Bottom mud in-situ remediation method
An in-situ remediation and bottom sludge technology, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, sludge treatment, etc., can solve problems such as unstable physical structure of the remediation system, limited effect, unstable location ecosystem, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
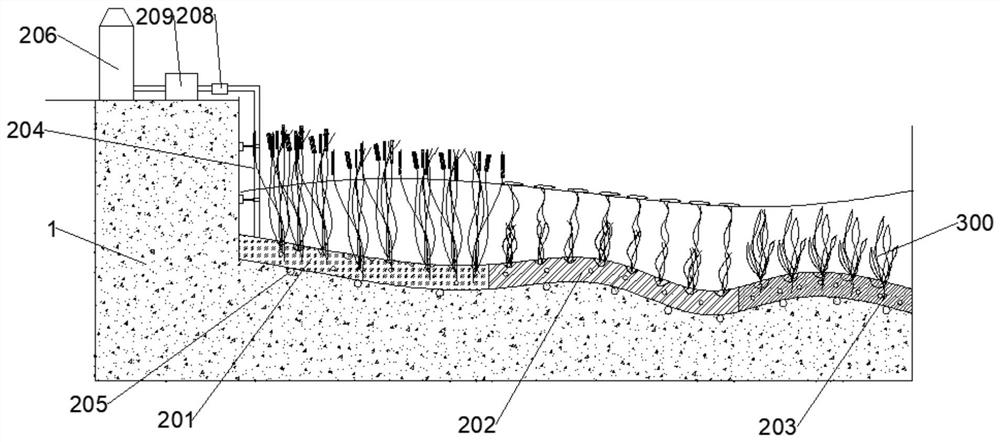
[0053] In-situ restoration of the bottom mud of the XX section to XX section of the Fuxi River in Zigong. The river section is 6.4 kilometers long and covers an area of 24.3 square kilometers;
[0054] Specific steps are as follows
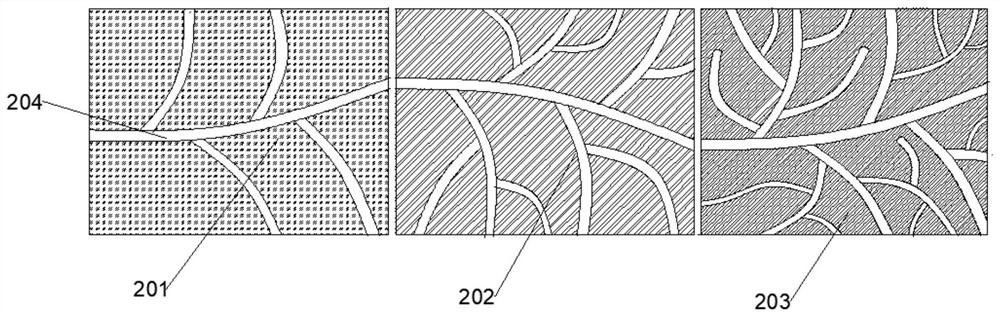
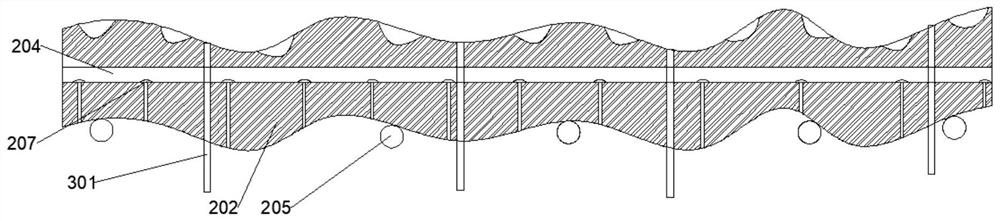
[0055] S1. Divide the water area to be repaired into multiple cells, the area of which is 50m*50m; number each cell, and randomly take sediment samples in each cell for testing. The specific testing items are: : Ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen and total phosphorus content, organic matter content, COD;
[0056] According to Pi=C i / S i
[0057] as well as
[0058] Pi is the pollution index of a single pollutant; P is the comprehensive pollution index of multiple pollutants; Ci is the measured concentration of pollutant i in the soil, Si is the evaluation standard of pollutant i; n is the total number of detection items.
[0059] Calculate the comprehensive pollution index P of each cell, aggregate the samples, and obtain the minimum val...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com