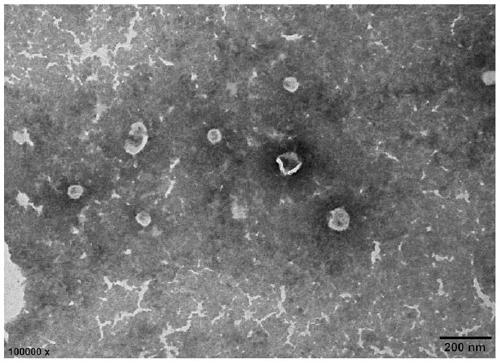
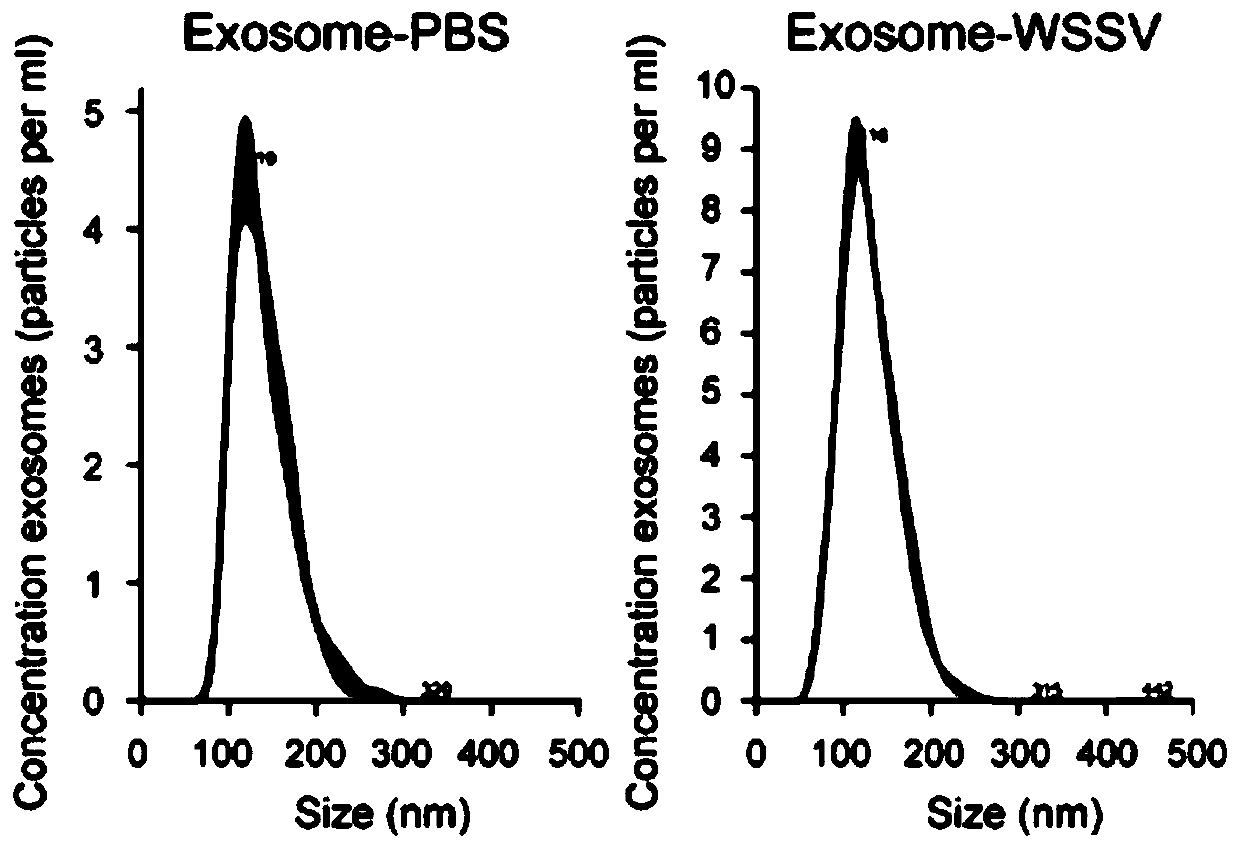
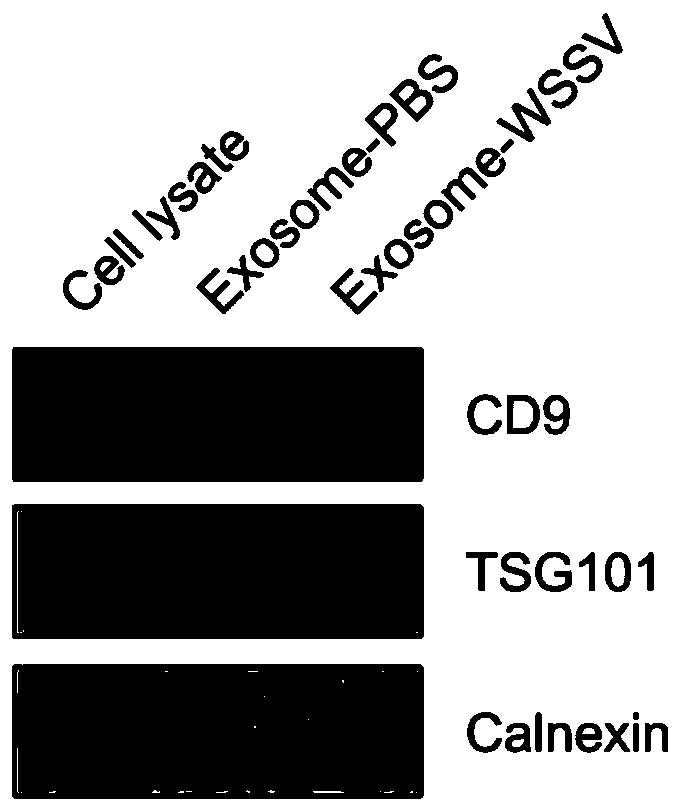
Method for separating scylla paramamosain tissue exosome
A technology of Scylla simulans and exosomes is applied in the field of separation of Scylla simulans tissue exosomes, which can solve the problems of inability to isolate pure exosomes and inapplicability, and achieve the effect of simple operation and high purity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Combining differential centrifugation, sucrose density gradient centrifugation and diafiltration to extract exosomes from the tissue of Scylla pseudocarpus, including the following steps:
[0042] S1): tissue extraction: take crab tissue, cut the tissue into pieces, and place in 2 mL of pre-cooled 0.3% trypsin solution;
[0043] S2): Tissue digestion: incubate and lyse at 37°C for 20 minutes; add 6 mL of pre-cooled 0.03% trypsin inhibitor to terminate the reaction;
[0044] S3): Low-speed centrifugation: Centrifuge the single-cell suspension of the tissue in S2) at 4°C and 800×g for 10 minutes in a low-temperature centrifuge. After the centrifugation, transfer the supernatant in the centrifuge tube to a new tube for later use, and discard the precipitate;
[0045] S4): centrifuge again at low speed: use a low-temperature centrifuge to centrifuge the supernatant obtained in S3) at 2000×g for 30 min at 4°C, transfer the supernatant in the centrifuge tube to a new tube aft...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Exosomes from the tissue of Scylla pseudocarpus were extracted by traditional simple differential centrifugation.
[0059] S1): tissue extraction: take crab tissue, cut the tissue into pieces, and place in 2 mL of pre-cooled 0.3% trypsin solution;
[0060] S2): Tissue digestion: incubate and lyse at 37°C for 20 minutes; add 6 mL of pre-cooled 0.03% trypsin inhibitor to terminate the reaction;
[0061] S3): Low-speed centrifugation: Centrifuge the single-cell suspension of the tissue in S2) at 4°C and 800×g for 10 minutes in a low-temperature centrifuge. After the centrifugation, transfer the supernatant in the centrifuge tube to a new tube for later use, and discard the precipitate;
[0062] S4): centrifuge again at low speed: use a low-temperature centrifuge to centrifuge the supernatant obtained in S3) at 2000×g for 30 min at 4°C, transfer the supernatant in the centrifuge tube to a new tube after centrifugation, and discard the precipitate;
[0063] S5): High-speed ...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Differential centrifugation and sucrose density gradient centrifugation (without diafiltration) were used to extract the exosomes from the tissue of Scylla pseudocarpus.
[0068] S1): tissue extraction: take crab tissue, cut the tissue into pieces, and place in 2 mL of pre-cooled 0.3% trypsin solution;
[0069] S2): Tissue digestion: incubate and lyse at 37°C for 20 minutes; add 6 mL of pre-cooled 0.03% trypsin inhibitor to terminate the reaction;
[0070] S3): Low-speed centrifugation: Centrifuge the single-cell suspension of the tissue in S2) at 4°C and 800×g for 10 minutes in a low-temperature centrifuge. After the centrifugation, transfer the supernatant in the centrifuge tube to a new tube for later use, and discard the precipitate;
[0071] S4): centrifuge again at low speed: use a low-temperature centrifuge to centrifuge the supernatant obtained in S3) at 2000×g for 30 min at 4°C, transfer the supernatant in the centrifuge tube to a new tube after centrifugation,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com