Optical fiber vibration measuring device and method for improving light source noise
A fiber optic vibration and measurement device technology, which is applied to the measurement device, uses optical devices to transmit sensing components, and measures ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic waves. Measurement accuracy, improvement of measurement accuracy, beneficial to suppress the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
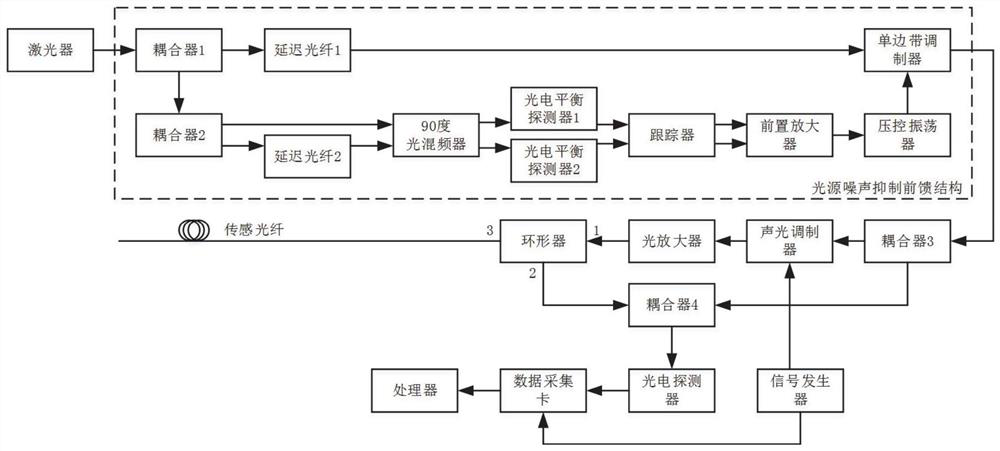
[0049] In a typical implementation of the present disclosure, such as Figure 1-Figure 2 As shown, a fiber optic vibration measurement device with improved light source noise is proposed.
[0050] The device includes: laser, light source noise suppression feedforward structure, coupler 3, acousto-optic modulator, erbium-doped fiber amplifier, circulator, sensing fiber, coupler 4, photodetector, data acquisition card, signal generator and processor.
[0051] The laser emits continuous light with a narrow line width, passes through the source noise suppression feed-forward structure, enters the coupler 3 with a specific power ratio, and is divided into two paths, one of which is converted into a light with acousto-optic modulation with a frequency shift function. The pulsed light with a specific width and period, after power compensation by the optical amplifier, enters the 1 port of the circulator, and then enters the sensing fiber through the 3 port of the circulator, and obt...
Embodiment 2
[0063] In another typical embodiment of the present disclosure, as Figure 1-Figure 2 As shown, a fiber vibration measurement method with improved light source noise is proposed.
[0064] Step 1, the laser outputs continuous light with a wavelength of 1550nm or 1330nm:
[0065]
[0066] Among them, A represents the light wave amplitude, v 0 Represents the light wave frequency, which is a constant of 193.5THz (corresponding to 1550nm wavelength) or 229.0THz (corresponding to 1310nm wavelength), θ(t) represents the phase noise of the light source, and t represents time.
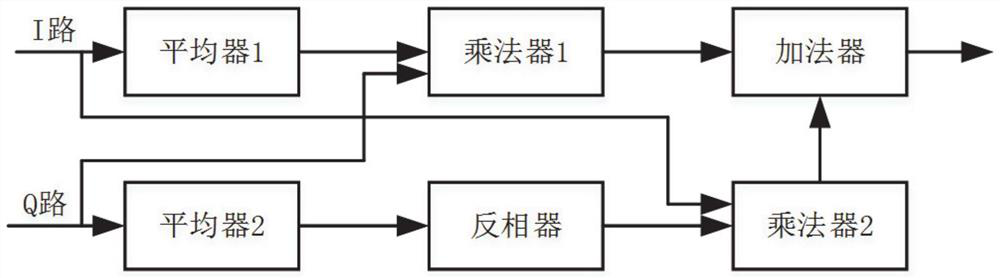
[0067] In the second step, the continuous light of the laser is divided into two paths, one of which uses the classic Mach-Zehnder interferometer to obtain two paths (I path and Q path) orthogonal interference signals:
[0068] I(t)=Bcos(2πν 0 τ+Δθ(t)) (2)
[0069] Q(t)=Bsin(2πν 0 τ+Δθ(t)) (3)
[0070] Δθ(t)=θ(t)-θ(t-τ) (4)
[0071] Among them, B represents the amplitude of the interference signal, Δθ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com