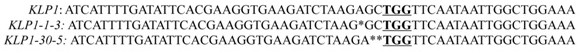A sort of klp1 Application of Genes in Improving Plant Resistance to Botrytis Botrytis Infection
A botrytis and plant technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of small molecular weight and unclear biological function of tomato KLP1 protein, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: tomato KLP1 Gene amplification and expression pattern analysis
[0038] 1. Obtain tomato in GeneBank database KLP1 The CDS sequence of the gene is 441 bp in length, encoding a protein containing 147 amino acids, its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and its encoded amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2,
[0039] according to tomato KLP1 Specific primers were designed for the CDS sequence of the gene, and the primer sequences were as follows:
[0040] PQB-KLP1-F: 5'-ATGGGTTTAAAAGGTAAGTTGATTG-3' (SEQ ID NO.3);
[0041] PQB-KLP1-R: 5'-AATCTTGTGGAGGTGACCCTCTA-3' (SEQ ID NO. 4).
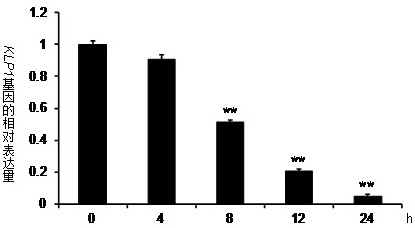
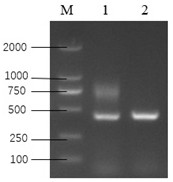
[0042] Use TRI Reagent to extract the total RNA of tomato, and use the reverse transcription kit to perform reverse transcription to obtain the cDNA chain, then use it as a template, use the above-mentioned specific primers to perform high-fidelity enzyme amplification on the obtained cDNA, and then the obtained The amplified product was recovered and purified and t...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: tomato KLP1 Generation of knockout mutants and homozygous lines
[0051] 1. Tomato KLP1 Obtaining knockout mutants
[0052] (1) Vector construction
[0053] KLP1 The full-length gene coding sequence (CDS) is shown in SEQ ID NO.9, input on the CRISPRdirect website KLP1 Based on the full sequence of the gene, suitable targets were screened according to the results. The selected targets were: GAAGGTGAAGATCTAAGAGC and GAACCCGTCACTCTTCTGAA, and primers were designed accordingly. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0054] KLP1-F0:
[0055] 5’-ATATATGGTCTCGTTTGAAGGTGAAGATCTAAGAGCGTTTTAGAGC
[0056] TAGAAATAGC-3' (SEQ ID NO. 10);
[0057] KLP1-R0:
[0058] 5’-ATTATTGGTCTCGAAACGAACCCGTCACTCTTCTGAACAAACTACA
[0059] CTGTTAGATTC-3' (SEQ ID NO. 11).
[0060] The plasmid pTX-043 was used as a template, KLP1-F0 and KLP1-R0 were used as primers, and the target sequence KLP0 (knockout target) was amplified by PCR with high-fidelity enzymes. The electrophoresis r...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3: Positive tomato KLP1 Phenotype Identification of Knockout Plants
[0074] 1. will KLP1 knockout line KLP1-1-3 with KLP1-30-5 The seeds of wild-type tomato (WT) and wild-type tomato (WT) were sown in nutrient soil and cultured in a greenhouse under the conditions of 16h light (26°C) / 8h dark (18°C). Then, choose about 4 weeks, the same size and growth KLP1 Gene knockout homozygous lines and wild type were divided into 3 groups, each group contained 3 tomato plants, and the concentration of spores was 10 6 The spore liquid inoculated the tomato leaves, put the leaves in a plastic box, covered with a layer of plastic wrap to maintain 100% humidity, kept at 22°C for 24-48 hours, then observed the incidence of tomato leaves and made statistics. The result is as Figure 4A with 4B As shown, compared with the wild type, KLP1 The diameter of the lesion on the leaves of the gene knockout homozygous lines was significantly reduced.
[0075] 2. Total RNA was e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com