Preparation method of short-fiber flaky cobalt carbonate negative electrode material
A technology of negative electrode materials and short fibers, which is applied in the field of chemistry and can solve the problems of little research on negative electrode materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] The preparation method of short fiber flake cobalt carbonate negative electrode material comprises the following steps:
[0018] (1) Fully dissolve 3.003g CO(NH2)2 and 2.4905g Co(CH3OOH)2 in 40ml deionized water respectively;
[0019] (2) Weigh 0.1g CTAB into the CO(NH2)2 solution, fully dissolve and stir;
[0020] (3) Add CO(NH2)2 dropwise to Co(CH;OOH)2, stir magnetically for 20 minutes, and finally transfer the mixed solution into a 100 ml reaction cap, and heat at a certain temperature for 10 hours;
[0021] (4) After heating to the specified time, cool down to room temperature naturally, wash with deionized water and ethanol for 3-4 times, and dry in vacuum at 50°C for 10 hours after cleaning to obtain a pink powder.
[0022] In order to compare the electrochemical performance of cobalt carbonate anode materials prepared at different temperatures, in the step (3), the water temperature was heated to 120°C, and the pink powder prepared at this temperature was named...
Embodiment 2
[0024] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that in step (3), the water temperature was heated to 160°C, and the pink powder prepared at this temperature was named CC-2.
Embodiment 3
[0026] The difference between this example and Example 1 and Example 2 is that in step (3), the water temperature was heated to 180°C, and the pink powder prepared at this temperature was named CC-3.
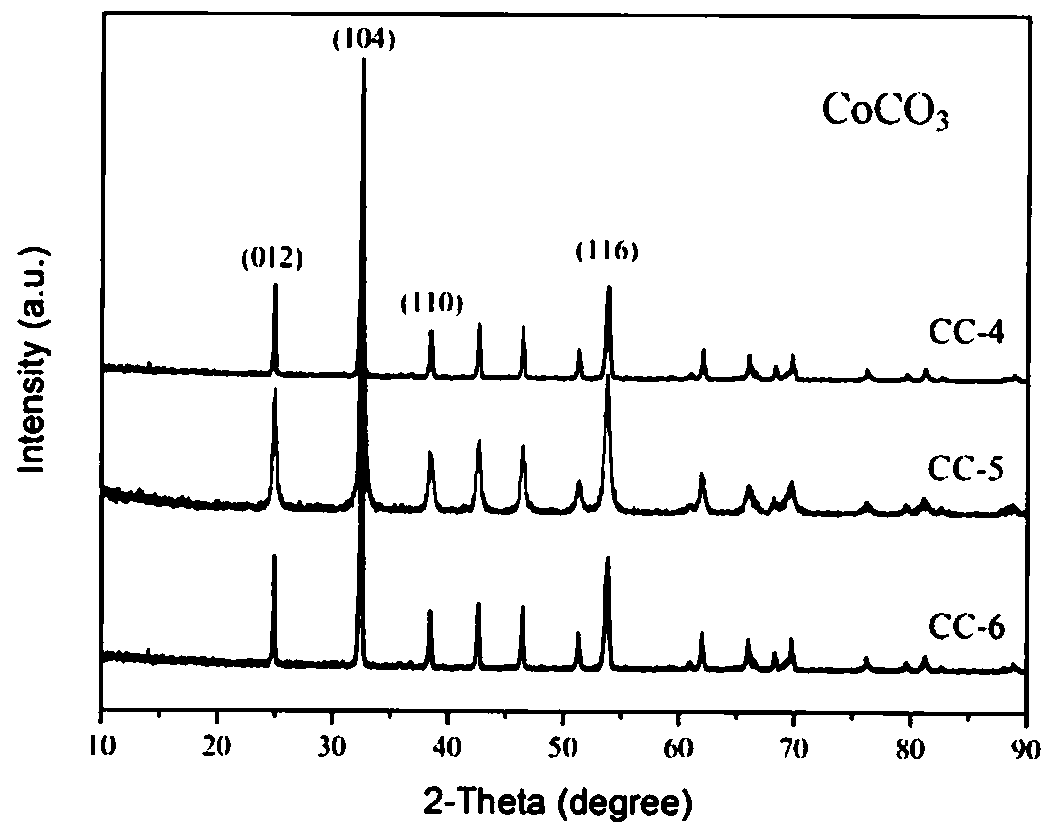
[0027] XRD was used to analyze the phases of the samples prepared at different temperatures, such as figure 1 As shown, the three strong peaks of the three groups of samples correspond to the CoCO3 (JCPDS No.11-0692) card, and the strong H peaks are obvious at 2θ of 32.6°C, 25°C and 53.8°C, and the crystallinity is good.
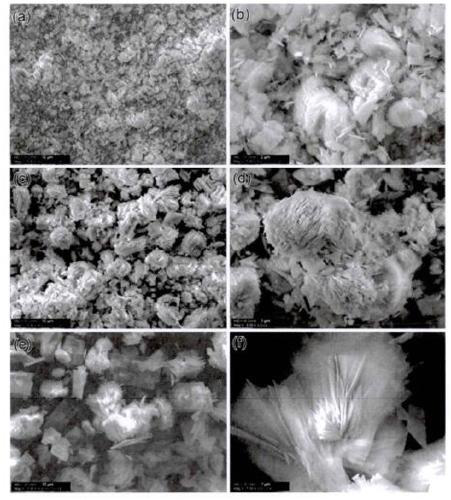
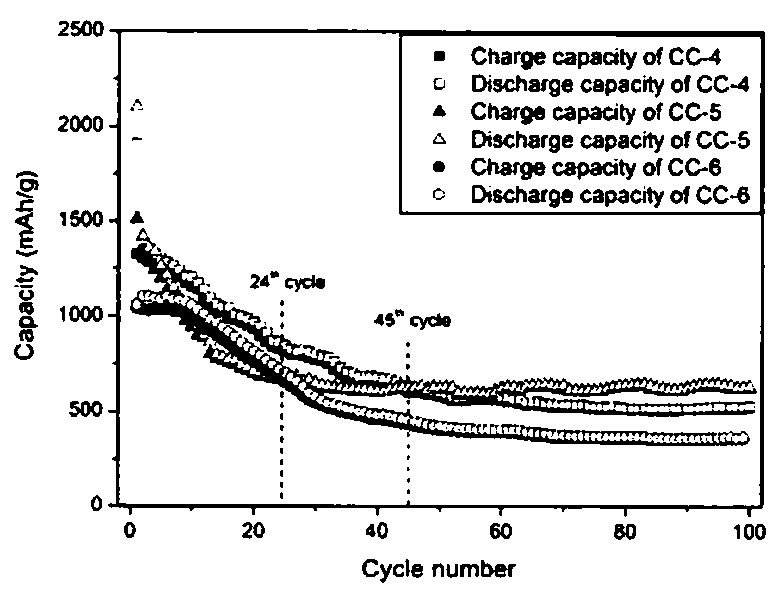
[0028] From figure 2 It can be seen from the figure that at 120°C, the basic material of CC-1 particles is flaky CoCO3, and the formed CoCO3 has different shapes and is relatively messy. At 160°C, the material that makes up the CC-2 particle unit is micron-short fiber-like CoCO3, which is superimposed into a unit after being assembled into a sheet, forming an explosive flower pattern, and the short fibers that do not participate in the sheeting are randomly ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com