Method for preventing and controlling soil-borne diseases of vegetables by aid of crop straws
A technology for crop straws and soil-borne diseases is applied in the field of preventing and controlling soil-borne diseases of vegetables, which can solve the problems of large differences in soil environment in the field, and achieve the effects of reducing the pressure of environmental pollution, cheap and easy to obtain sources, and simple operation methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
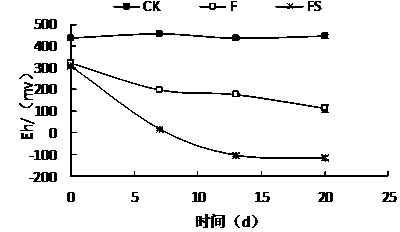
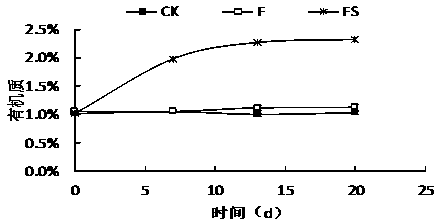
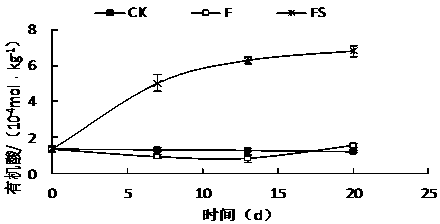
[0025] Effects of Rice Straw Flooding on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
[0026] The test soil was taken from the hot pepper production greenhouse in Gaogou Town, Huaian, and the rice straw was taken from the rice field of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences. The pathogen was Phytophthora capsici ( Phytophthora capsici ), which can be obtained from the Agricultural Microorganism Culture Collection Center of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. The pepper variety tested was Luojiao No. 5. The spore liquid of Phytophthora capsici was evenly added to the test soil, so that the concentration of Phytophthora spores in the soil was 200 Phytophthora spores / gram of dry soil. Three treatments were set up in the experiment: (1) Control (CK): After the soil was inoculated with Phytophthora capsici, the soil moisture content was kept at 16-18%, and it was placed naturally. (2) Conventional flooding (flooding, F): the soil is inoculated with Phytophthora capsici a...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 Effect of rice straw flooding on soil cellulase activity
[0034] Collect the soil after flooding and drying in Example 1, and measure the activity of soil cellulase.
[0035] It can be seen from Table 1 that the soil cellulase activity of rice straw flooded soil was higher than that of the control and conventional flooded. Soil enzyme activity is an important indicator of soil biological properties. Generally, healthy soil has higher soil cellulase activity. In addition, the main component of the cell wall of Phytophthora capsici is cellulose, and the increase of cellulase activity in the soil can inhibit the growth of Phytophthora capsici or degrade the pathogen, reducing the probability of occurrence of Phytophthora capsici.
[0036] Table 1 Effect of rice straw flooding on soil cellulase activity
[0037] control regular flooding Rice straw flooded cellulase activity 0.14±0.01 0.16±0.02 0.31±0.02
[0038] Note: The uni...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: Inhibitory effect of rice straw flooding on the growth of Phytophthora capsici in soil
[0040] The amount of Phytophthora capsici in each treatment was determined by quantitative PCR (RT-PCR) method on the soil treated by flooding in Example 1. Determination method of Phytophthora capsici: the kit used for soil DNA extraction was FastDNA SPIN Kit for Soil produced by MP Company, and the soil DNA was extracted according to the instructions. The specific primers are CAPFW (5'-TTTAGTTGGGGGTCTTGTACC-3') and CAPRV1 (5'-CCTCCACAACCAGCAACA-3'), and the target fragment size is about 450bp. The RT-PCR reaction kit used TaKaRa's SYBR premix Ex Taq. Fluorescent quantitative PCR amplification system: 2×SYBR PreMix Ex Taq (TaKaRa) 10 μL, 50×ROX Reference DyeⅡ(TaKaRa) 0.4 μL, 20 μmol / L primers 0.4 μL, template 2 μL, ddH2O 6.8 μL, amplification system 20 μL . The reaction program was: 95°C for 30 s, 1 cycle; 95°C for 5 s, 60°C for 34 s, 40 cycles. Fluorescence qua...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com