Method for calculating metabolic levels of different brain regions after spinal cord injury by <13>C labeled glucose
A technology for spinal cord injury and glucose, applied in diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of inapplicability, low sensitivity, and failure to give metabolic pathways, etc., and achieve high accuracy and simple calculation methods Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
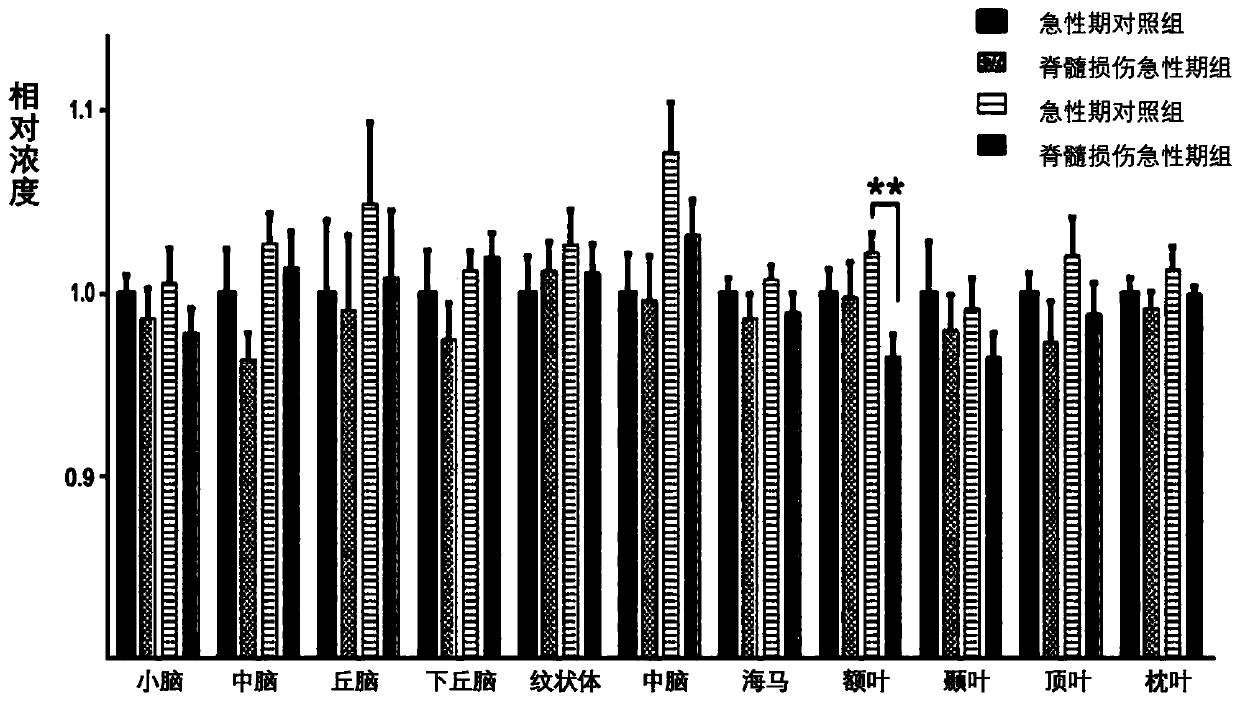
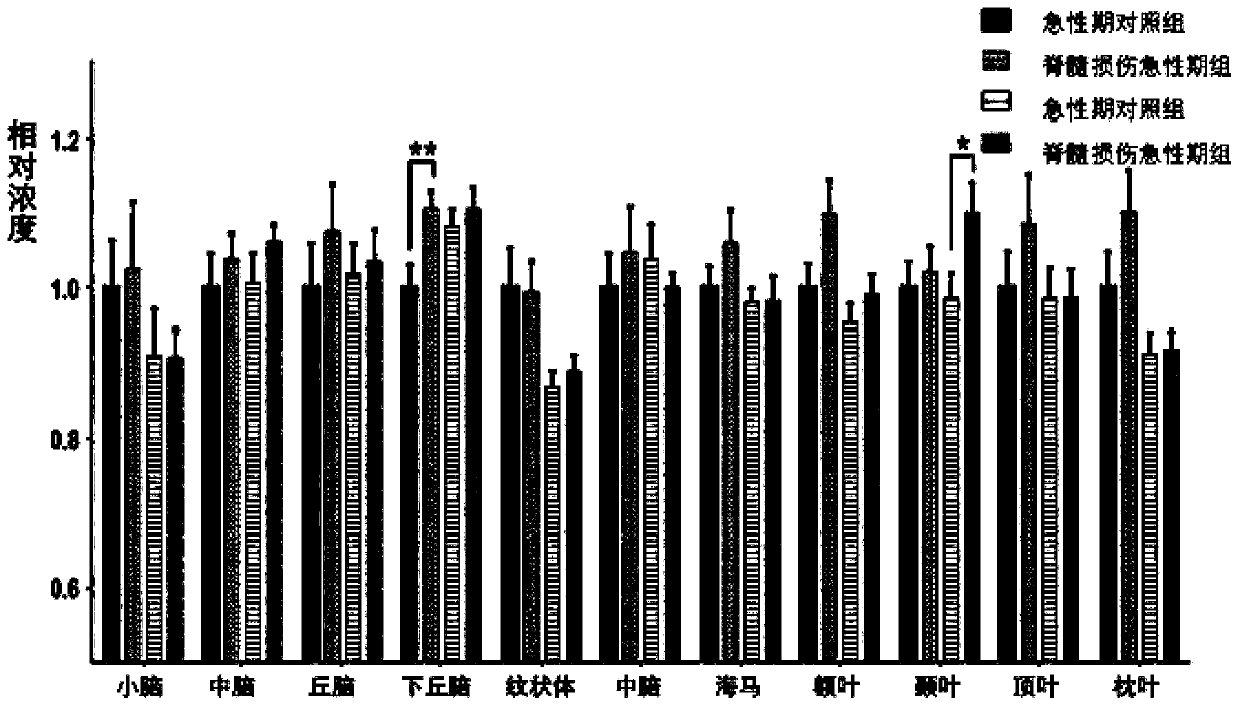
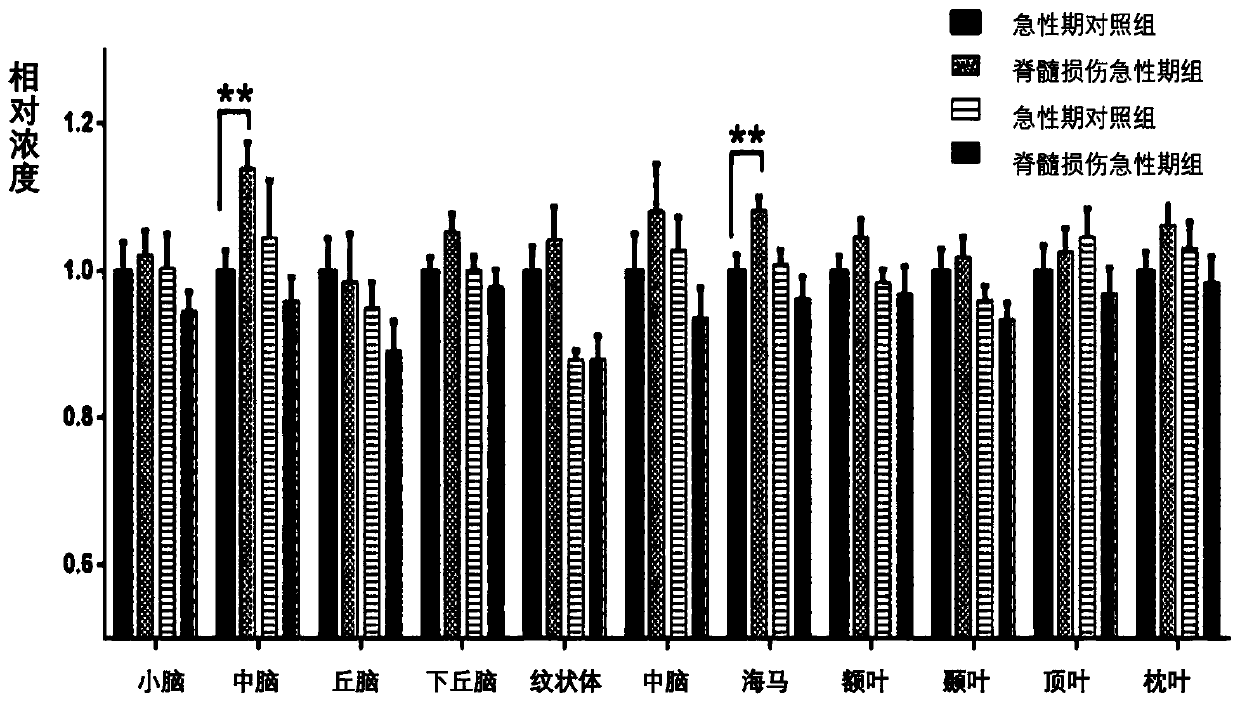
[0054] 13 C-labeled glucose calculates the cortex, subcortical tissue neurotransmitter, energy metabolite concentration and metabolic abundance after rat T10 spinal cord injury, and the method includes the following steps:
[0055] Allen percussion apparatus was used to complete the rat model of spinal cord injury at T10 level. On the 3rd day after injury, 4.0% to 5.0% isoflurane mixed with air was anesthetized on the day of the experiment, and 1.5% to 2.5% isoflurane was used to maintain the anesthesia. The caudal vein was cannulated with PE50 tubing, and the infusion line was connected to the swivel and suspended in the center of the cage to avoid entanglement of the line during the movement of the rat. The other end of the rotation is connected to the infusion pump with a PE50 tube, and injected through the tail vein at a variable speed [1- 13 C] Glucose for 20 minutes. Rats were then sacrificed by head-focused microwave irradiation. After microwave treatment, blood samp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com