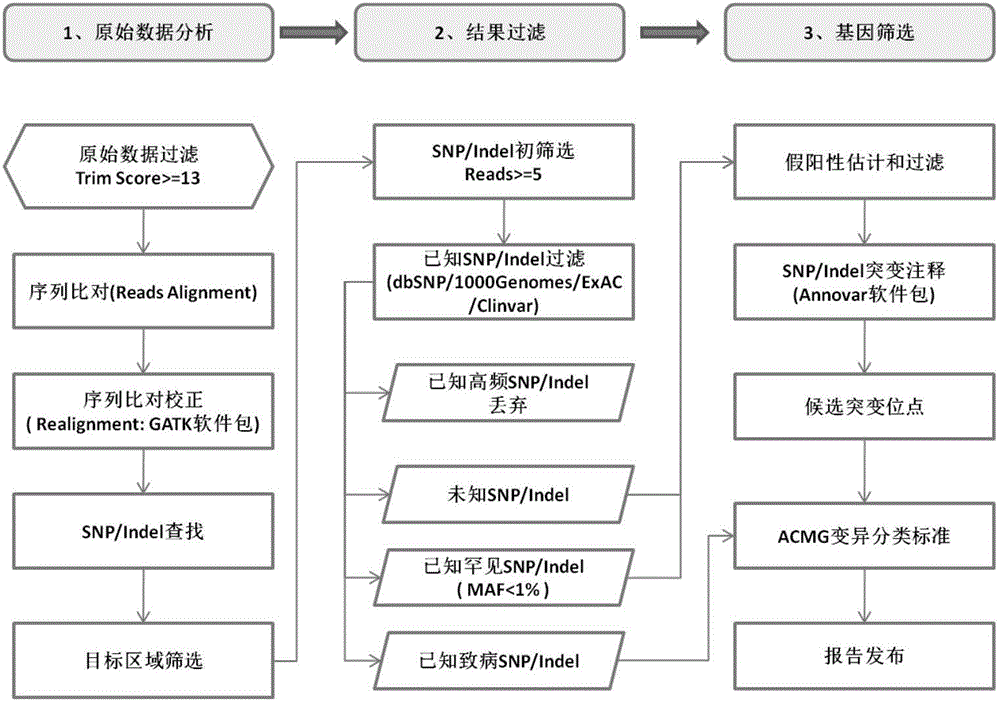
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a non-treatment-purpose method for screening mutation of pathogenic genes relevant with hypertrophic cardiac myopathy. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting genomes; (2) carrying out multiplex PCR amplification on target genes; (3) constructing a target gene library; and (4) sequencing the target gene library by virtue of a next-generation semiconductor sequencing platform, and screening gene mutation sites relevant with the hypertrophic cardiac myopathy. The method is simple, convenient, rapid and low in cost, multiple samples can be detected once, the foundation is laid for the screening of the hypertrophic cardiac myopathy, and the road is exploited for the clinic molecular diagnosis.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
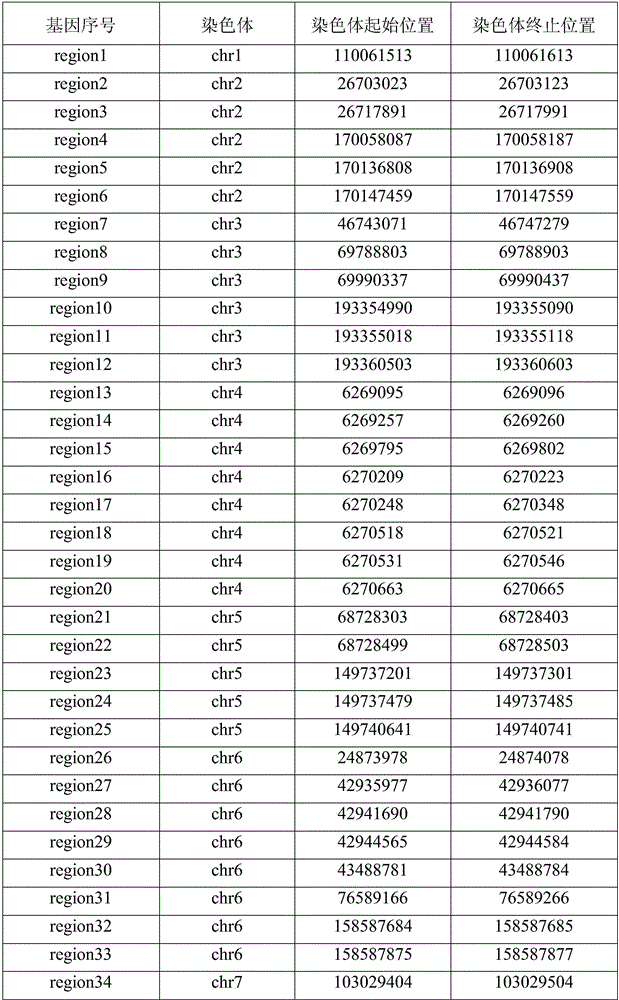
Targeting-based new generation sequencing deafness gene detection set and kit, and detection method
InactiveCN106399504AWide coverageImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationData informationTest sample
The invention discloses a targeting-based new generation sequencing deafness gene detection set and kit, and a detection method. The deafness gene detection set comprises 258 genes, 81 non CDS regions and a whole mitochondrial group. The detection method comprises the steps: designing primers for a part of or all of deafness disease genes and loci; with a to-be-tested sample DNA as a template, carrying out PCR amplification with the primers, and constructing a deafness detection gene library based on the amplified product; and according to the deafness detection gene library, establishing a sequencing template, carrying out high-throughput sequencing, and analyzing sequencing data information. The invention also discloses the related kit. Not only can conventional known mutations be detected out, but also new mutation types also can be detected out; in addition, sequencing and analysis of a large number of objective regions also can be completed within a short period of time, and positions, possible to generate pathogenic mutation, of all exons and regulatory regions of the hundreds of genes associated with deafness are subjected to related sequencing and analyzing.
Owner:SUZHOU BASECARE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
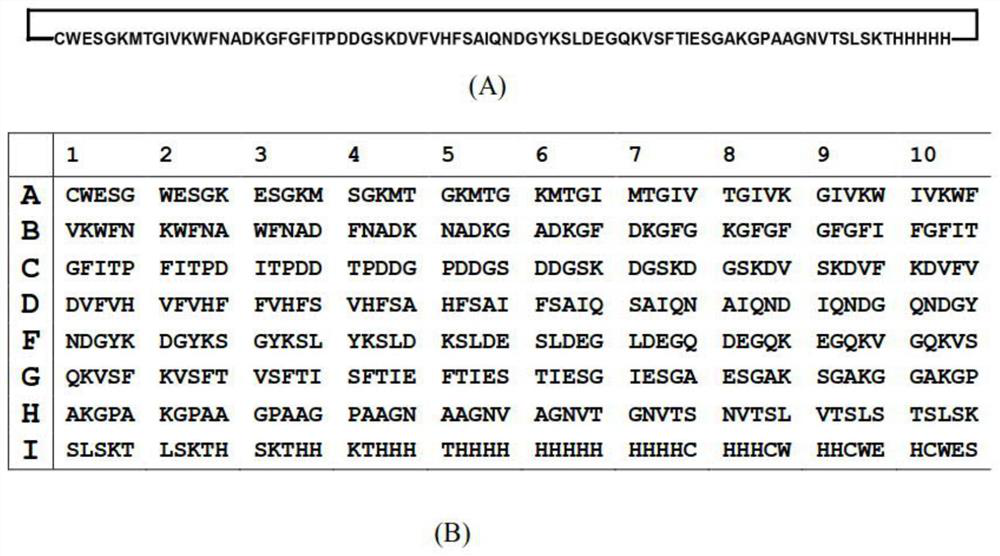
Peptide library constructing method
ActiveCN111727194AReduce in quantityNo need for elutionPolypeptide with affinity tagFusion with post-translational modification motifCyclic peptideChemical synthesis
An improved peptide library preparation method is provided for constructing complete virtual peptide libraries such as a complete virtual tripeptide library, tetrapeptide library, pentapeptide library, hexapeptide library, heptapeptide library, or a complete octapeptide library, etc. The method includes constructing an expression vector for the expression of cyclic peptides. Each cyclic peptide displays an array of peptides of different sizes and sequences, and the number of cyclic peptides needed for constructing a complete virtual peptide library can be dramatically reduced compared with conventional chemical peptide synthesis. Furthermore, the cyclic peptide libraries can be readily reproduced by the expression and purification of the cyclic peptides using the constructed gene libraries.
Owner:HUNAN ZONSEN PEPLIB BIOTECH CO LTD
Optimization of pest resistance genes using DNA shuffling
InactiveCN1314911APromote growthSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAgricultural scienceA-DNA
The present invention provides methods for obtaining pest resistance genes that are improved over naturally occurring genes for conferring pest resistance to plants. The method involves the use of DNA shuffling of pest resistance genes to generate a library of recombinant pest resistance genes, and then screening the library to identify those genes that show an improved property of interest.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Methods for creating antibody libraries
InactiveUS20110053803A1Reduce in quantityPeptide librariesImmunoglobulinsAntibody fragmentsVariable domain
Methods and composition for the preparation of gene libraries of antibodies or parts of antibodies which contain the variable domains. For example, in certain aspects methods for providing polynucleotide library involving annealing and extending are described. Furthermore, the invention provides polynucleotide or antibody fragment libraries prepared by the methods.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Tumour antigen protein and tumour antigen peptide
A tumor antigen protein and its tumor antigen peptide used to prepare the medicine for treating lung cancer are disclosed. Said tumor antigen protein can generate the peptide fragment by cell endolysis. Said peptide fragment can bind with the (MHC)-I molecular compatible with main tissue and can be recognized by T cells. The DNA sequence coding said tumor antigen protein has the nucleotide sequence No.AF497803 in GenBank.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Gene sequencing chip and gene sequencing method
ActiveCN107118955AHighly integratedPrecise handlingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrofluidicsLibrary preparation
The invention provides a gene sequencing chip. The gene sequencing chip comprises an upper substrate and a lower substrate, wherein the upper substrate comprises a plurality of liquid inlets used for liquid drops to enter; the lower substrate is opposite to the upper substrate and separated from the upper substrate by a gap; the gap is used for storing the liquid drop; the lower substrate comprises a liquid drop operation area; the liquid drop operation area comprises a plurality of first line arrays used for preparing a gene library, and a plurality of second line arrays used for gene sequencing; each of the plurality of first line arrays is adjacent to each of the plurality of first line arrays. The gene sequencing chip and the gene sequencing method can accurately control minute drop to perform liquid drop movement, fusion and separation operation through a digital microfluidic technology, and programmatically accomplish all steps of the entire gene sequencing from library preparation up to gene detection on one chip. The chip is high in integration level, can accurately control the liquid drop, reduces the consumption of reagents, and is simple and mature in preparation technology.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
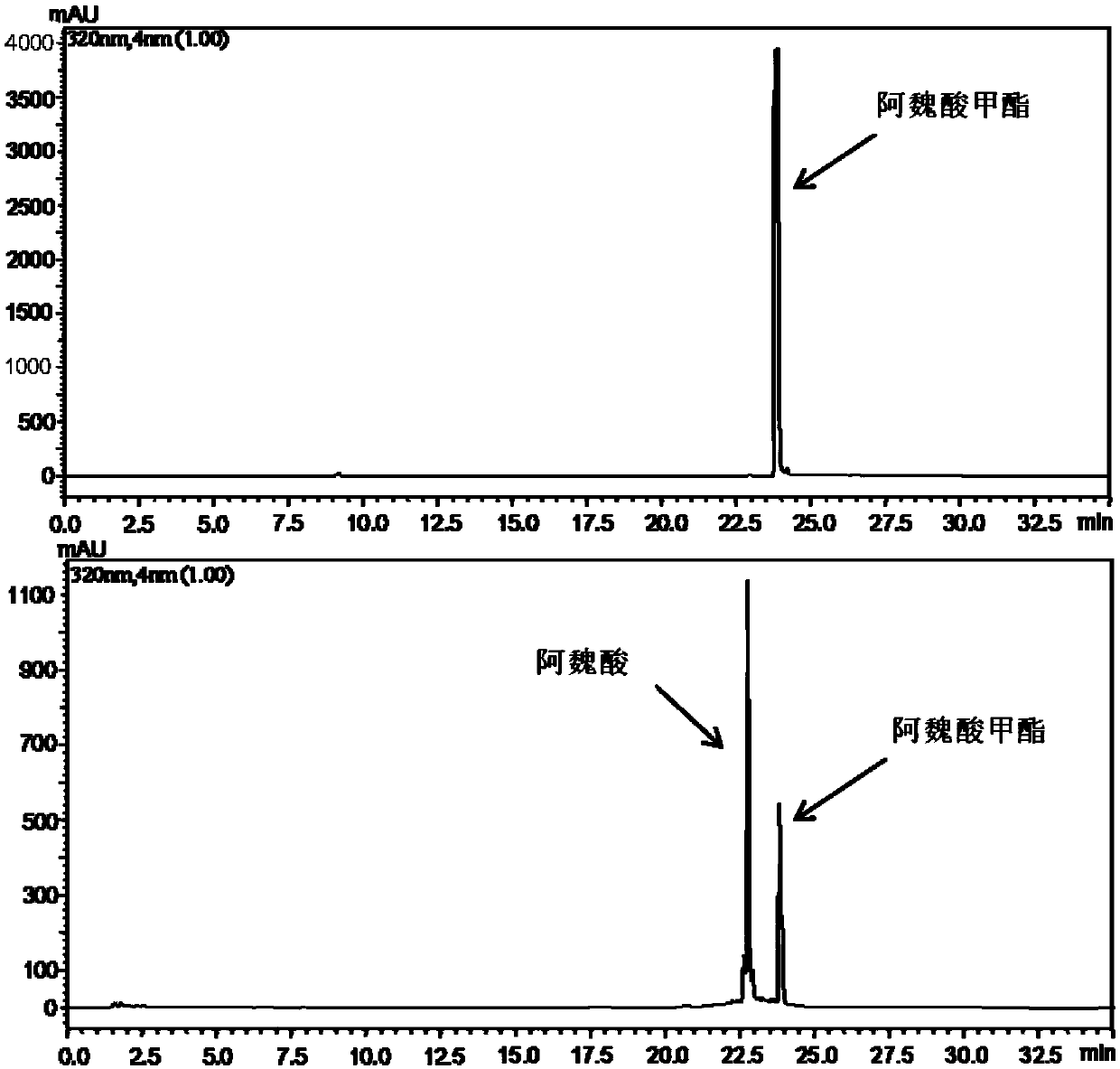
Feruloyl esterase and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN109652392AIncrease enzyme activityHigh hydrolytic activityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliCefazolin
The invention provides feruloyl esterase and a preparing method and application thereof. A feruloyl esterase gene coming from a soil macro gene library have the nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The gene contains a tetrapeptide SXXK sequence motif which is rarely seen, and after the esterase gene is inserted into plasmid pET28a(+), the gene is transformed into escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to achieve heterogeneous expression. The molecular weight of purified recombinase (DLFae4) is 38.3 kDa. Besides, it is put forward for the first time that novel feruloyl esterase can hydrolyze penbritin, penicillin, cefazolin and other lactam antibiotics. As is shown by site-directed mutagenesis experiments, a catalysis triplet of DLFae4 is composed of serine(S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302), and the mutation of any of serine (S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302) can cause loss of the catalysis capability of DLFae4. DLFae4 has a high hydrolytic activity on methyl ferulate and has good heat stability. In the presence of cellulase, DLFae4 can obviously increase the amount of ferulic acid released from destarched wheat bran. Due to peculiar activities and enzymatic characteristics of novel feruloyl esterase, novel feruloyl esterase can be applied to feed, paper making, food, pharmacy and other fields.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular Analysis
InactiveUS20080003566A1Easy to prepareAvoid crosstalkMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular analysisBioinformatics
The present invention relates to a method of determining the sequence and / or occurrence frequency of a number of variable gene inserts from a gene library, which inserts exhibit a desired specific characteristic, wherein each variable gene insert is flanked (5′) and (3′) by known sequences, the method comprising; selecting the number of inserts by their ability to exhibit the desired specific characteristic, conducting polymerase chain reaction to amplify the selected number of variable gene inserts to produce components of a mixed PCR product, ligating the components of the mixed PCR product to produce a concatenated sequence and sequencing or determining the occurrence of the gene inserts in the concatenated sequence.
Owner:VAUX DAVID
Method and device for detecting gene mutation and expression quantity
ActiveCN112397144AEfficient enrichmentApplicable developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsNucleotideRelated gene
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting gene mutation and expression quantity. The method comprises the following steps: S1, extracting RNA, interrupting, and carrying out reversetranscription to obtain cDNA; S2, constructing a gene library by adopting cDNA; S3, capturing and enriching a target gene from the gene library by utilizing specific hybridization of a capture probe and the target region; S4, sequencing by using a high-throughput sequencer to obtain RNA targeted sequencing data; S5, analyzing changes of gene mutation and expression quantity in the RNA targeted sequencing data, wherein the step S5 specifically comprises the following substeps: S51, analyzing the gene expression quantity; S52, analyzing gene overexpression; S53, carrying out gene fusion analysis; S54, carrying out the fusion mutation expression quantity analysis; S55, carrying out the single nucleotide variation analysis; S56, analyzing the expression quantity of the mononucleotide variationmutation. RNA transcripts expressed by tumor-related genes can be efficiently enriched, and the expression quantity and mutation conditions of the tumor genes in tumor tissues are analyzed.
Owner:ZHENYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY JIANGSU CO LTD
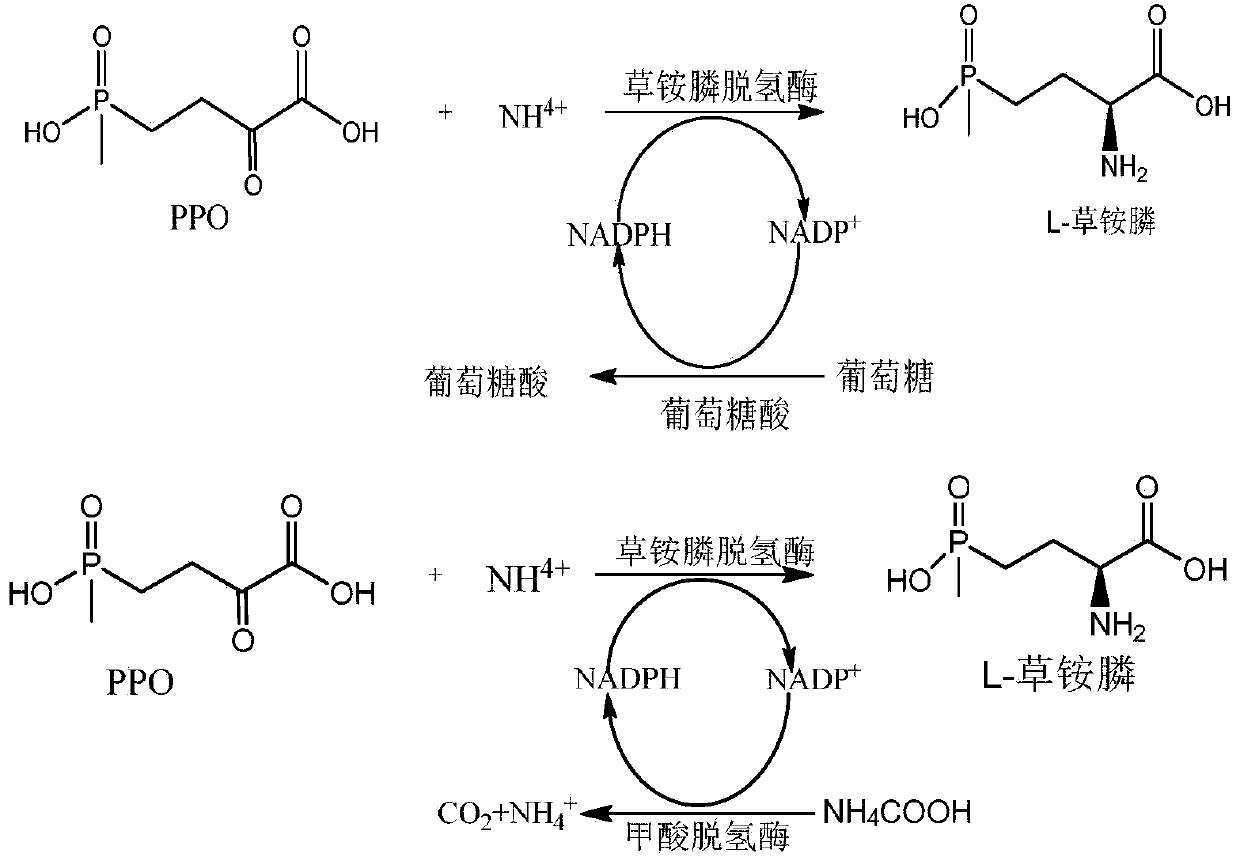
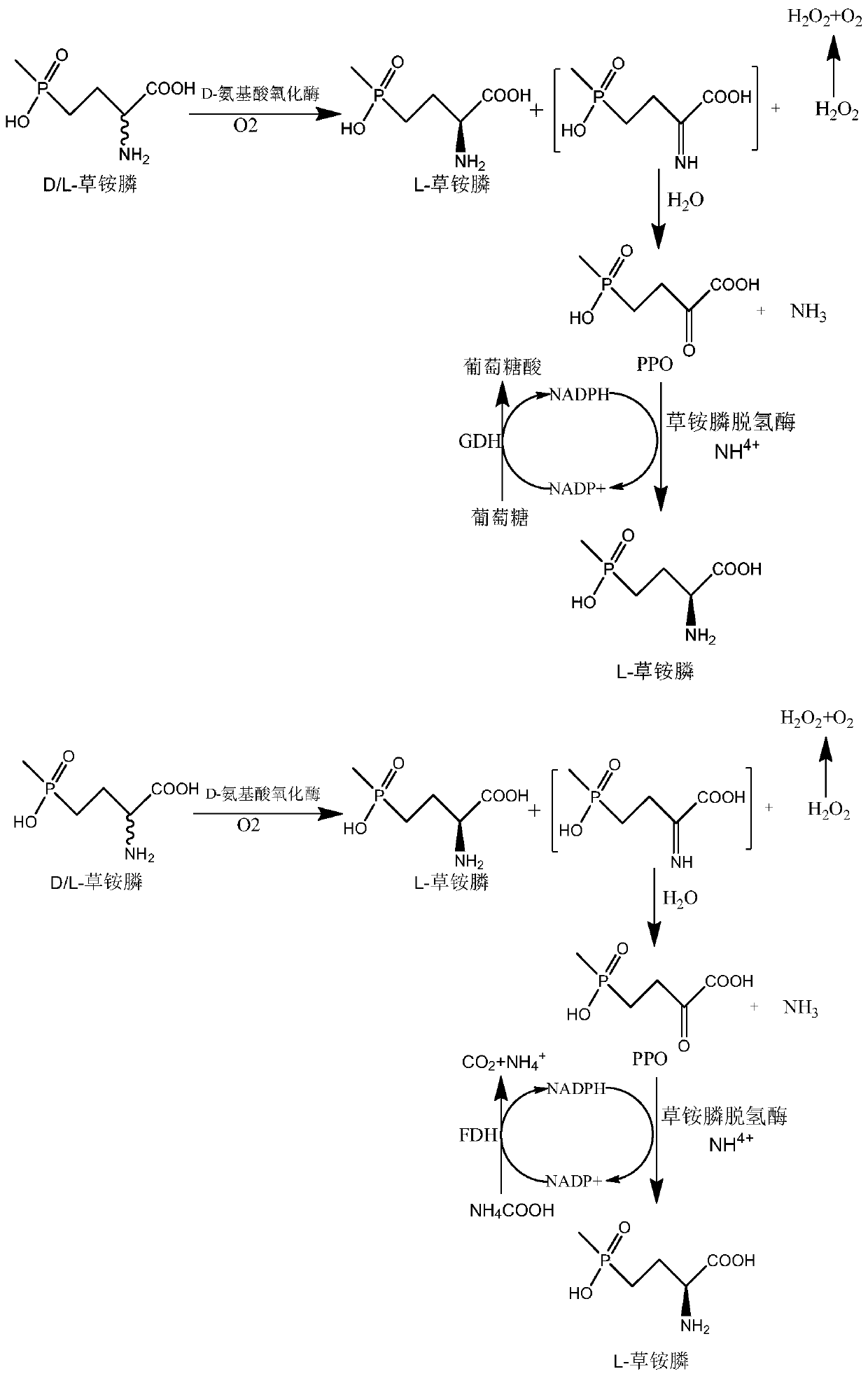
Recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase, genetically engineered bacterium and application of recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase in preparation of L-glufosinate-ammonium
InactiveCN110885803AIncrease enzyme activityImprove catalytic performanceBacteriaEnzymesEngineered geneticMutant
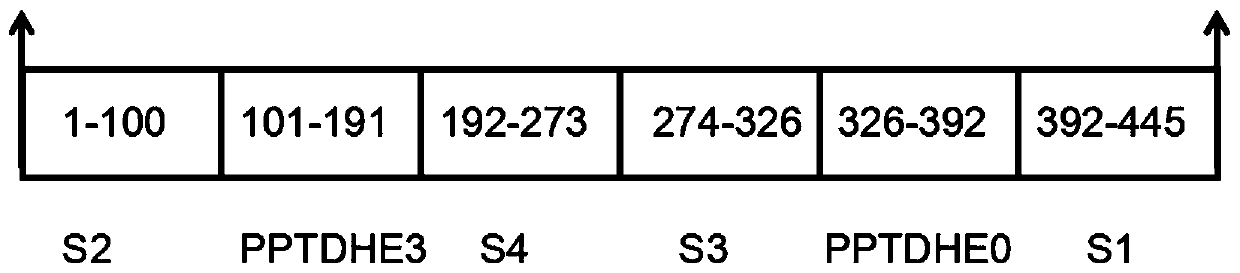
The invention discloses recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase, a genetically engineered bacterium and application of recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase in preparation of L-glufosinate-ammonium. The amino acid sequence of the recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. According to the invention, a gene library of the recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase is constructed through a staggered extension pcr gene rearrangement technology, and the recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase with high enzyme activity, catalytic performanceand stereoselectivity is screened from the gene library; the activity of the recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase is respectively improved by 31% and 35% in comparison with the activity of aprevious mutant PPTDHE3-A164G and the activity of a previous mutant PPTDHE0-V375S; and finally, 108 g / L of 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethyl phosphine oxide)-butyric acid is completely catalyzed to producethe L-glufosinate-ammonium, and only 20min is needed (transaminase generally needs 40h), wherein the ee value is larger than 99.5%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for designing, amplifying and sequencing twelve pairs of floccularia luteovirens microsatellite primers
InactiveCN105969862AEliminate distractionsEliminate cumbersome stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationNucleotide diversityFloccularia luteovirens
The invention relates to a method for designing, amplifying and sequencing twelve pairs of floccularia luteovirens microsatellite primers. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting genome DNA of three floccularia luteovirens populations among which the geographic interval is more than 300km by using an improved CTAB method; (2) randomly selecting an individual genome DNA respectively from the three populations, mixing, detecting the quality of total DNA, preparing a gene library, and performing Illumina HiSeq<TM>2500 sequencing after the gene library is qualified in examination in depot; (3) splicing sequenced data, detecting simple sequence repeats (SSR) in the total DNA sequence by using SR search software, and performing primer design by applying primer3; (4) preparing an SSR primer having an annealing temperature of 50-60 DEG C by adopting a temperature gradient method; (5) respectively performing PCR amplification on the genome DNA of the three floccularia luteovirens populations, and sequencing and verifying to obtain 12 pairs of primers with polymorphism; and (6) calculating the number N of allelic genes, haplotype diversity H<d> genetic differentiation coefficient F<ST>, nucleotide diversity P, G<ST> and the value of pi. The method is beneficial to large-scale research.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
Enhance-like element gene for enhancing foreign protein expression and application of gene
InactiveCN102965375AIncreased expression level propertiesIncrease resistanceVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationBacterial strainCapsid
The invention discloses an enhance-like element gene ER1 for enhancing foreign protein expression in prokaryotic cells. The enhance-like element gene has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 (Sequence Identity No) or a truncated sequence of the nucleotide sequence, wherein the gene sequence is screened by establishing a fusion expression reporter gene recombinant vector; the fusion reporter gene consists of major capsid protein L1 gene of human papilloma virus and chloramphnicol acetyltransferase (CAT); the gene fragments to be selected are linked with the sieving recombinant vector and is transformed so as to establish a gene library; and the recombinant bacterial strain containing the enhance-like element gene sequence is screened based on the chloramphenicol resistance, so as to obtain the enhance-like element sequence which can improve the activity of chloramphenicol of the fusion reporter gene of the strain and promotes the foreign protein expression.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing all-pig-source monoclonal antibody with single B cell PCR technology
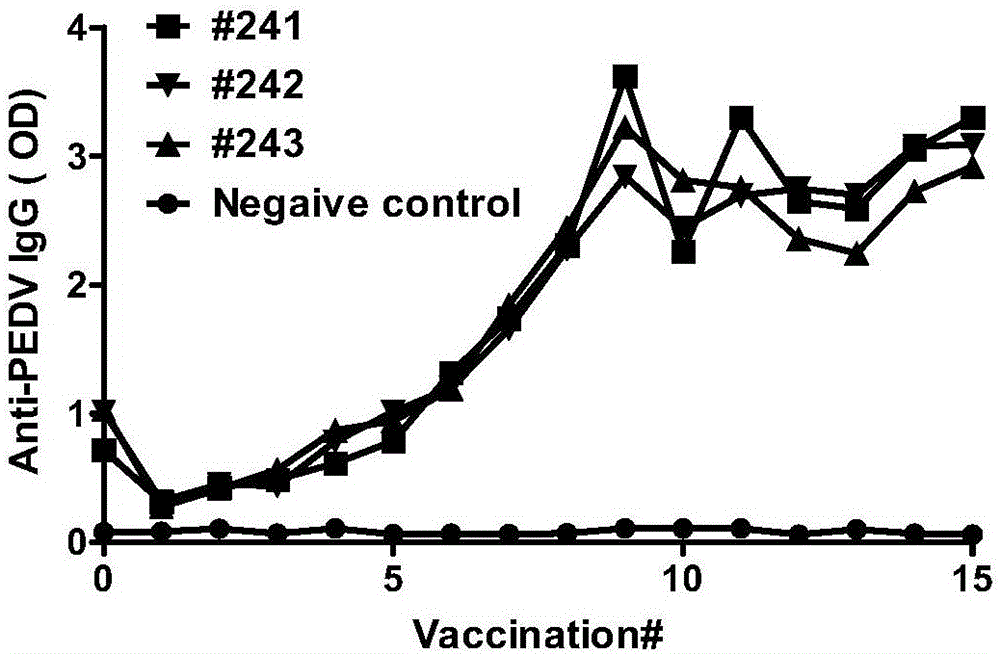
ActiveCN106086009AHas neutralizing antibody titersImprove efficiencyImmunoglobulins against virusesOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic libraryPolymerase chain reaction
The invention discloses a method for producing an all-pig-source monoclonal antibody with a single B cell PCR technology and belongs to the technical field of biology. An existing pig antibody gene library is used, multiple types of primers are designed, an antibody variable region gene is amplified from a single B lymphocyte with a nested PCR (polymerase chain reaction), and the all-pig-source monoclonal antibody with neutralizing antibody activity is screened. The method for producing the all-pig-source monoclonal antibody with a high-throughput single B cell technology is firstly established; compared with conventional antibody preparation technologies, the method has the advantages of being high in efficiency and good in gene diversity, covering all pig sources and the like. A new technological means is provided for research of antibody immune response and separation of a therapeutic antibody after proposal of the method.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
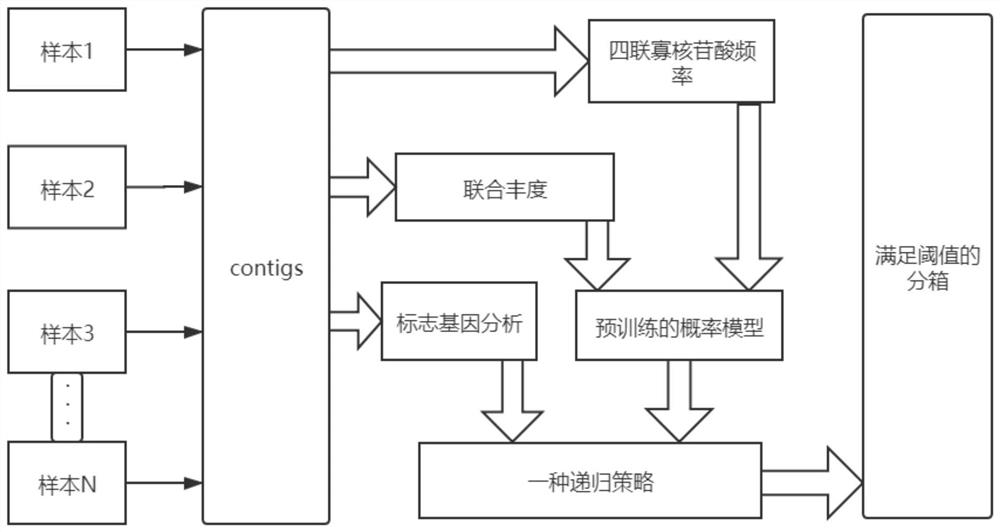
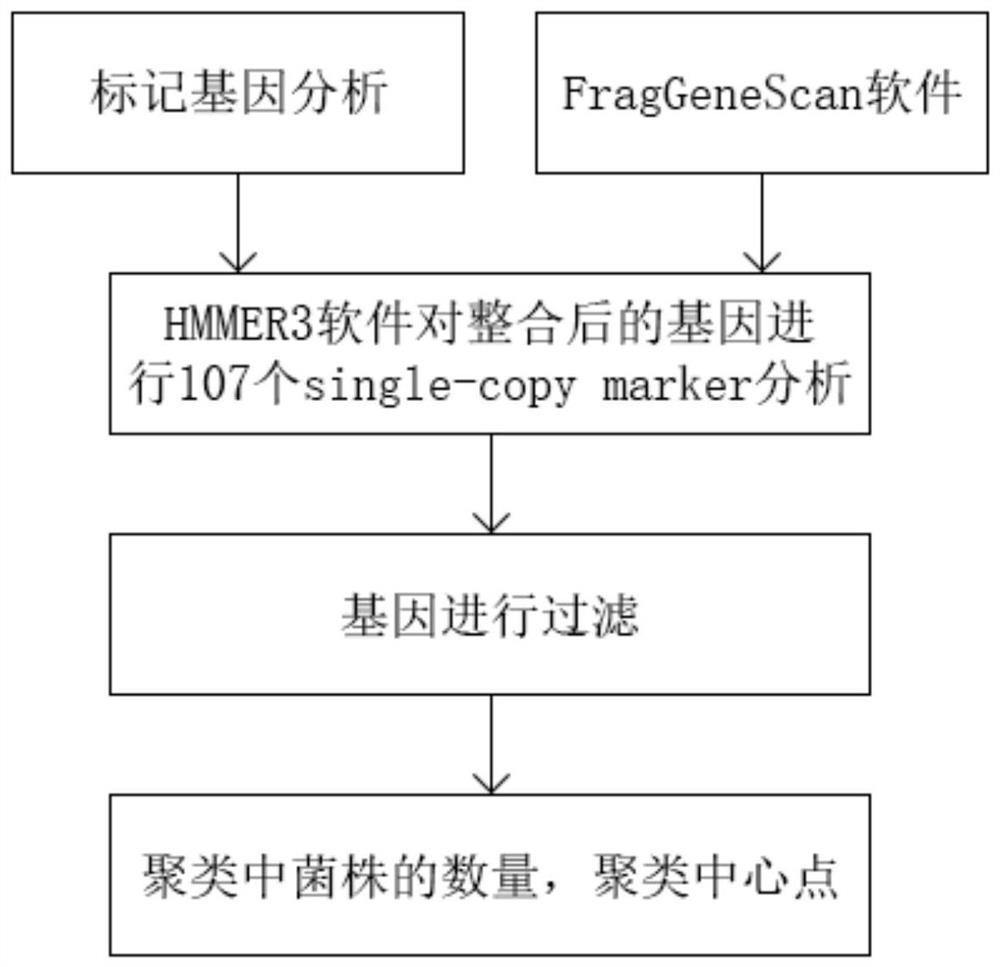
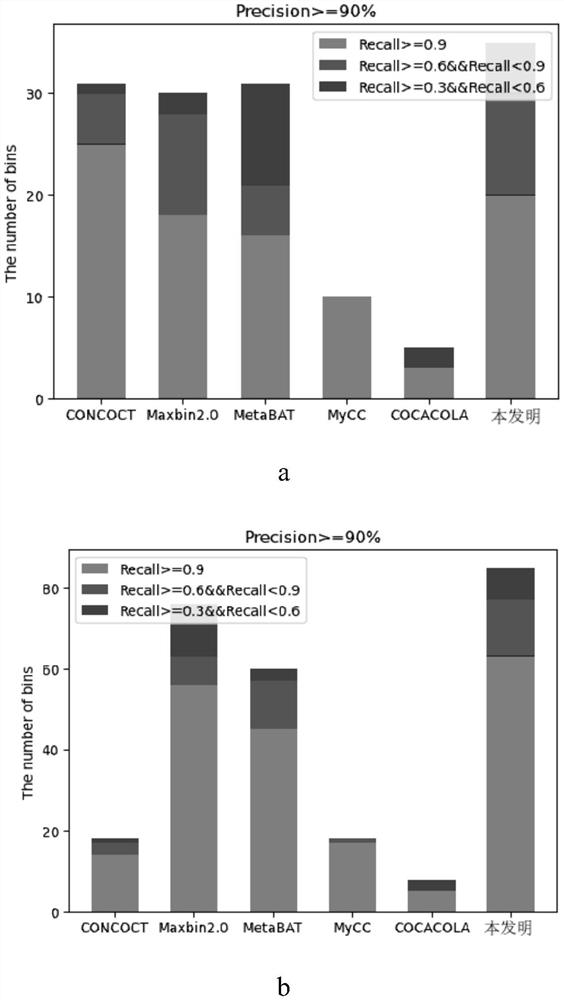
Unsupervised clustering method and system for metagenome contigs
PendingCN112466404ASimplify complexityQuality improvementBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorContig
The invention discloses an unsupervised clustering method for metagenome contigs, which comprises the following steps of: before clustering, putting reads of each sample together to construct a gene library, assembling the reads into contigs by using an assembling tool, and performing feature vectorization on each contigs according to the frequency of quadruple oligonucleotides and co-abundance, then carrying out clustering according to a pre-trained probability model and a recursion strategy, introducing CheckM to carry out clustering result quality detection and simplify the complexity of asample and taking the clustering result as an algorithm termination condition, and taking a result obtained by Marker gene analysis as strain number initialization and clustering center sequence initialization in algorithm initialization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
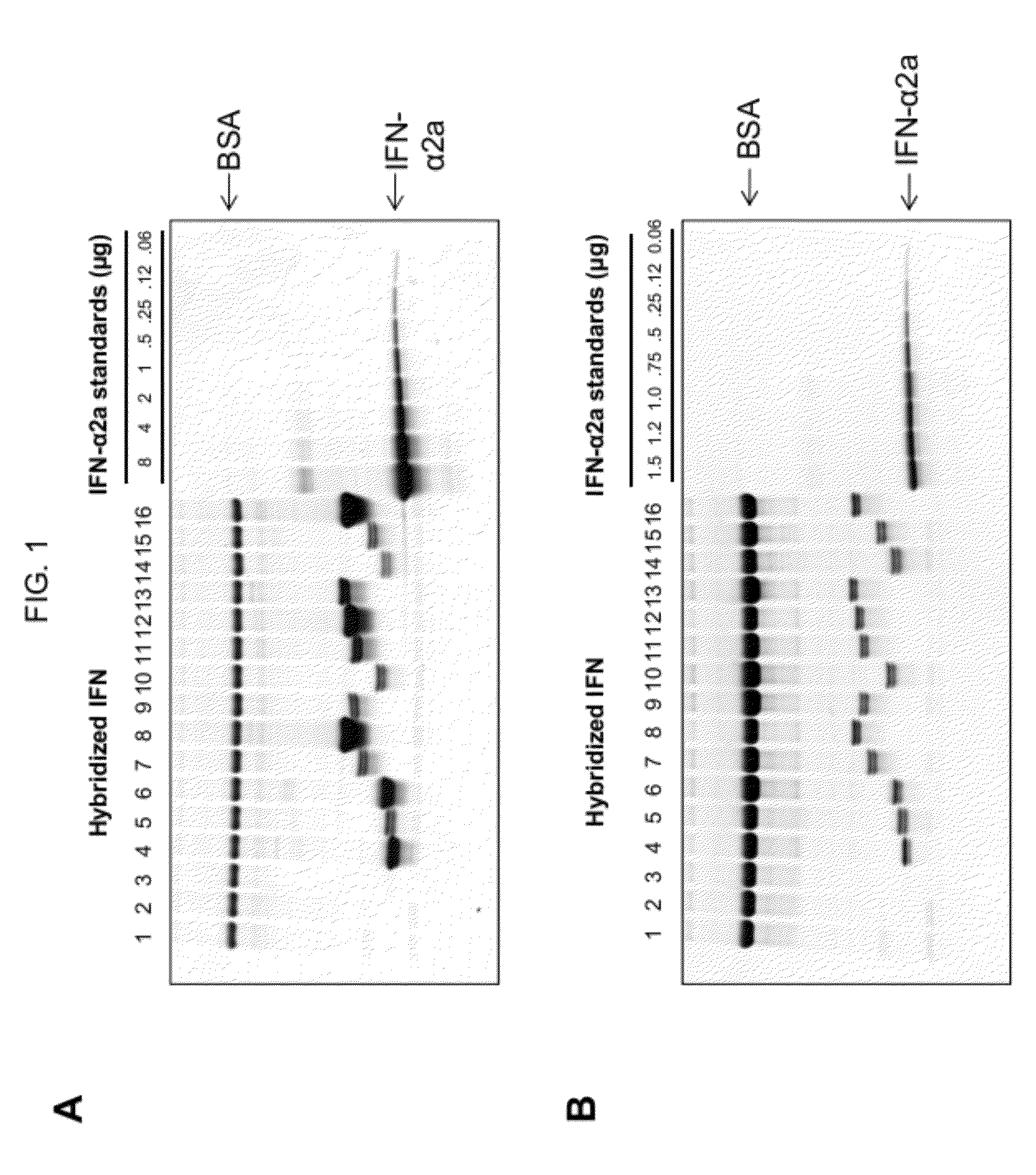
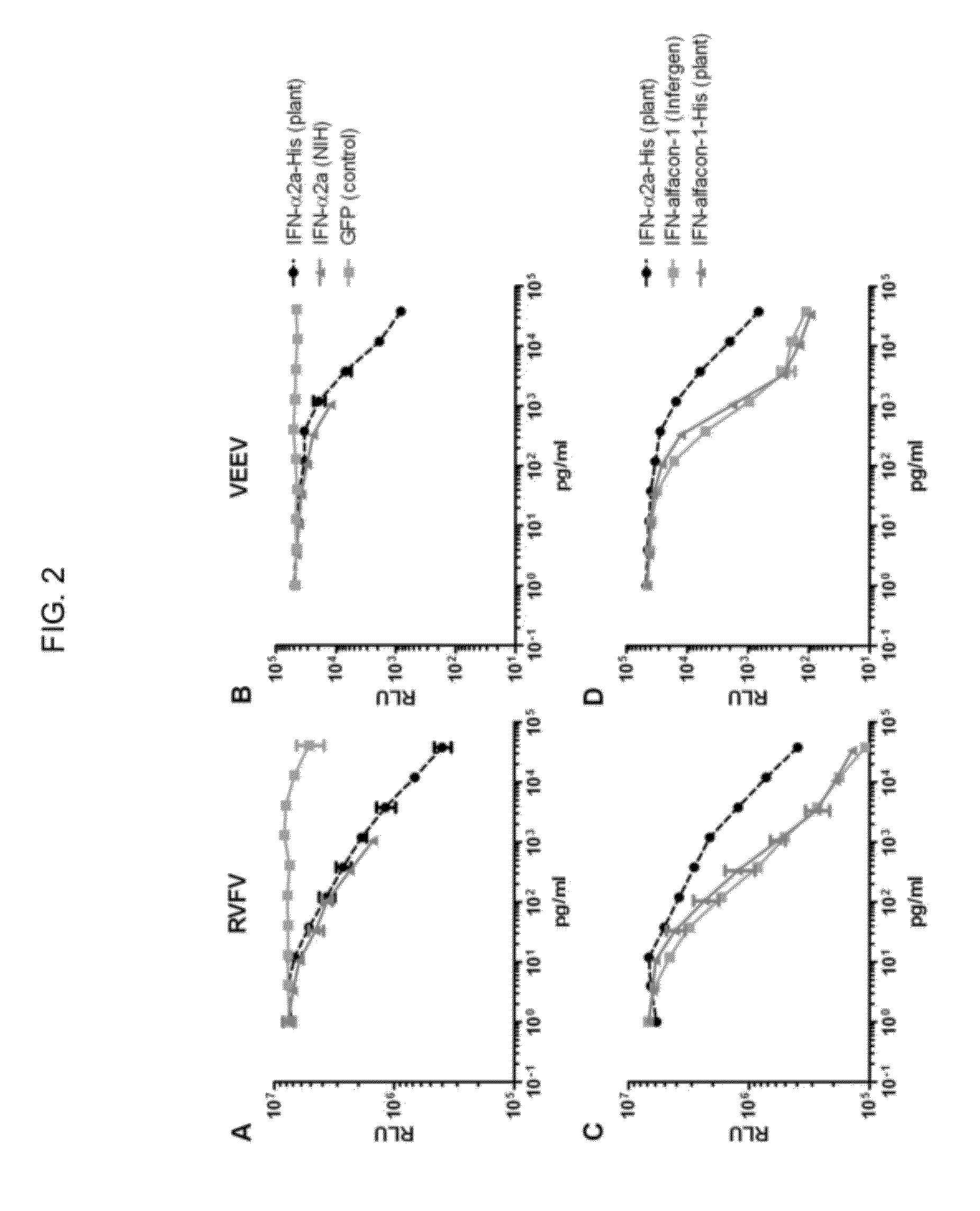
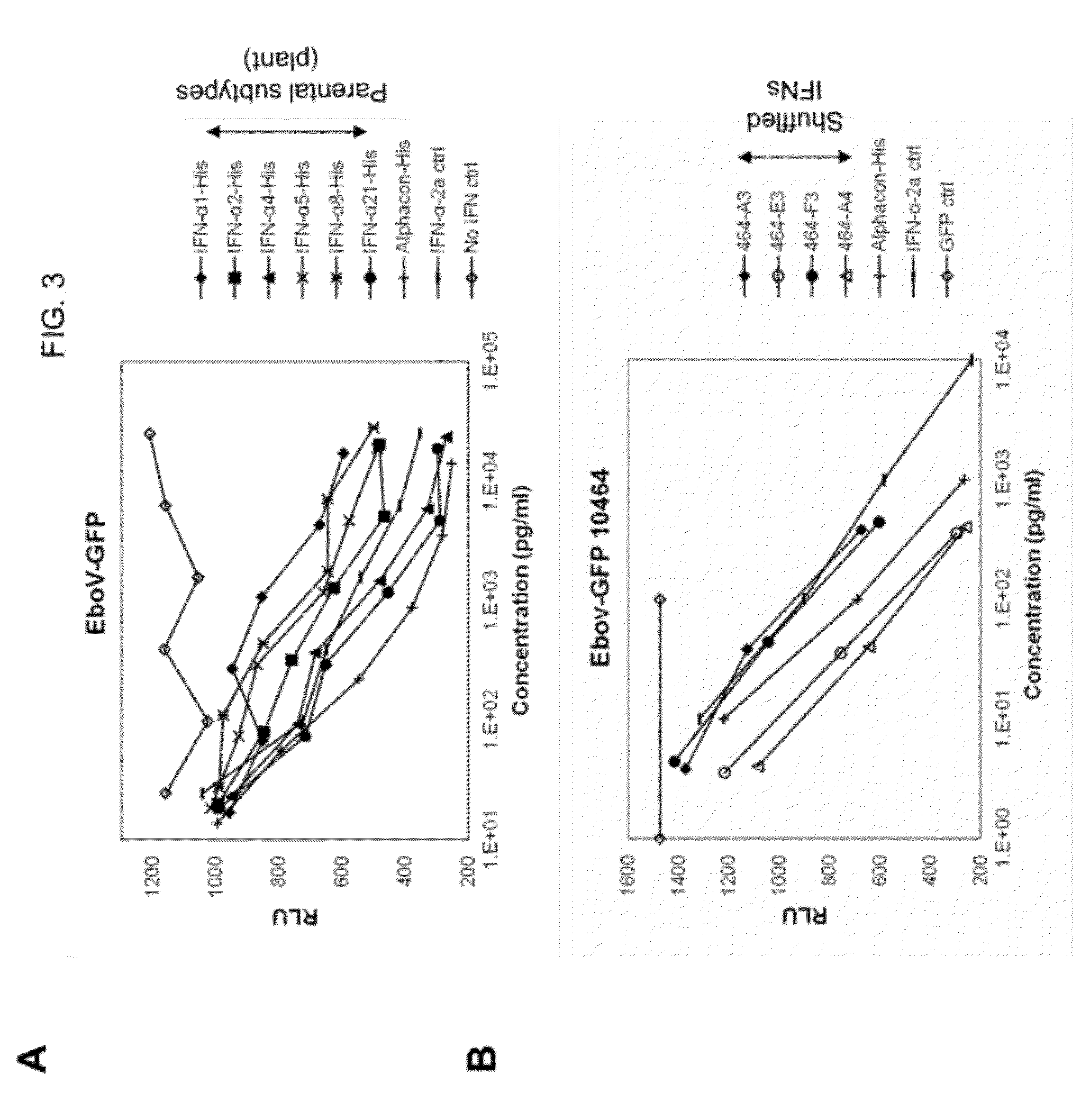
Selection and characterization of novel plant-derived recombinant human interferons with broad spectrum activity
InactiveUS20120302733A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide preparation methodsHybrid typeHighly pathogenic
Methods to derive novel hybrid type 1 interferons that are broadly active against highly pathogenic viruses of biodefense significance are described. Libraries of hybrid interferon genes were produced using gene shuffling, the proteins were expressed, and screened for activity against viruses of interest. Sequences of several broadly active hybrid interferons are described.
Owner:PADGETT HAL S +2
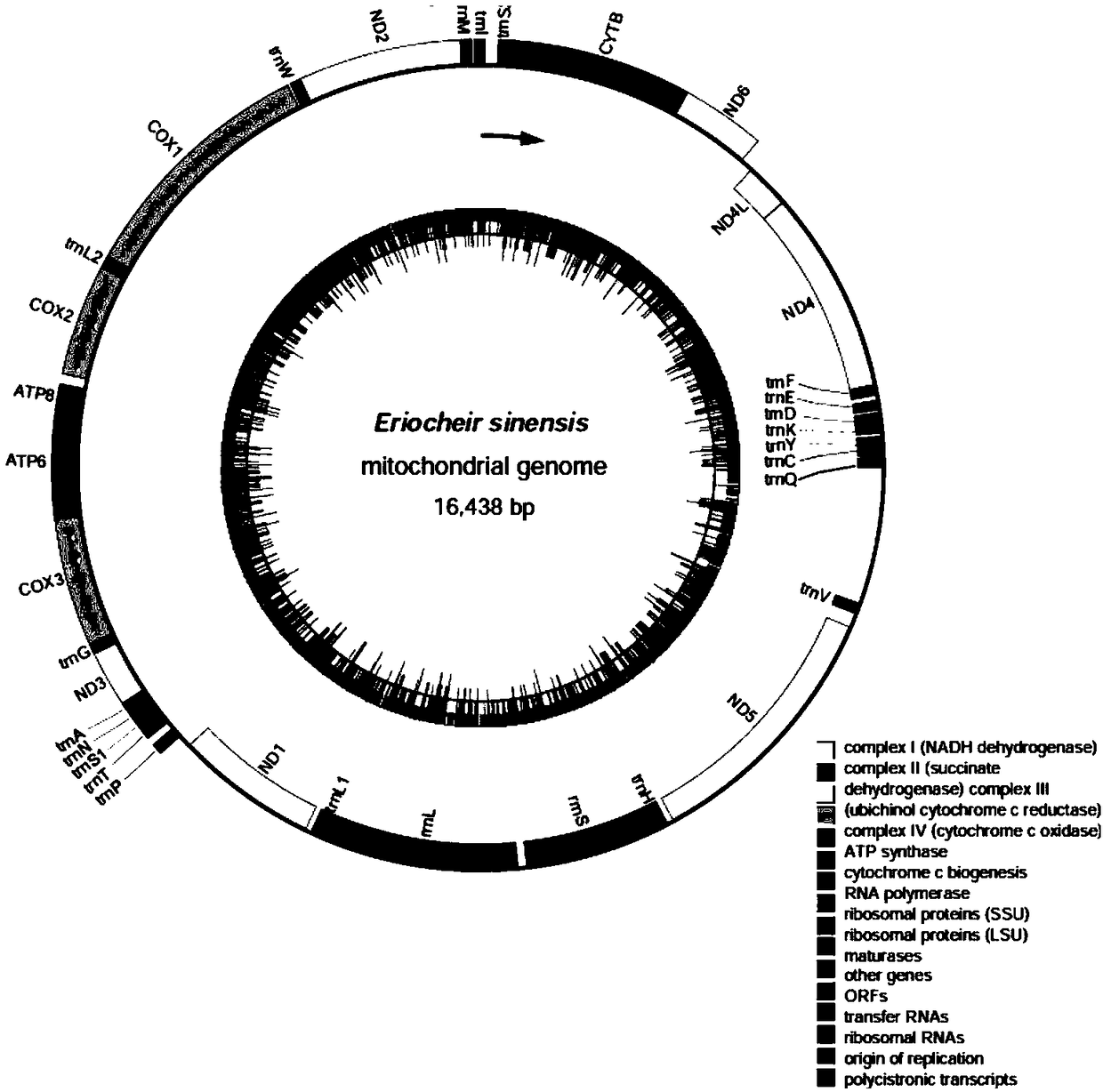
Method for precisely determining mitochondrion whole genome sequence of eriocheir sinensis
ActiveCN109280700AOvercome workloadOvercome costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence designMuscle tissue
The invention relates to a method for precisely determining a mitochondrion whole genome sequence of eriocheir sinensis and the whole genome sequence obtained by using the method. The method comprisesthe following steps of (1) extracting the whole genome DNA in eriocheir sinensis muscle tissues, building a gene library, and performing sequencing by using a second generation sequencing technology;(2) screening a sequencing read segment by referring to the mitochondrion whole genome sequence of closely related species; eliminating nuclear DNA segments; then performing mitochondrion genome splicing; and performing prediction annotation on the protein-coding genes, rRNA and tRNA of the spliced mitochondrion genome; and (3) comparing the spliced mitochondrion genome sequence and the mitochondrion genome sequence of the closely related species; performing PCR amplification on a corresponding second generation sequencing sample according to a conservative region by referring to a mitochondrion whole genome sequence design primer of the closely related species; sequencing a PCR amplification product by using a first generation sequencing technology; and correcting the spliced mitochondrion genome sequence. The method has the advantages of high speed and high accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for separating and purifying insect pathogenic fungoid thallus from infected insect haemolymph
InactiveCN1807580ANo pollution in the processFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmGenetic Materials
This invention discloses a method for segregation purifying insect pathogenic fungi thalline from suscepted insect bloodlympha. It is prepared through steps as follows: deal with blood cell of suscepted insects with a series of enzymes to destroys and removes their germ plasms; finally seperate and purify to get the products. Adopt the achieved pathogenic fungi thalline to extract DNA and mRNA, which has no insect germ plasm pollution according to PCR and RT-PCR verification. The DNA and mRNA extracted can be used to construct gene library, it also lays solid foundation for further uncovering entomogenous fungi invading mechanism.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Novel feruloyl esterase and preparation method and application thereof
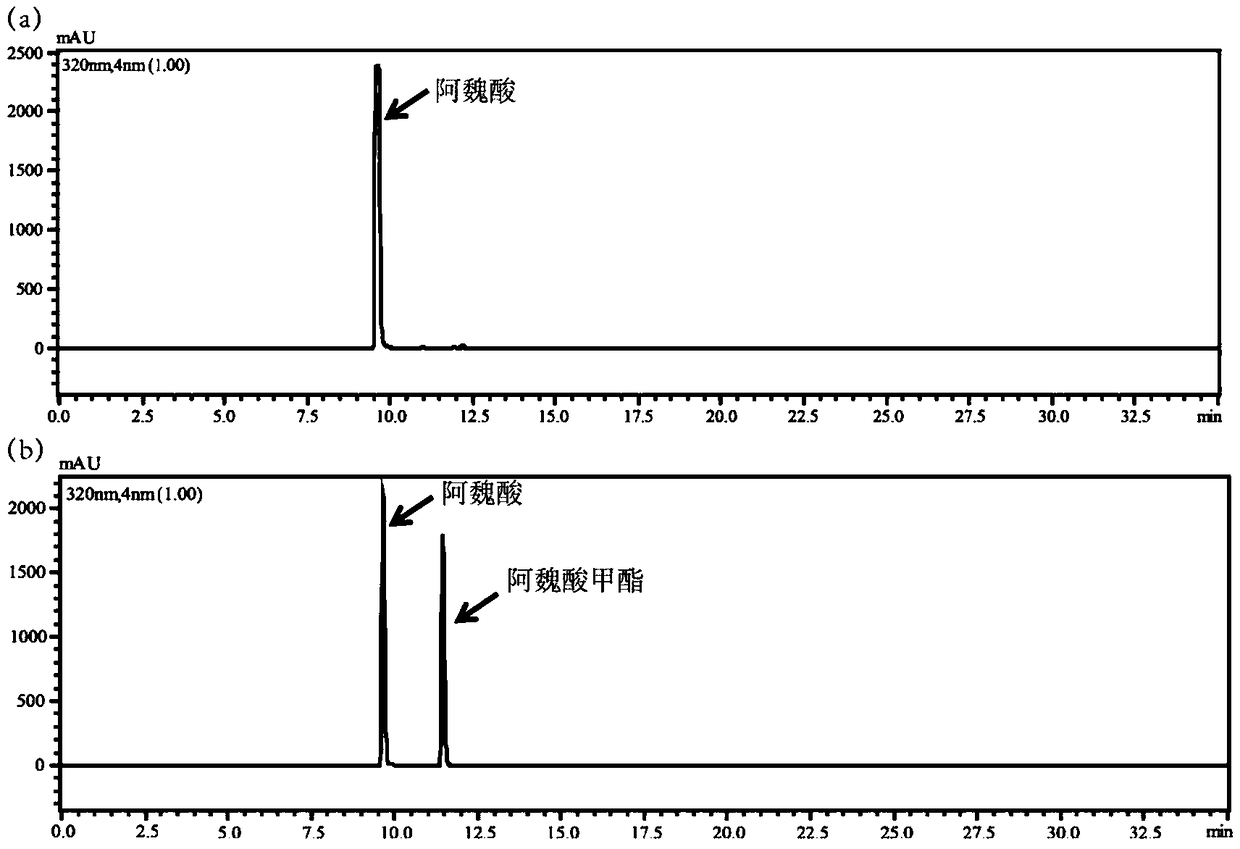
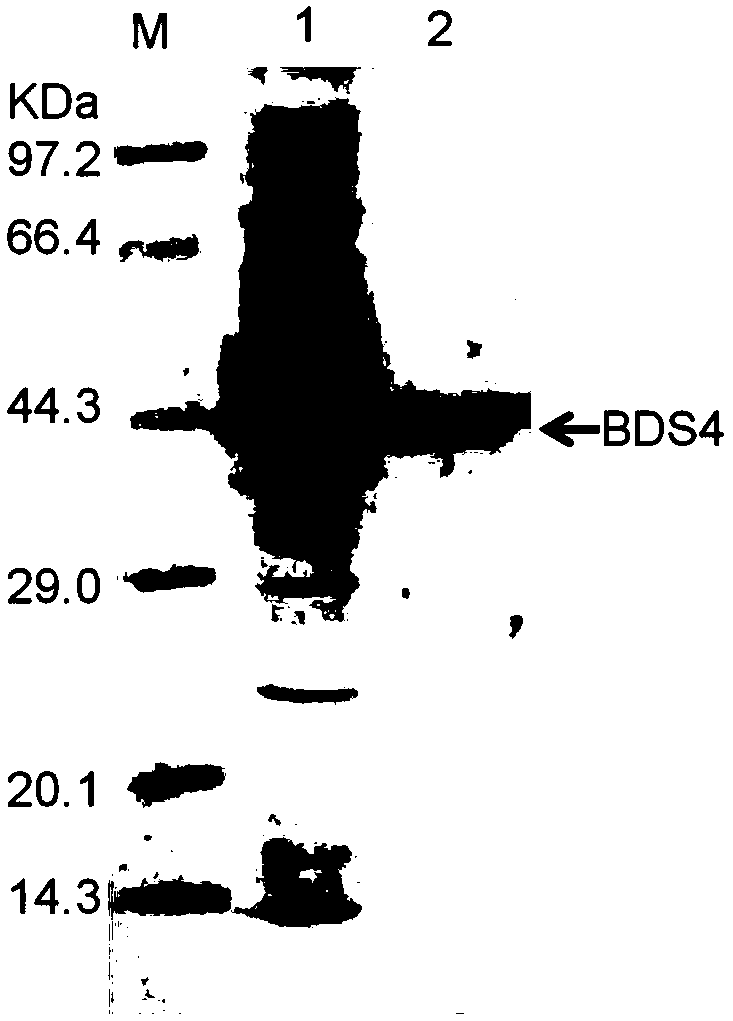
The invention provides a feruloyl esterase gene derived from a soil macrogene library. The nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence of the feruloyl esterase gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ IDNO.2. The esterase gene is inserted into a plasmid pET-28a(+) and transformed into escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to achieve heterologous expression. The molecular weight of a purified recombinant enzyme (BDS4) is 38.8 kDa. In addition, it is proposed for the first time that novel feruloyl esterase can hydrolyze various plasticizers such as dimethyl phthalate, diethyl phthalate and dibutyl phthalate. It is shown through site-directed mutagenesis experiments that a catalytic triplet of BDS4 consists of serine (S158), aspartic acid (D256) and histidine (H286), and the mutation of any of the threeamino acids can lead to the loss of catalytic capability of BDS4. In the presence of xylanase, BDS4 can significantly increase the amount of ferulic acid released from de-starched wheat bran. The novel feruloyl esterase can be applied in the fields of feed, paper making, food, pharmacy and the like due to the unique activity and enzymatic properties of the novel feruloyl esterase.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Clone and application of alcohol fermentation gene of unit cell fungus through motion ferment
This invention establishes a motion fermentation monocell XW 101 plasmid gene library, ethanol dehydrogenase II gene partial sequence is used as probe for screening or cloning ethanol dehydrogenase II gene from above said library, then connecting the same to shuttle plasmid carrier of broad host range, finally conducting to wild type motion fermentation monocell bacteria or colon bacillus. Said cloned ethanol dehydrogenase II coded gene sequence is as illustrated in SEQ ID No.1. The wild type motion fermentation monocell bacteria introduced with ethanol dehydrogenase II coded gene can greatly increase the prodn. rate of ethanol due to obviously speeding-up fermentation.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for quickly building differential expression gene library
ActiveCN103114086ASimplify operating proceduresReduce experimental errorLibrary creationProtein nucleotide librariesSubtraction hybridizationEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a method for quickly building a differential expression gene library. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly extracting total mRNA of infected goose parvovirus and uninfected goose parvovirus goose bursas of fabricius; synthesizing double strands cDNA for enzyme digestion by utilizing the obtained mRNA, and then separating into 2 pipes, respectively adding different adaptors for connecting; carrying out forward subtractive hybridization on the double strands cDNA with the adaptors, then carrying out reverse subtractive hybridization on a forward subtractive hybridization product, carrying out the primary PCR (polymerase chain reaction)) amplification after reverse subtractive hybridization, and carrying out the secondary PCR amplification by taking diluent as a template after diluting an amplification product; and finally carrying out denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis on a product of the second PCR amplification, and dying after electrophoresis to obtain the differential expression gene library of the goose parvovirus stress bursa of fabricius. The gene library built by the method does not have false positive. The method has the characteristics of high speed, high sensitivity, strong specificity, low cost, convenience in operation, and the like.
Owner:山东施得维特生物工程有限公司
Surface antigen 1 of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment and encoded gene thereof
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment, encoded gene and use thereof. According to the invention, the surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment is filtered from a base through establishing a Toxoplasma gondii human immunoglobulin, ELISA, diluting the prothrombin time, sequencing analysis, etc. Through expression purifying and authenticating, the human antigen Fab fragment is authenticated to specifically identify the tachyzoite-bradyzoite recombination SAG1 of Toxoplasma gondii and have higher affinity with the tachyzoite-bradyzoite recombination SAG1 of Toxoplasma gondii, for being identified with the specificity of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite-bradyzoite. The human antigen Fab fragment of the invention does not contain Fc segment and does not activate the alexin or cause the histopathological damages of human immune response, etc. when the function of restricting the invasion of Toxoplasma gondii to the host cell is exerted. The surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment is safe and reliable when applied for the human body. The antigen medicine for treating toxoplasmosis or the antigen targeted medicine can be prepared.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Enhanced subsample gene capable of improving expression of foreign protein and application thereof
InactiveCN103602684AIncrease resistanceImprove practicalityVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationCapsidChloramphenicol Acetyl Transferase Gene
The invention discloses an enhanced subsample gene capable of improving expression of foreign protein in a prokaryotic cell. The gene has a nucleotide sequence or a truncated sequence thereof shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The gene is screened by constructing a fusion expression report gene recombinant carrier. The fusion expression report gene consists of a truncated sequence L11 of a main capsid protein L1 of a human papilloma virus and a chloramphnicol acetyl transferase gene (CAT). A to-be-screened gene segment and the recombinant carrier for screening are connected and converted for constructing a gene library, and a recombinant strain comprising the gene sequence of the enhanced subsample is screened by improving the resistance of chloramphnicol, so that the enhanced subsample sequence is obtained. The sequence can be used for improving the resistance of chloramphnicol of the fusion expression report gene recombinant carrier and the expression level of the foreign protein.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
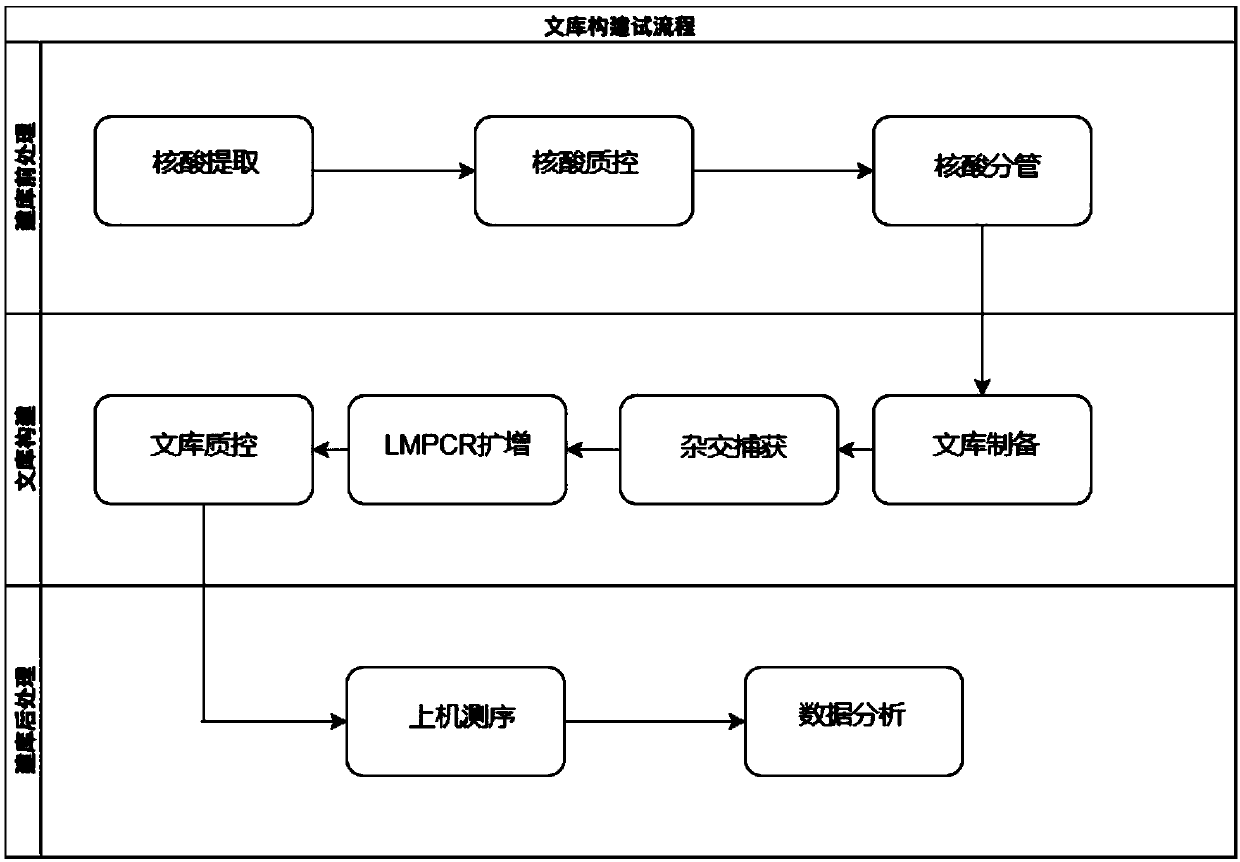
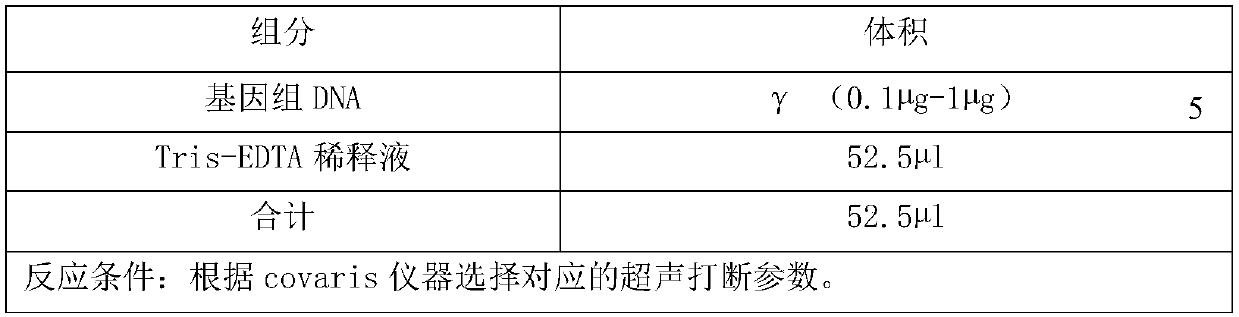
Constructing method of genetic testing library for inherited arrhythmias and kit for inherited arrhythmias
InactiveCN109593828AEfficient captureImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationHybridization probeGenetic Screening (procedure)
The invention discloses a constructing method of a genetic testing library for inherited arrhythmias and a kit for inherited arrhythmias, and relates to mutation of KCNH2, KCNQ1, SCN5A, RYR2, CASQ2, TRDN and CALM1 genes. Target regions are exon regions of coded amino acid of the seven genes, 20 base regions on the upstream of an exon and 20 base regions on the downstream of the exon; for ensuringall coverage of the target regions, after a preparation library is adopted, a target region library is obtained by a hybridization probe capturing method; then the library is amplified by adopting anLMPCR method; the library is purified to obtain a sample library for sequencing. The constructing method comprises simple and quick steps, so that the constructing cost of the library is effectively reduced; in addition, related genes of arrhythmia are covered; by combination with an illumine high throughput sequencer, the mutation of the related genes can be quickly and accurately obtained; the constructing method and the kit have important significance for the inherited arrhythmias.
Owner:ANNGEEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
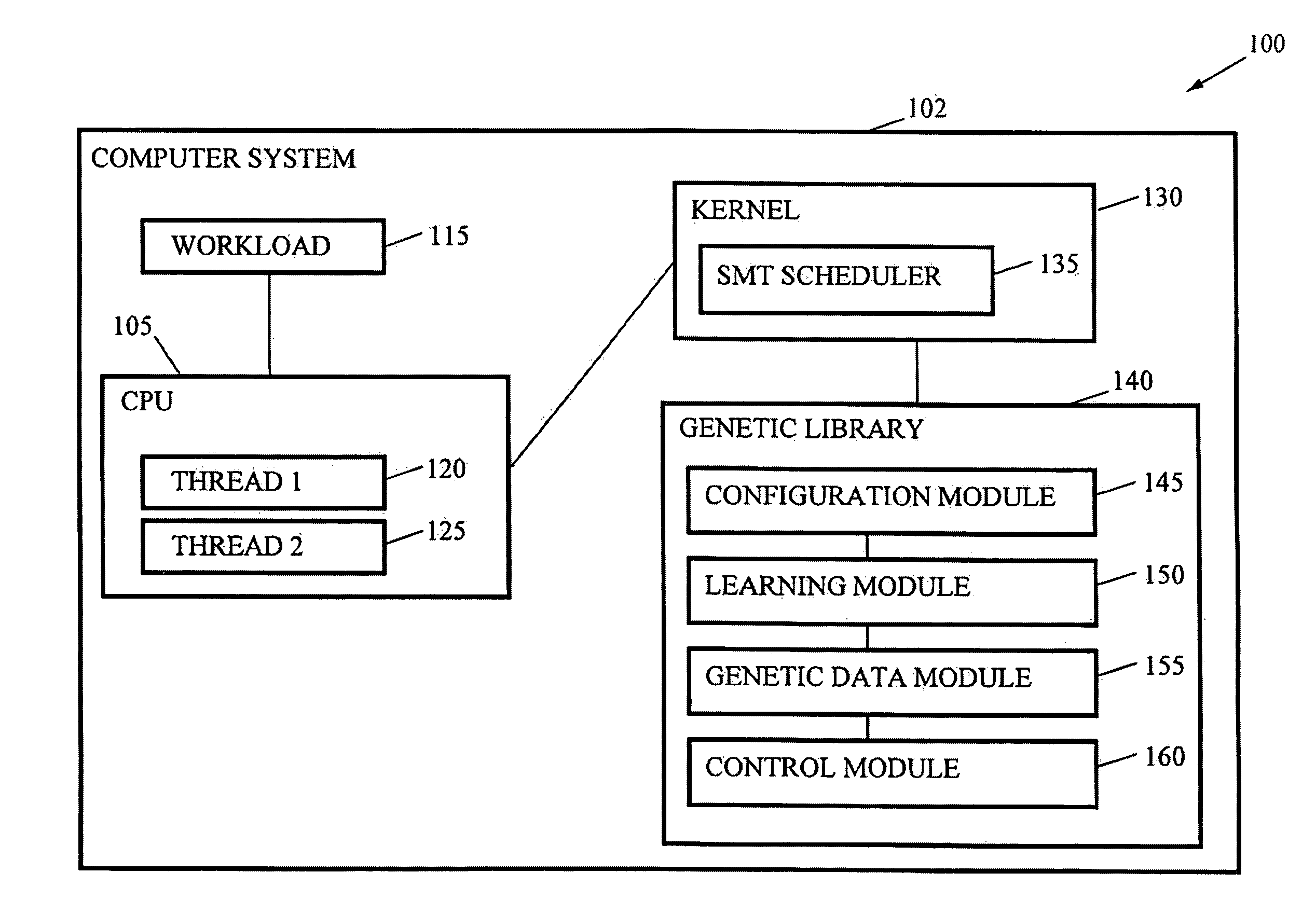
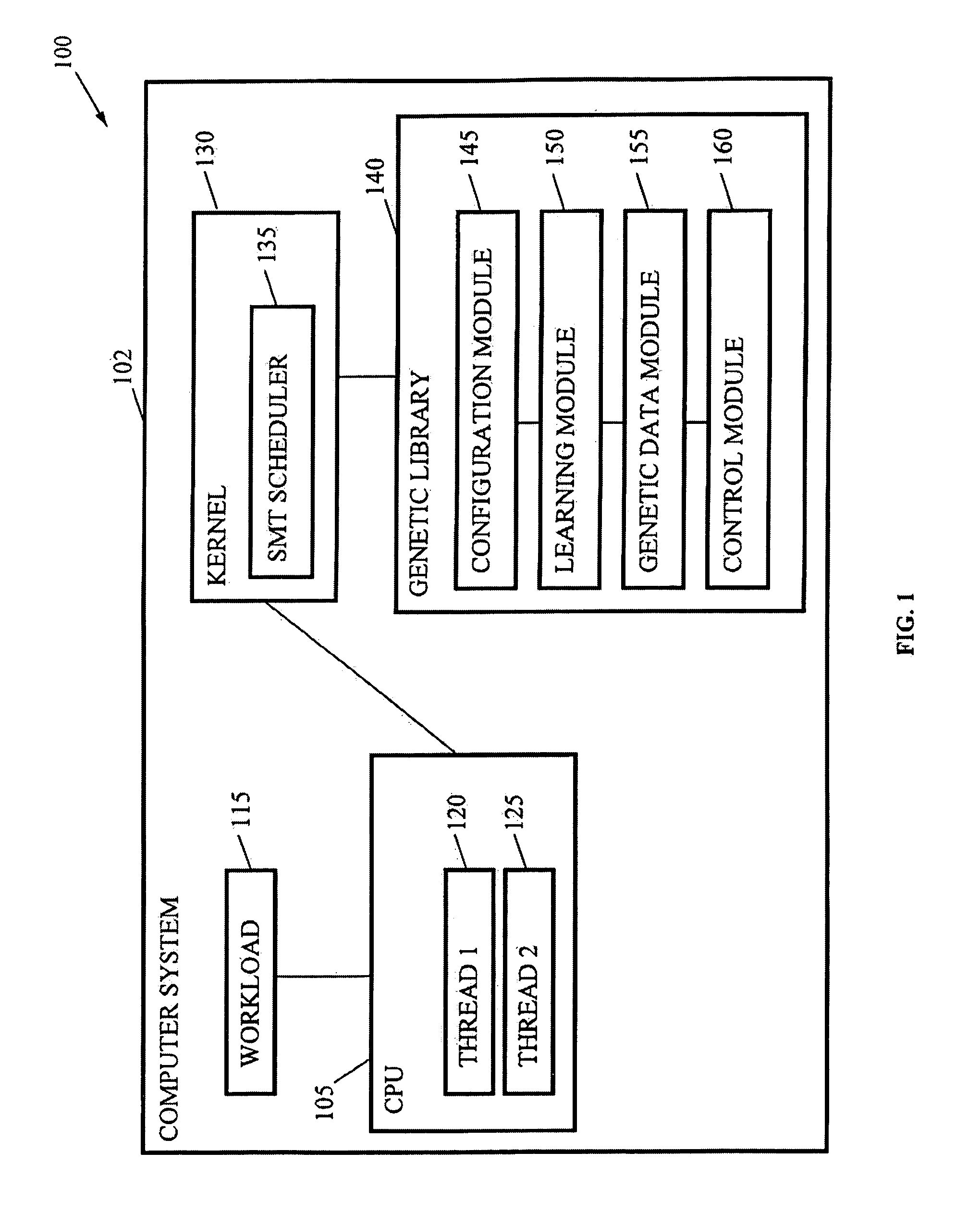
Autonomic SMT System Tuning
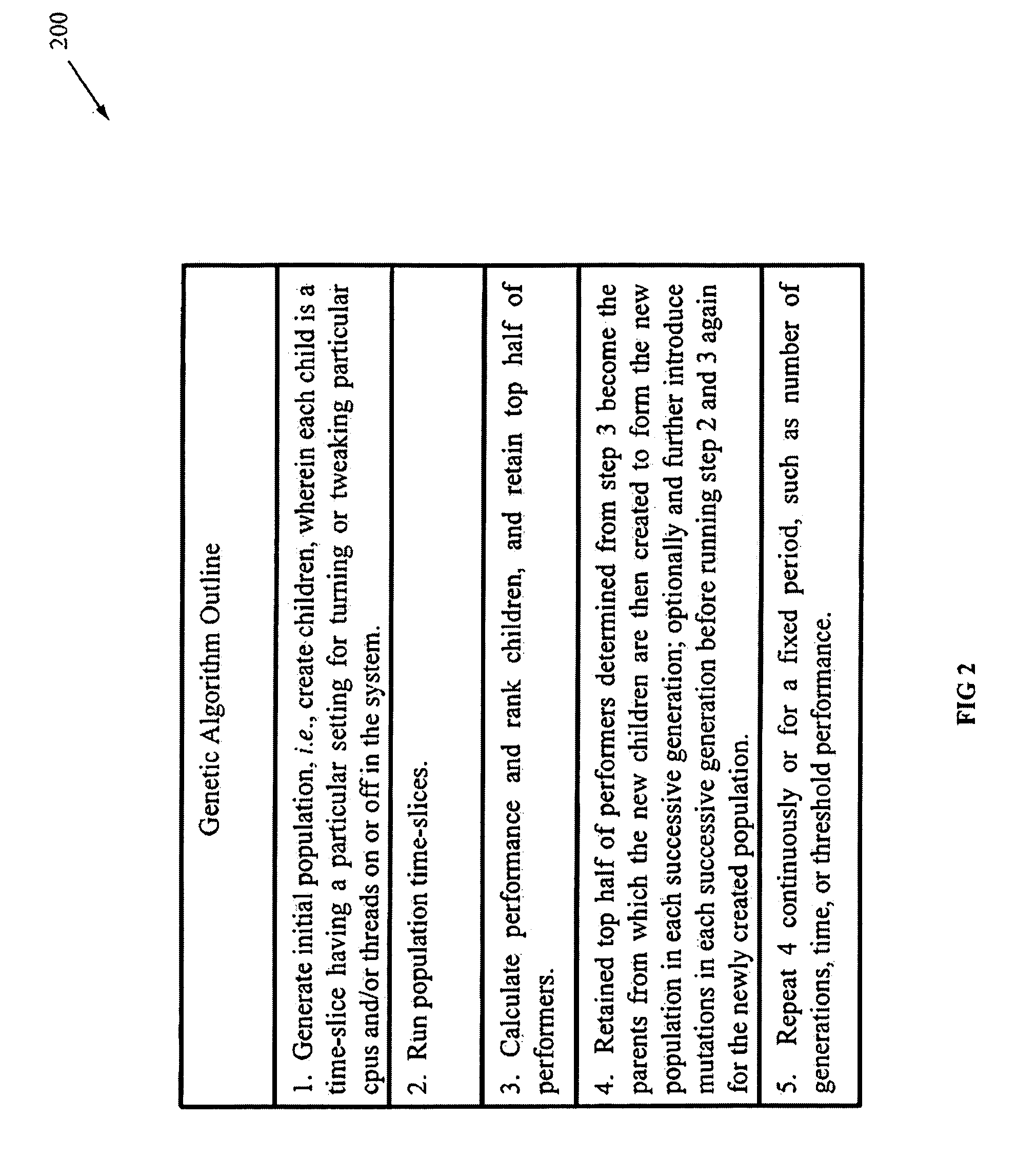
InactiveUS20080177682A1Easy to handleImprove throughputDigital computer detailsElectric digital data processingComputerized systemWorkload
Methods, systems, and media are disclosed for autonomic system tuning of simultaneous multithreading (“SMT”). In one embodiment, the method for autonomic tuning of at least one SMT setting for an optimized processing, such as via throughput, latency, and power consumption, of a workload on a computer system includes calling, by a kernel, an SMT scheduler having at least one hook into a genetic library. Further, the method includes obtaining, by the SMT scheduler through the at least one hook, genetic data from the genetic library for the optimized processing of the workload. Further still, the method includes tuning, by the SMT scheduler and based on the obtaining, the at least one SMT setting for at least one cpu of the computer system.
Owner:MOILANEN JACOB LORIEN +1
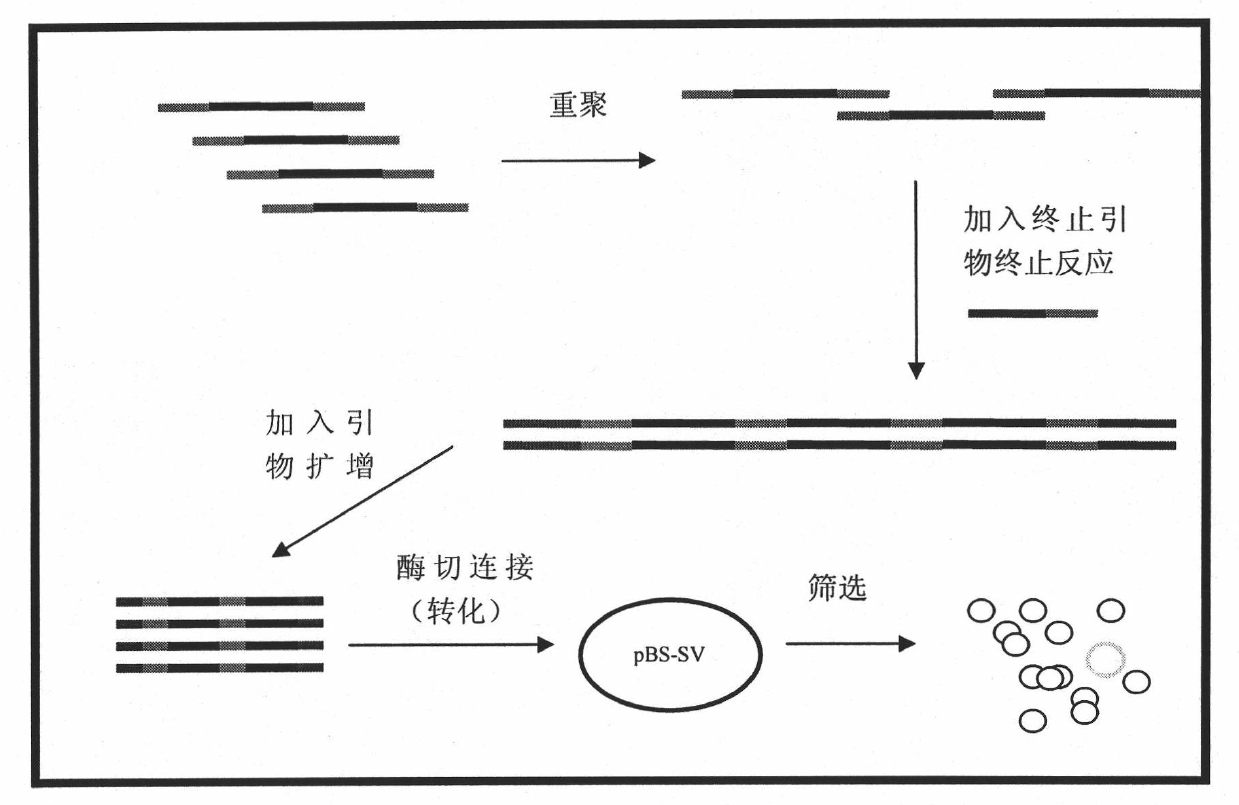
Novel method for building ultra-high capacity gene library based on combination principle and PCR
InactiveCN101792934ABreaking through the limitations of transformationWide avenueLibrary screeningLibrary creationReceptorPcr method
Directed evolution of enzyme is an effective way to change enzyme properties and improve utility value thereof. However, the existing methods for directed evolution all rely on existing genes, and only perform reconstruction on the basis of the well-discovered genes. Therefore, the existing methods can do nothing for absent or newly-minted screening targets in nature. The invention uses random segments with shared joints, connects, combines and reunites the random segments by a PCR method to obtain a huge gene library which is randomly combined. In theory, the library consists of random gene sequences, and screens at random target traits so as to create novel genes and break through the limitation of the previous direction evolution method which can only perform reconstruction on the existing genes. The invention (building an ultra-high capacity gene library) enables the directed evolution and medicine screening not to be limited by gene library diversity, provides a huge resource library for screening, and plays an active role in some targets which are difficult to screen the existing gene library such as screening of target receptor, discovering of unnatural condition enzyme, detection of new target substances and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
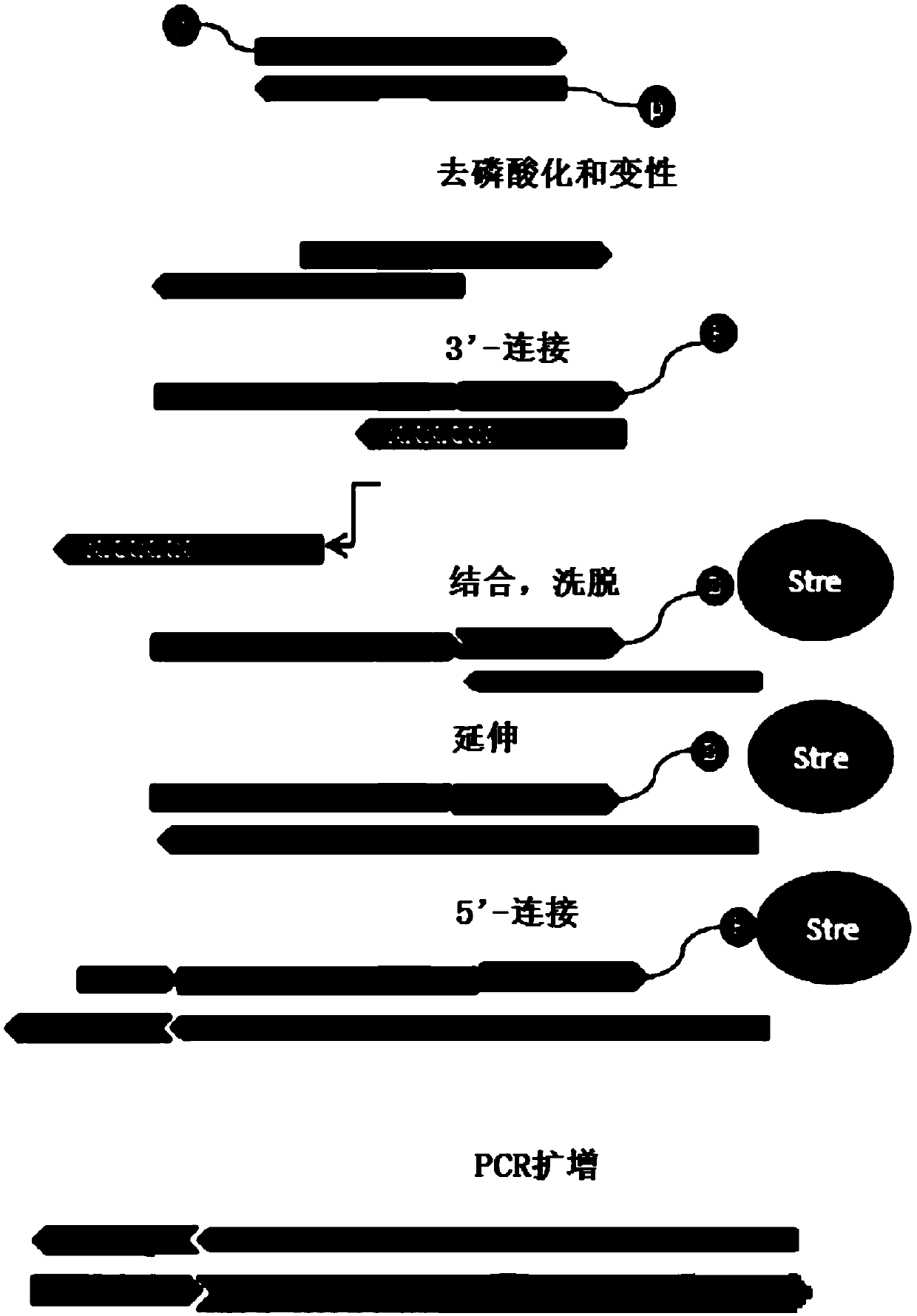
Method for treating single-stranded DNA, and applications thereof
ActiveCN110791813AIncrease profitIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSingle strandDouble strand
The invention discloses a method for treating single-stranded DNA, and applications thereof, and relates to the field of gene sequencing, particularly to a method for constructing a library based on single-stranded DNA. The method comprises: linking a first linker to the 3' tail end of single-stranded DNA, wherein the first linker is linked to binding agent, and comprises two partially complementary strands, the two partially complementary strands are respectively a first strand and a second strand, and the second strand has 5-10 basic groups more than the first strand; and adsorbing the single-stranded DNA linked to the first linker by using an adsorbent so as to remove the second strand, so that the double-stranded DNA containing the single-stranded DNA is obtained. According to the invention, the gene library constructed by the method has advantages of high molecular utilization rate, low initial quantity of samples for library construction and low minimum detection limit.
Owner:BGI GUANGZHOU MEDICAL LAB CO LTD +2
Method for storing information in vivo by using DNA
The invention belongs to the field of bioinformatics, and discloses a method for storing information in vivo by using DNA. The method includes: using PCR to amplify target fragments with different homology arms from a gene library with encoding information, assembling these fragments onto a plasmid vector using Gibson, transforming the plasmid vector into a microorganism for storage. The method uses DNA to encode the stored information in vivo, can successfully assemble different DNA fragments for encoding information by Gibson assembly on the carrier, and realize storage of digital information in vivo, and has advantages of low cost, easy storage and long storage time. In addition, because the information to be stored is cloned into the plasmid through Gibson assembly, the plasmid can bestably inherited in the presence of resistance, so that the information will not be lost, can be stably stored in a cell, and can be extracted when needed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com