MRI hip joint inflammation segmentation and classification automatic quantitative grading sequential method
A quantitative grading, hip joint technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of high consistency of voxel values in the inflammatory area, affecting quantitative accuracy, poor quantitative results, etc., to improve the classification effect and classification effect, and improve the classification accuracy. , the effect of improving quantitative accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
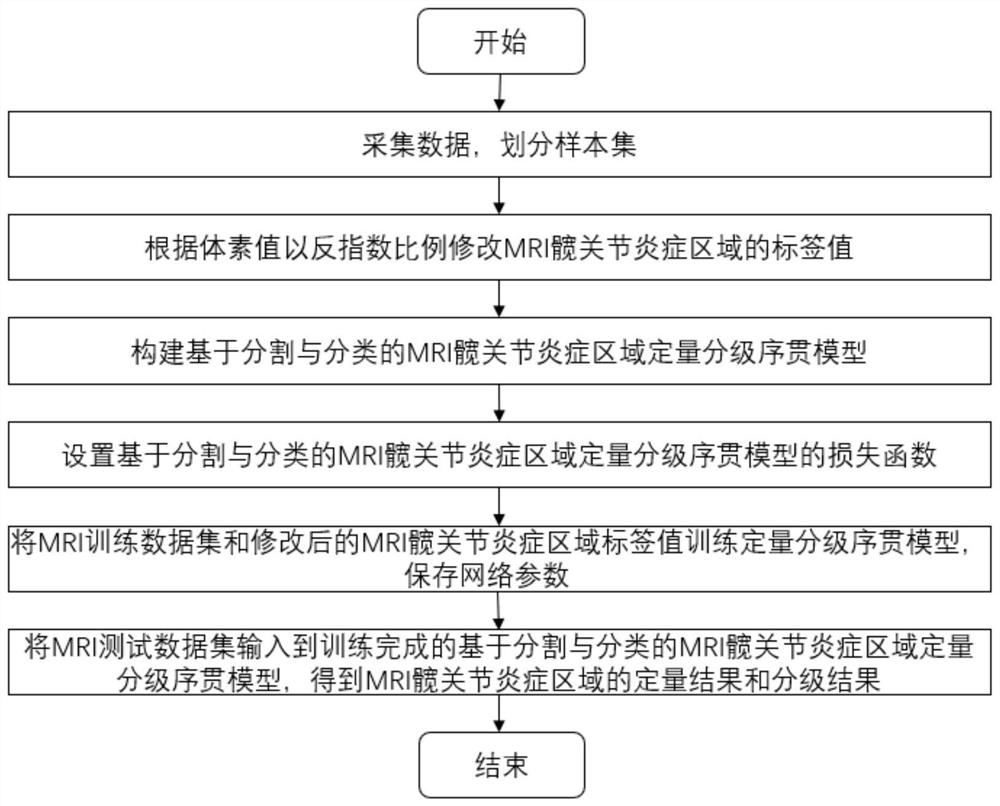
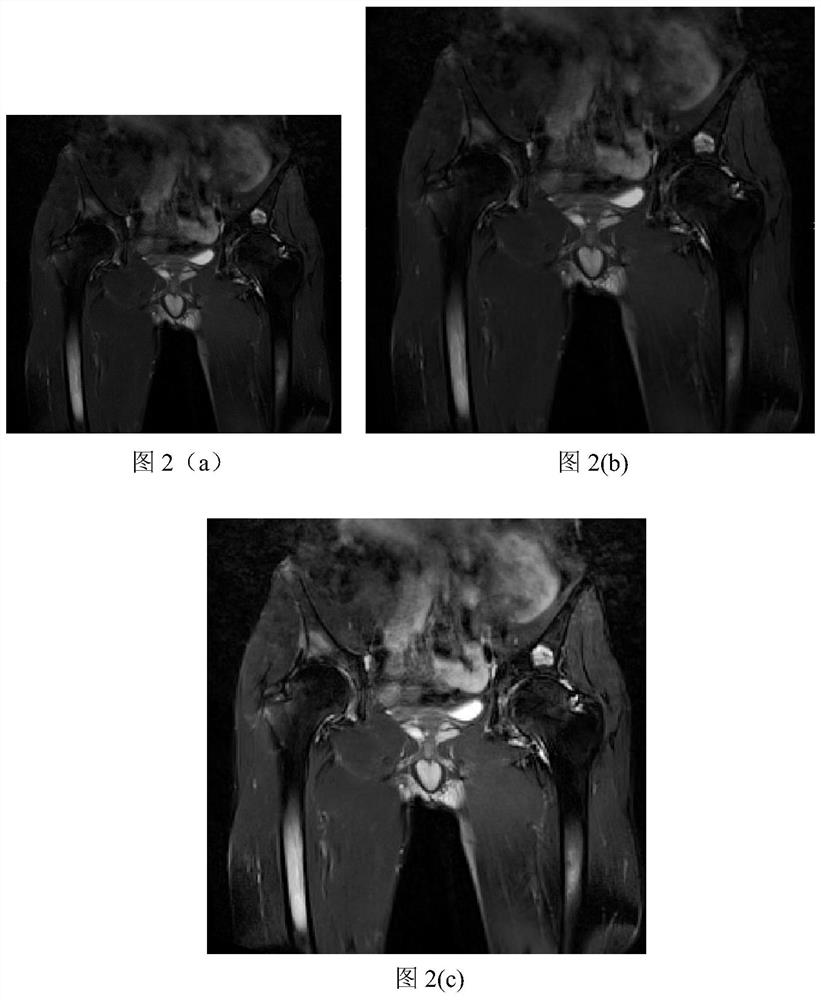
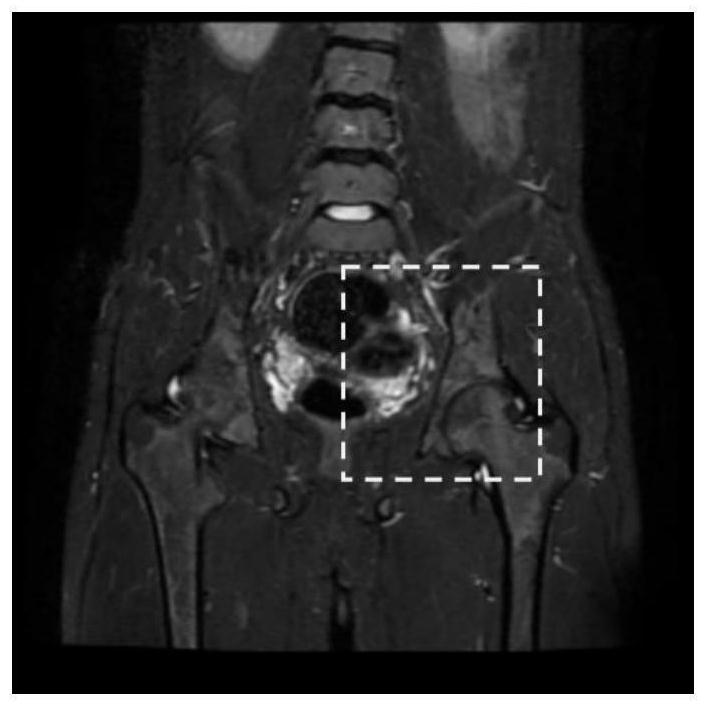
[0024] With the development of imaging technology, it provides a new way for doctors to understand the patient's illness. Doctors can combine imaging data to have a better understanding of spinal arthritis. Using MRI data, doctors can understand the disease of patients with spinal arthritis. However, when image processing algorithms are used to segment and classify MRI hip joint inflammation areas on MRI images, the shape and size of the MRI hip joint inflammation areas vary greatly, resulting in poor segmentation results. The MRI hip joint inflammation area as a whole The small proportion leads to poor classification of MRI hip inflammation. Aiming at the current situation, the present invention proposes an integrated automatic quantitative grading method combining segmentation and classification through thinking, exploration and experimentation, that is, MRI hip joint inflammation segmentation and classification automatic quantitative grading sequential method, which is used ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The MRI hip joint inflammation segmentation and classification automatic quantitative grading sequential method is the same as that in Example 1, and the construction in step (3) of the present invention can automatically quantify the MRI hip joint inflammation area quantitative grading sequence based on segmentation and classification. The model is used for the automatic quantitative grading of multi-scale MRI hip joint inflammation areas, including the following steps:
[0040] (3.1) Constructing the segmentation classification model and multi-scale convolution module based on deep learning: firstly, using the mainstream segmentation network 3DResUNet of deep learning, classification network ResNet-50, and support vector machine, the segmentation classification model of MRI hip joint inflammation area was constructed. Aiming at the problem of large differences in the shape and size of inflammatory areas, the multi-scale convolution model GMS is composed of different vo...
Embodiment 3
[0048] MRI hip joint inflammation segmentation and classification automatic quantitative grading sequential method is the same as embodiment 1-2, the loss function of the two models described in the step (3.3) of the present invention, for the MRI hip joint inflammation area based on segmentation and classification Quantitative hierarchical sequential model training, which is expressed as follows:
[0049] Among them, the loss function L of the 3DResUNet part seg Expressed as follows:
[0050] L seg =L dice +λ*L wce
[0051]
[0052]
[0053] The loss function L of the segmentation model seg It is composed of two kinds of loss functions, which are the dice loss function L of the medical data segmentation network dice and weighted cross-entropy loss function L wce . Among them, C represents the maximum number of label categories, N represents the total number of pixels, c represents the category number, n represents the pixel number, p cn Indicates the probabilit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com