Method for producing parasitic wasps of fruit flies by means of drosophila melanogaster
A technology for parasitic wasps and fruit flies, which is applied in the field of using Drosophila melanogaster to mass-produce Drosophila parasitoids, can solve the problems of sticky culture medium, host escape, slow speed, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] In order to make the above-mentioned characteristics and advantages of the device for collecting mature larvae and pupae of Drosophila melanogaster more obvious and easy to understand, the following specific examples are given together with the accompanying drawings for a detailed description as follows.
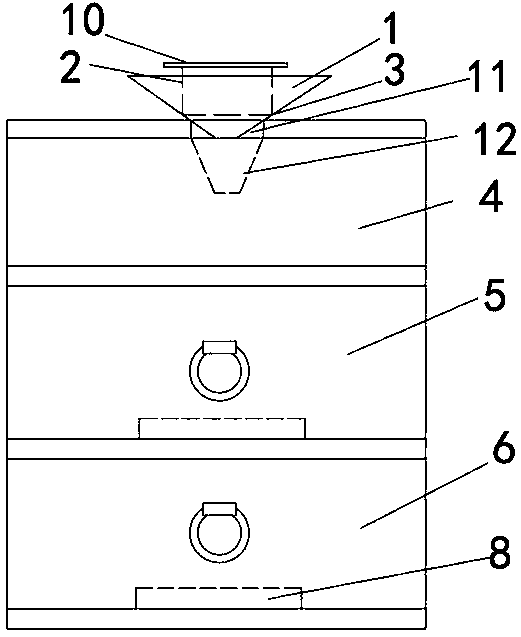
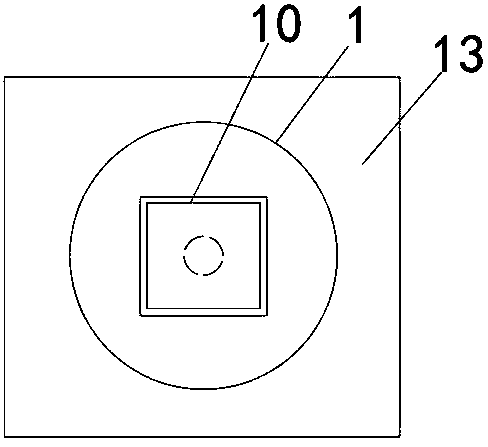
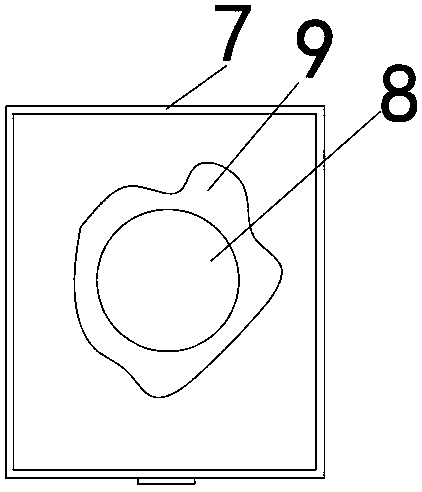
[0048] Such as Figure 1~3 As shown, a device for collecting mature larvae and pupae of Drosophila melanogaster, including a square box 2 vertically placed in a paper funnel 1, the square box is made of plastic, and the lower end of the paper funnel extends to a chest of drawers 13. On the inner top, the paper funnel is in the shape of a cone, and an arc-shaped insect collecting seam 3 is formed at the contact between the lower end of the square box and the inner wall of the paper funnel. There are three layers in the drawer cabinet. The insect-collecting layer 5 and the cleaning layer 6 all have drawers, and the light gradient layer runs through up and down. The bott...
Embodiment 2
[0055] (1) Propagation and egg collection of wild-type Drosophila melanogaster;
[0056] The seed flies of wild-type Drosophila melanogaster are introduced into the breeding cage to multiply, and water and adult feed are placed in the egg-collecting cage, and 300 pairs of seed flies are sucked from the breeding cage with an insect extractor, and imported into the egg-collecting cage to raise; When ovum, place 48 hours in the ovum collection cage with the petri dish that fills medium, to collect enough ovum; Described adult feed is yeast extract: the mass ratio of sucrose is 1:5.
[0057] (2) Collection of pupae of Drosophila melanogaster and rearing and parasitism of Drosophila chinensis:
[0058]1) Put the collected culture medium containing Drosophila melanogaster eggs into an air-permeable empty container and raise it until the mature larvae appear, and place the culture medium containing the mature Drosophila melanogaster larvae in the collected medium to collect the matur...
Embodiment 3
[0073] (1) Propagation and egg collection of the residual wing strain Drosophila melanogaster;
[0074] Introduce the seed flies of the wevg strain into breeding cages for multiplication, place water and adult feed in the egg-collecting cages, absorb 300 pairs of seed flies from the breeding cages with an insect extractor, and introduce them into the egg-collecting cages for breeding; When ovum, place 48 hours in the ovum collection cage with the petri dish that fills medium, to collect enough ovum; Described adult feed is yeast extract: the mass ratio of sucrose is 1:5.
[0075] (2) Collection of pupae of Drosophila melanogaster and rearing and parasitism of the Japanese gall wasp:
[0076] Take the petri dish after egg collection in step (1), place it in an air-permeable empty container and raise it until the 2nd instar larvae appear.
[0077] The raising and parasitism of described fruit fly parasitoid are:
[0078] 1) Use a 5L square transparent plastic tank as the bee b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com