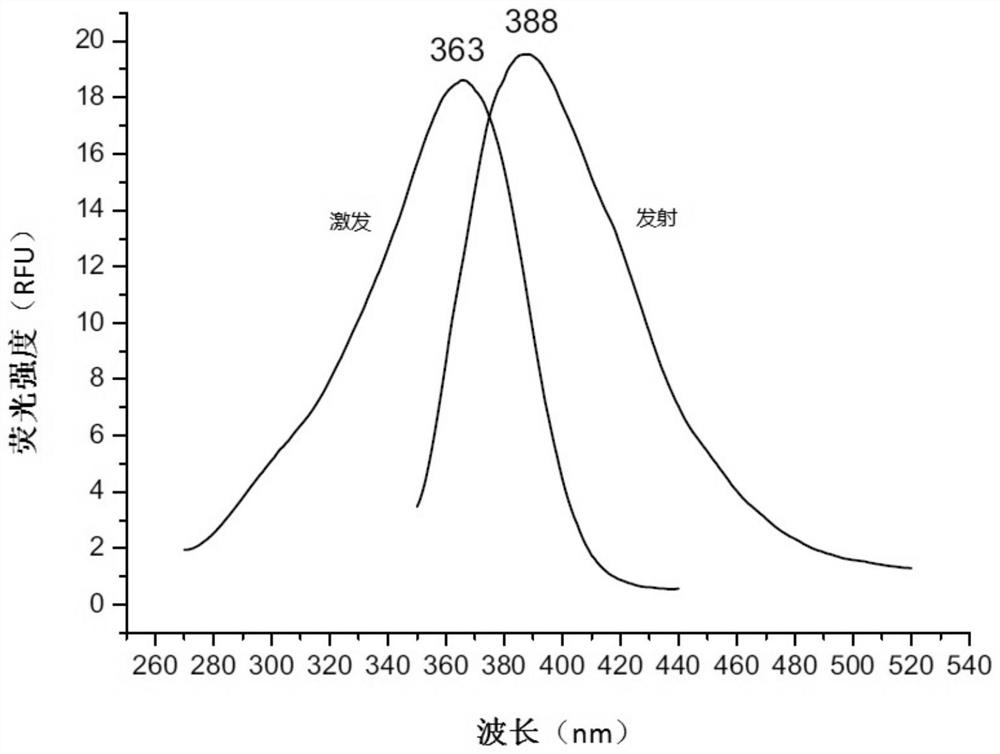
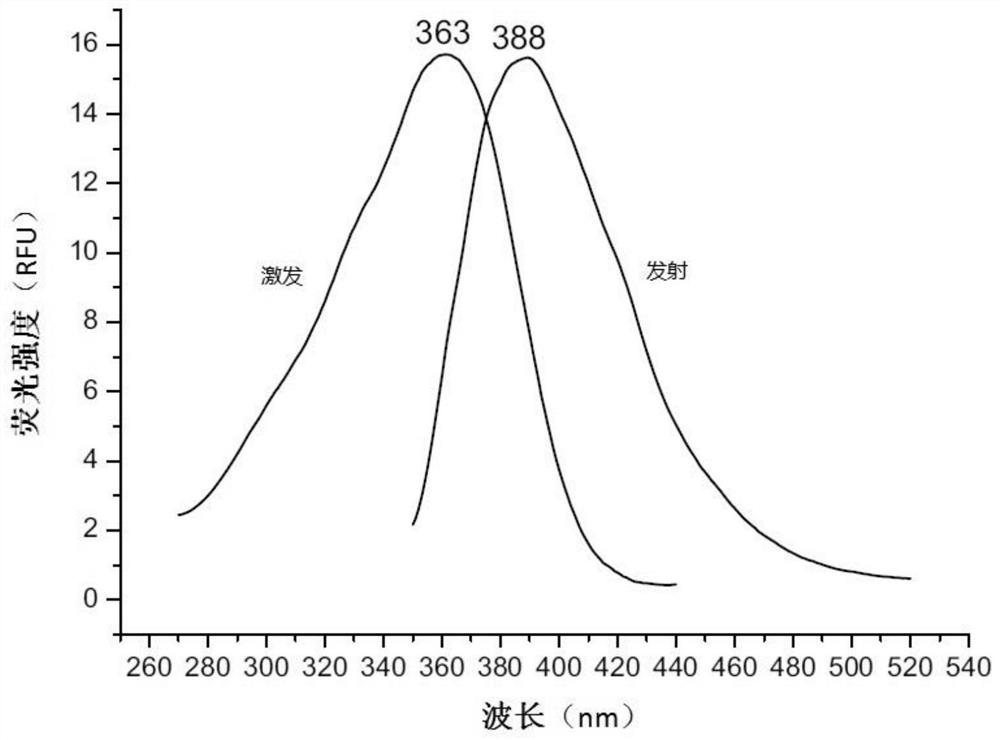
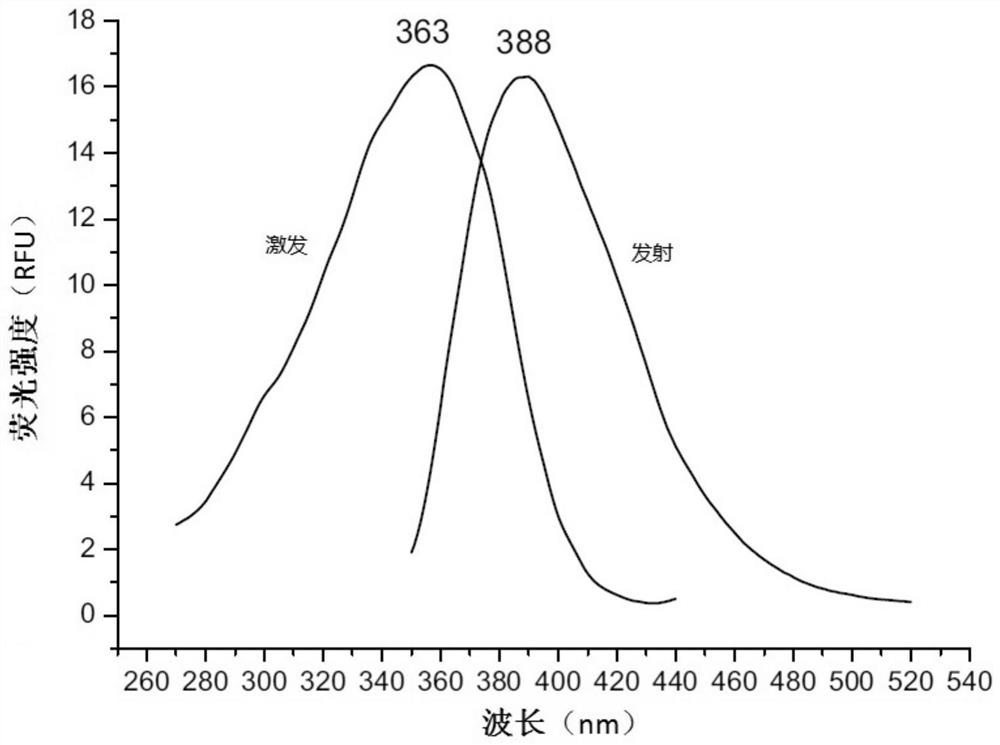
Fluorescent probe for screening drugs acting on ryanodine receptor
A technology of ryanodine receptors and fluorescent probes, applied in the field of fluorescent probes, can solve the problem of not being able to judge whether the drug is selective or not
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] A fluorescent probe for screening drugs acting on ryanodine receptors, made by the following method:
[0050]
[0051] 1) Preparation of compound 2-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid (intermediate S-1-1):
[0052] Disperse phthalic anhydride (1.48g) in 12ml of anhydrous dichloromethane, and slowly add (A-1)-NH 2 (0.73g) and stirred for 3h. The resulting precipitate was filtered and washed with petroleum ether and ethyl acetate to obtain 1.83 g of a white solid.
[0053] Yield 83%.
[0054] 2) Preparation of fluorescent probe I-A1:
[0055]2-(tert-Butylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid (500mg) was dissolved in 2.3ml of acetic anhydride, at 30°C, 0.28ml of perchloric acid was slowly added to the resulting suspension and stirred for 4h. The resulting precipitate was filtered and washed with ether. The white precipitate (540 mg) was dissolved in 7 ml of anhydrous THF, 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (374 mg) and 0.74 ml of anhydrous triethylamine were added, and the reaction mixture w...
Embodiment 2
[0060] A fluorescent probe for screening drugs acting on ryanodine receptors, made by the following method:
[0061]
[0062] 1) Preparation of compound 2-(tert-amylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid (intermediate S-2-1):
[0063] Disperse phthalic anhydride (592 mg) in 4.7 ml of anhydrous dichloromethane, and slowly add (A-2)-NH 2 (348mg) and stirred for 3h. After the reaction was completed, dichloromethane was spin-dried under reduced pressure, purified by silica gel chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 2:1), and 489 mg of a white solid was obtained.
[0064] Yield 52%.
[0065] 2) Preparation of fluorescent probe I-A2:
[0066] 2-(tert-Amylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid (258mg) was dissolved in 1.4ml of acetic anhydride, and 0.14ml of perchloric acid was slowly added to the resulting suspension at 30°C and stirred for 4h. The resulting precipitate was filtered and washed with ether. The white precipitate (286 mg) was dissolved in 3.9 ml of anhydrous THF, 7-amino-4-methylcou...
Embodiment 3
[0071] A fluorescent probe for screening drugs acting on ryanodine receptors, made by the following method:
[0072]
[0073] 1) Preparation of compound 2-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-ylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid (intermediate S-3-1):
[0074] Disperse phthalic anhydride (1.48g) in 12ml of anhydrous dichloromethane, and slowly add (A-3)-NH 2 (1.29g) and stirred for 3h. After the reaction was completed, dichloromethane was spin-dried under reduced pressure, and purified by silica gel chromatography (dichloromethane:methanol=50:1) to obtain 1.71 g of a white solid.
[0075] Yield 62%.
[0076] 2) Preparation of fluorescent probe I-A3:
[0077] Dissolve 2-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-ylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid (500 mg) in 2.3 ml of acetic anhydride, and slowly add 0.28 ml of Perchloric acid and stirred for 4h. The resulting precipitate was filtered and washed with ether. The white precipitate (500 mg) was dissolved in 6.5 ml of anhydrous THF, 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (292 mg) and 0.58...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com