Single-spore propagation method for Gigaspora rosea mycorrhiza fungi
A technology of giant cyst mold and fungus, which is applied in the field of single spore propagation of giant cyst mold rhizogenes, can solve problems such as increased labor costs, inability to know the infection status of inoculated plants mycorrhiza, and inability to monitor the cultivation process in real time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Preparation: Mycorrhizal fungus agent of Gigaspora rosea, which is obtained from polyspore propagation by conventional pot planting method. It is a mixture of spores, hyphae, infected root segments and soil and sand substrates. It is approved by the French National Scientific Research Institute. Provided by Professor Christophe ROUX of the center; carrot hairy roots, provided by Mr. Li Airong, Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and preserved in our research group with M medium.
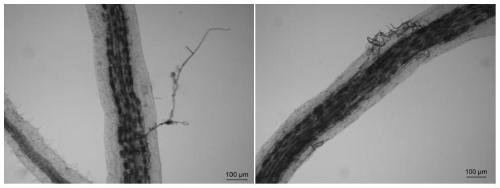
[0035] (1) Separation, screening and surface disinfection of the mycorrhizal fungus spores of Megacystis rosea rubrum: Weigh 5 g of the fungal agent, and use the wet sieve decantation method to collect the spores between the 80 mesh and 180 mesh sampling sieves; , use a pipette to absorb spores with relatively uniform color and texture for surface disinfection; the disinfection method is: soaking in 0.02g / ml ammonium chloride T solution on ice twice, each time for 10min, a...
Embodiment 2
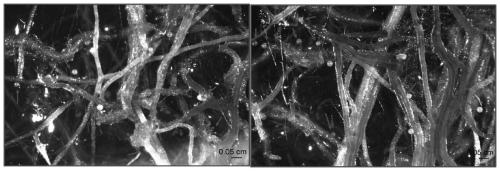
[0047] According to the method of embodiment 1, carry out the mycorrhizal fungus propagation of Megacystis rosea rubrum, the difference is: step (4) has chosen another high-yield spore single-spore propagation line, and numbering is GRspore-3 to carry out enlarged cultivation (expanded cultivation effect is as follows figure 1 shown on the right).
[0048]The detection of the number of spores in the multiplication spore suspension: in the ultra-clean bench, use a sterile dropper to respectively draw 1ml of the multiplication spore suspension obtained in the step (5) of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 and place it in two petri dishes, add an appropriate amount of After dilution with distilled water, the number of spores was counted under a stereomicroscope, and the results are shown in Table 1. Wherein, the formula for calculating the total number of spores for propagation is: number of spores in 1 ml of suspension × volume of total spore suspension (ml).
[0049] Detection of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com