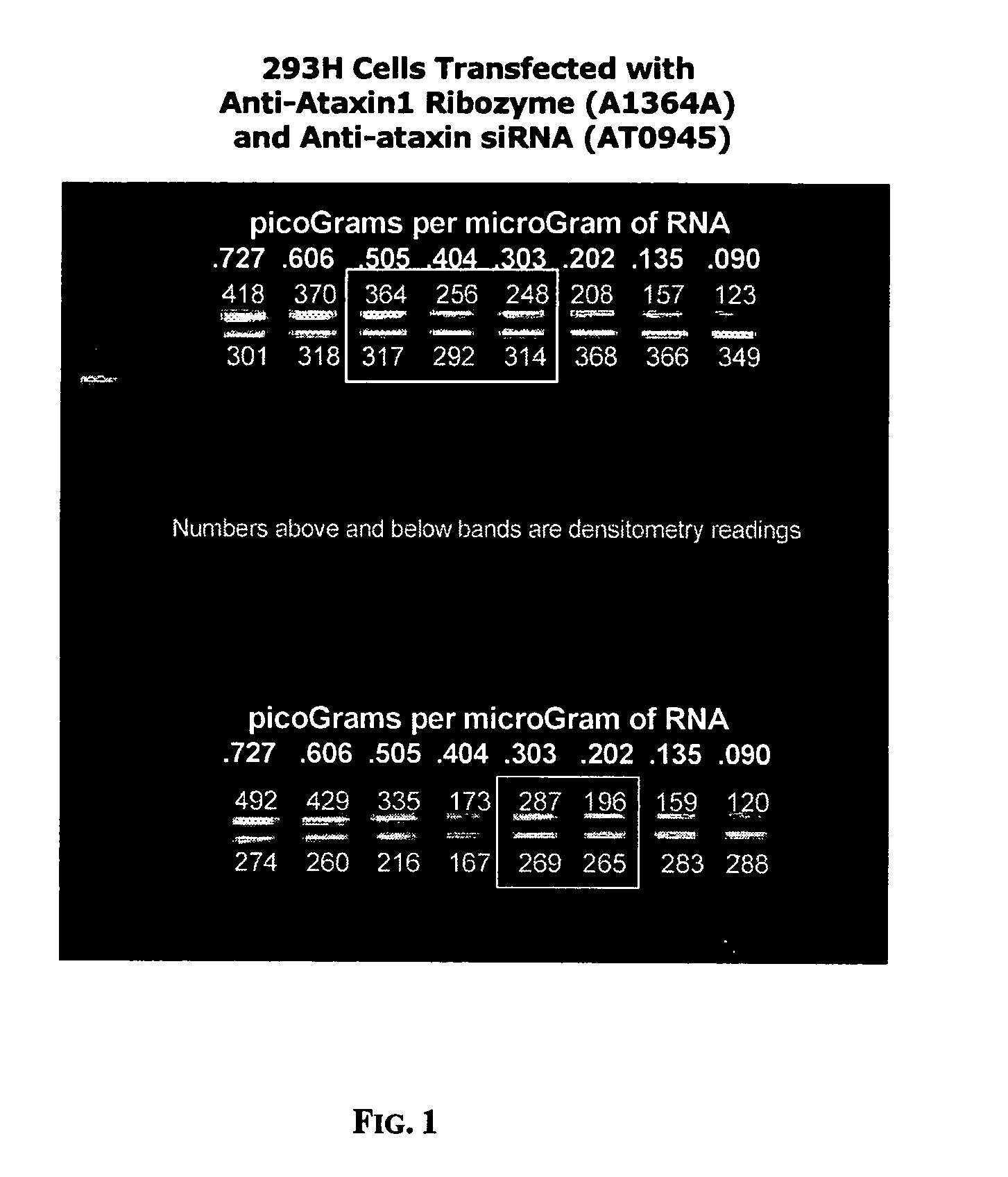
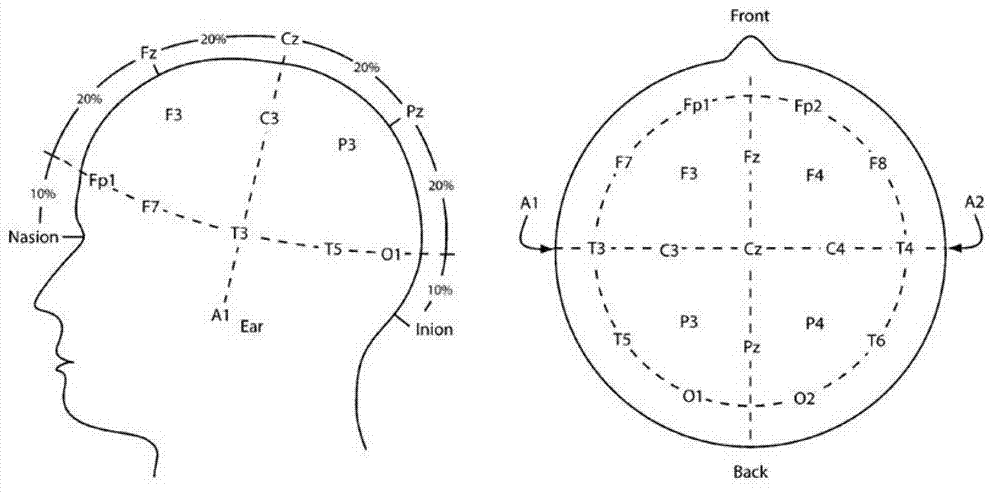
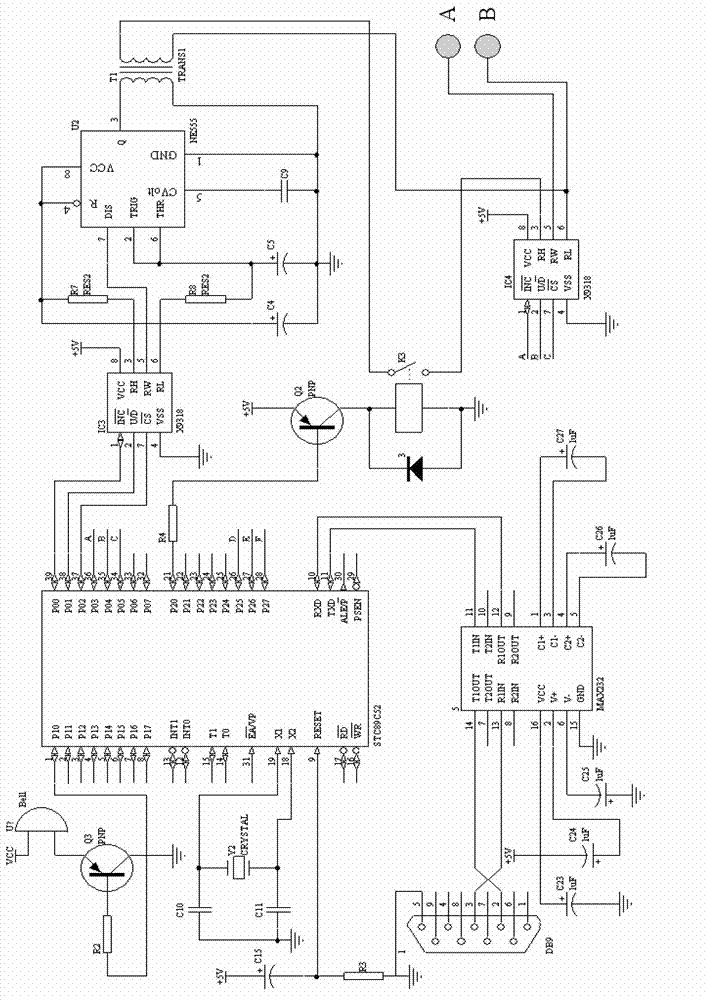
Patents
Literature
445 results about "Cerebral cortex part" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
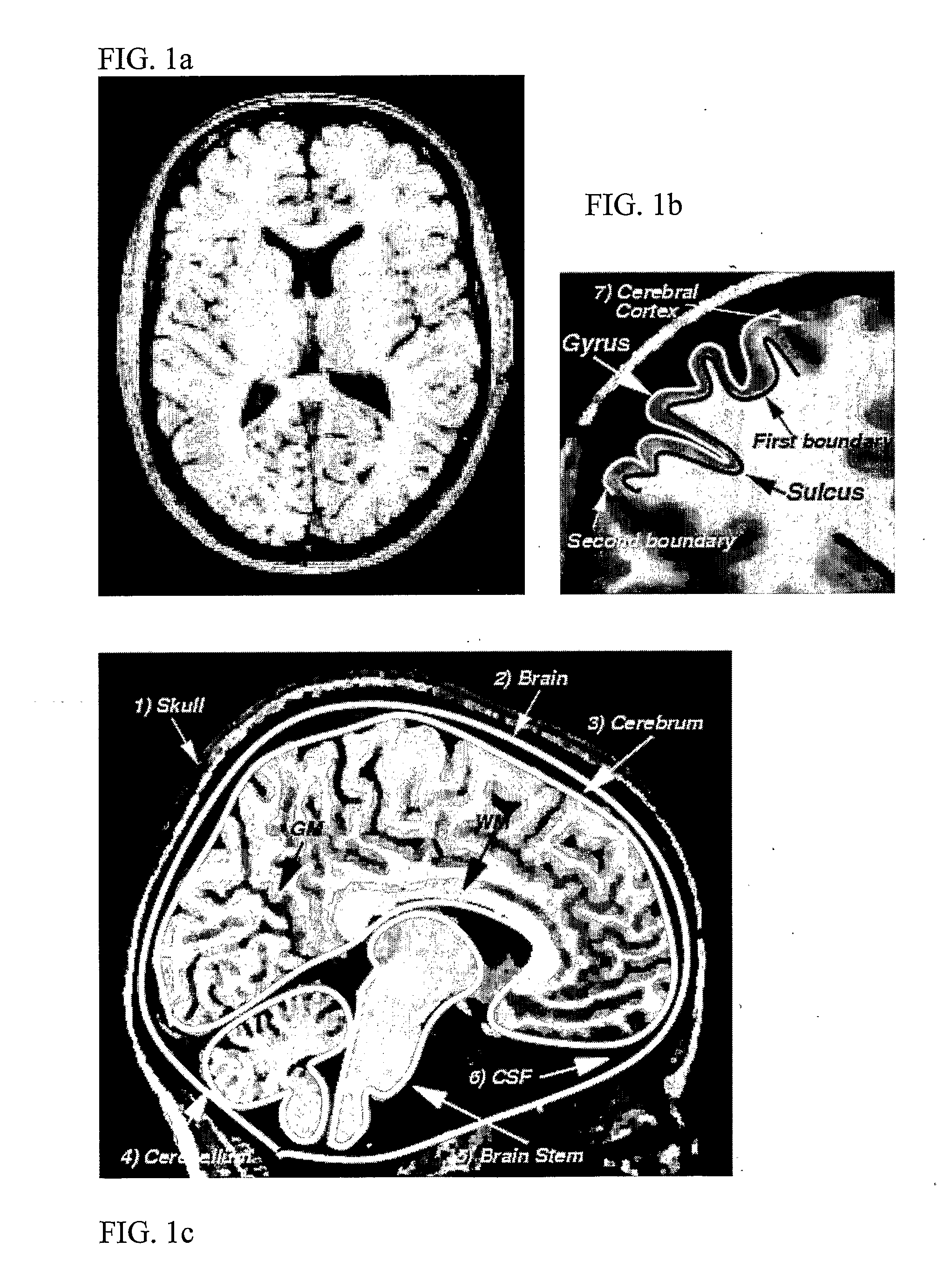
The cerebral cortex is a most important part of the brain. In humans, it is by far the largest part of the brain. Though this cannot be seen directly, different parts of the cortex have different functions (see diagram).
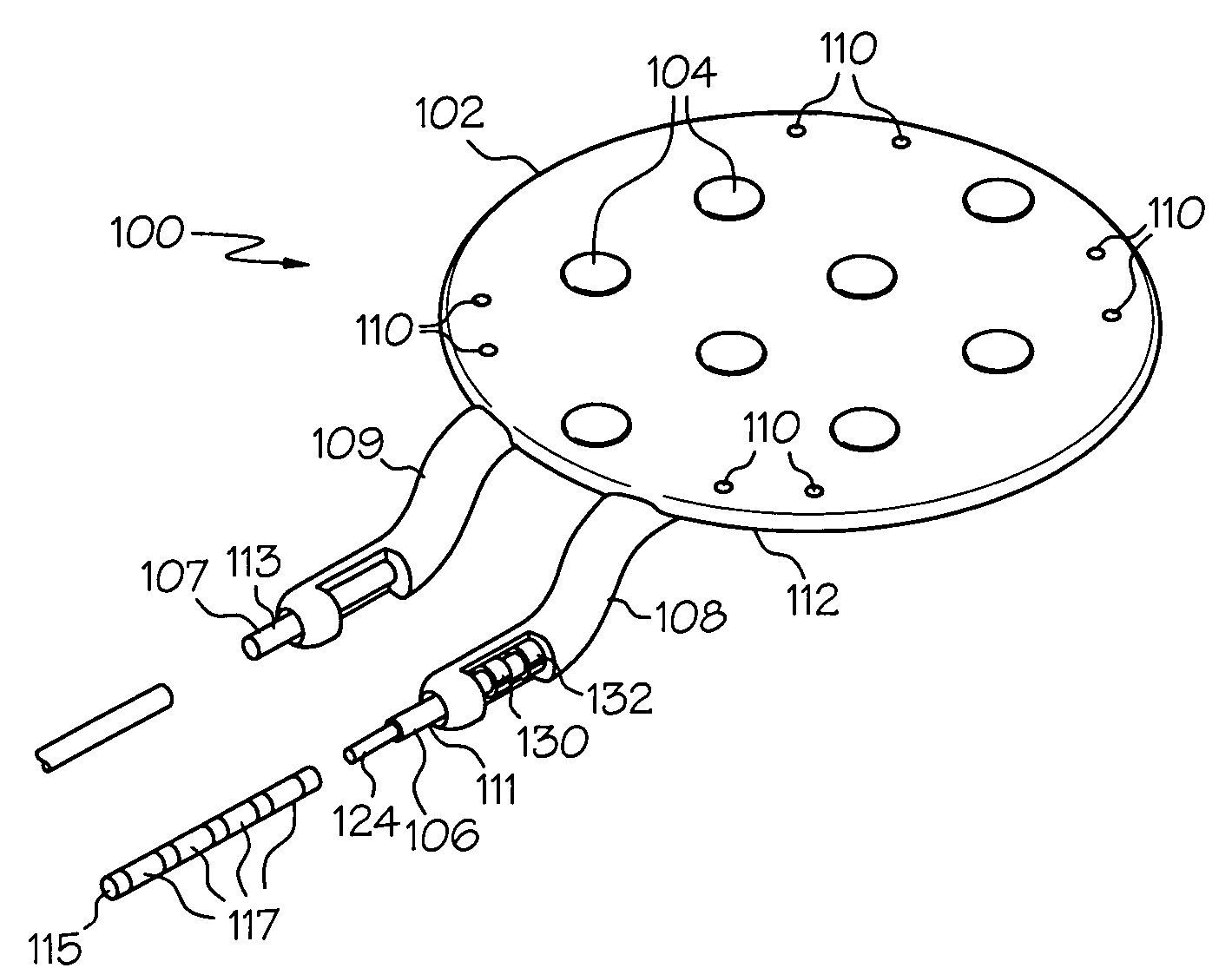
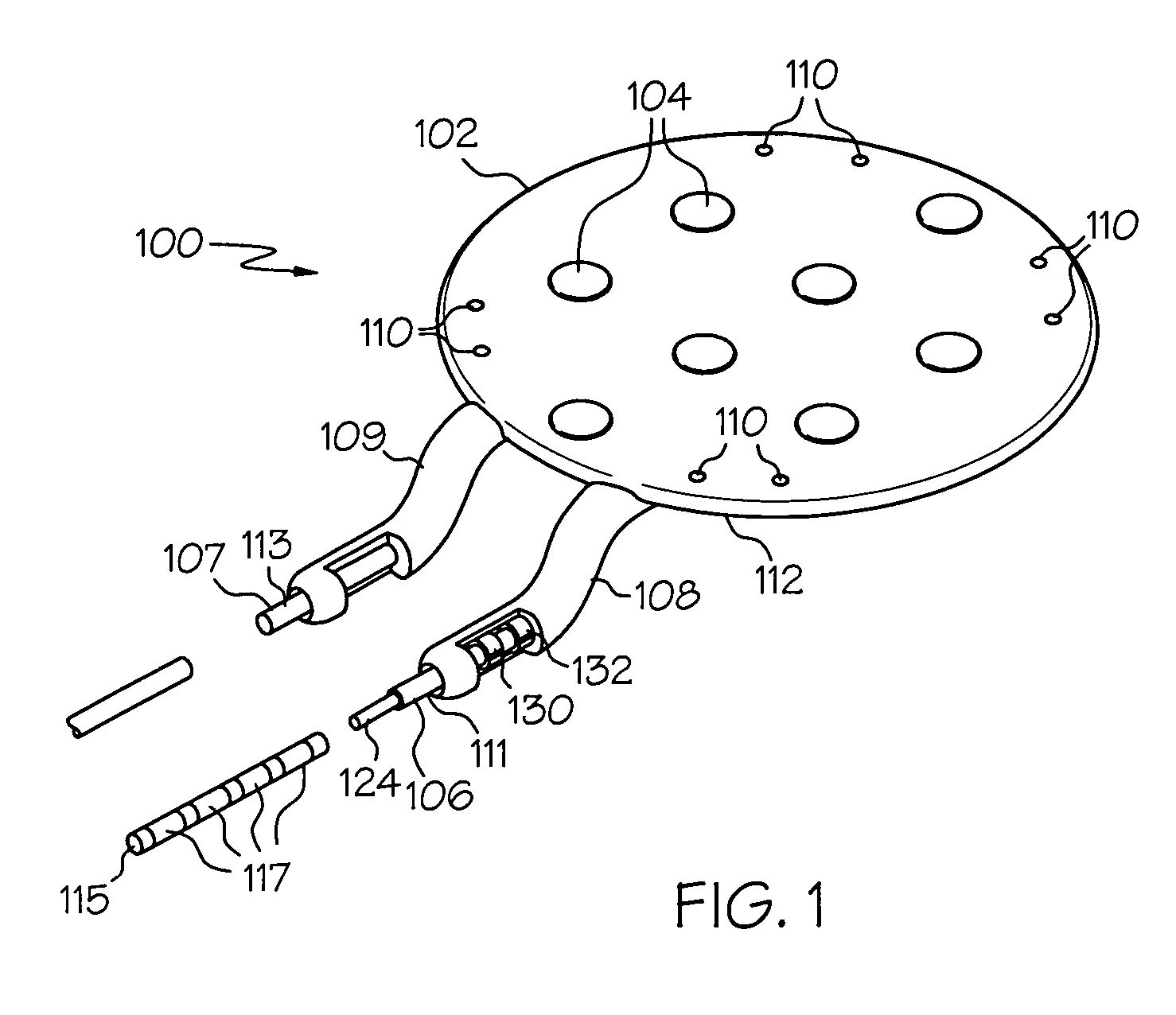
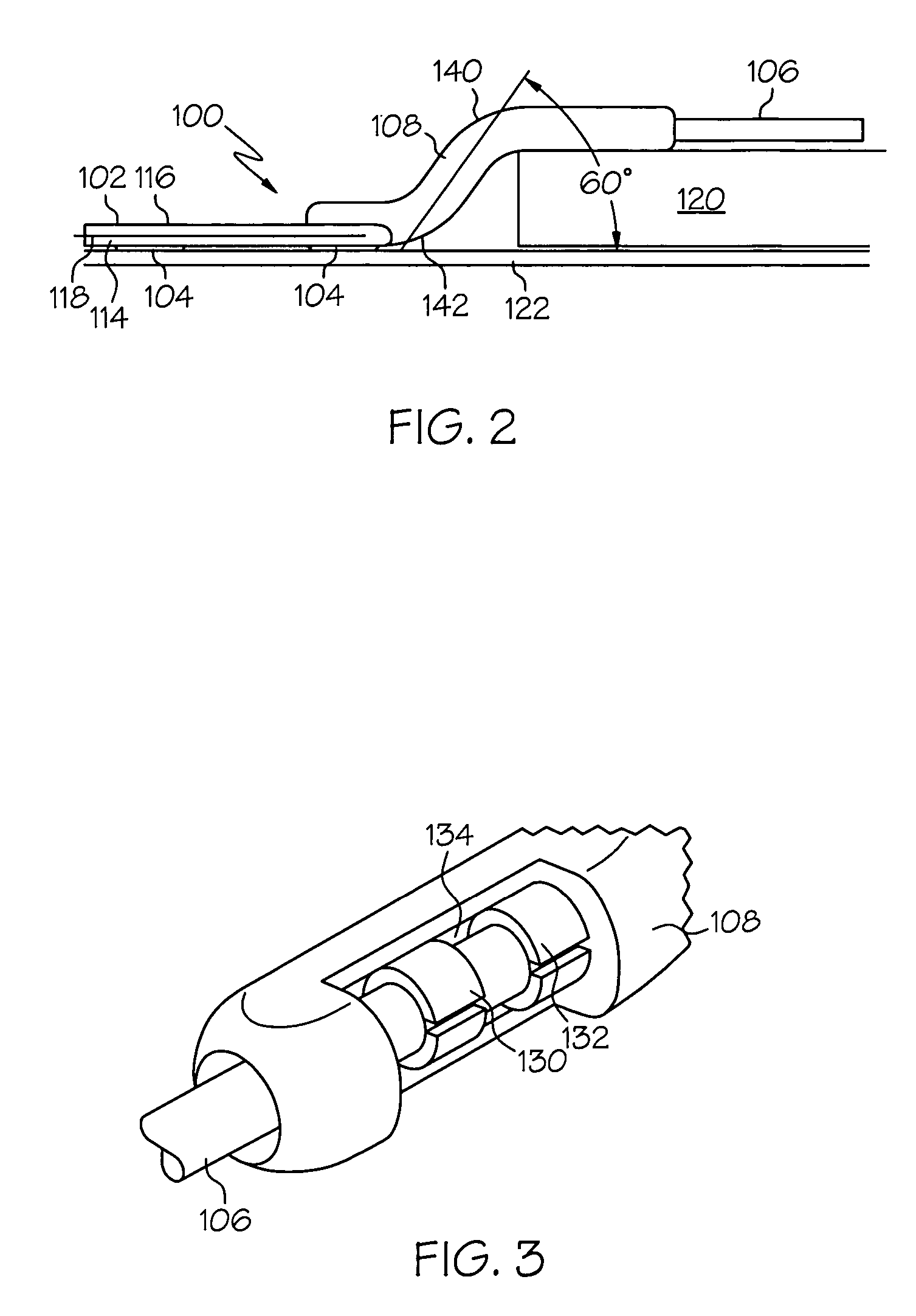
Implantable cortical neural lead and method
A neural lead and method of treating neurological disorders by stimulation of the cerebral cortex of the brain is provided. The lead is designed for reduction of strain between the lead body and the lead paddle caused by the position of the lead body above the cranium and the lead paddle beneath the cranium. The lead is also designed to include a two dimensional chronic electrode array for better stimulation coverage of the target area of the cerebral cortex. A method of treating a neurological disorder by stimulating the cerebral cortex is also presented.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
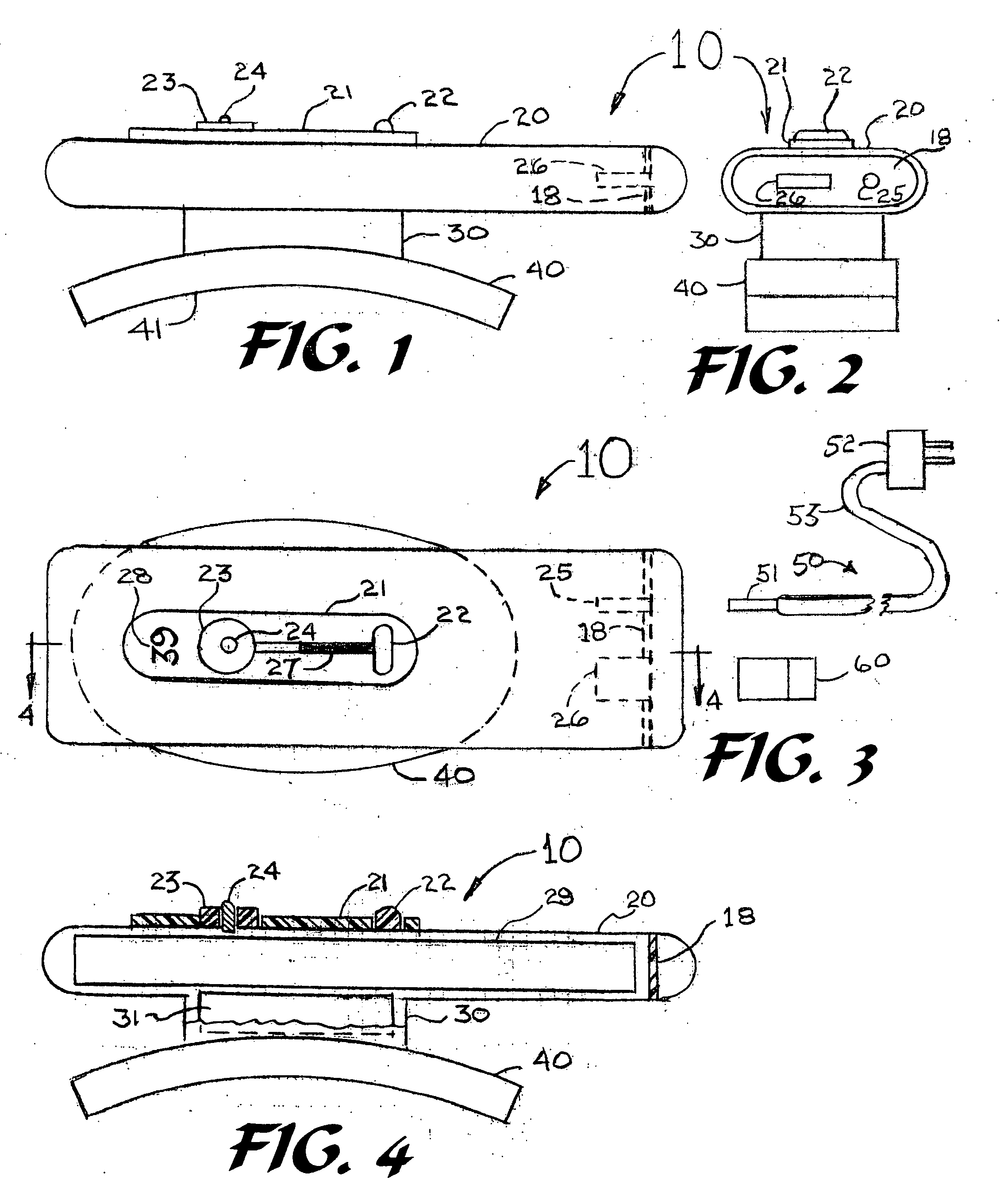
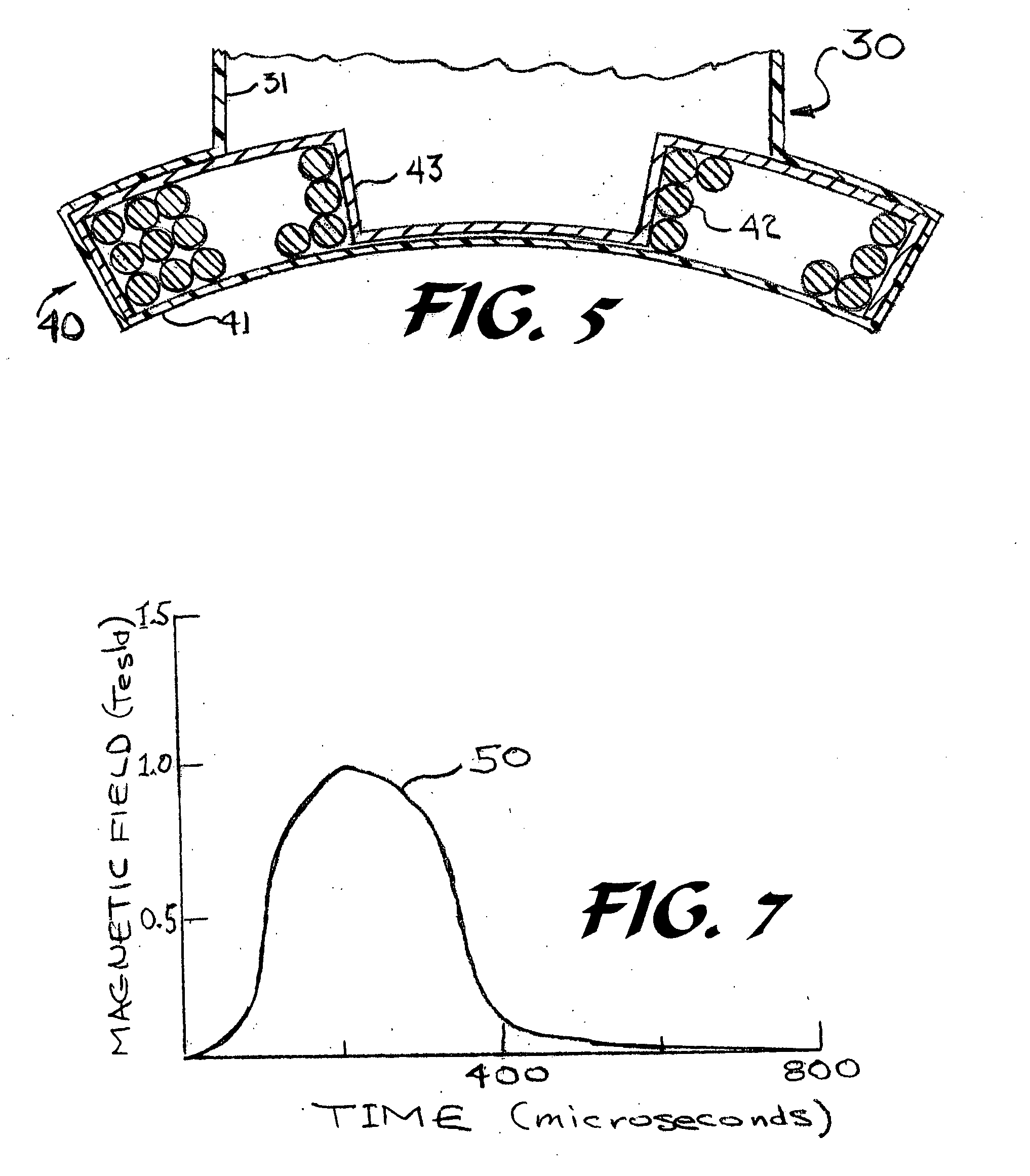
Magnetic pulsing system for inducing electric currents in a human body
ActiveUS20070142886A1Convenient treatmentElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsHuman bodyDisease
Disclosed is a means and method for the treatment of migraine headaches and other disorders of the human body by the application of one or more intense magnetic pulses. By placing an intense magnetic field pulse(s) onto a certain region of the brain, an electrical current can be generated in the cerebral cortex that can stop a migraine headache in some patients or at least decrease its severity. The device to perform this function can be called a “magnetic pulser system.” This system can be made in one piece and powered by plugging into a household or automobile receptacle or from a battery. The pulser system uses capacitors that are first charged to a high voltage and then discharged into a coil that creates the intense magnetic pulse. Both visual and auditory signals can be provided by the pulser system to assist the patient in using the device.
Owner:ARUENE CORP
Insertion of medical devices through non-orthogonal and orthogonal trajectories within the cranium and methods of using
ActiveUS20120046531A1Increase riskLow impedanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryBiomedical engineeringNon orthogonal
The invention comprises an elongated device adapted for insertion, including self-insertion, through the body, especially the skull. The device has at least one effector or sensor and is configured to permit implantation of multiple functional components through a single entry site into the skull by directing the components at different angles. The device may be used to provide electrical, magnetic, and other stimulation therapy to a patient's brain. The lengths of the effectors, sensors, and other components may completely traverse skull thickness (at a diagonal angle) to barely protrude through to the brain's cortex. The components may directly contact the brain's cortex, but from there their signals can be directed to targets deeper within the brain. Effector lengths are directly proportional to their battery size and ability to store charge. Therefore, longer angled electrode effectors not limited by skull thickness permit longer-lasting batteries which expand treatment options.
Owner:HUA SHERWIN
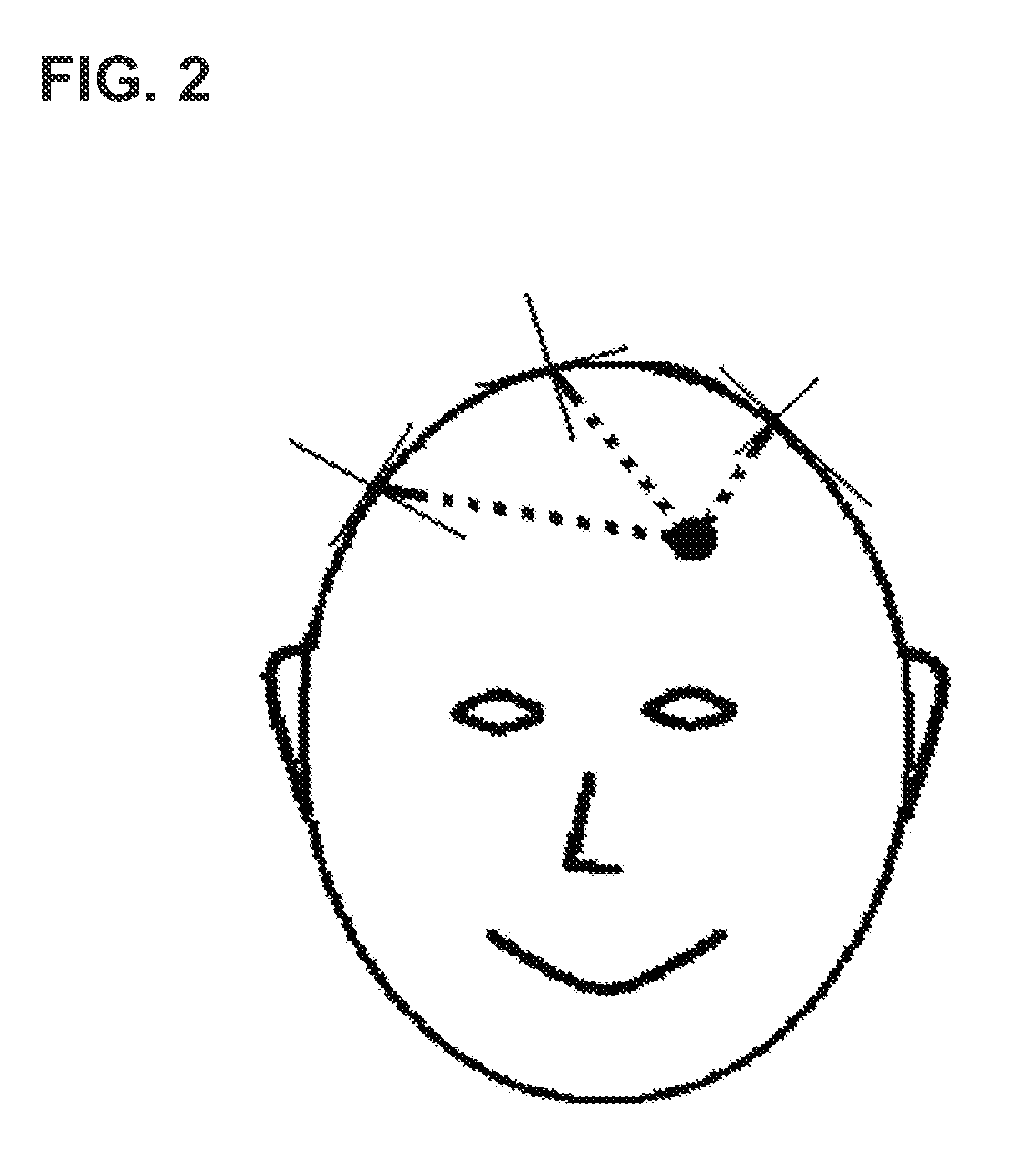
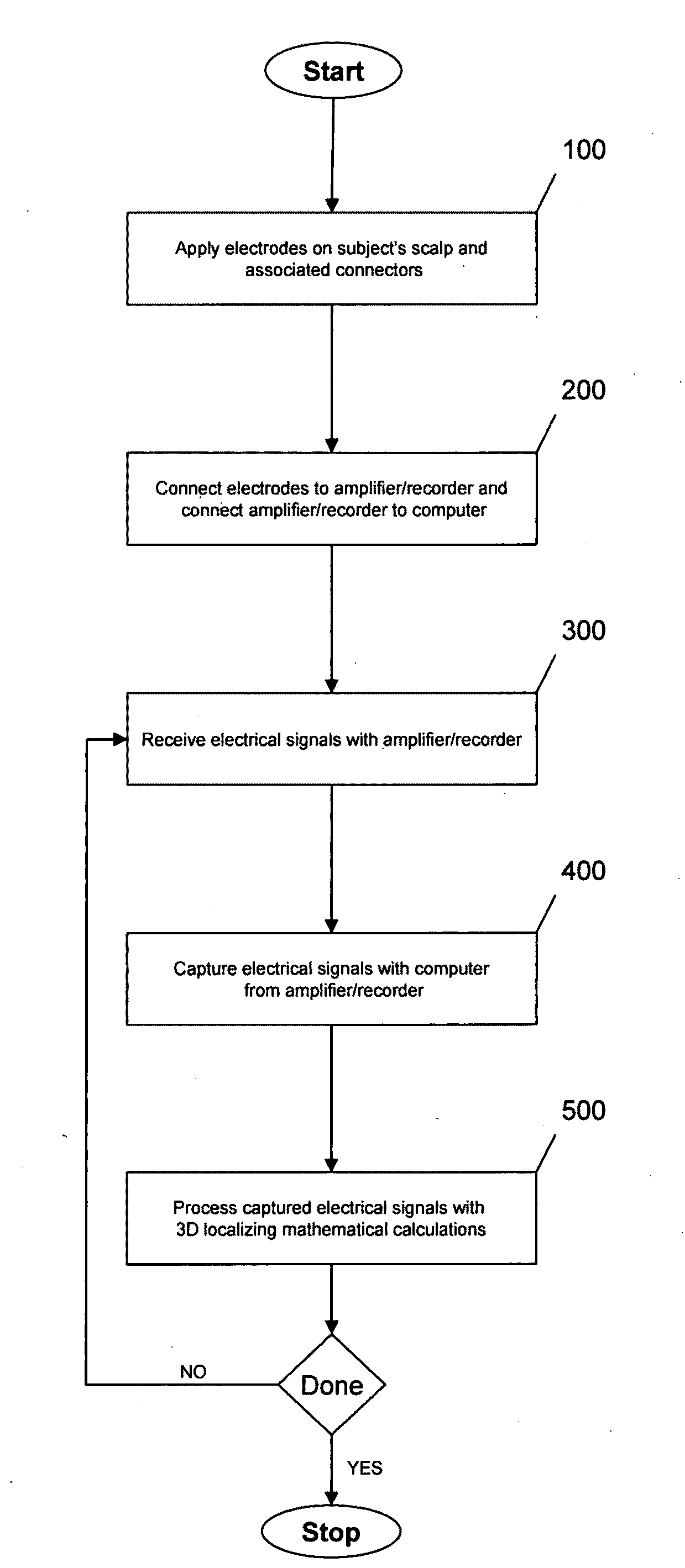
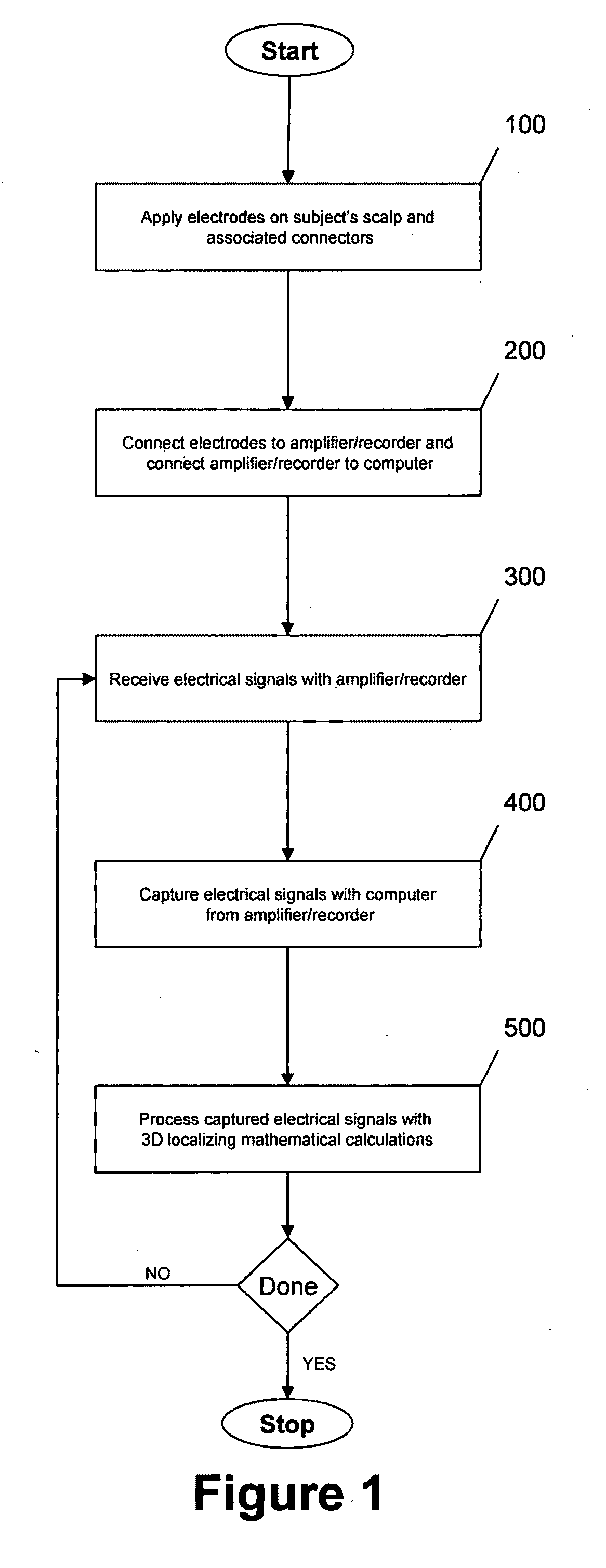
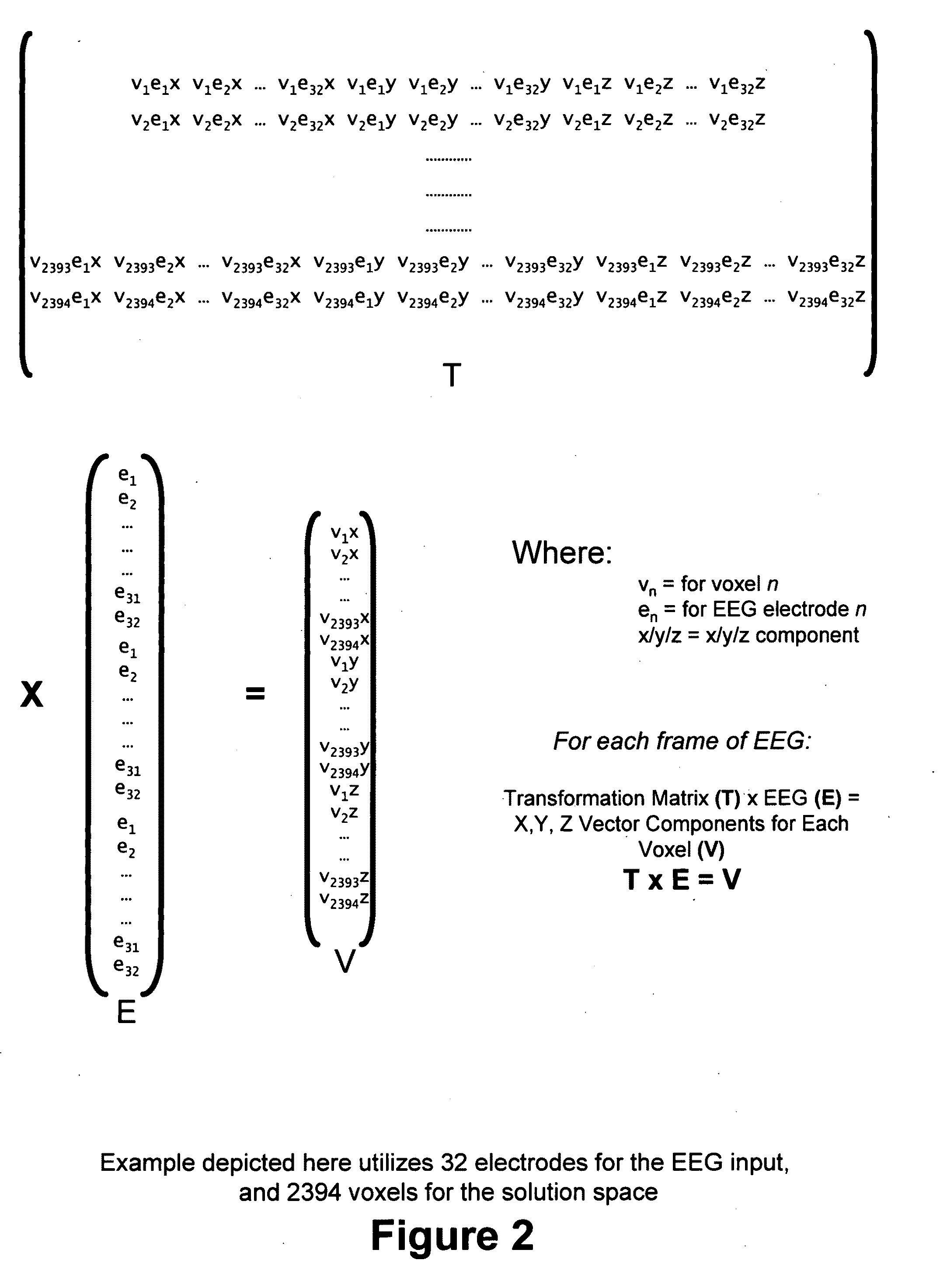
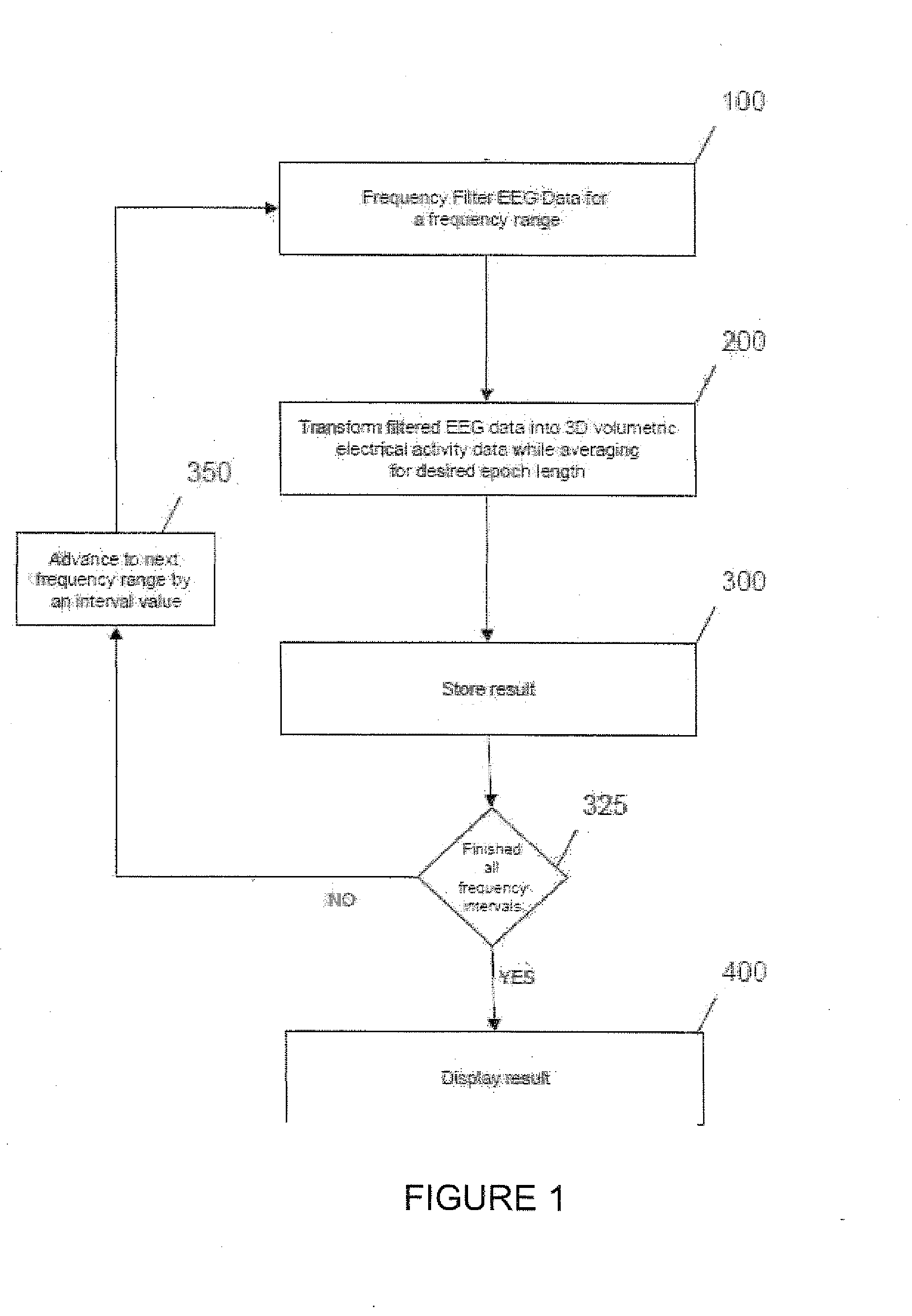
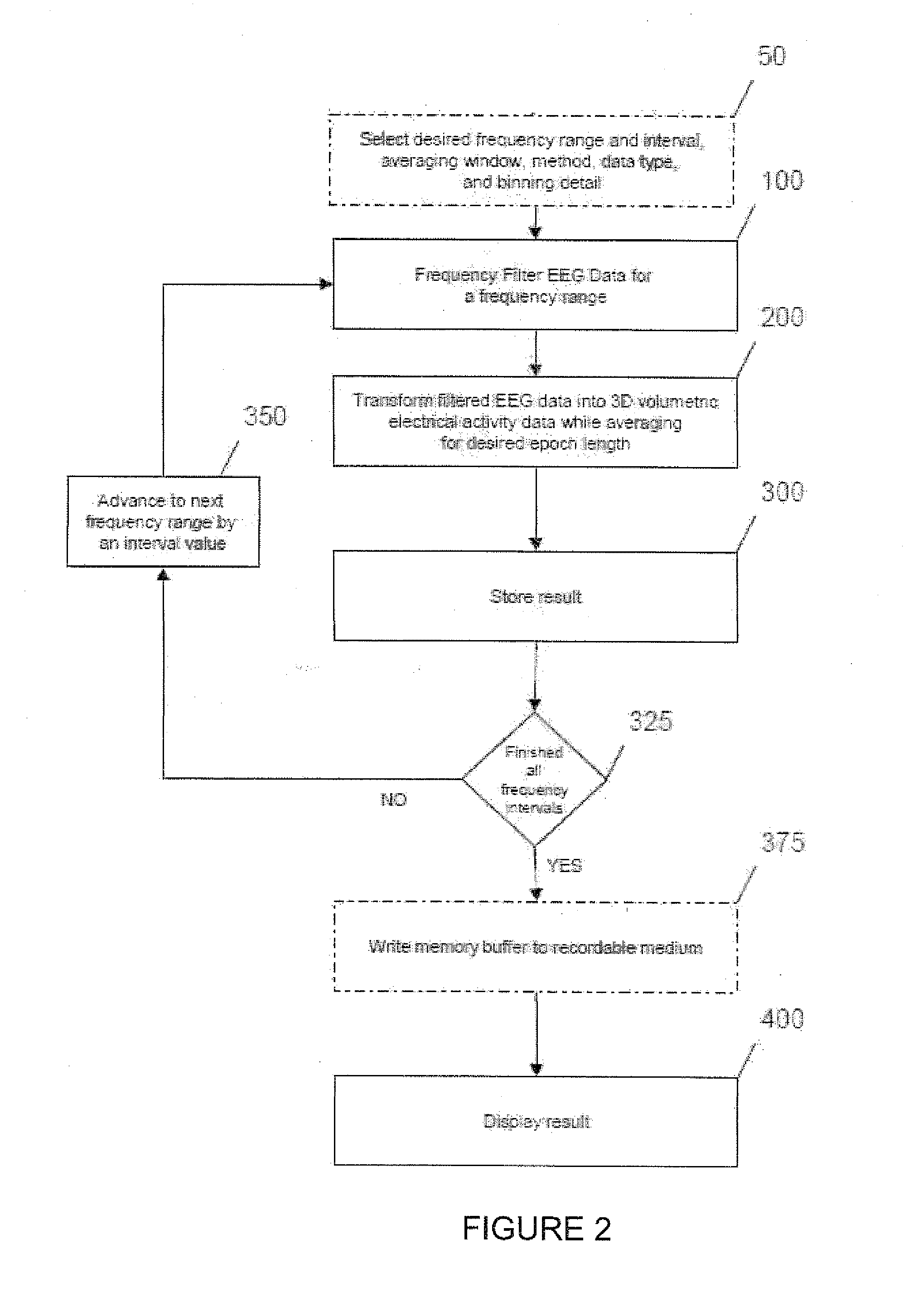
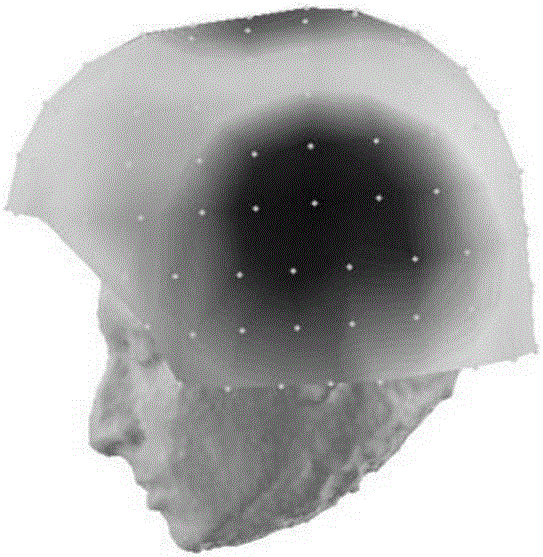
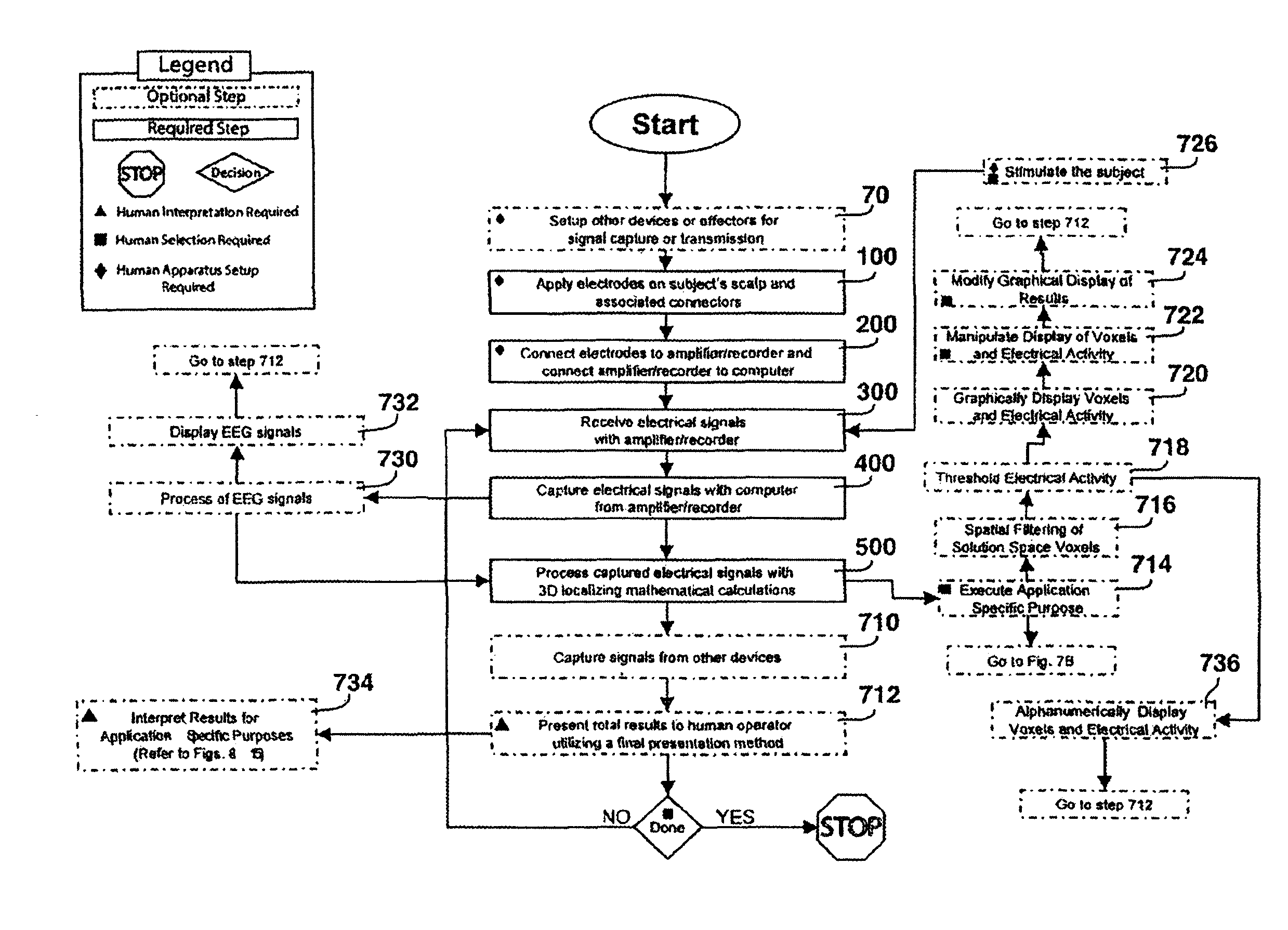
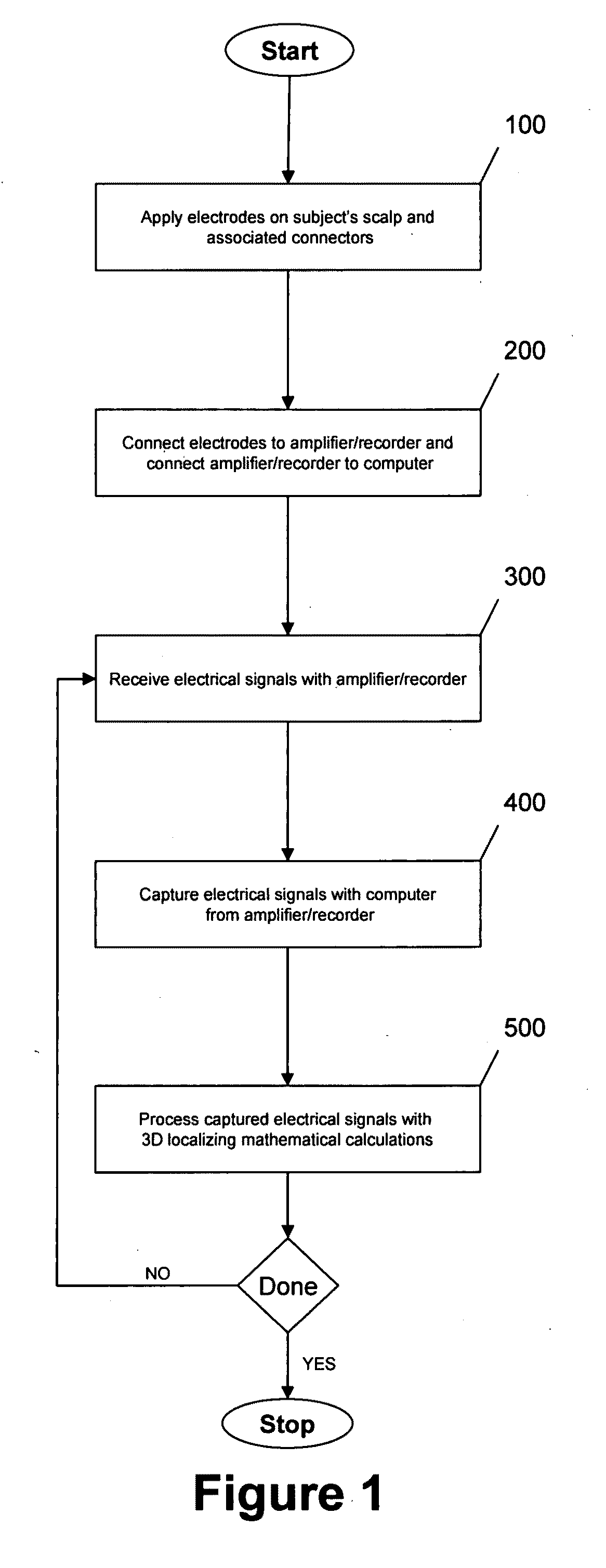
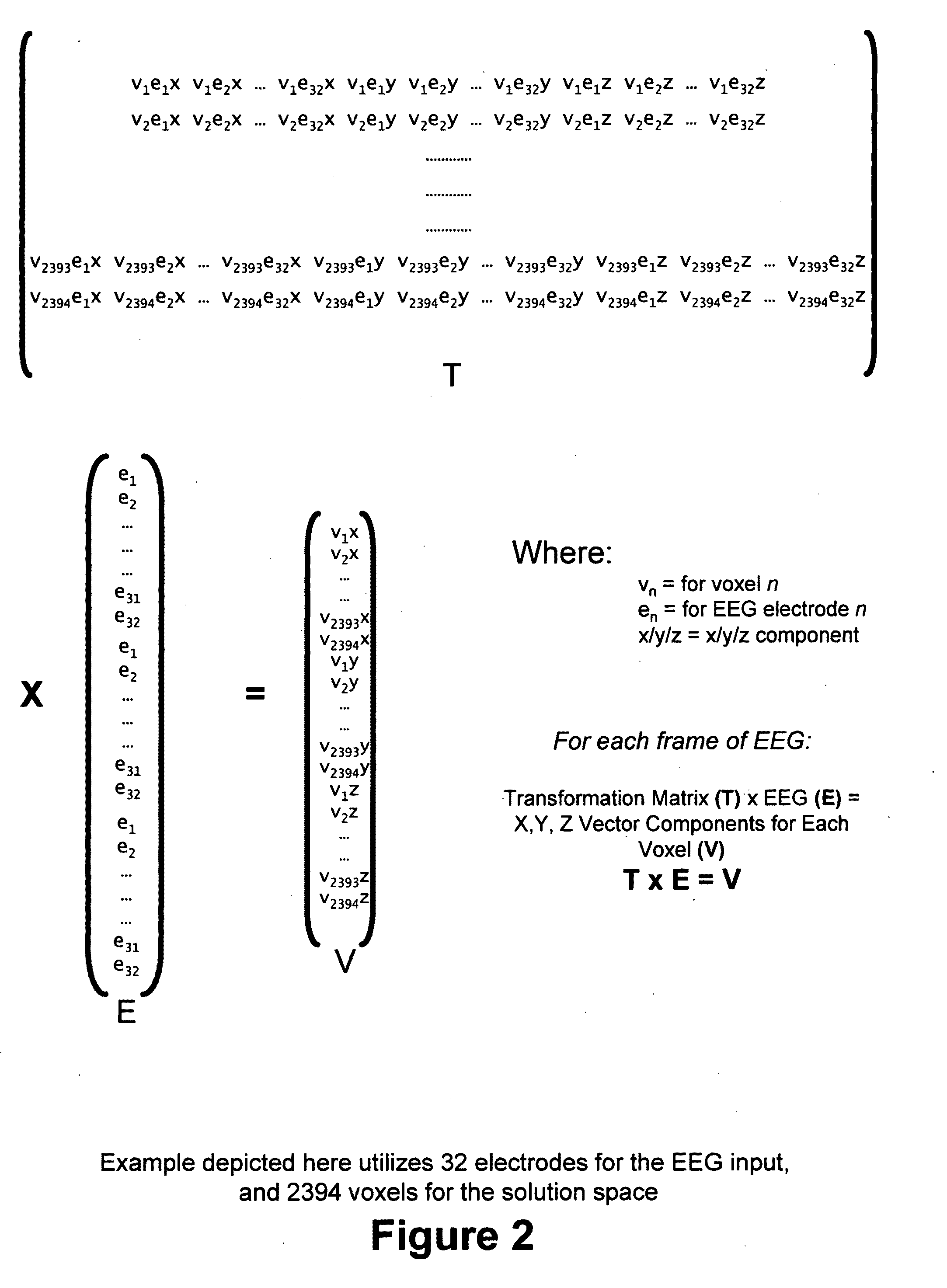
Three-dimensional localization, display, recording, and analysis of electrical activity in the cerebral cortex
The present invention describes a method and apparatus to localize the electrical signals measured from a subject's scalp surface, preferably in near-real time, and to generate dynamic three-dimensional information of the electrical activity occurring within the cerebral cortex of the brain. In the preferred embodiment, it can produce images that can be immediately inspected and analyzed by an operator in near-real time, resulting in a powerful new cortical imaging modality, which we denote as Dynamic Electrocortical Imaging (DECI). The present invention involves the use of a computer, an electroencephalographic (EEG) amplifier, EEG electrodes, and custom software. It can measure healthy and diseased cortical events and states in both conscious and unconscious subjects. This is useful, as it allows for the diagnosis, monitoring and treatment of cortical disorders, while also furthering the understanding of the human brain and lending use to additional non-medical applications such as in entertainment, education, lie-detection and industry. The invention in one embodiment is implemented using software in conjunction with readily available EEG hardware. Furthermore, this same method can be applied to pre-existing data and when doing so, EEG hardware is not required. Having a practical near-real time 3D imaging system brings a far more accessible technology to doctors, researchers, individuals, and private clinics to better diagnose, monitor, treat and understand many of the conditions and abnormalities of the brain.
Owner:DOIDGE MARK S +1
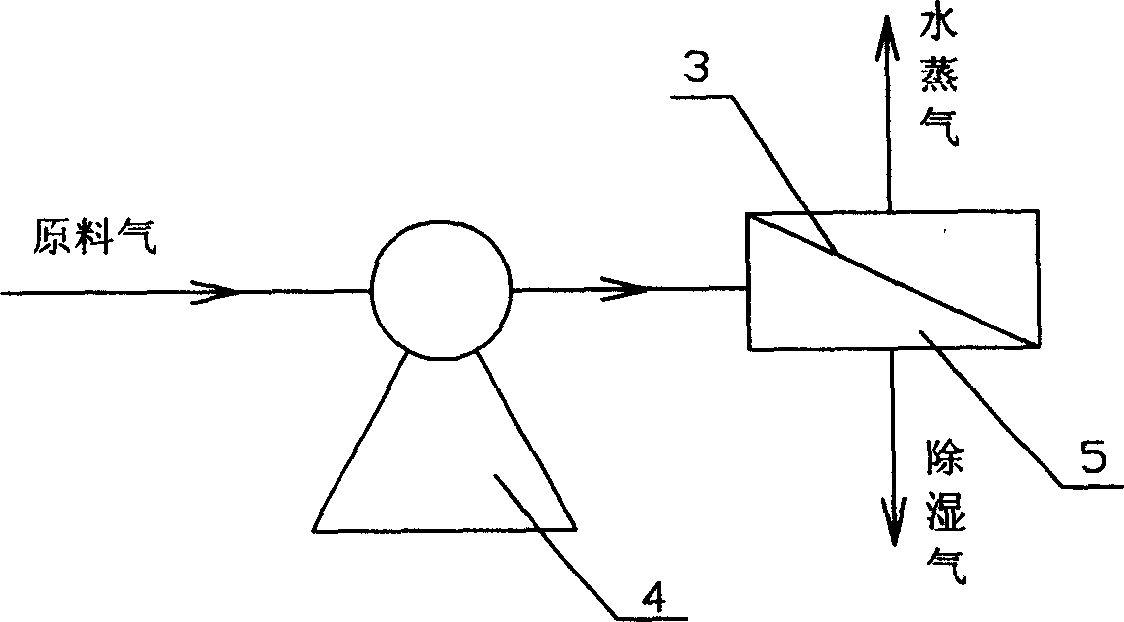
A hydrophilic-hydrophobic bipolar composite membrane and method for preparing same
InactiveCN1864829ASpeed up penetrationReduced Diffusion ResistanceSemi-permeable membranesLighting and heating apparatusChemical industrySupporting system
The invention discloses a hydrophilic-hydrophobic bipolar complex membrane and the method for preparing the same. Said complex membrane comprises two layers, the bottom one is porous supporting system, and upper one is ultra-fine cerebral cortex; said porous supporting system is hydrophobic membrane and nonpolar, to avoid condensation of water vapour; ultra-fine membrane is hydrophilic membrane and polar, and LiCl with 1-5% by weight of main component can be doped to increase polarity; the thickness of porous supporting system is 30-100 um, and that of ultra-fine cerebral cortex is 5-20 um. The invention is characterized by simple process and low cost. The prepared bipolar complex membrane is characterized by good penetration property and gas selectivity, high intensity and wide application in water treatment, air conditioner engineering, energy, chemical industry, metallurgy and biochemical engineering. The product is especially suitable for air dehumidification and heat recycle of air cinditioner new gas.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
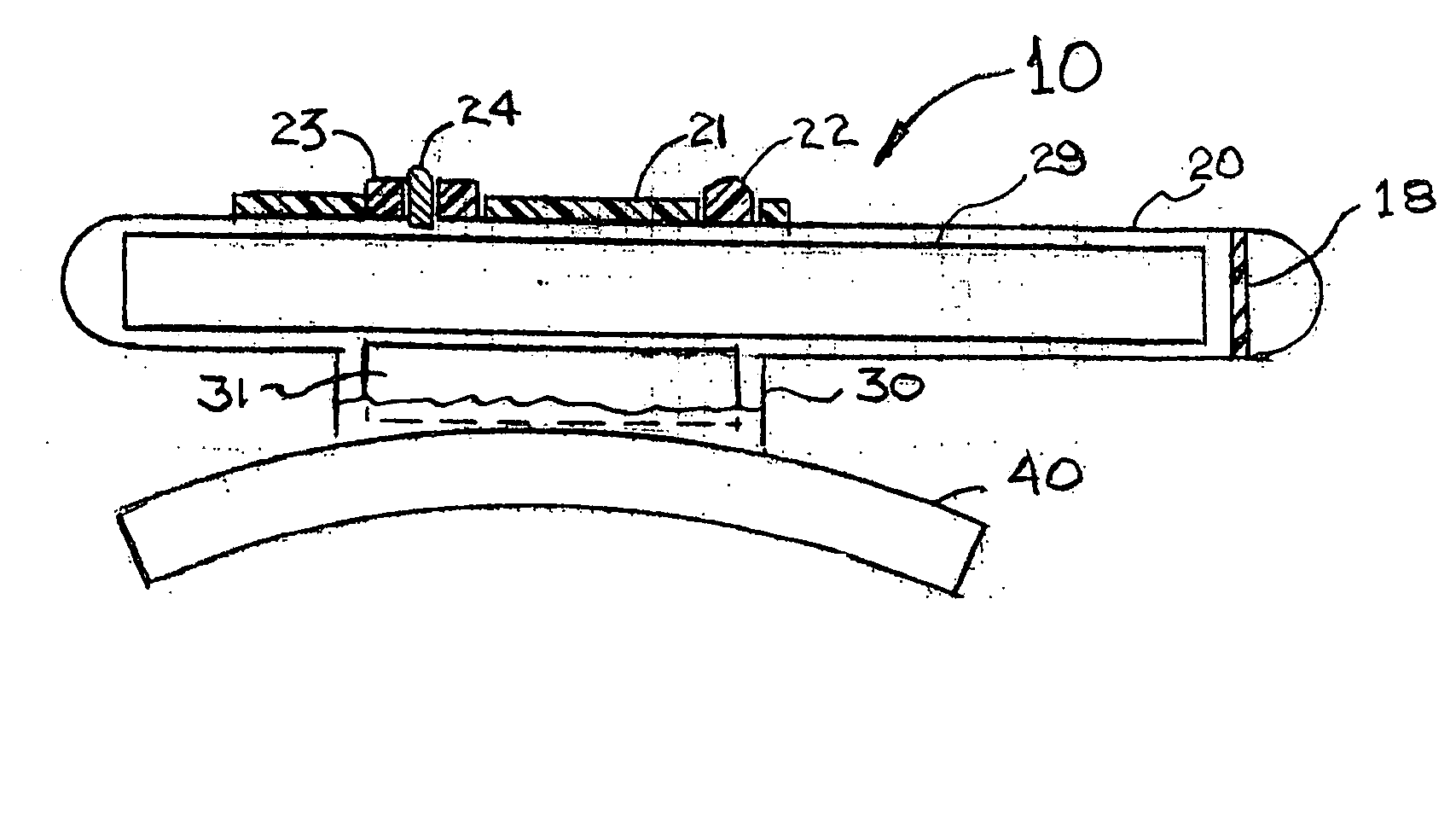
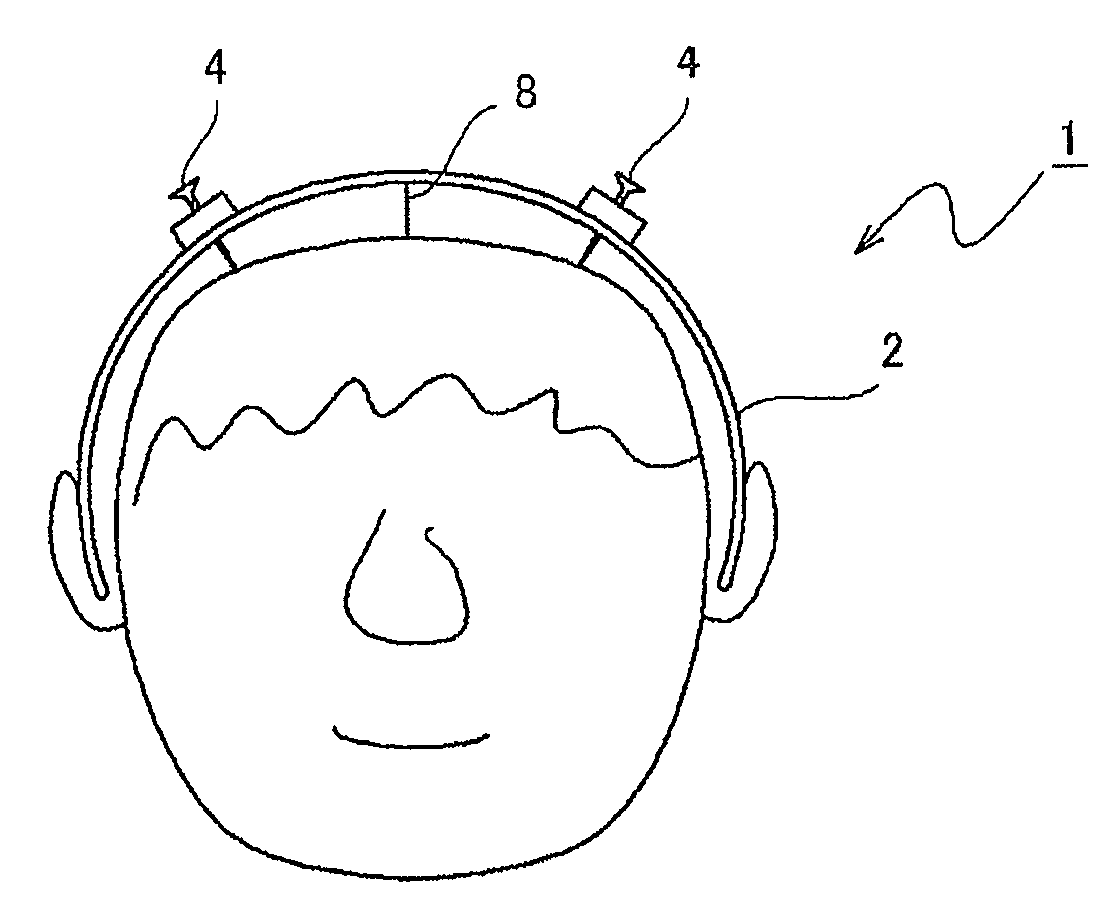
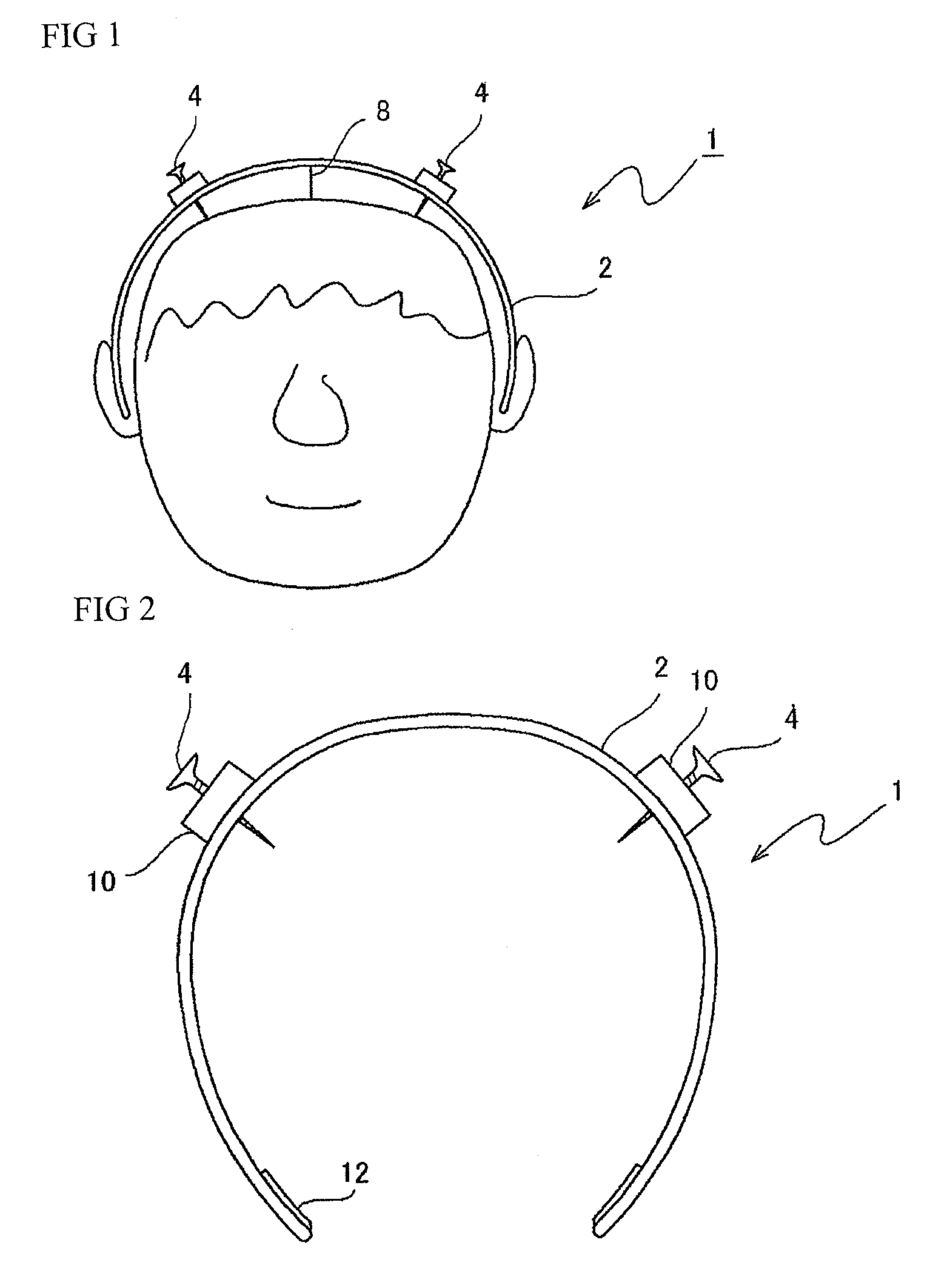
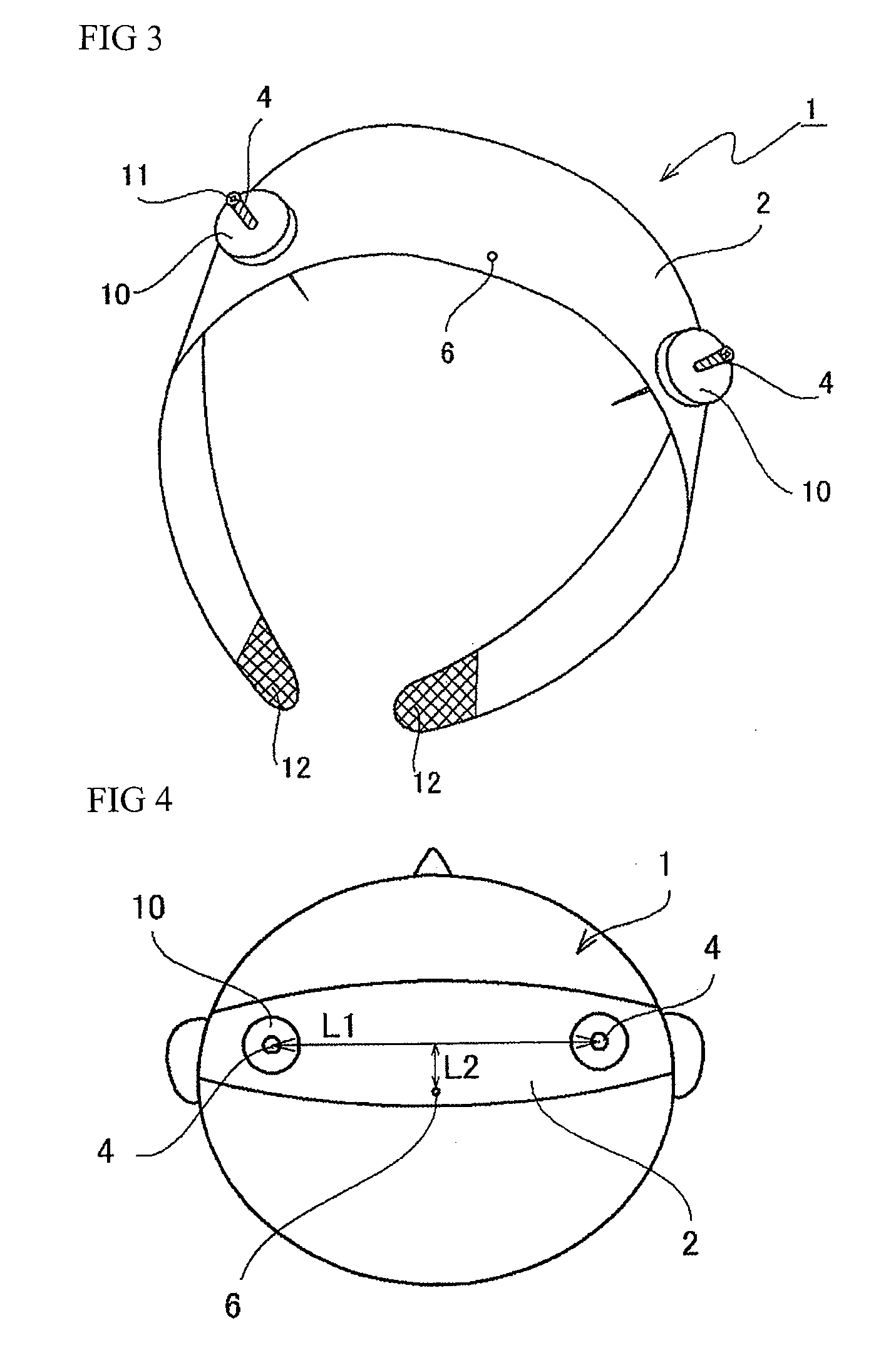
Transcranial electrical stimulation device
InactiveUS8150537B2Accurately positioning electrodeEffectively stimulatedHead electrodesMedicineTranscranial Electrical Stimulations
A transcranial electrical stimulation device 1 having a wearing equipment 2 detachably worn onto a patient's head and at least a pair of electrodes 4 attached to the wearing equipment 2, the device for electrically stimulating a motor area of a patient's cerebral cortex by outputting current from the electrode 4 connected to a current generator. An engagement part 6 capable of engaging the wearing equipment 2 to a scalp with a thread-like body 8 is provided to the wearing equipment 2, and the electrode 4 is attached to the wearing equipment 2 protrudably to the head side of the electrode 4, and tip of the electrode 4 is capable of subcutaneously piercing through the head. It is unnecessary to bore a patient's skull outer layer with a drill, and a mounting of the electrode can be performed in a short time. The electrodes can be accurately positioned at predetermined positions of a patient's head, and the motor area of a cerebral cortex can be effectively stimulated.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY
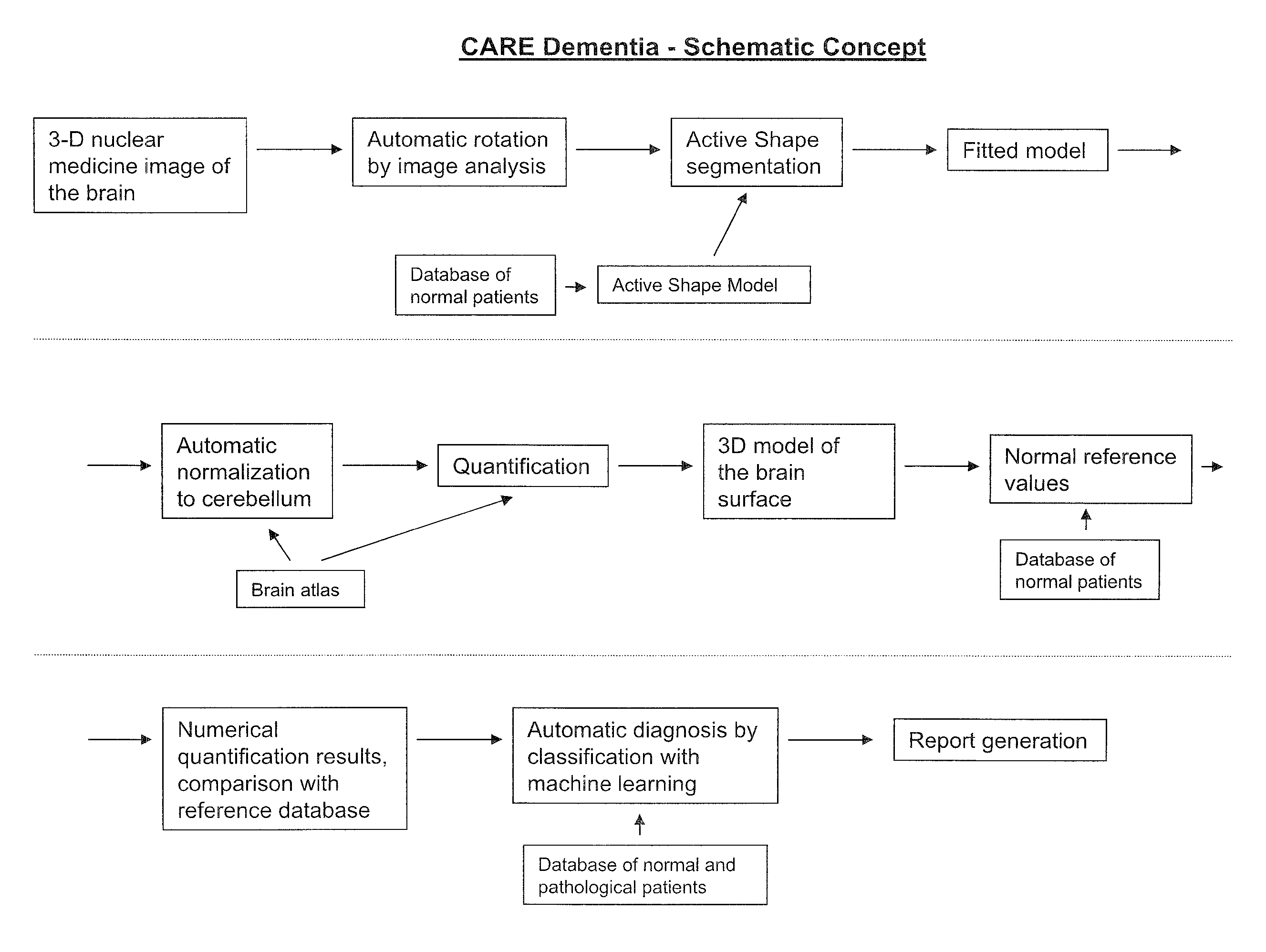
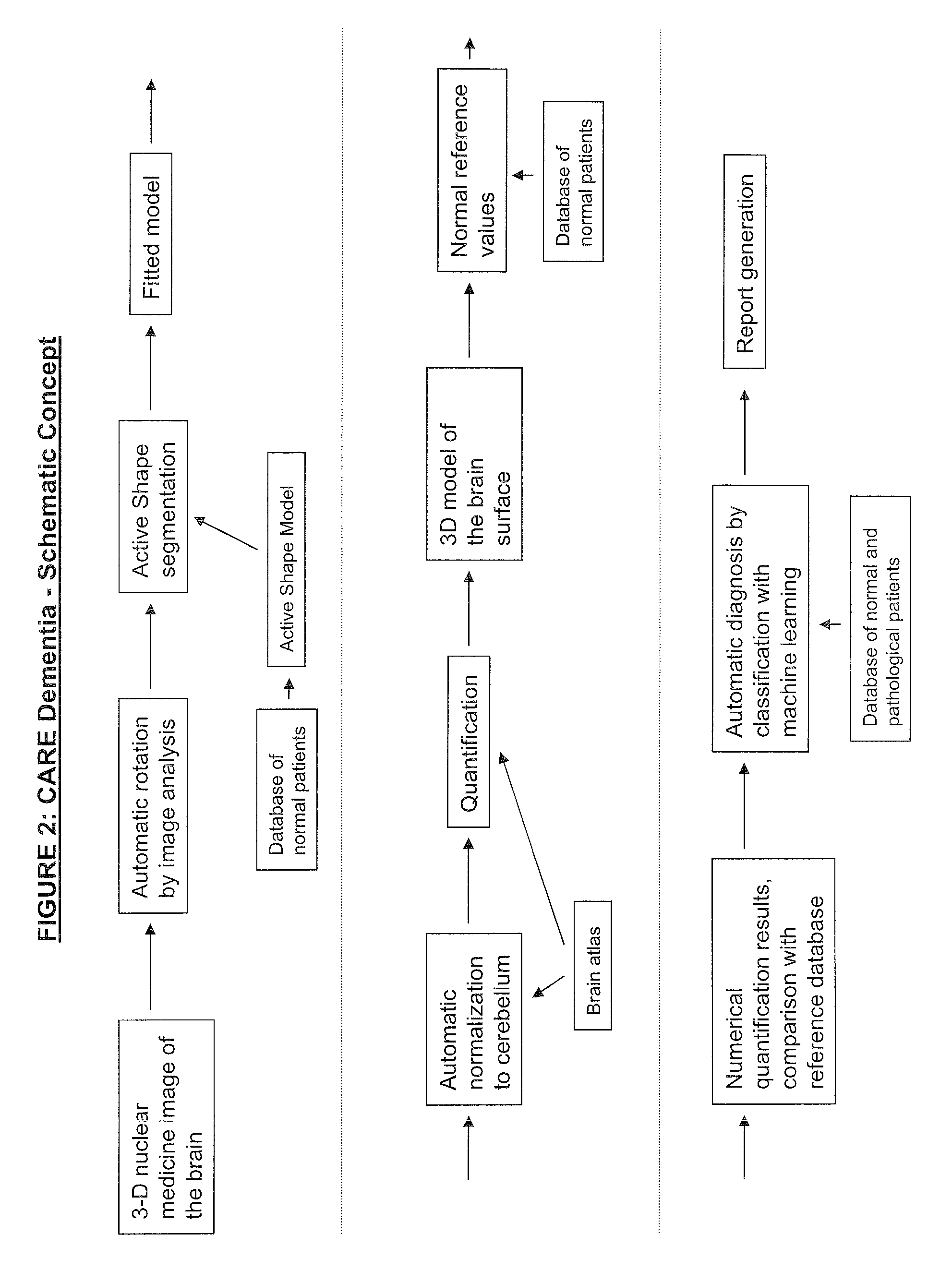
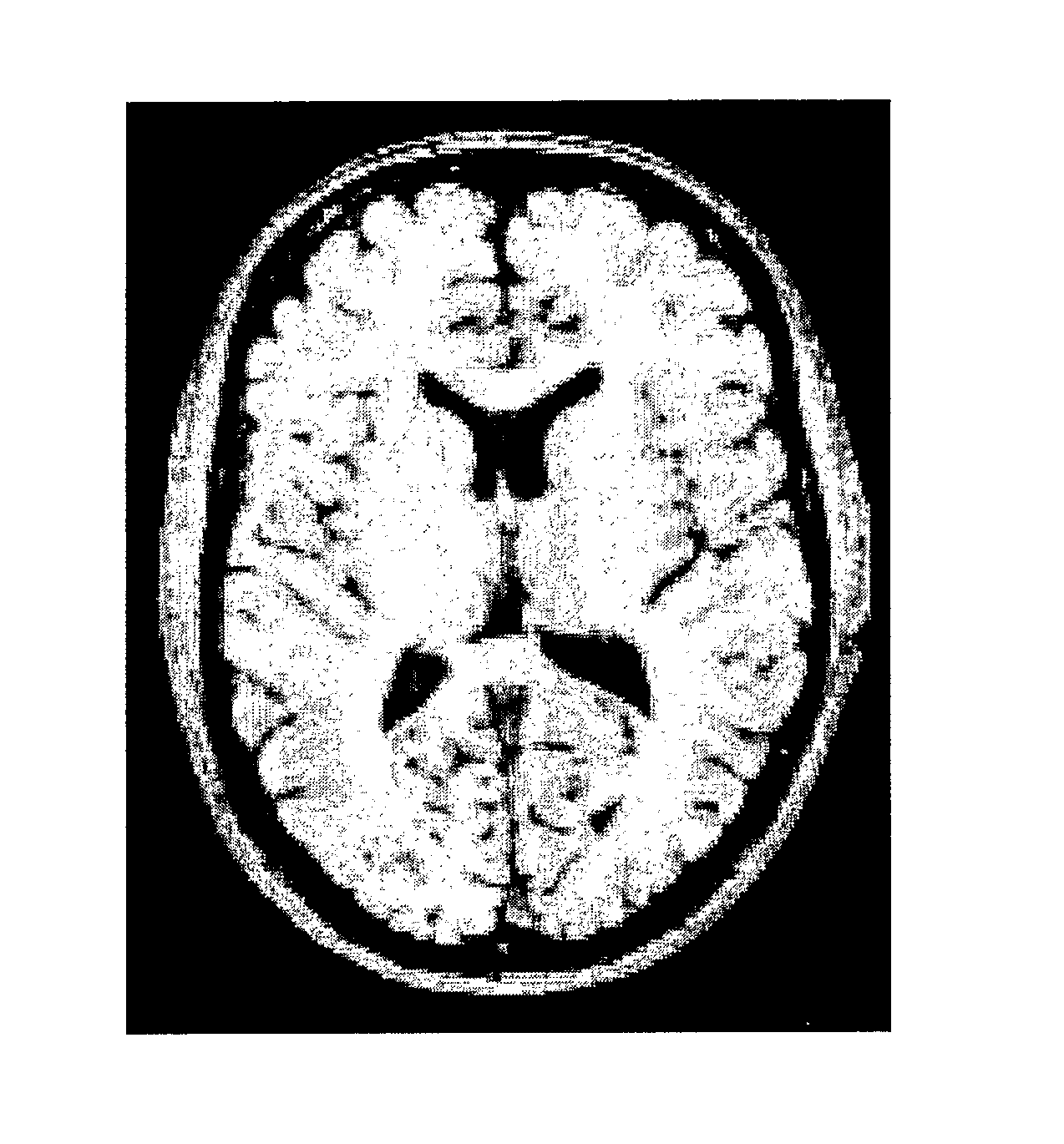
Automatic interpretation of 3-D medicine images of the brain and methods for producing intermediate results
ActiveUS8199985B2Shorten the timeAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFully automatic
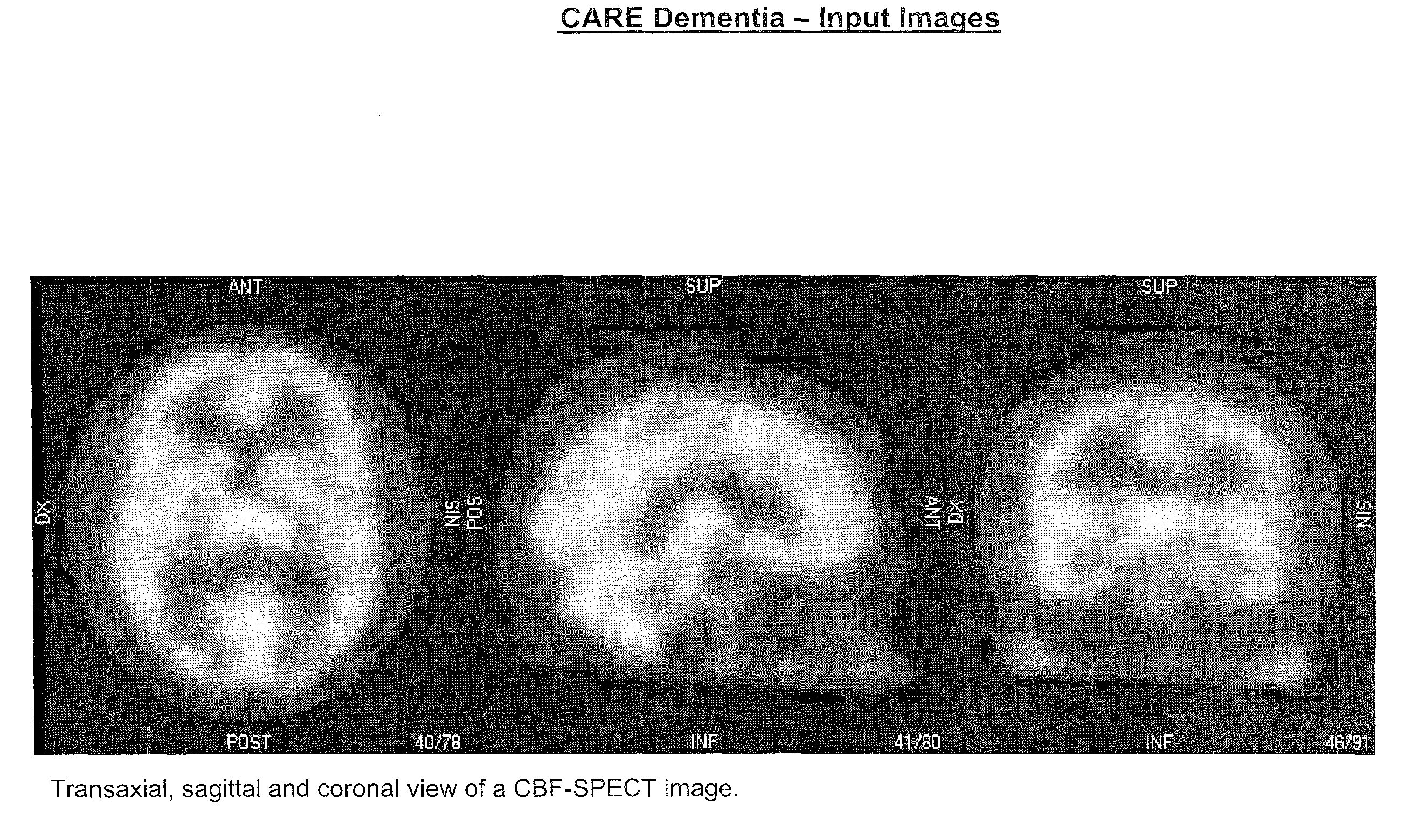
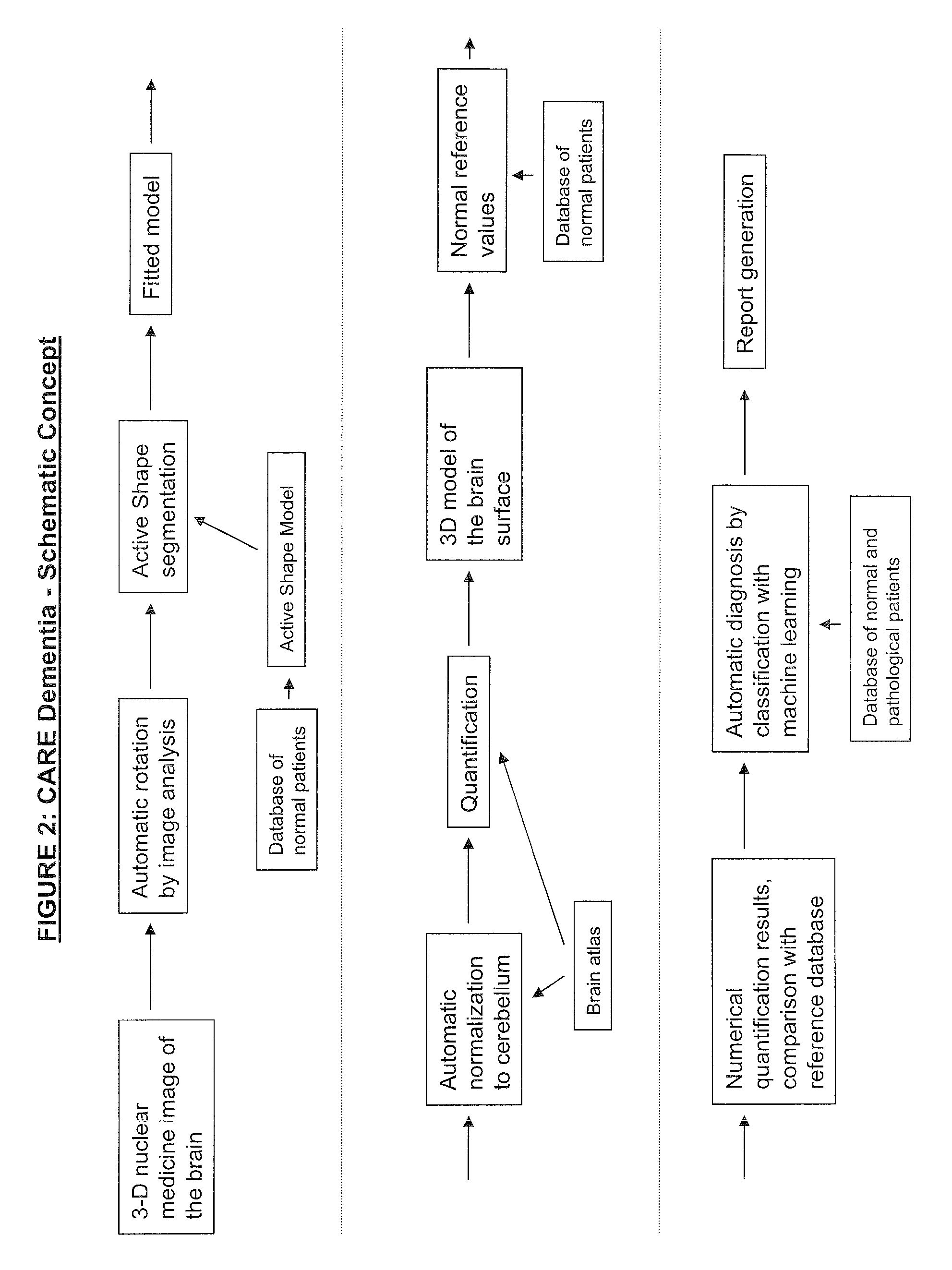
Methods for fully automatic quantification and interpretation of three dimensional images of the brain or other organs. A system for Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of diseases affecting cerebral cortex from SPECT images of the brain, where said images may represent cerebral blood flow (CBF). The methods include image processing, statistical shape models, a virtual brain atlas, reference databases and machine learning.
Owner:EXINI DIAGNOSTICS
Computerised Cortex Boundary Extraction From Mr Images
InactiveUS20080170791A1Improved and robust and accurateAccurate modelingImage enhancementImage analysisDigital dataData set
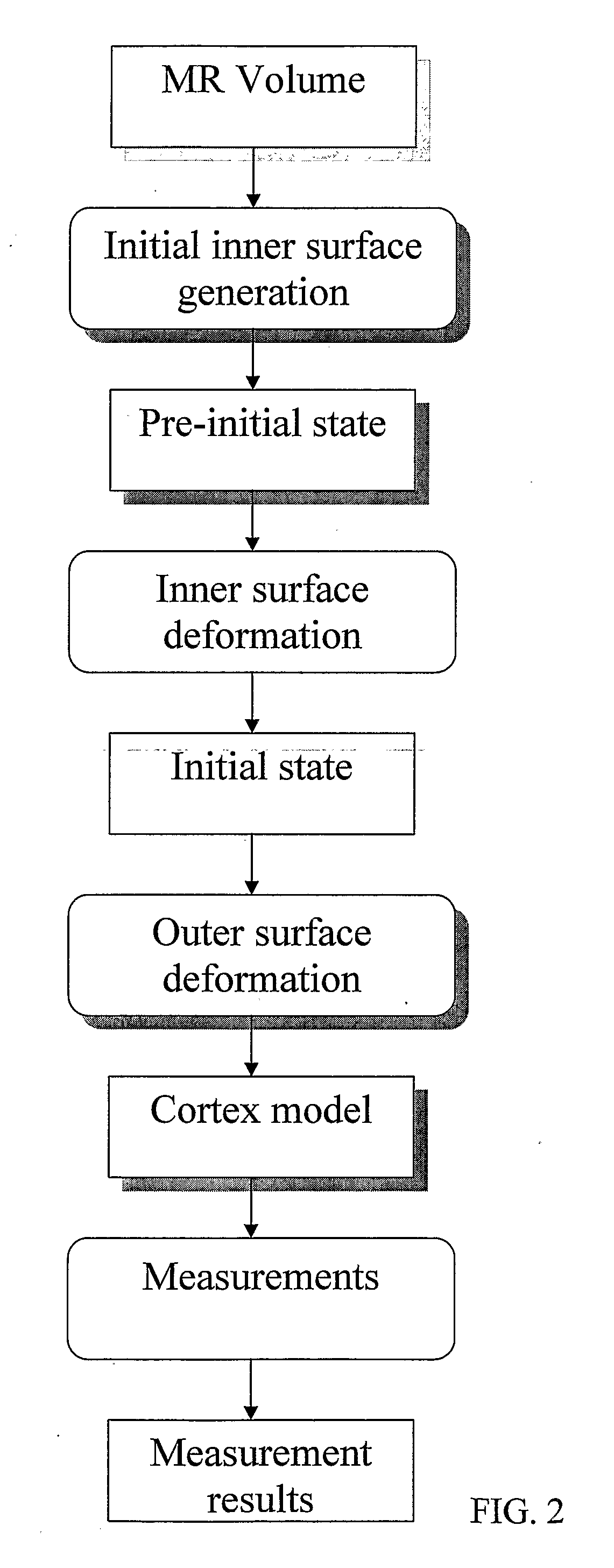
Method for processing digital images, such as magnetic resonance images of a brain. The images contain a first object, for example the cerebrum white matter, a second object, for example the cerebral cortex, and a third object, for example the cerebrospinal fluid. The method involves providing a digital dataset representing a deformable curve or surface that in an initial state approximates the boundary between the first object and the second object. Further, a vector force field is provided that for each point on the deformable curve or surface defines a direction from the point approximately towards the second boundary between the second and the third object, and this vector force field is applied for iteratively deforming the deformable curve or surface convergently towards the second boundary. In order to reconstruct a folded structure of the second object, for example the cortex, the vector force field also involves a normal vector field with a vector normal or approximately normal to the deformable curve or surface for each point on the deformable curve or surface.
Owner:AALBORG UNIV
Automatic interpretation of 3-d medicine images of the brain and methods for producing intermediate results
ActiveUS20100067761A1Shorten the timeAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFully automatic
Methods for fully automatic quantification and interpretation of three dimensional images of the brain or other organs. A system for Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of diseases affecting cerebral cortex from SPECT images of the brain, where said images may represent cerebral blood flow (CBF). The methods include image processing, statistical shape models, a virtual brain atlas, reference databases and machine learning.
Owner:EXINI DIAGNOSTICS
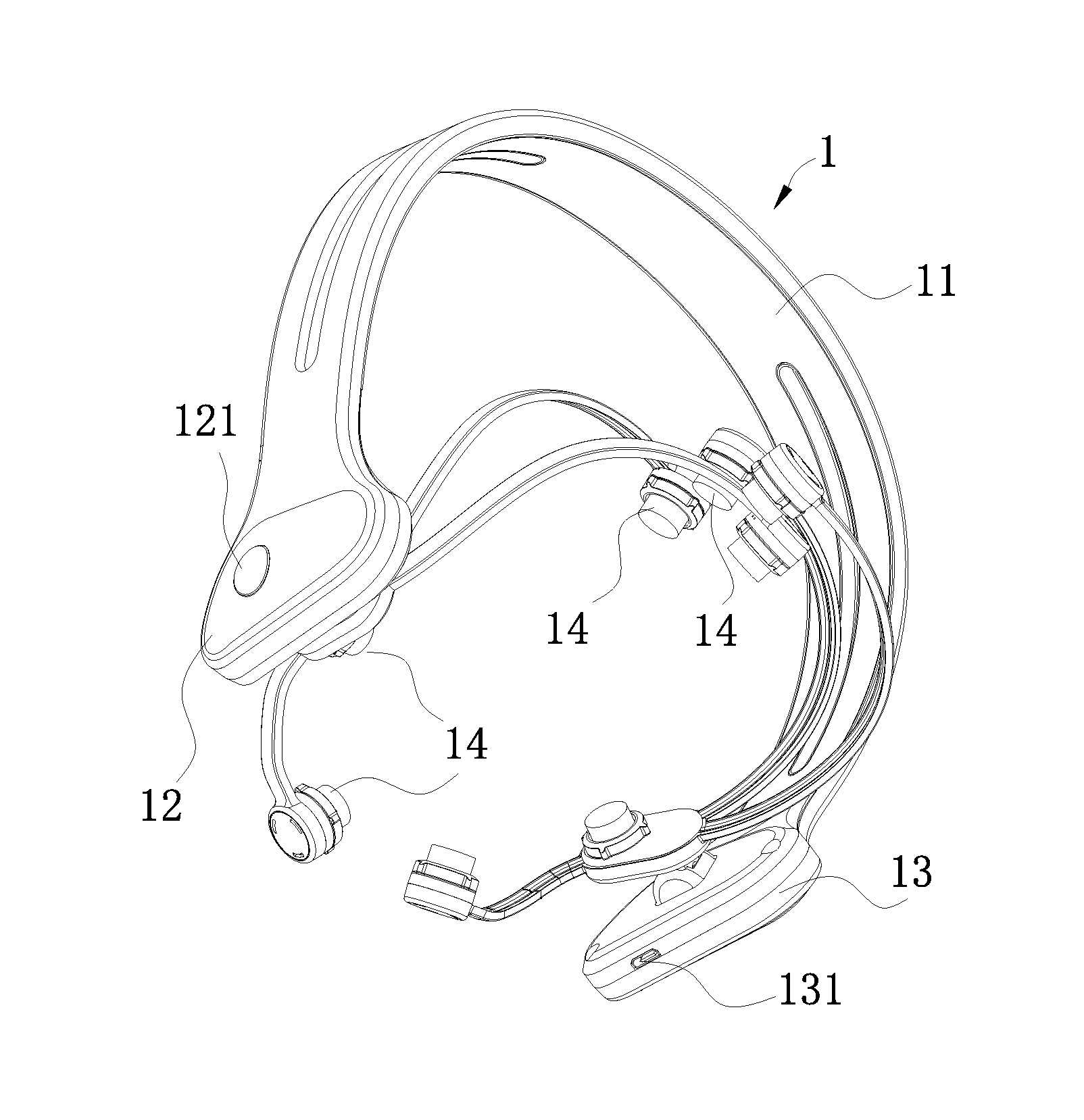
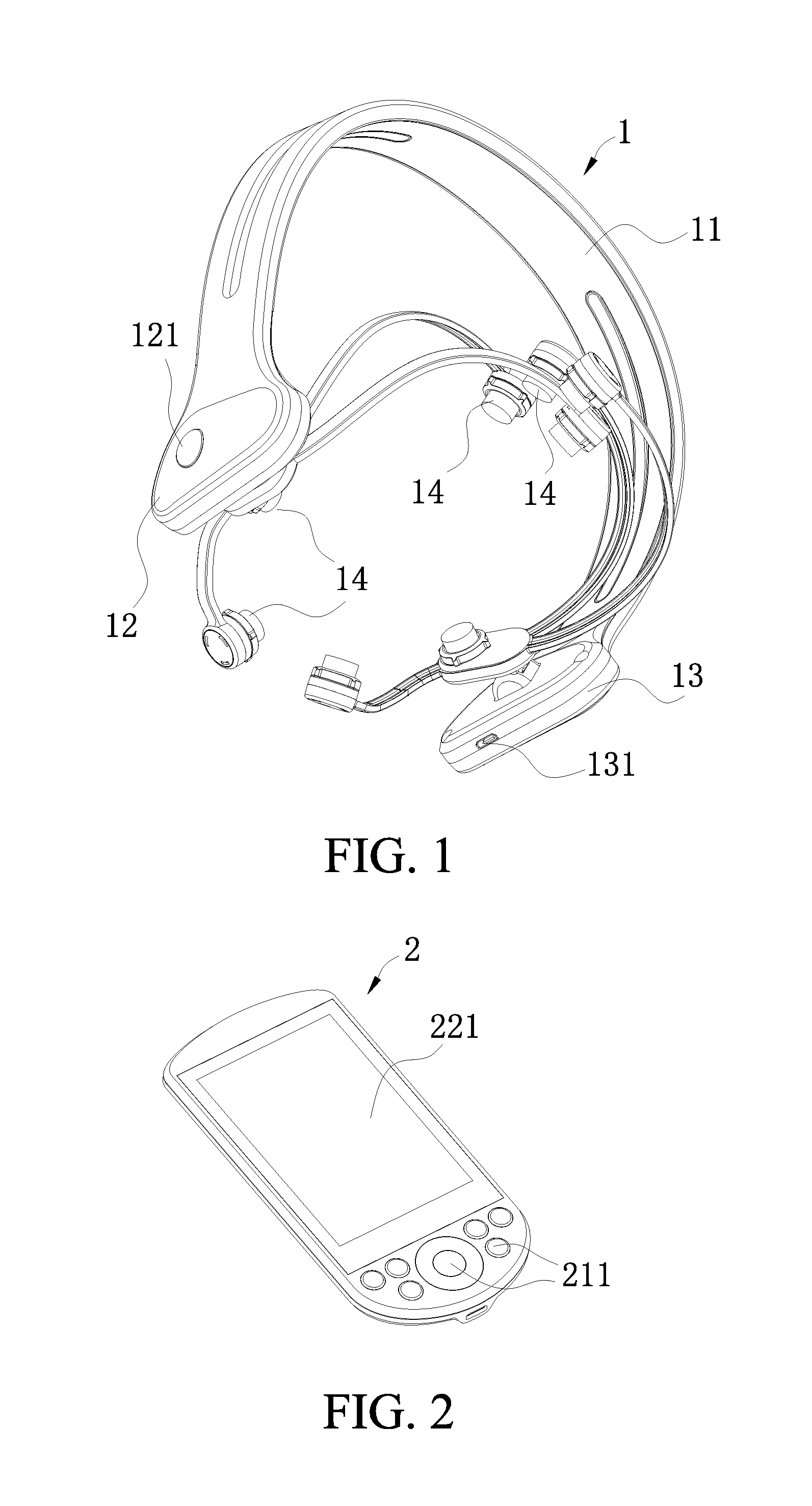
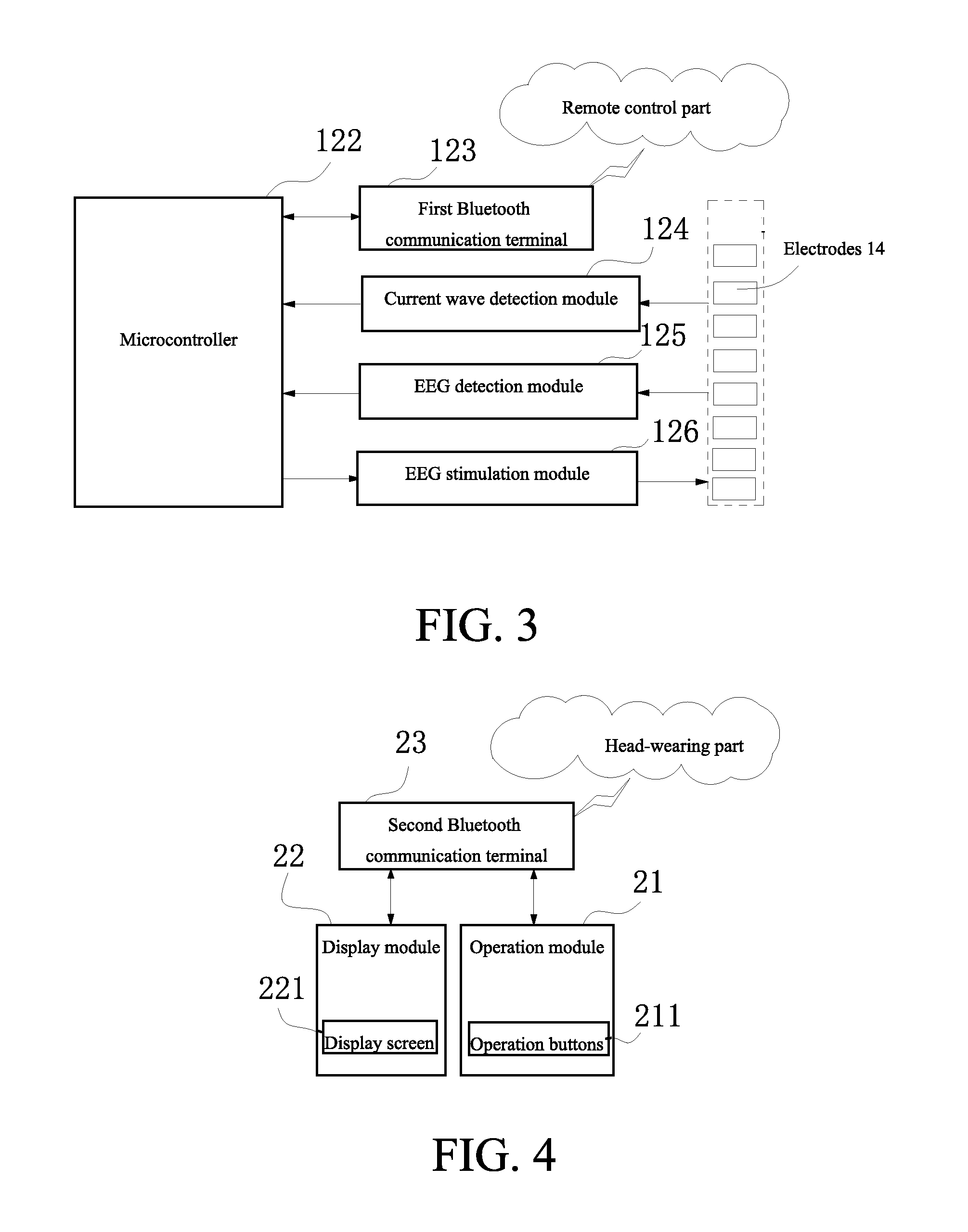
Head-wearing wireless control transcranial electrical stimulation device
InactiveUS20160074657A1Easy to carryEasy to operateHead electrodesExternal electrodesMicrocontrollerWireless control
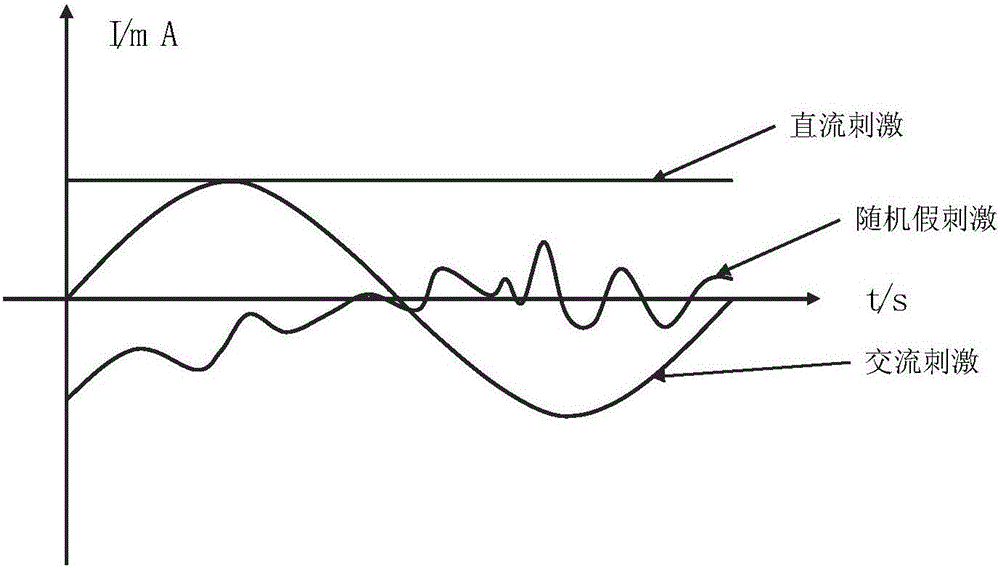
A head-wearing wireless control transcranial electrical stimulation device includes a head-wearing part and a remote control part. An integrated circuit board is arranged within a cavity of a first end of the head-wearing part. The integrated circuit board controls a microcontroller. The microcontroller is connected with and controls a plurality of electrodes for contacting a human body through circuit modules. The microcontroller receives a control instruction from the remote control part through a Bluetooth communication terminal, and then controls the plurality of the electrodes to exert an alternating current or a direct current having preset density and frequency to a cerebral cortex. The microcontroller receives an electrode feedback signal, and sends the electrode feedback signal after being pre-processed to a display module of the remote control part to be displayed through the Bluetooth communication terminal.
Owner:ADVANCE ELECTRONICS & MEDICAL IND COMPANY
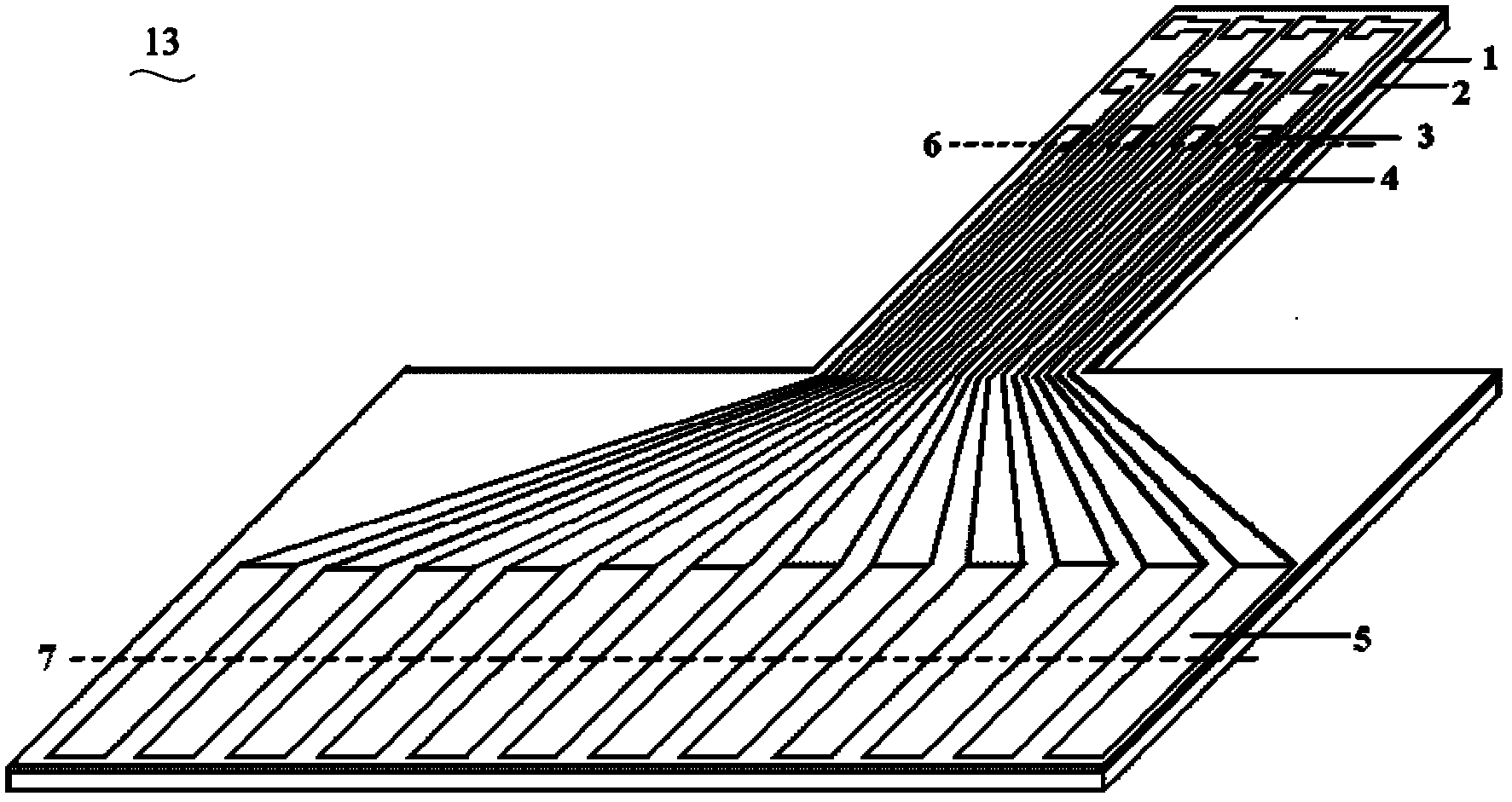
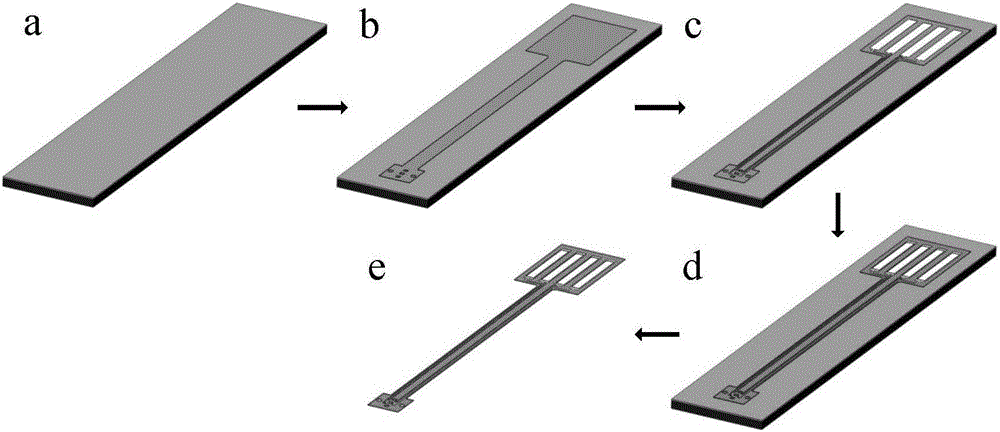
Flexible intracranial cortex microelectrode chip, and preparation method and packaging method and packaging structure thereof
InactiveCN102544052AGuaranteed space fitEfficient deliverySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUltrasound attenuationMicroelectrode
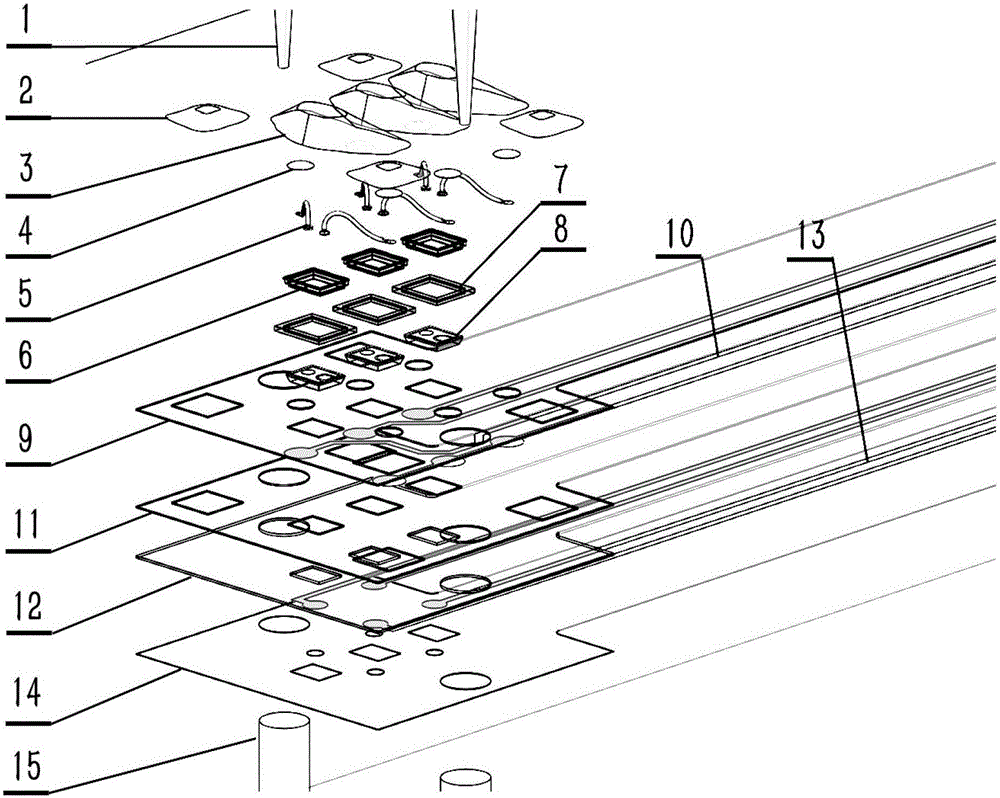
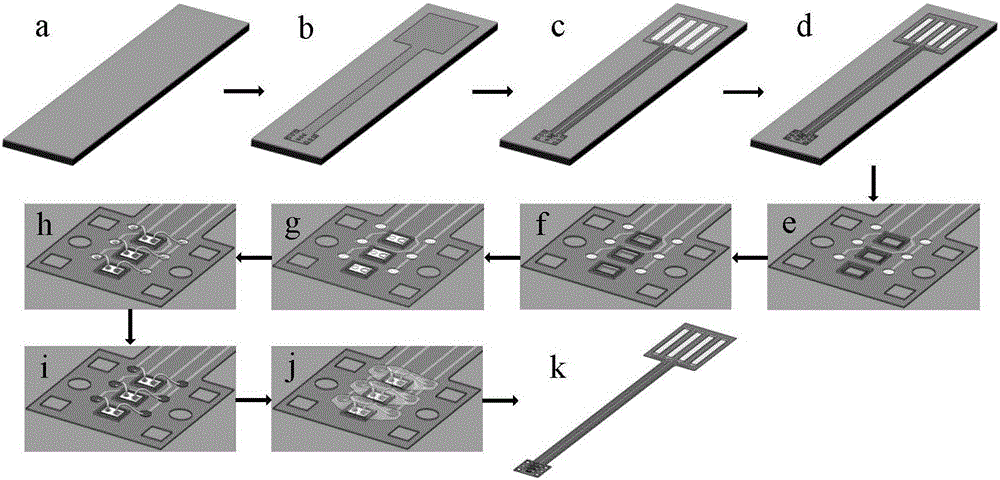
The invention relates to a flexible intracranial cortex microelectrode chip, which comprises a flexible substrate, a microelectrode unit, an electrode lead which is electrically connected with the microelectrode unit, a lead welding spot which is electrically connected with the electrode lead, and an insulating layer which is arranged on the flexible substrate and covers the electrode lead, wherein the microelectrode unit, the electrode lead and the lead welding spot are arranged on the flexible substrate. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the flexible intracranial cortex microelectrode chip, a packaging structure for the flexible intracranial cortex microelectrode chip, and a method for packaging the flexible intracranial cortex microelectrode chip. The flexible intracranial cortex microelectrode chip has high flexibility and can be well adhered to cerebral cortex, information is detected, and electrical stimulation is applied. Better flexible matching between the flexible intracranial cortex microelectrode chip and the cerebral cortex can be realized, and in the long-term implantation process, attenuation of organism response on performance of the electrode is effectively reduced; and moreover, tissue damage, inflammatory response, incrustation, hemorrhage and other conditions are avoided.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
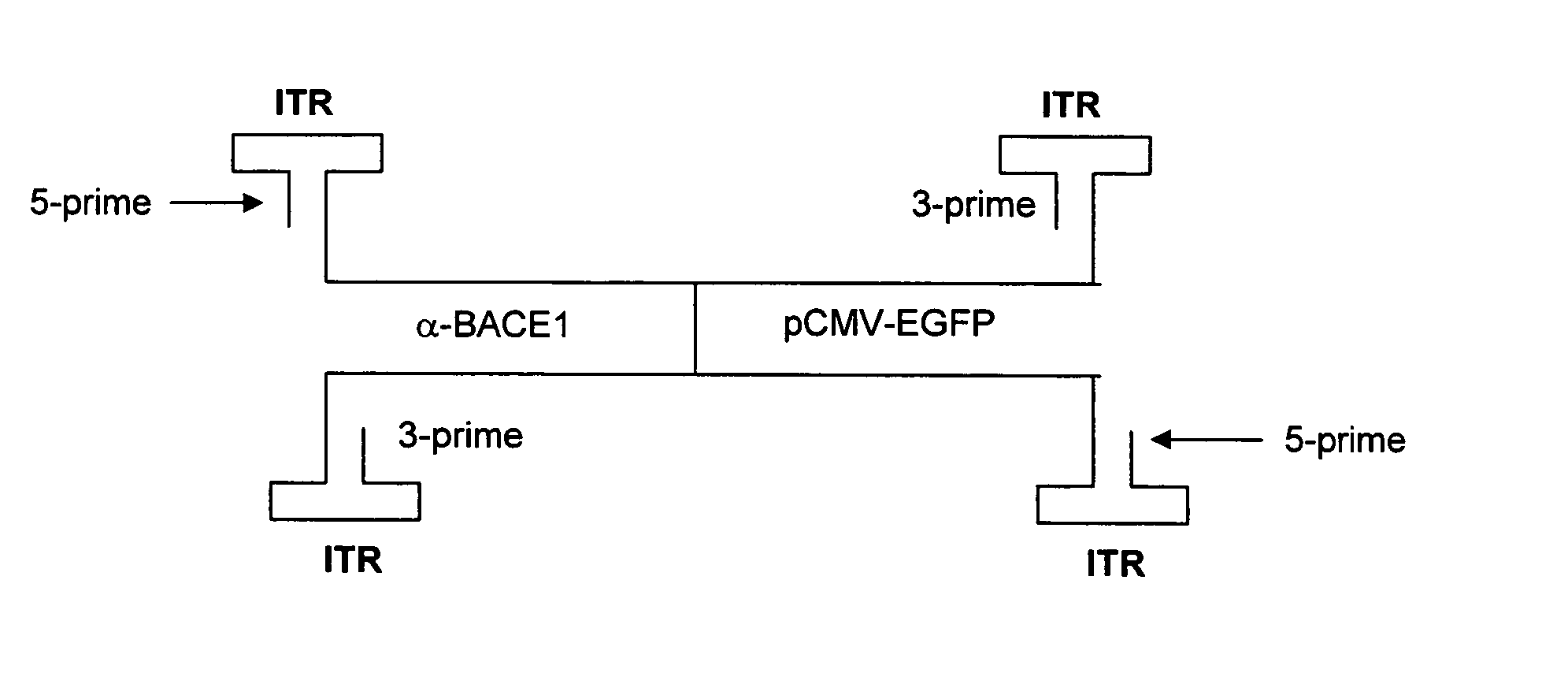
Devices, systems and methods for improving memory and/or cognitive function through brain delivery of siRNA
InactiveUS20060178328A1Reduce riskImprove memory functionNervous disorderSpecial deliveryDna encodingSmall interfering RNA
The present invention relates to devices, systems, and methods for improving memory and / or cognitive function by brain delivery of compositions of small interfering RNA or vectors containing the DNA encoding for small interfering RNA. Such compositions can be administered using devices, systems and methods for direct delivery of the compositions to the brain, or using devices, systems, methods of delivery, and compositions that deliver small interfering RNA or vectors containing the DNA encoding the small interfering RNA across the blood-brain barrier. The present invention also provides valuable small interfering RNA vectors, and methods for reduction of BACE1 levels in the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, or other regions of the brain that have beneficial effects on improving memory and / or cognitive function in a subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
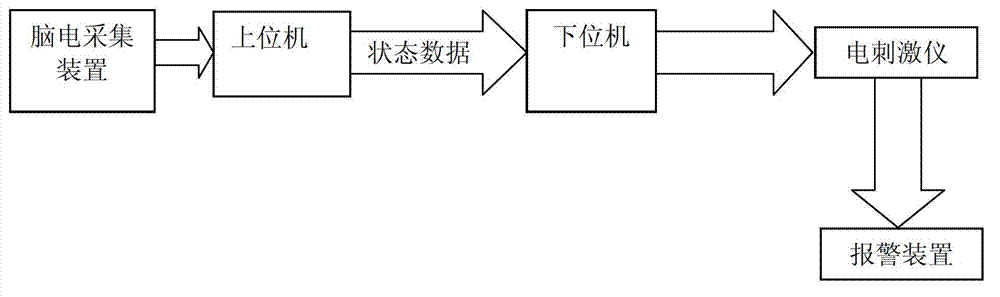
System and method for detecting and relieving driving fatigue based on electrical acupoint stimulation
InactiveCN103111020AReal-time monitoring of driving statusRelieve driving fatigueDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityDriver/operator
The invention discloses a system and a method for detecting and relieving driving fatigue based on electrical acupoint stimulation. The system comprises an electroencephalogram acquisition device, an upper computer, a lower computer and an electrical stimulation instrument, an input end of the electroencephalogram acquisition device is connected to the cerebral cortex of a driver, an output end of the electroencephalogram acquisition device is connected with the upper computer which is connected with the lower computer, the lower computer is connected with an input end of the electrical stimulation instrument, and a pulse output end of the electrical stimulation instrument is connected to a meridian point, capable of reliving brain fatigue, of the driver through an electrode. The method includes: acquiring electroencephalogram signals of the driver in real time; and extracting fast-wave and low-wave frequency band signals in the electroencephalogram signals, computing a ratio of fast-wave average power spectra to low-wave average power spectra, judging the driving state of the driver according to reduction of the ratio, and controlling the electrical stimulation instrument to start and enter a corresponding working mode. Driving states of the driver are monitored in real time, and electrical stimulation is performed to the driver in good time, so that driving fatigue is relieved better, driving safety is improved, and hidden danger of traffic caused by fatigue driving is reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
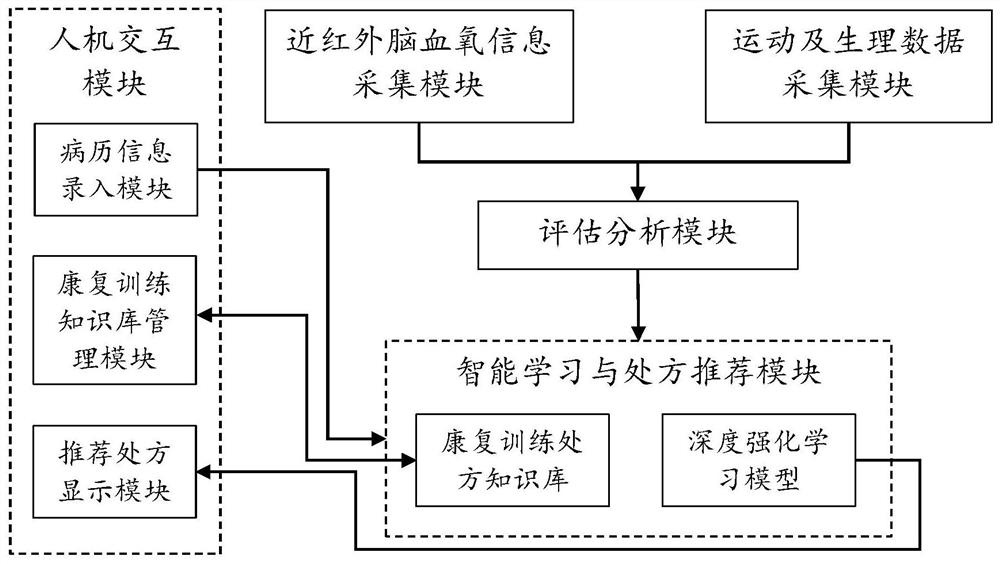
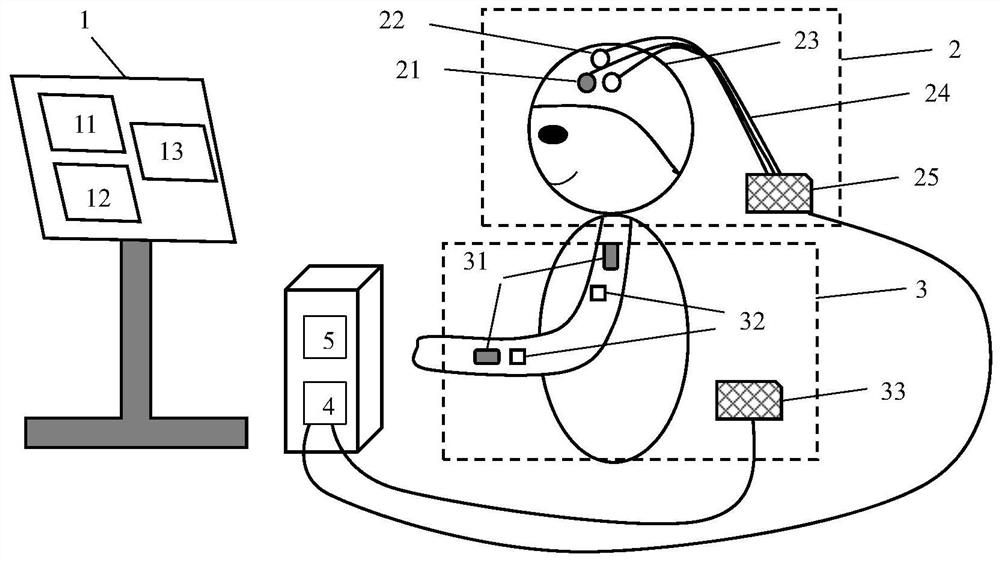
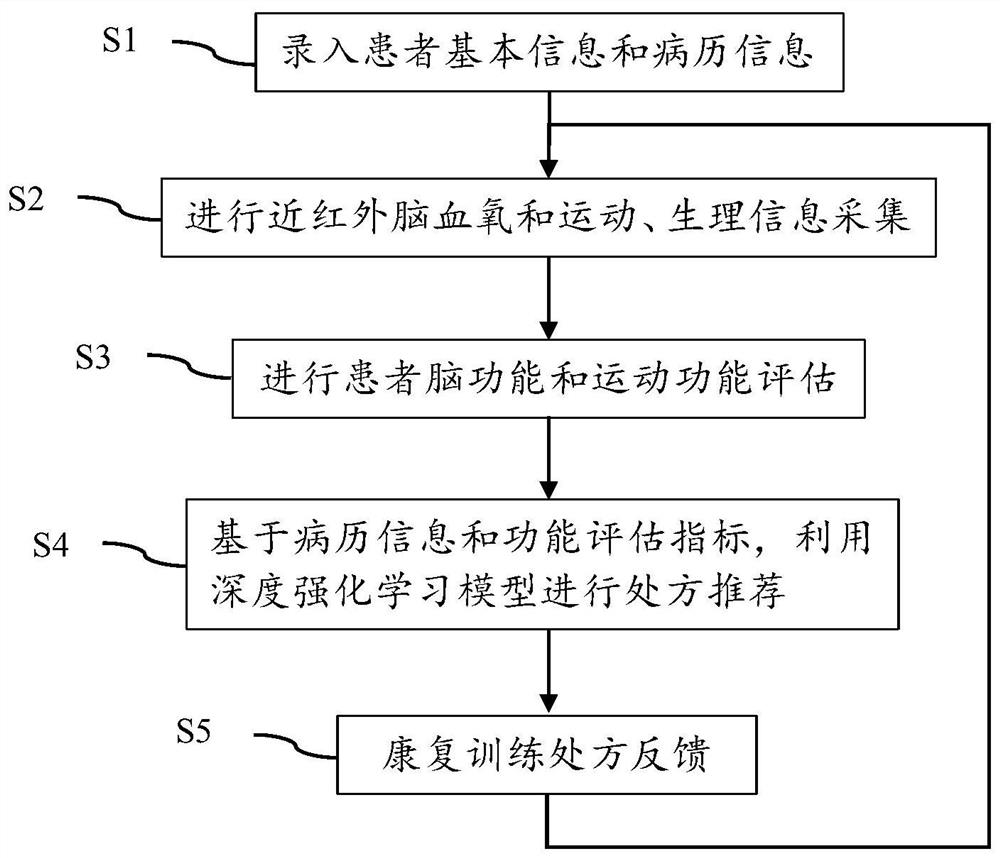
Self-adaptive recommendation method and system for rehabilitation training prescription based on deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN111816309AIncrease contentAlleviate manual evaluationPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationMedical recordMuscle functions
The invention provides a self-adaptive recommendation method and system for a rehabilitation training prescription based on deep reinforcement learning. The method comprises the following steps: 1) collecting basic information and medical record information of a patient; 2) acquiring cerebral cortex blood oxygen data of different brain regions of the patient and movement and myoelectricity data ofaffected limbs of the patient; 3) calculating brain function evaluation indexes during exercise and rehabilitation training of the patient by utilizing the brain blood oxygen data, and calculating exercise function evaluation indexes and muscle function evaluation indexes during exercise and rehabilitation training of the patient by utilizing the exercise data and the myoelectricity data so as todynamically evaluate the brain function, the exercise function and the muscle function of the patient; 4) inputting the brain function, motion function and muscle function evaluation indexes obtainedin the step 3) into a pre-established deep reinforcement learning model to train the deep reinforcement learning model and automatically generate a rehabilitation training prescription; and 5) feeding back the rehabilitation training prescription generated in the step 4) to a doctor and the patient for rehabilitation training. By means of the method and system, self-adaptive adjustment of the training prescription can be achieved.
Owner:DANYANG HUICHUANG MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Method for Identifying Images of Brain Function and System Thereof
InactiveUS20170079538A1Early detectionElectroencephalographyMedical imagingSource reconstructionFrequency spectrum
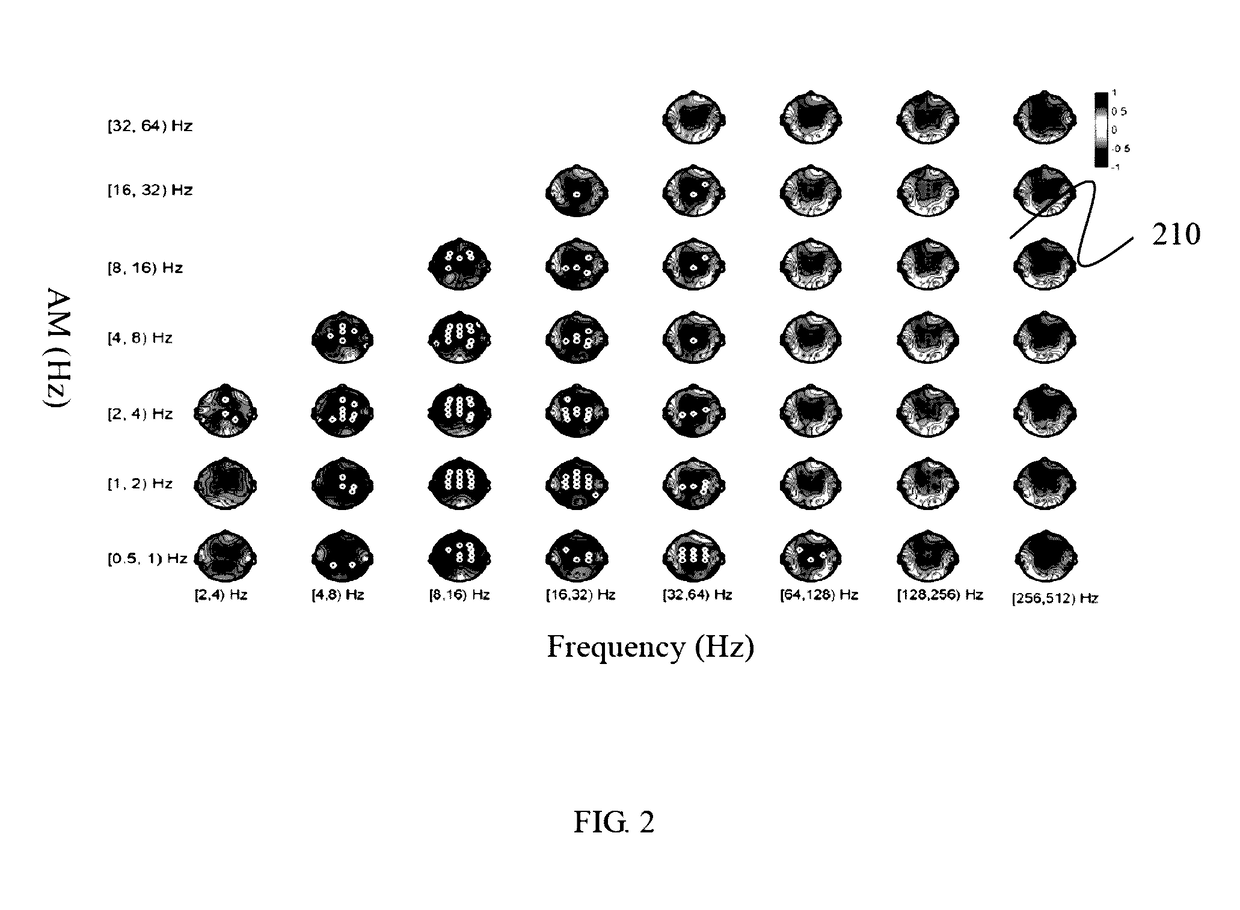
The present invention provides a method for identifying images of brain function. In the beginning, choosing one of the brain data collected by multichannel scalp EEG / MEG, and using a mode decomposition method to obtain a plurality of intrinsic mode functions for each brain data, transforming the intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) in the same frequency scale into a plurality of source IMFs across the cerebral cortex by a source reconstruction algorithm, and classifying each source IMF in the same frequency scale into a plurality of frequency regions corresponding to the different brain sites. Then, repeatedly choosing a source IMF, and obtaining an amplitude envelope line through each absolution value of the source IMF. Further to obtain a plurality of source first-layer amplitude IMFs decomposed from the function of the amplitude envelope line by the mode decomposition method. Until obtaining the source first-layer amplitude IMFs from each source IMF, classifying each source first-layer amplitude IMF in the same amplitude frequency scale into a plurality of amplitude frequency regions corresponding to the different brain sites. In the end, a brain amplitude modulation spectrum is provided for analyzing the relationship between each frequency region and each amplitude frequency region.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Method for using virtual reality technique to help user executing training rehabilitation
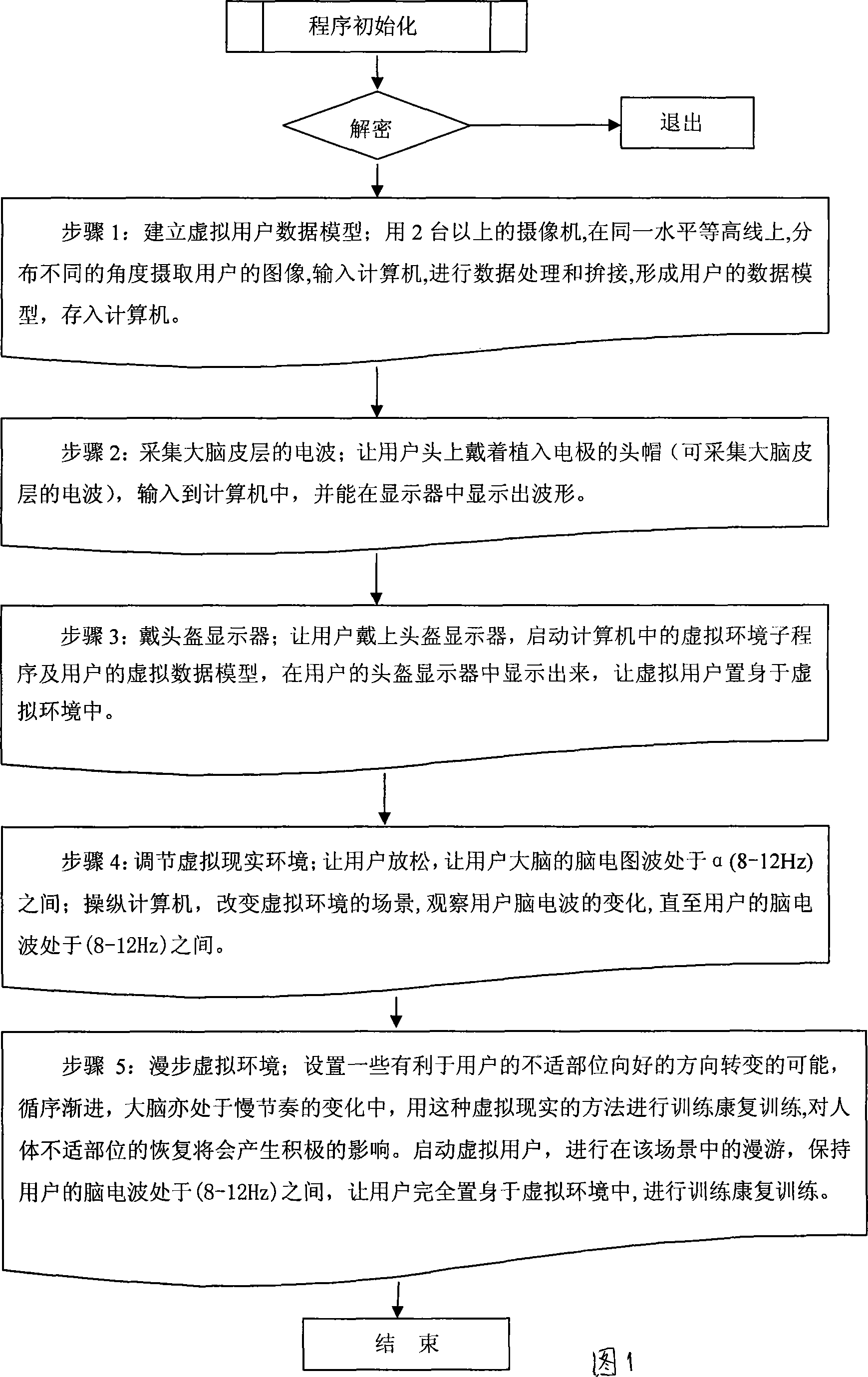
InactiveCN101234224AFeeling better psychologicallyTraining helpsInput/output for user-computer interactionData processing applicationsMethods of virtual realityHuman body
The invention provides a method of helping a user make training recovery by adopting the virtual reality technology, which comprises the following steps: step 1. Collecting three-dimensional model data of user; forming a model of three-dimensional human body data and storing the model into a computer; step 2. Collecting electric waves of the cerebral cortex; step 3. Wearing a helmet mounted display on the eyes of user and connecting the display to the computer, the user seeing that the virtual user are in the virtual reality environment through the helmet mounted display; step 4. Regulating the virtual reality environment to cause the electroencephalogram waves to exist between Alpha (8 to 12 Hz). Recovery training is made by adopting the method of virtual reality, which has a positive effect on recovery of uncomfortable human body parts.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Magnetic Imaging Device To Inventory Human Brain Cortical Function
Systems and methods detect electrical activity in the human brain in the form of the generated magnetic fields and map the magnetic field strength to the surface of the cerebral cortex. By mapping the measured magnetic fields to the sulcal-defined gyrus of the cerebral cortex rather than to its three-dimensional volume, the data complexity and the resulting image are dramatically reduced. The device allows an inventory of brain function, including, but not limited to, vision, sound, sensory, and cognition, with the sensors placed over the corresponding region or regions of interest of the brain.
Owner:FORD JOHN P
Method for correcting brain tissue deformation in navigation system of neurosurgery
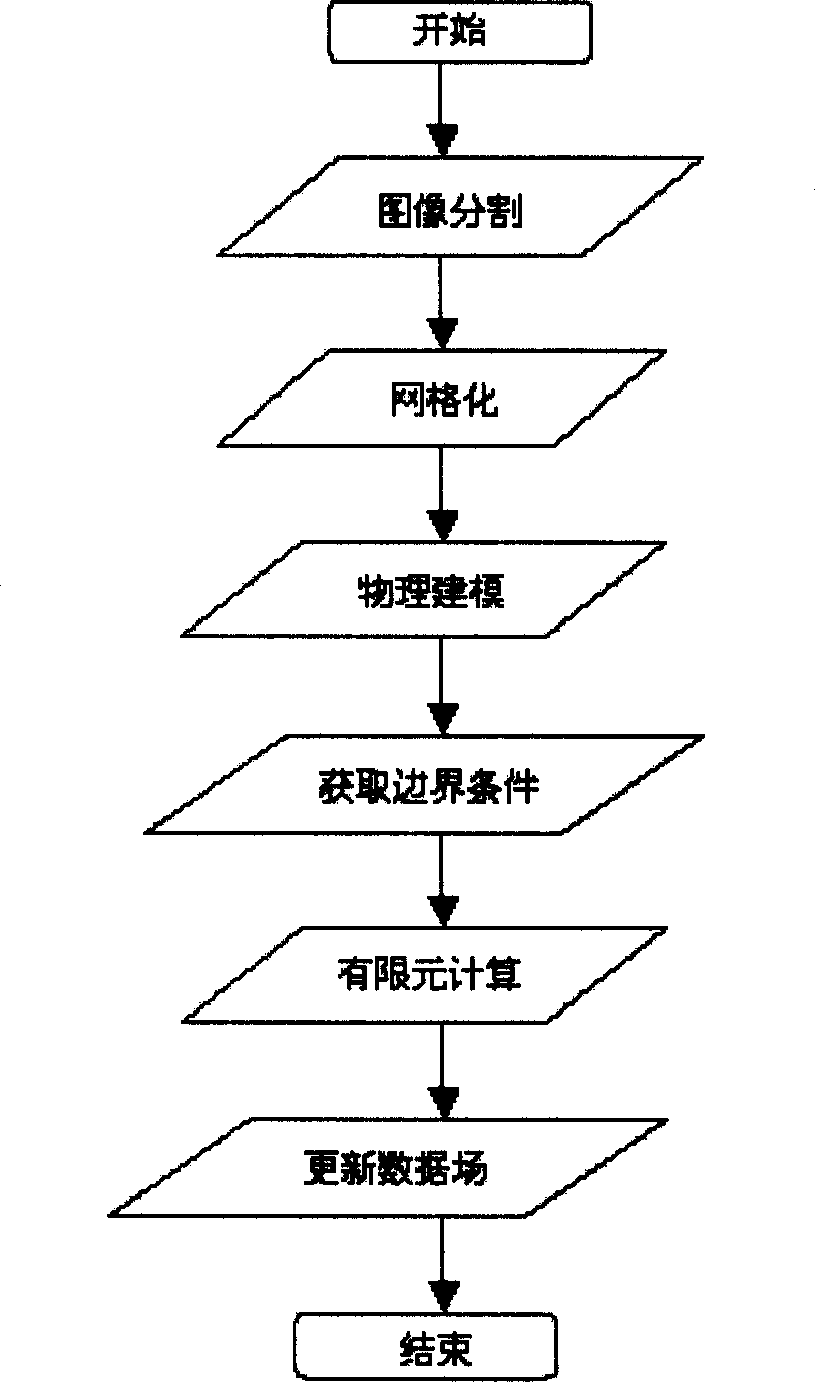
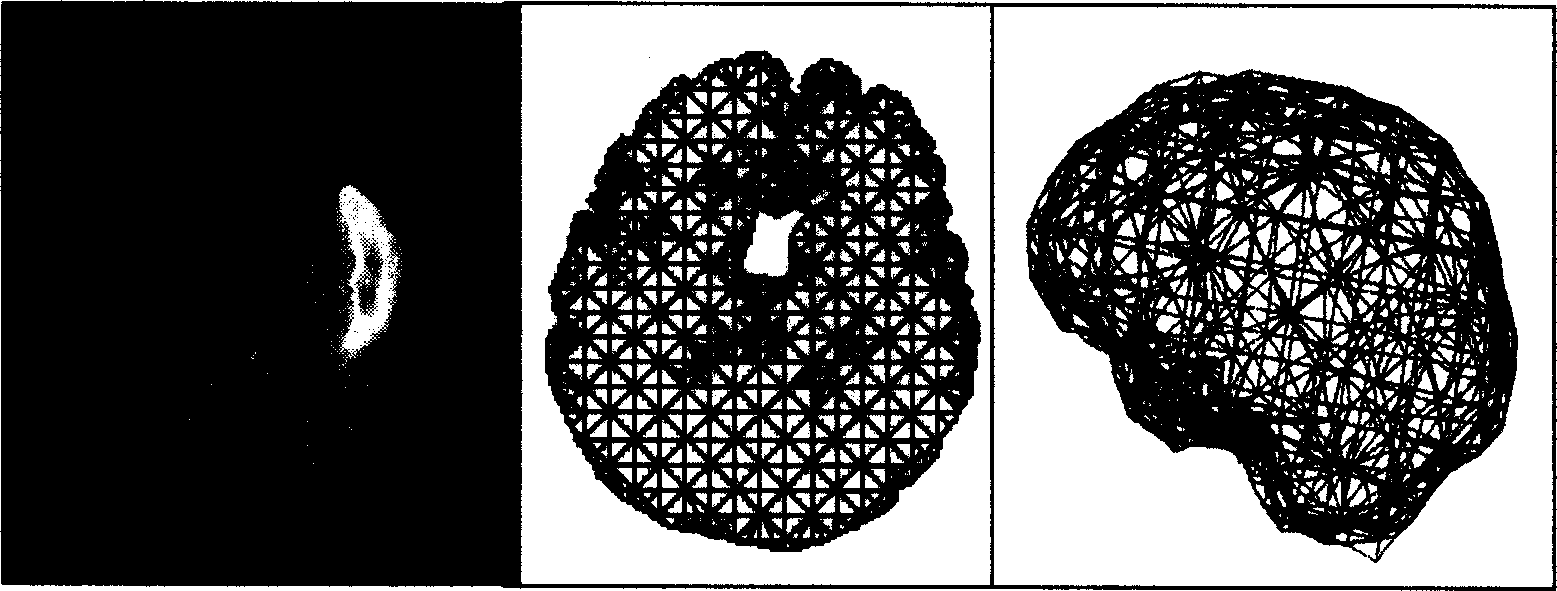
InactiveCN1582863AEffective correctionEasy to implementDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsBiomechanicsData field
A method for correcting the deformation of cerebral tissue in the navigation system of neurosurgical operation includes such steps as obtaining target tissue (cerebral tissue) by 3D automatic division algorithm based on MRI, generating the lattice of cerebral tissue, assigning the relative biomechanical attribute to each lattice unit, creating physical mode, tracking the movement of exposed cerebral cortex layer, finit element calculating to obtain the deformation for cerebral tissue, and updating the 3D data field before operation by an algorithm to direct the operation.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
EEG noise elimination method based on dual-density wavelet neighborhood related threshold processing
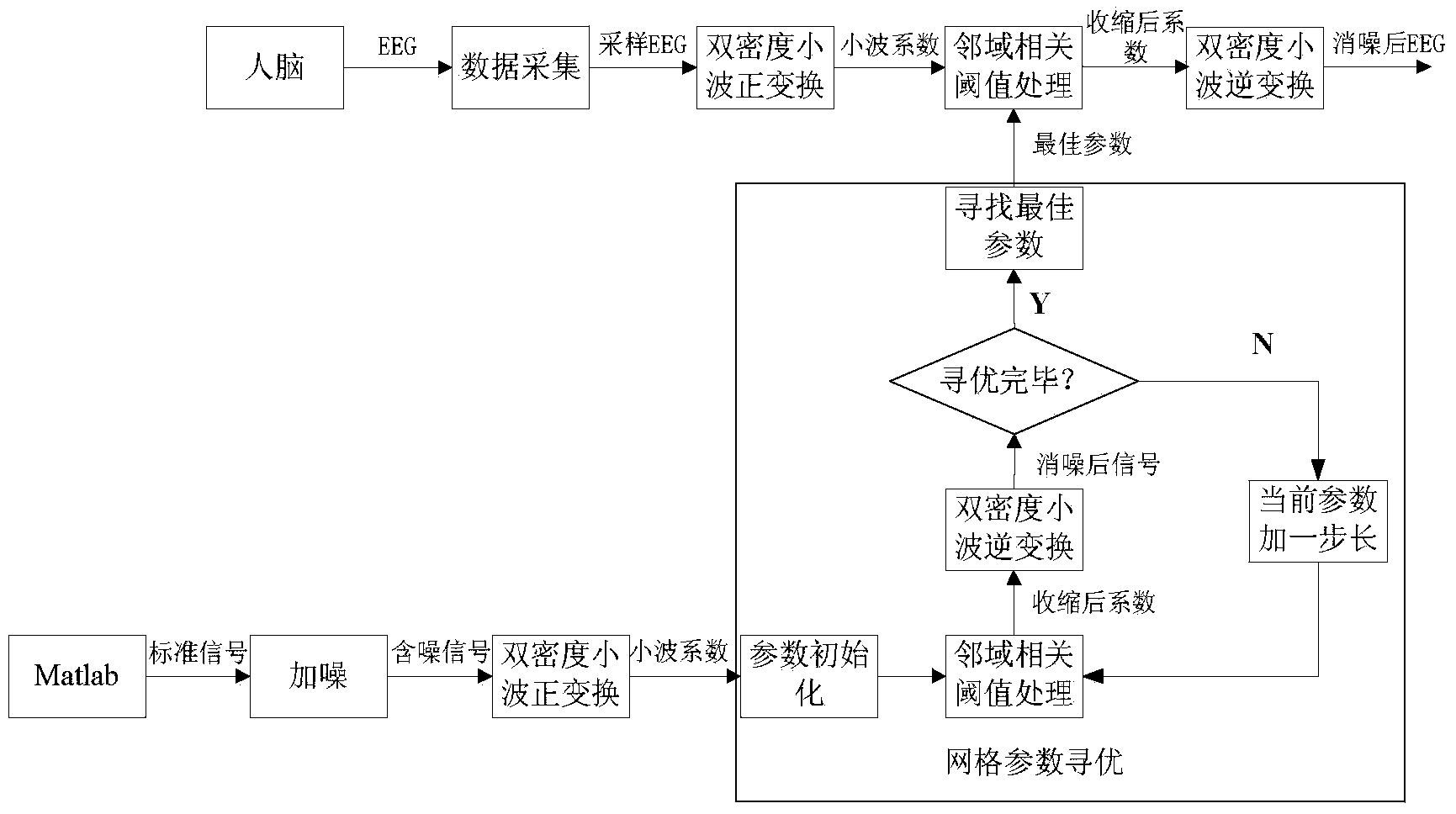
ActiveCN103610461APreserve detailed featuresReduce biasDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Decomposition
The invention relates to an EEG noise elimination method based on dual-density wavelet neighborhood related threshold processing. At present, noise elimination is carried out on an EEG mostly by adopting classic discrete wavelet transform to be combined with a traditional threshold method, and defects exist in an existing noise elimination method with the combination of the classic wavelet transform and the traditional threshold method. The EEG noise elimination method comprises the steps: firstly collecting an EEG from a cerebral cortex, then using dual-density wavelet forward transform for conducting decomposition on the EEG to obtain multi-layer signal high-frequency coefficients, utilizing a neighborhood related threshold processing algorithm for contraction according to the partial statistics dependency of wavelet coefficients, and finally reconstructing the contacted wavelet coefficients to obtain signals with noise eliminated. According to the characteristics of the EEG and the characteristics of interference noise, the signal to noise ratio is used as an objective function, a grid optimum seeking method is adopted to seek the optimum in three adjustable parameters of the neighborhood related threshold processing algorithm, then the noise is effectively smoothed, and the detail features of the EEG are reserved.
Owner:平湖市泰杰包装材料有限公司
Slow-wave sleep enhancing system and slow-wave sleep monitoring method
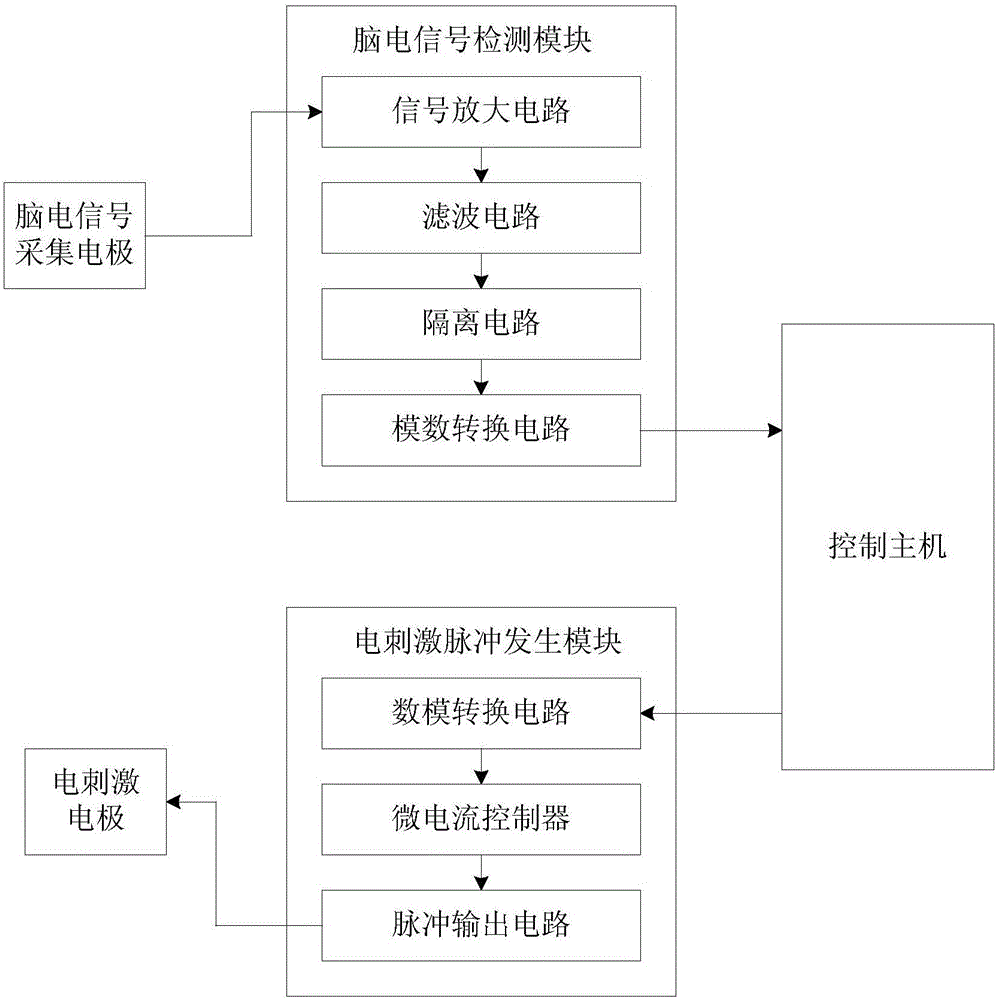
InactiveCN106175690AEnhance memoryConsolidate memoryDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrical stimulationsCerebral cortex
The invention provides a slow-wave sleep enhancing system and a slow-wave sleep monitoring method. The slow-wave sleep enhancing system comprises a brain electricity collecting part, an electrical stimulation part and a control host; the brain electricity collecting part comprises a brain-electricity-signal collecting electrode and a brain-electricity-signal detecting module; the brain-electricity-signal detecting module is used for magnifying, filtering and analog-digital conversion of brain-electricity signals collected by the brain-electricity-signal collecting electrode respectively, and then is used for outputting the processed brain-electricity signals to the control host; the control host monitors the sleep state of a user according to the received brain-electricity signals, and if the user is in the slow-wave sleep state, a stimulation instruction is output; the electrical stimulation part comprises an electrical-stimulation pulse generation module and an electrical stimulation electrode; the electrical-stimulation pulse generation module receives the stimulation instruction, and outputs a stimulation current according to the stimulation instruction, and the electrical stimulation electrode transmits the stimulation current to the scalp to control the cerebral cortex. According to the slow-wave sleep enhancing system and the slow-wave sleep monitoring method, it is detected that the user is stimulated when the user enters the slow-wave sleep, and brain-activity arrhythmia caused by user stimulation at other moments is avoided.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
LED optical stimulation and electrographic recording integrating flexible neural electrode device and manufacturing method thereof
The invention provides an LED optical stimulation and electrographic recording integrating flexible neural electrode device and a manufacturing method thereof. The device comprises an optical stimulation electrode and a recording electrode, wherein both the optical stimulation electrode and the recording electrode comprise bottom polymer insulating layers, top polymer insulating layers and middle gold circuit layers; a plurality of holes are formed in the bottom polymer insulating layers and the top polymer insulating layers; steel pins sequentially run through the holes in the optical stimulation electrode and the recording electrode; and when the optical stimulation electrode and the recording electrode are in gluing connection, the optical stimulation electrode and the recording electrode are prevented from becoming displaced. According to the method, the optical stimulation electrode and the recording electrode are independently manufactured, and then the optical stimulation electrode and the recording electrode are bonded. According to the flexible neural electrode device disclosed by the invention, on the basis of direct contact between LED and brain tissues, light transparency is guaranteed, and meanwhile, influence on recording results due to a photoelectric effect between light and the recording electrode is effectively avoided; the electrodes, which are relatively thin, can guarantee shape preservation when attached to cerebral cortex; and the requirements of acute experiments and long-term implant experiments can be satisfied.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
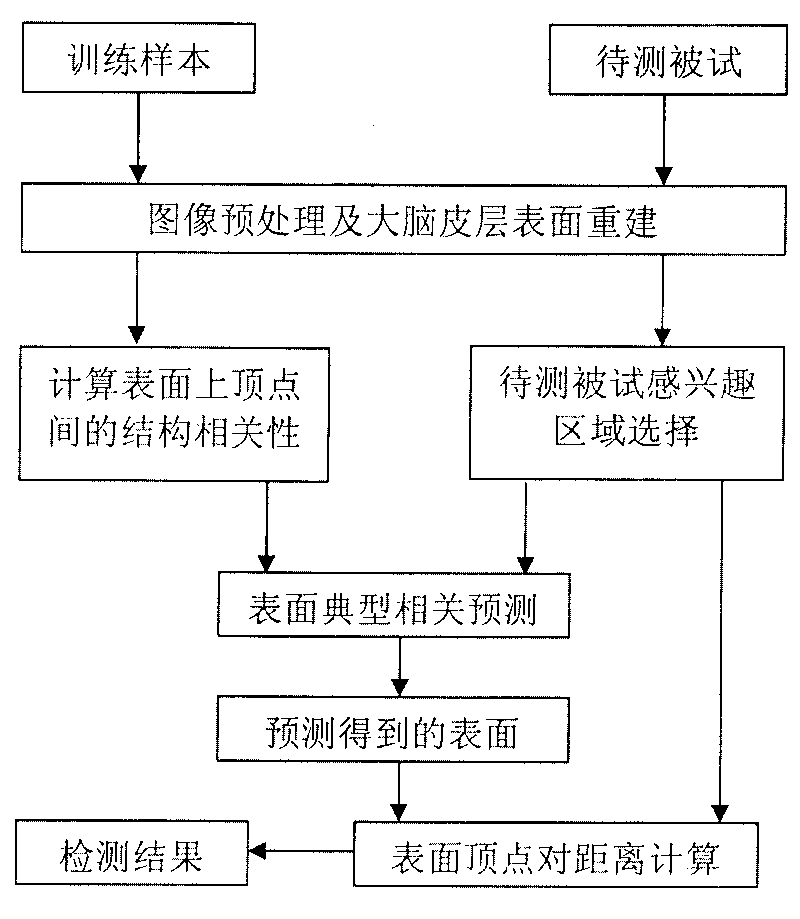
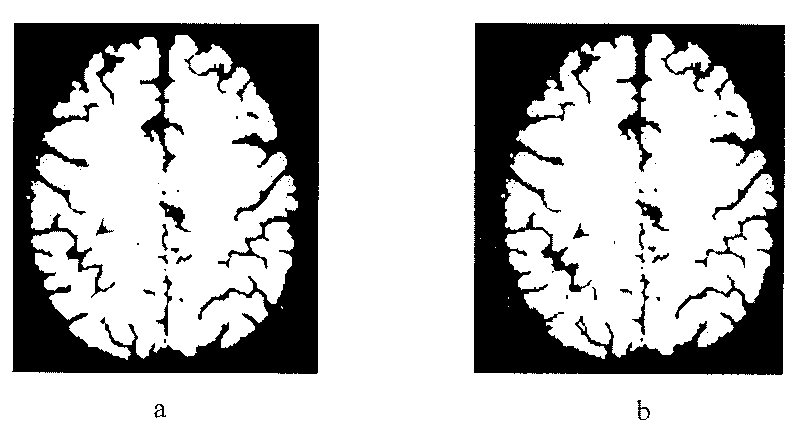
Related prediction model-based method for detecting structural deformation in magnetic resonance image
ActiveCN101739681AExact topologyGeometrically preciseImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringStructural deformationMedicine
The invention relates to a related prediction model-based method for detecting structural deformation in a magnetic resonance image, which is technically characterized in that: a group of normally tested triangular cerebral cortex surfaces which are registered to a standard template is utilized to calculate the structural dependence between the vertex on the group of surfaces and other vertexes; the structural dependence and typical related prediction models are utilized to predict an expected position of the vertex existing in a cerebral atrophy area according to a vertex position of a normal area without structural deformation of the brain; the vertex position obtained by the prediction models is compared with the vertex position before prediction to quantize the deformation on the cerebral cortex surface due to the cerebral atrophy so as to quantize the degree of the structural deformation of the brain resulted from the cerebral atrophy. Compared with other methods, the method has the main advantage that: the method can detect the presence of the structural deformation of the brain and quantize the degree of the structural deformation under the condition that only a single time-point magnetic resonance structure image is available.
Owner:JIANGSU MORNING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD +1
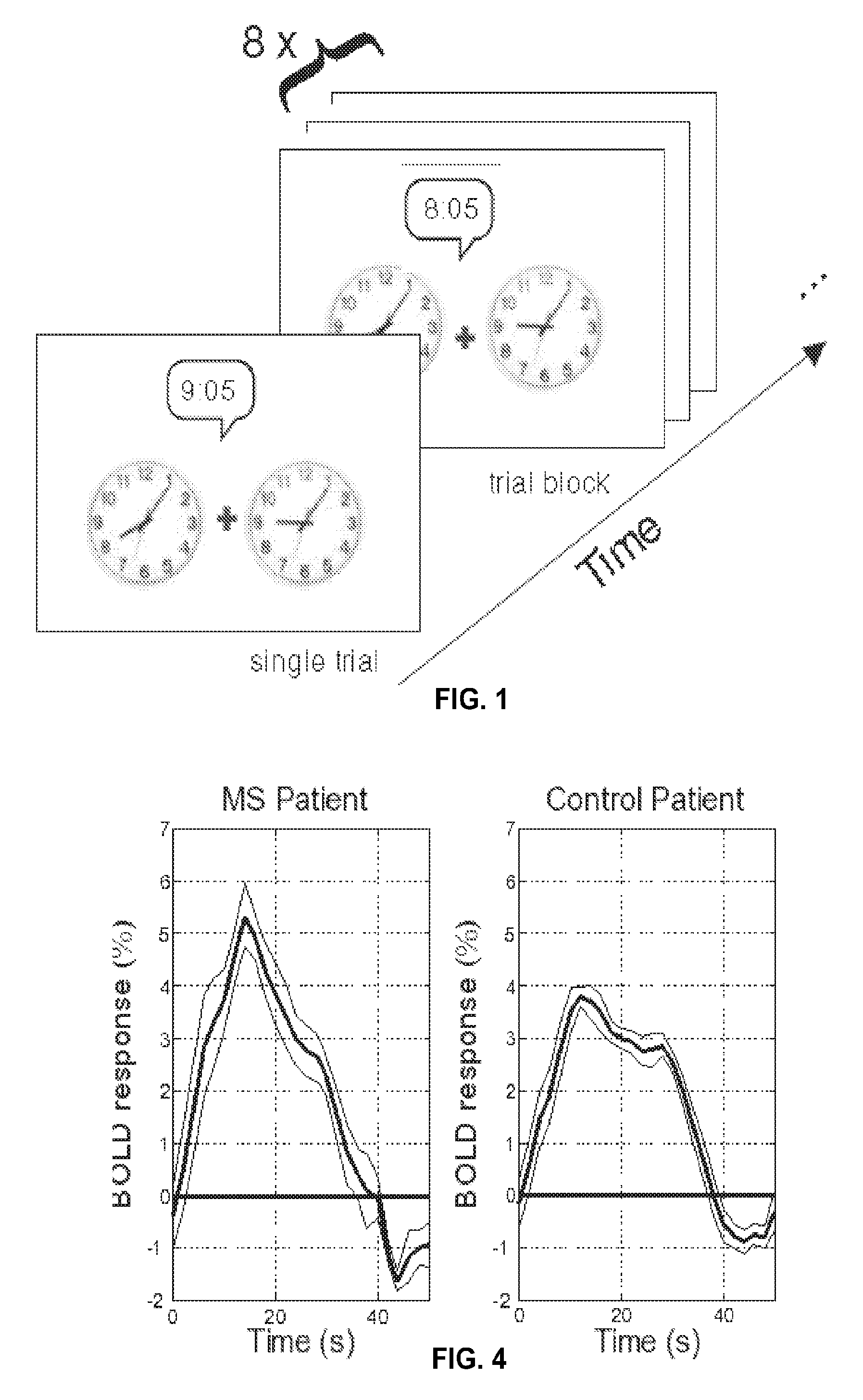
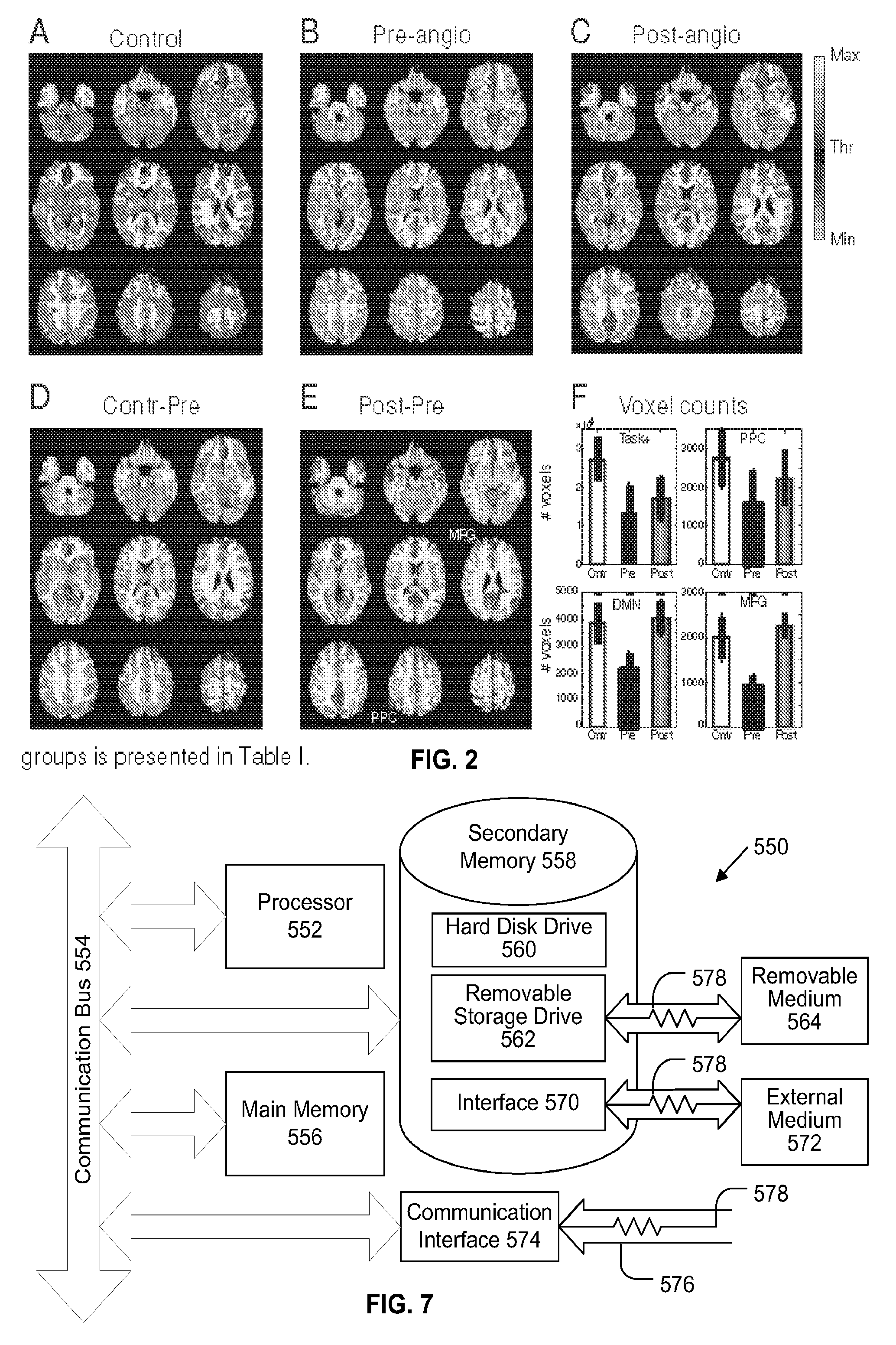
Method to Diagnose and Measure Vascular Drainage Insufficiency in the Central Nervous System
InactiveUS20120277572A1Increased post-stimulus undershootReturn to normal activitiesSensorsBlood flow measurementDiseaseBiological activation
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, may be caused or aggravated by insufficient venous draining from the central nervous system. Functional MRI measures the surge of blood flow into localized regions of cerebral cortex in response to activation of those regions by performing visual, auditory or executive tasks. These fMRI measurements are based on blood-oxygen-level dependence. The resulting fMRI / BOLD data is converted to hemodynamic response data and analyzed to determine any abnormality in the hemodynamic response data. Vascular drainage insufficiency is identified in the presence of abnormal hemodynamic response data. Abnormal hemodynamic response data can be determined by a negative trough in a graph of the HDR data or by the duration, depth, or area of the negative trough.
Owner:HUBBARD DAVID R
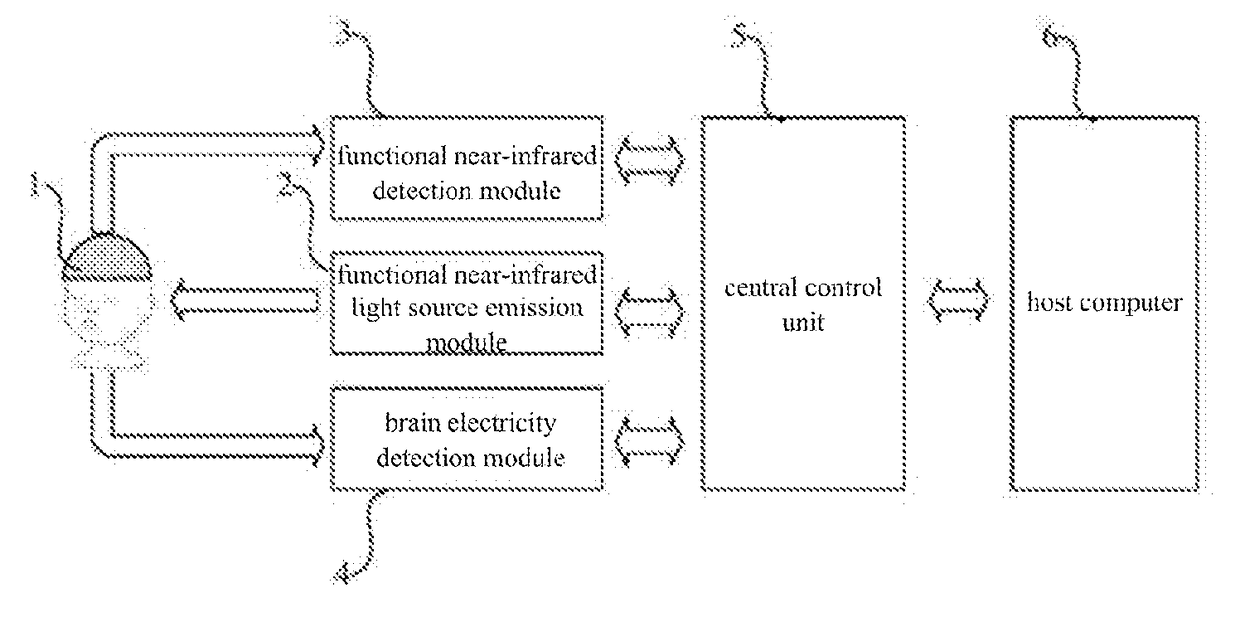
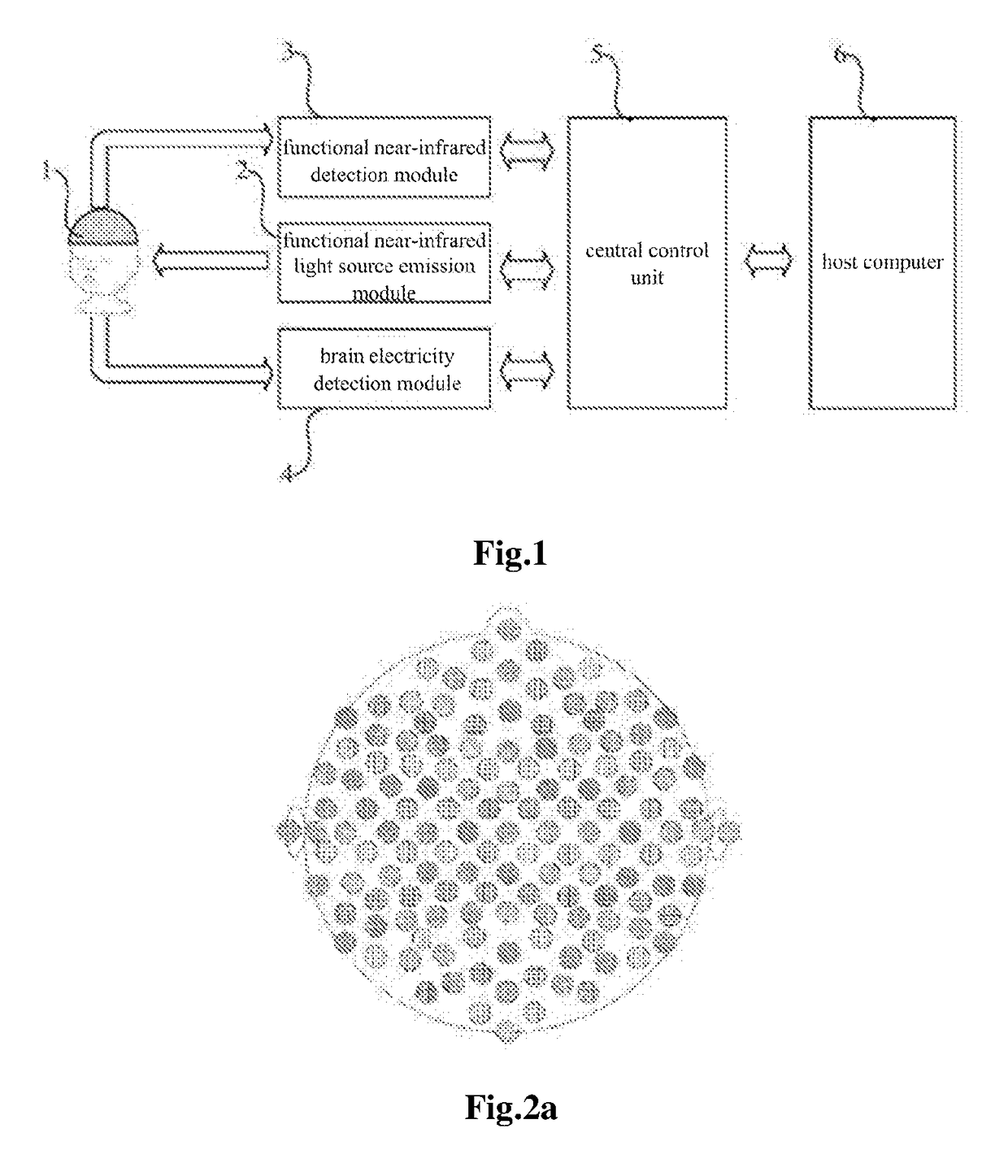
Method and System for Brain Activity Detection
ActiveUS20170224246A1Improve consistencyCapableElectroencephalographySensorsCarrier signalEngineering
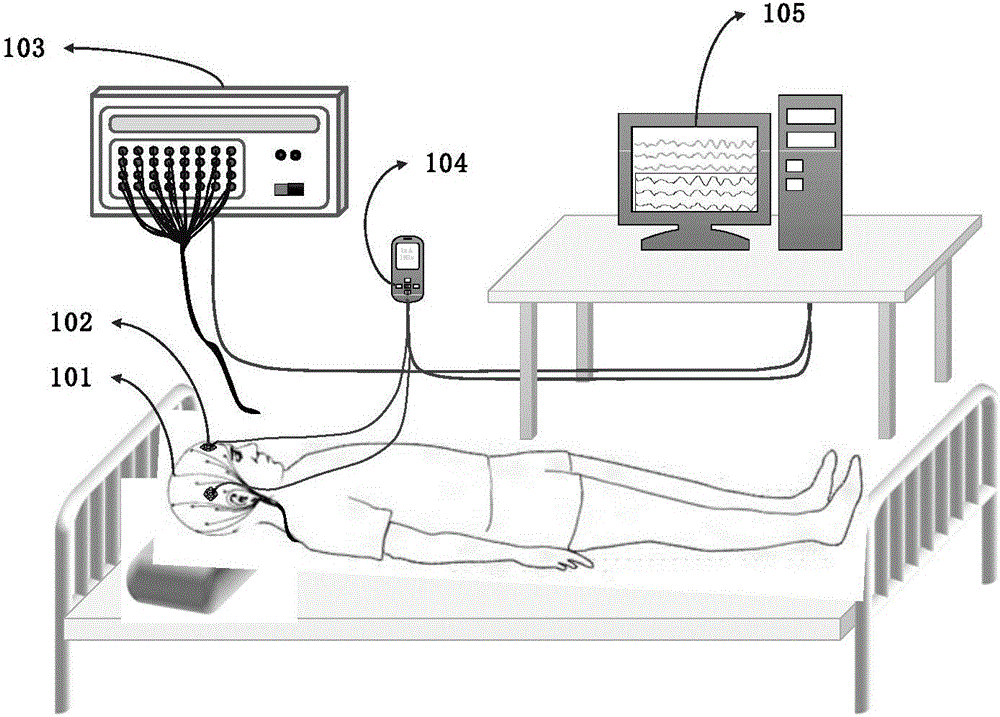
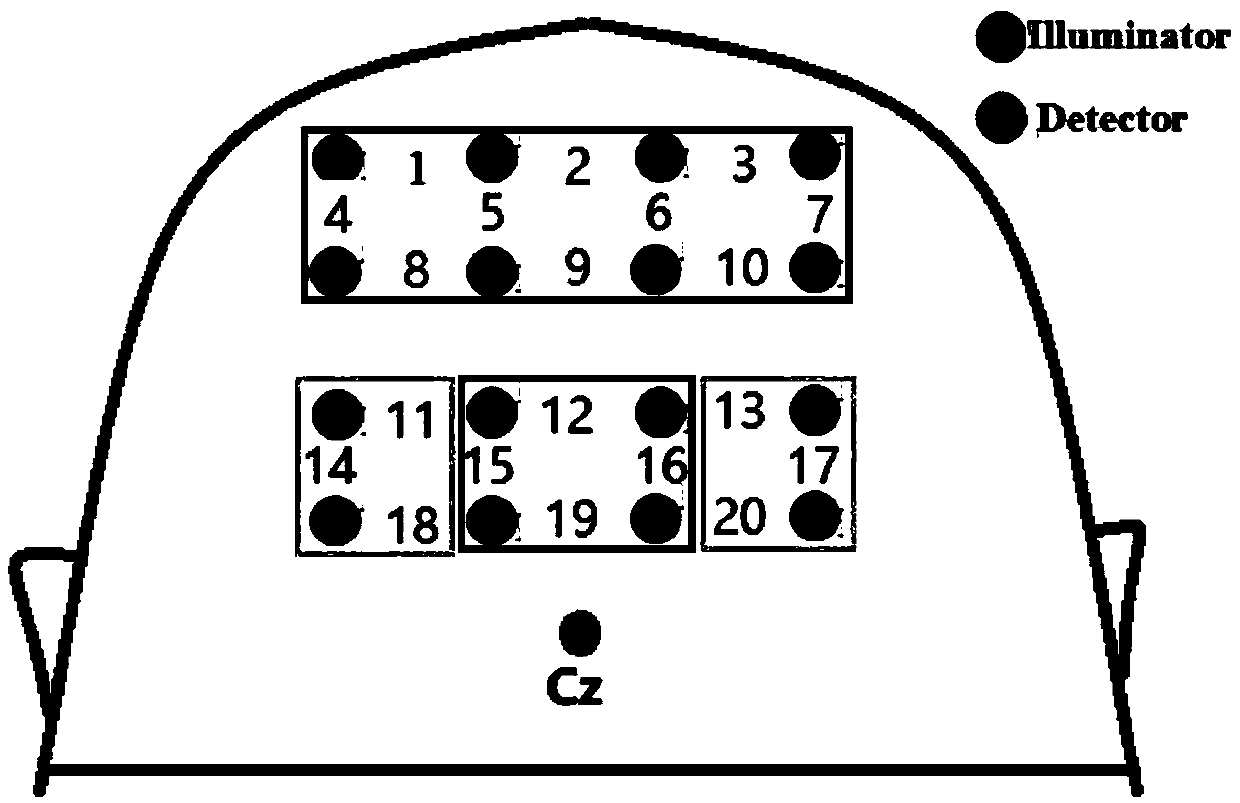
Disclosed are a method and system for brain activity detection. The method is: performing multi-channel synchronous collections of brain electrical signals and cerebral cortex blood oxygen signals simultaneously, and ensuring synchronicity of the collected signals among channels, and collecting said brain electrical signals and said cerebral cortex blood oxygen signals of all locations at the same time. The system comprises: a functional near-infrared light source emission module (2) which employs the frequency division multiplexing technique, wherein the light source is modulated by carrier of different frequencies, said signal is accessed from the multi-functional joint collection helmet (1) through a transmission optical fiber to irradiate the scalp, and after being scattered and absorbed by the brain, the attenuated light signal is processed by the functional near-infrared detection module (3); the functional near-infrared detection module (3) is used for detecting weak optical signals of the scalp; the brain electricity detection module (4) is used for detecting weak electrical signals of the scalp; the central control unit (5) is used for synchronizing and fusing data flows, sending control commands to each functional module, and uploading data to the host computer (6). The method and system can control the interference to be the minimum and have good time scale consistency.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Hemoglobin information based recognition method for multiple walking gait adjusting intents
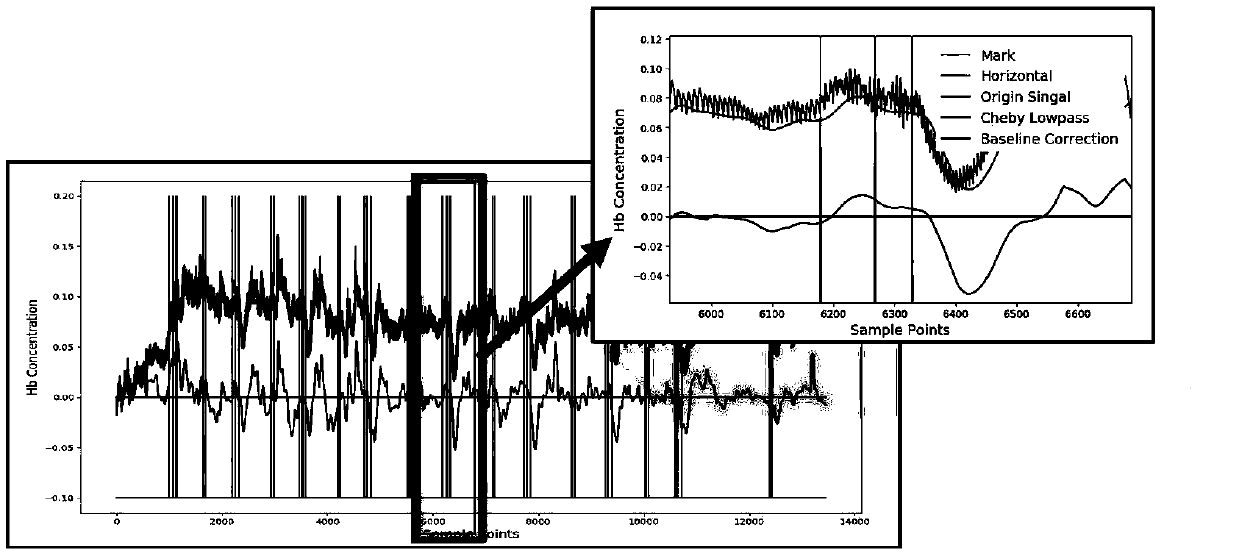
ActiveCN109567818ALower requirementReduce sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEffect of gait parameters on energetic costImaging technique
The invention discloses a hemoglobin information based recognition method for multiple walking gait adjusting intents. The hemoglobin information based recognition method for the multiple walking gaitadjusting intents, disclosed by the invention, is characterized by comprising the steps: carrying out data preprocessing on cerebral cortex hemoglobin concentrations recorded at walking gait adjusting moments, wherein the cerebral cortex hemoglobin concentrations recorded at the walking gait adjusting moments are obtained in a manner that a testing experiment is performed by using a near infraredspectrum brain imaging technique (NIRS) and testees finish corresponding walking gait adjusting tasks in a fixed region; subjecting preprocessed cerebral cortex hemoglobin information to corresponding channeling according to distribution of cerebral functional areas, and calculating and extracting relevant parameters as characters; modeling a detection model for four kinds of gait adjusting intents by applying a pattern recognition algorithm. The method has the beneficial effect that the testing experiment is performed by using the near infrared spectrum brain imaging technique, and thus, themethod is simple and convenient.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
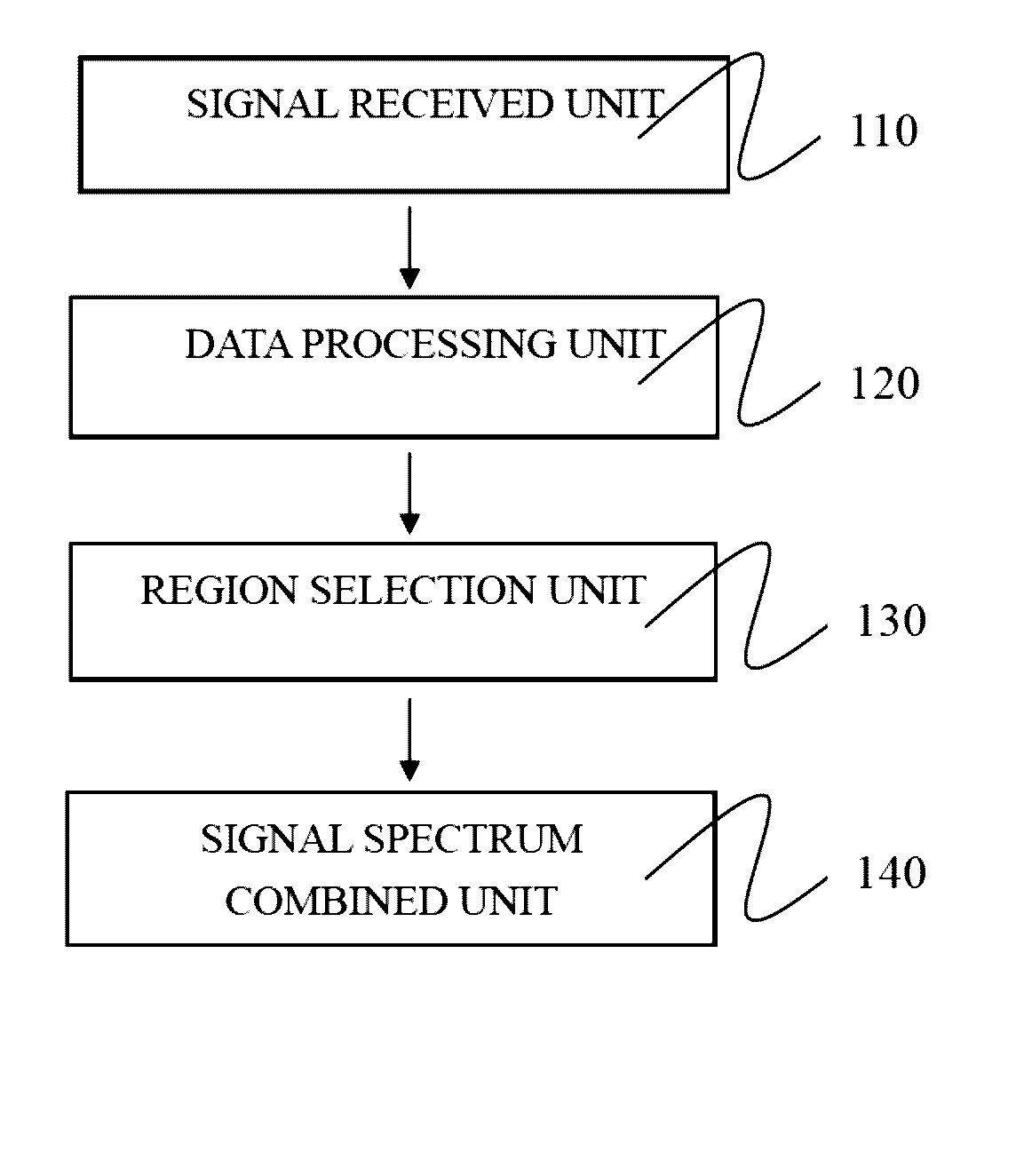
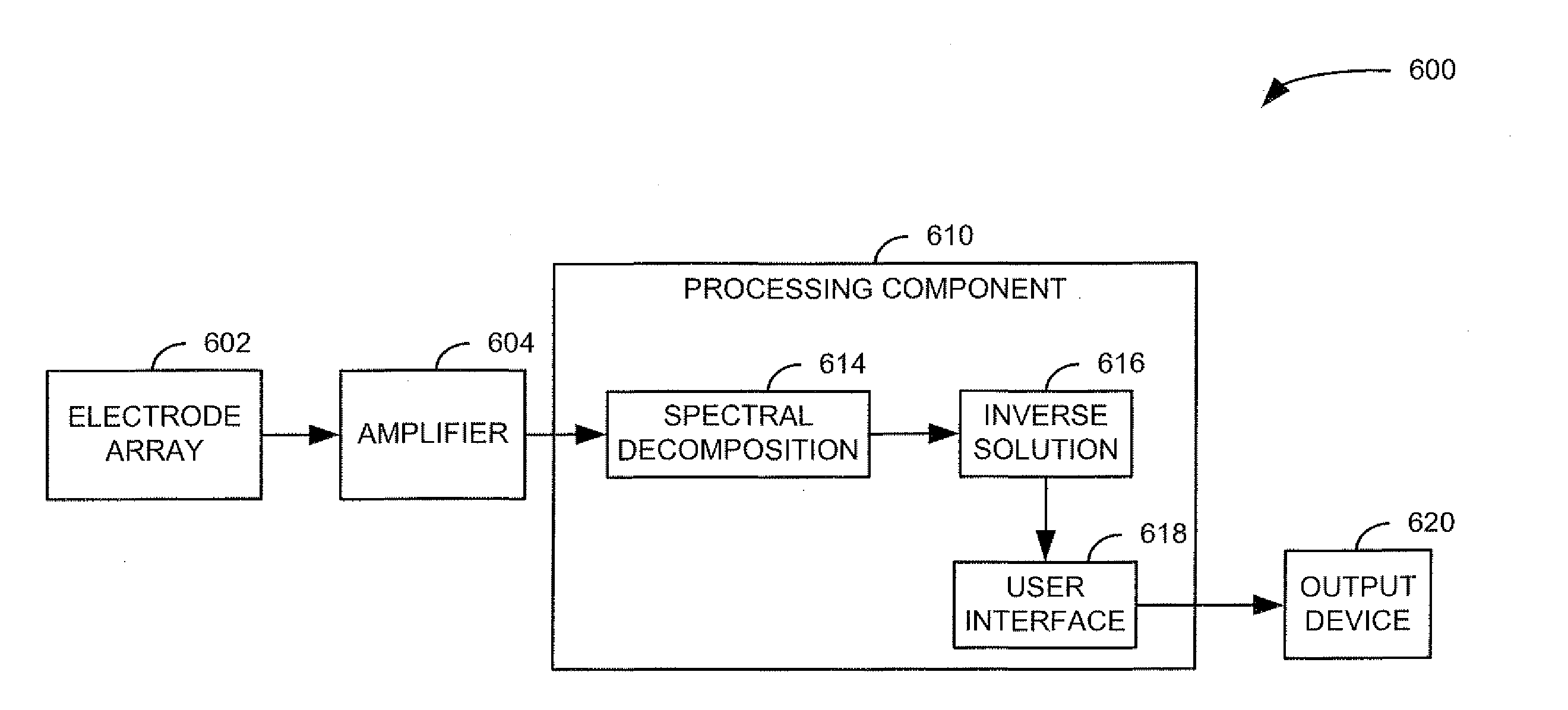
Spectral decomposition and display of three-dimensional electrical activity in the cerebral cortex
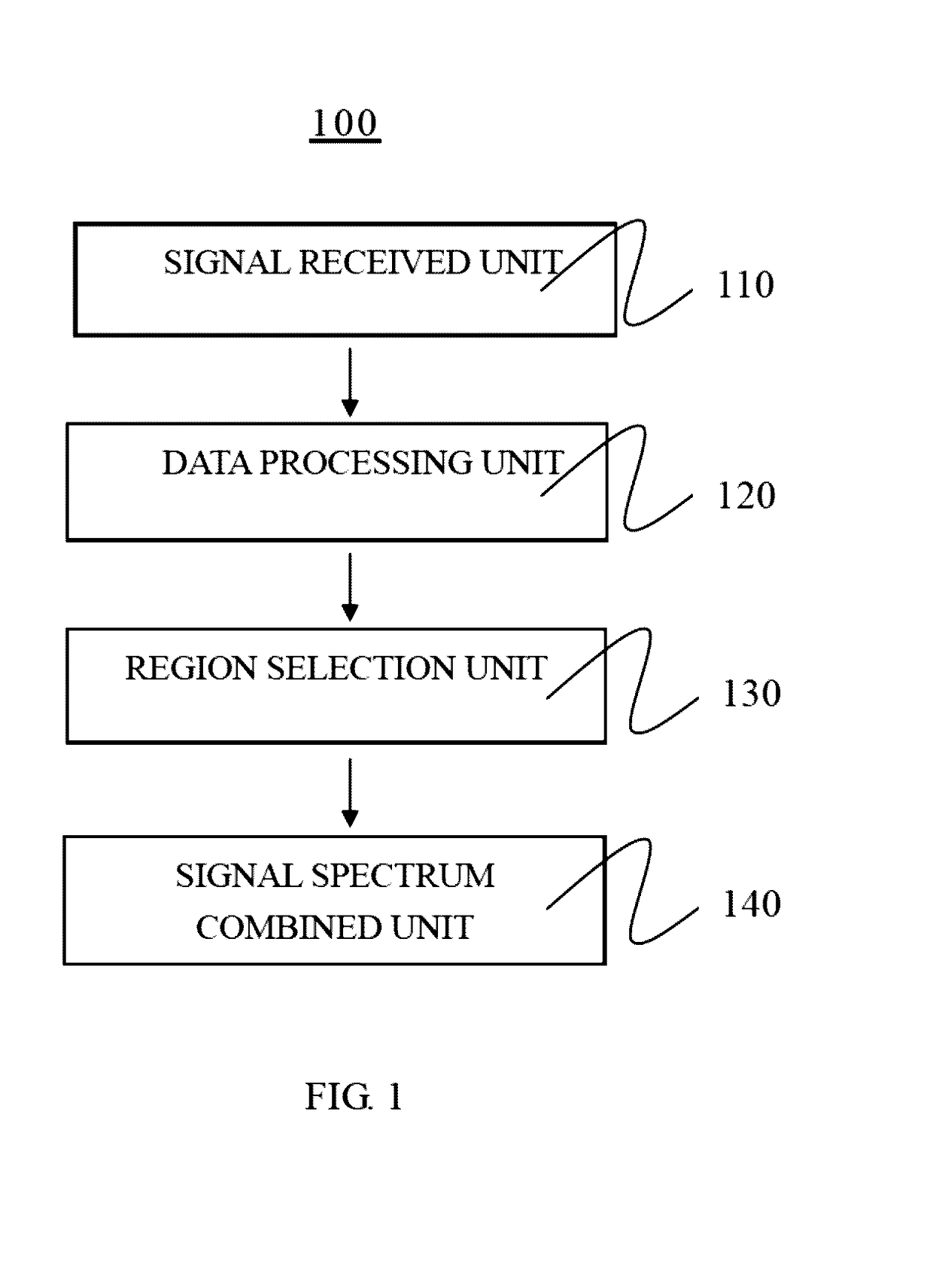
Systems and methods are provided for measuring electrical activity within a brain of a patient. An electrode array is configured to take measurements of electrical potential as raw electroencephalographic (EEG) data. A data processing component includes a spectral decomposition component configured to divide the raw EEG data into a plurality of frequency intervals, within a total range of frequencies and an inverse solution component configured to transform the raw EEG data associated with each frequency interval into a spatial mapping of electrical activity as to provide a set of parameters, with each parameter representing an average electrical activity at an associated location within the brain over an epoch of interest.
Owner:CEREBRAL DIAGNOSTICS CANADA
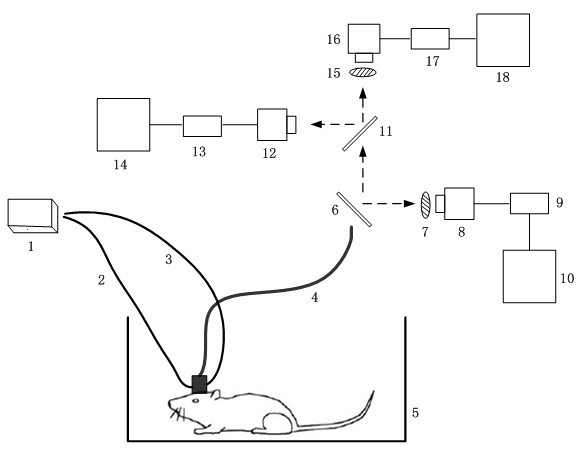
Multi-mode imaging system for observing cerebral cortex functions of moving animals
The invention discloses a multi-mode imaging system for observing cerebral cortex functions of moving animals, comprising a light source device, an image transferring optical fiber, a light transferring optical fiber, a spectroscope, an intrinsic signal imaging part, a laser speckle contrast imaging part, a fluorescence Imaging part, an animal activity room, an image acquisition card, a computer, wherein the light source device generates three light sources needed by an imaging mode, the image transferring optical fiber is used for transferring the cerebral cortex images to a spectroscope when the animals moves around freely; the light transferring optical fiber transfers the light of the light source to the cerebral cortex of the aminals; the spectroscope divides imaging light beam transferred by the image transferring optical fiber into three beams and carries out intrinsic signal imaging, laser speckle contrast imaging and fluorescence Imaging; the intrinsic signal imaging part is used for the intrinsic signal imaging; the laser speckle contrast imaging part for laser speckle contrast imaging; the fluorescence Imaging part is used for fluorescence Imaging; the animal activity room is used for the experiment animals to move freely; the image acquisition card is used for image acquisition and the computer for system control and image receiving and processing.In the invention, optical fiber light and image transferring can be used to multi-mode imaging when the animals are conscious and active and the invention comprises intrinsic signal imaging, laser speckle contrast imaging and fluorescence Imaging.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
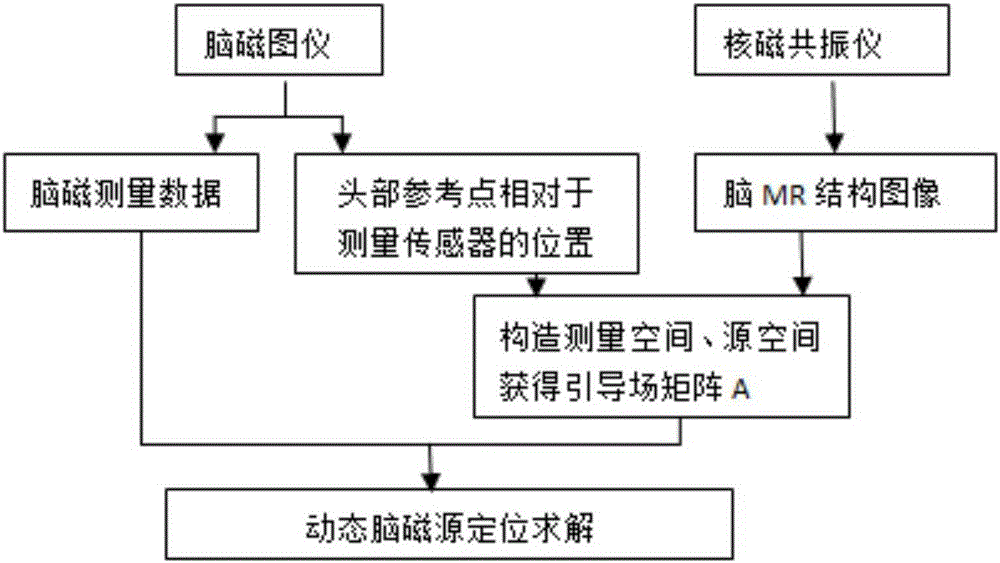
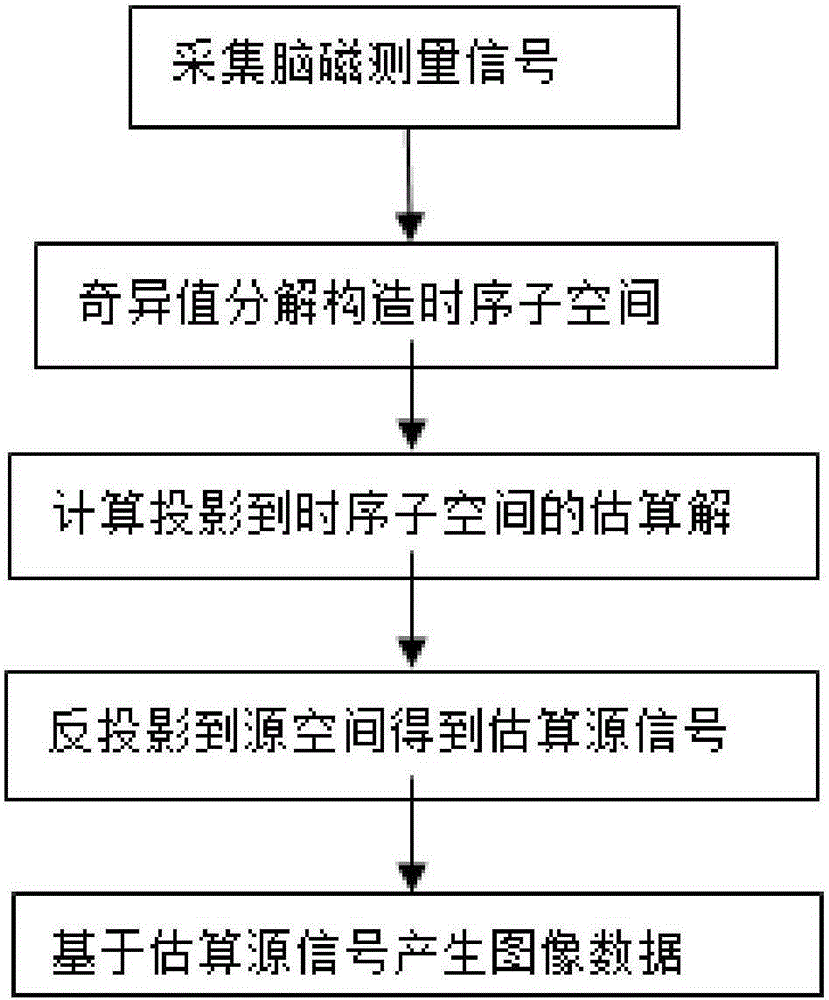
Location method for dynamic neuromagnetic source
ActiveCN105212895ARealize reverse estimation solutionDynamic positioning is faster and more preciseImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringTime domainMagnetoencephalography
The invention discloses a location method for a dynamic neuromagnetic source. The location method comprises following steps: collecting a brain MR structure image and a magnetoencephalography MEG signal B and setting measurement space; setting space where a source signal is formed in the cerebral cortex as source space; determining the space-shifting relation between measurement space and source space and further determining the relation between an MEG signal B and a source signal matrix X, constructing subspace for the time domain, projecting the MEG signal B and the source signal matrix X to the subspace for the time domain, solving in order to obtain a source signal X, and extracting position information of the source signal X and intensity information thereof so that a location process for the dynamic neuromagnetic source is finished. The location method for the dynamic neuromagnetic source has following beneficial effects: the technical problem that the dynamic neuromagnetic source is not easily positioned is solved; and especially the technical problem that a transmitting process for a mutant neuromagnetic source signal is not easily studied is also solved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Three-dimensional localization, display, recording, and analysis of electrical activity in the cerebral cortex
The present invention describes a method and apparatus to localize the electrical signals measured from a subject's scalp surface, preferably in near-real time, and to generate dynamic three-dimensional information of the electrical activity occurring within the cerebral cortex of the brain. In the preferred embodiment, it can produce images that can be immediately inspected and analyzed by an operator in near-real time, resulting in a powerful new cortical imaging modality, which we denote as Dynamic Electrocortical Imaging (DECI). The present invention involves the use of a computer, an electroencephalographic (EEG) amplifier, EEG electrodes, and custom software. It can measure healthy and diseased cortical events and states in both conscious and unconscious subjects. This is useful, as it allows for the diagnosis, monitoring and treatment of cortical disorders, while also furthering the understanding of the human brain and lending use to additional non-medical applications such as in entertainment, education, lie-detection and industry. The invention in one embodiment is implemented using software in conjunction with readily available EEG hardware. Furthermore, this same method can be applied to pre-existing data and when doing so, EEG hardware is not required. Having a practical near-real time 3D imaging system brings a far more accessible technology to doctors, researchers, individuals, and private clinics to better diagnose, monitor, treat and understand many of the conditions and abnormalities of the brain.
Owner:DOIDGE MARK S +1
Multi-brain-computer interface method for three characteristics of SSVEP (Steady State Visual Evoked Potential), blocking and P300
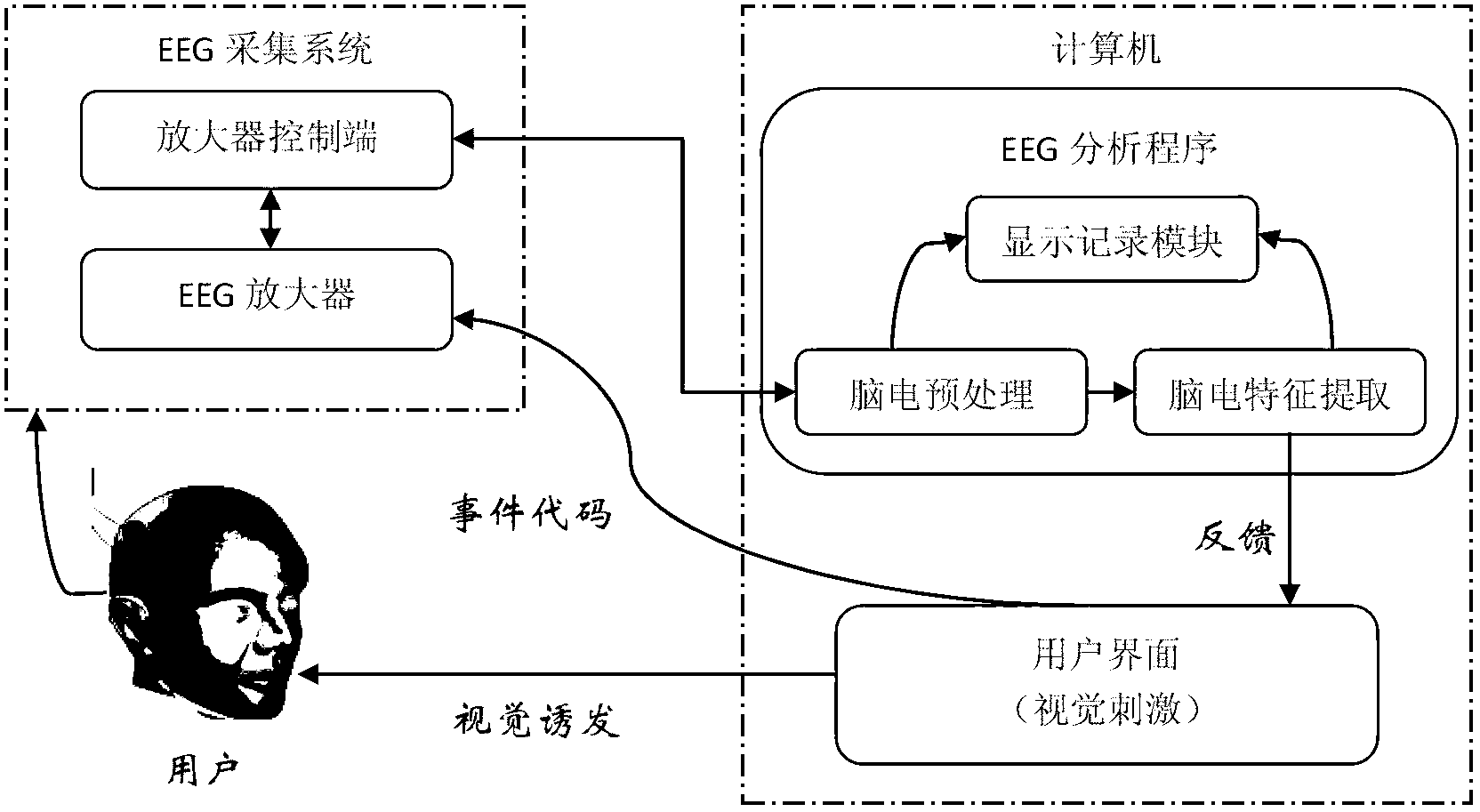
ActiveCN102799267AImprove transfer rateInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingMedical equipmentBrain computer interfacing
The invention relates to the field of medical equipment in order to improve the transmission rate of system information greatly. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the multi-brain-computer interface method for three characteristics of SSVEP (Steady State Visual Evoked Potential), blocking and P300 comprises the following steps: adopting a computer and an electroencephalogram acquisition system including an electroencephalogram electrode, an electroencephalogram amplifier and an electroencephalogram filter, wherein the computer further comprises an EEG (Electroencephalo-Graph) analytical program and a stimulation and induction user interface; acquiring electroencephalogram data of multiple channels by using the electroencephalogram acquisition system; generating an electroencephalogram signal from cerebral cortex, detecting the electroencephalogram signal by using the electroencephalogram electrode, amplifying by using the electroencephalogram amplifier, and filtering and inputting to the computer; and carrying out subsequent data process on the acquired electroencephalogram data to extract corresponding SSVEP, SSVEP blocking and P300 characteristic signals, thus the characteristics are applied to mode recognition of experimental tasks. The multi-brain-computer interface method is mainly applied to the design and manufacturing of the medical equipment.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com