Method for simulating fracture toughness of layered rock based on extended finite elements
An extended finite element and fracture toughness technology, applied in the field of layered rock fracture toughness simulation based on extended finite element, can solve the problems of large amount of calculation, difficult to accurately capture the crack propagation process, etc., and achieve the effect of accurate calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
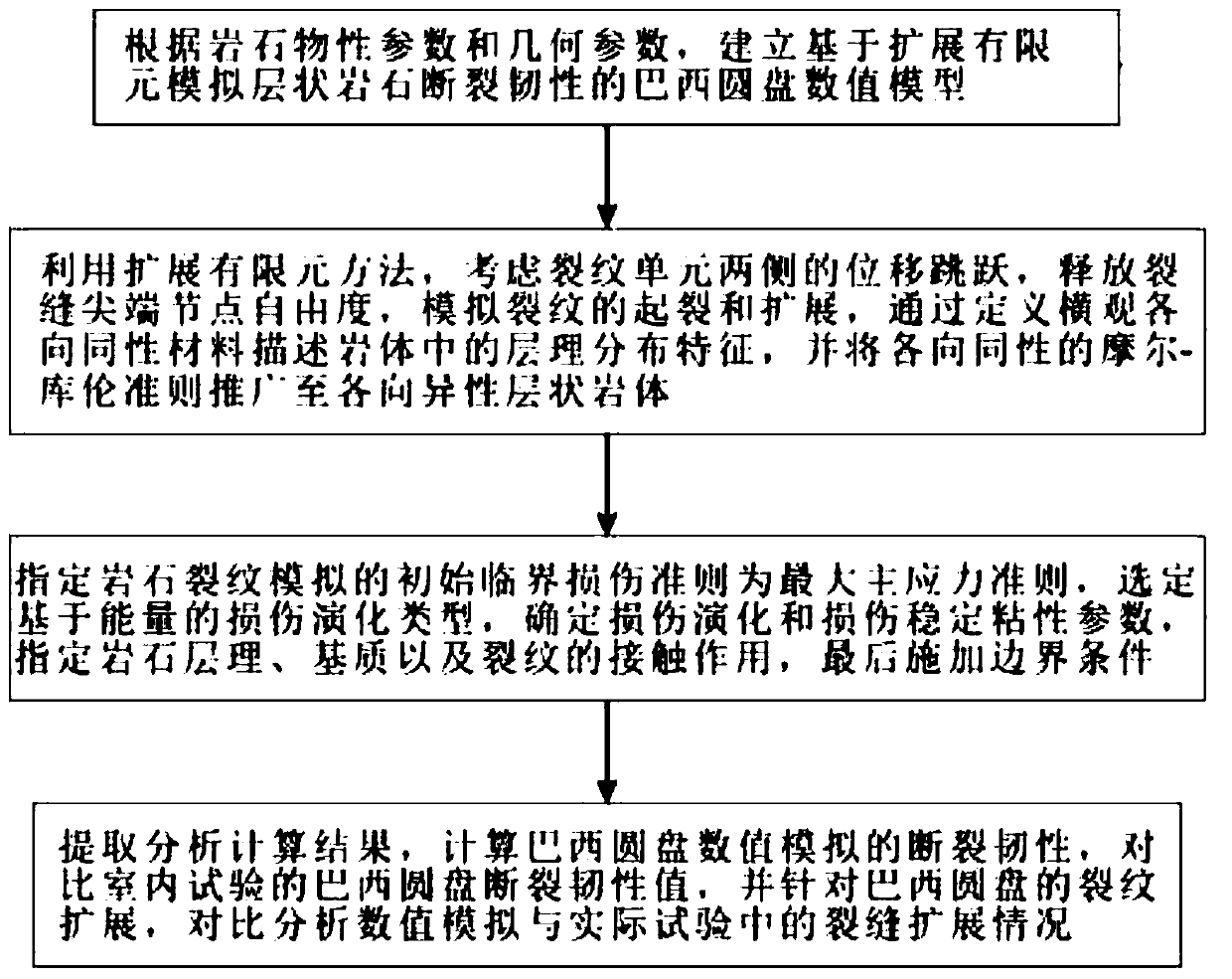
[0027] Such as figure 1 A method for simulating the fracture toughness of layered rocks based on extended finite elements is shown, including the following steps:
[0028] A. According to the physical parameters of the layered rock and the geometric parameters of the experimental specimens, a Brazilian disc numerical model based on the extended finite element simulation of fracture toughness is established;
[0029] B. Using the extended finite element method, considering the displacement jump on both sides of the crack unit, by releasing the degree of freedom of the crack tip node, the crack initiation and expansion are simulated; the bedding distribution in the rock mass is described by defining a transversely isotropic material characteristics, and extend the isotropic Mohr-Coulomb criterion to anisotropic layered rock mass;
[0030] C. Take the initial critical damage criterion of rock crack simulation as the maximum principal stress criterion, select the damage evolution...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment discloses a specific implementation manner on the basis of the foregoing embodiments.
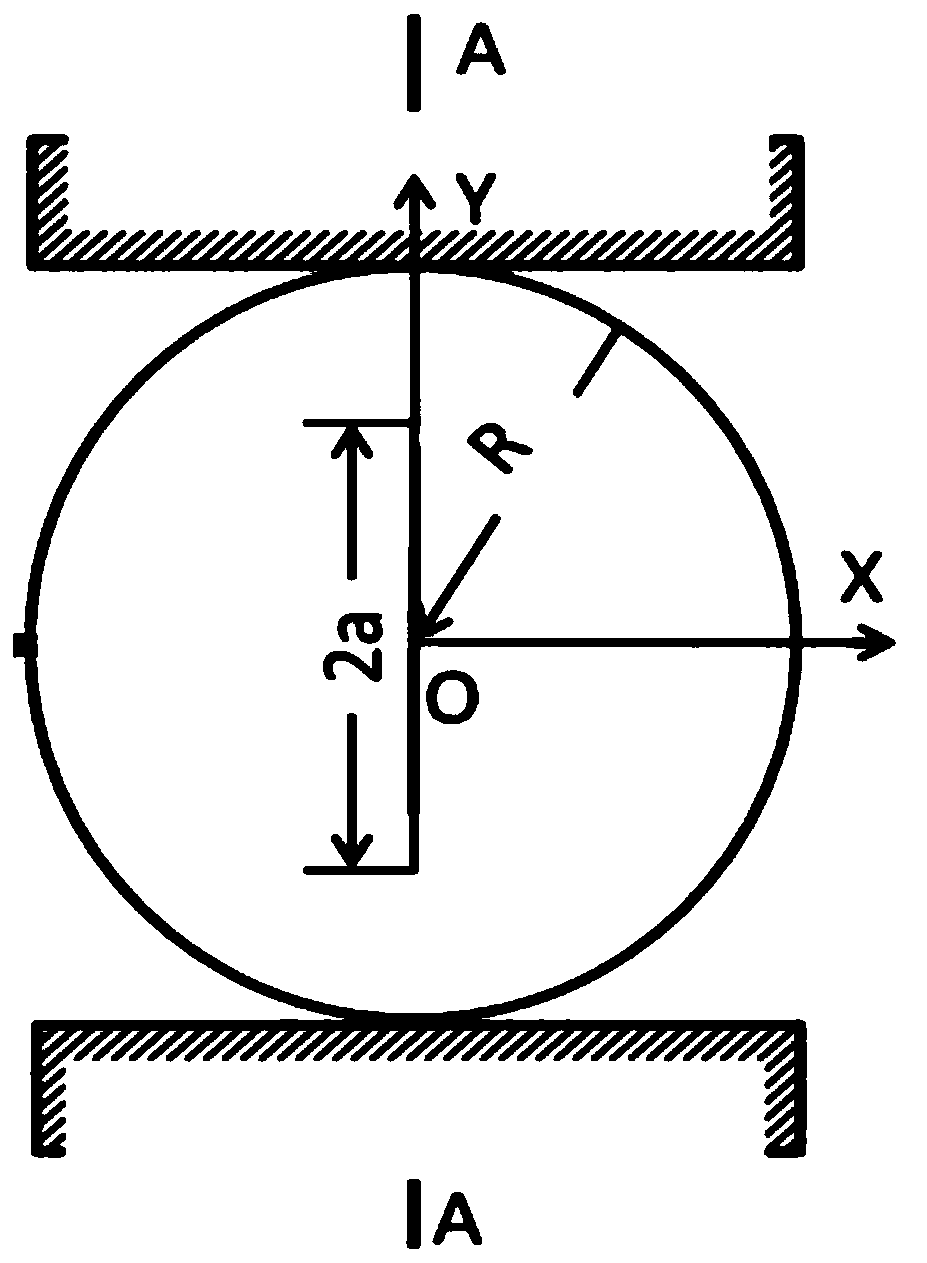
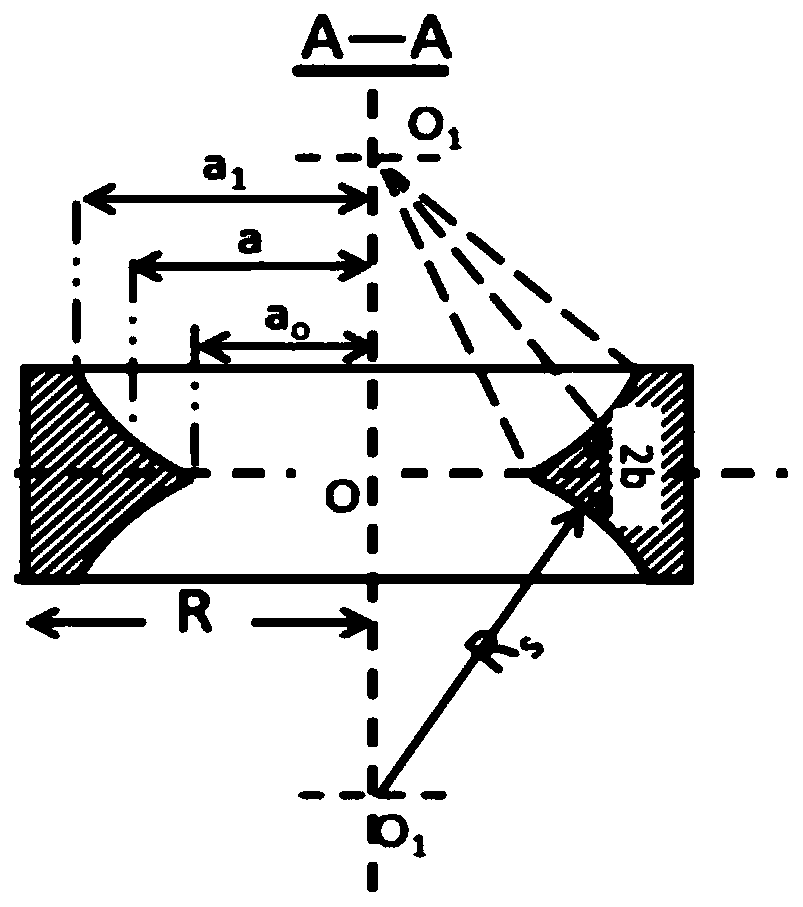
[0034] A. According to the physical parameters of layered rocks and the geometric parameters of experimental specimens, the numerical model of the Brazilian disc based on the extended finite element simulation of fracture toughness, that is, the CCNBD numerical model, was established. Taking shale as an example for illustration, see Tables 1 and 2 below and figure 2 , image 3 Specific parameters of the model are shown for illustration.
[0035] Table 1. Geometric parameters of Brazilian disk specimens
[0036] Diameter (mm) 74 Thickness (mm) 30 2a 0 (mm)
18 2a 1 (mm)
52 Bulk density (g / cm 3 )
2550
[0037] Table 2. Petrophysical parameters
[0038] direction Young's modulus (GPa) Poisson's ratio Shear modulus (GPa) X 3.8e10 0.16 16.38E9 Y 1.8e10 0.1 8.18E9 Z 1.8e10 0.1 8.18E9...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com