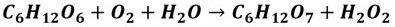Relaxation nuclear magnetic resonance method for detecting glucose content of liquid biological sample
A biological sample and nuclear magnetic resonance technology, which is applied in the field of biochemical method analysis and detection, can solve the problems of interference with the specificity of detection methods, and achieve the effect of improving detection ability and low detection limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
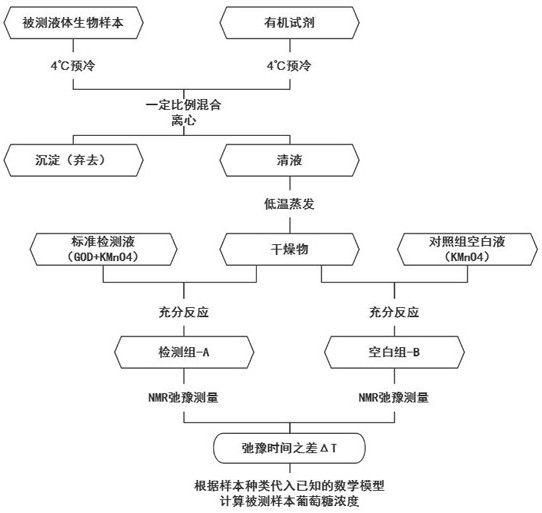
[0037] A sample of the BSA solution was tested, the glucose content of which was unknown.
[0038] 1. Measure 500uL of the sample, place it at 4°C for pre-cooling, add 1000uL of absolute ethanol that is also pre-cooled at 4°C, invert and mix well, place it at 4°C for precipitation for 20 minutes, and centrifuge at room temperature (3500 rpm, 10 minutes) ;
[0039] 2. Centrifuge the supernatant obtained in step 1, divide it into groups A and B, take 150uL each, and place it in a drying oven at 85°C to evaporate until completely;
[0040] 3. Add 1mL each of the standard detection solution and standard blank solution in the same ratio as the data model corresponding to the BSA solution sample to the dry matter A and B groups obtained in step 2, oscillate to dissolve and mix well, and let it stand for 1 hour to make it fully reaction;
[0041] 4. Take 200uL of the samples obtained in step 3 after the completion of the reaction and put them into a 7.5mm nuclear magnetic resonance...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The production of the standard detection solution and the standard blank solution is taken as an example to detect samples with a glucose concentration range of 1-20mM.
[0045] 1. Calculate the required minimum concentration of potassium permanganate according to the reaction equation and scale it up appropriately. Weigh 0.15g of potassium permanganate and dissolve it in 4mL of pH 5 acetic acid buffer at room temperature;
[0046] 2. Weigh 5 mg of glucose oxidase and dissolve it in 4 ml of acetic acid buffer at pH 5 at room temperature;
[0047] 3. Measure 2mL of the glucose oxidase solution in step 2, add 40uL of the potassium permanganate solution in step 1, turn over and mix well, take 1mL of it and dilute it to 20mL with pH 5 acetic acid buffer to obtain a standard detection solution;
[0048] 4. Measure 20uL of the potassium permanganate solution in step 1, dilute it to 20mL with pH 5 acetic acid buffer, turn over and mix well to obtain a standard blank solution....
Embodiment 3
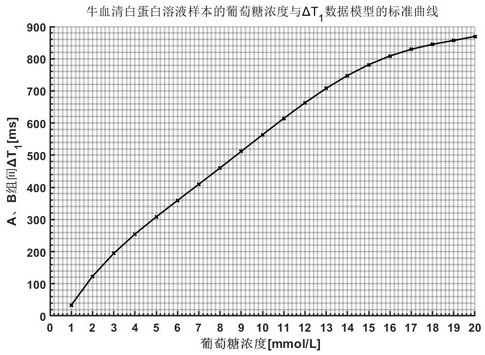
[0050] The establishment of data models under specific categories, taking BSA solution samples as an example.
[0051] 1. Weigh 2g bovine serum albumin and dissolve it in 40mL pH 5 acetic acid buffer solution at room temperature to obtain a 50g / LBSA solution;
[0052] 2. Weigh 0.18g of anhydrous glucose and dissolve it in 10mL of the BSA solution in step 1 at room temperature to obtain a BSA solution with a glucose concentration of 100mM;
[0053] 3. Measure 40, 80, 120, 160, 200, 240, 280, 320, 360, 400, 440, 480, 520, 560, 600, 640, 680, 720, 760, 800uL. The glucose concentration in step 2 is 100mM BSA solution, use the BSA solution in step 1 to dilute to 4mL to obtain glucose concentrations of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 , 16, 17, 18, 19, 20mM BSA solution, pre-cooled at 4°C;
[0054] 4. Measure 500uL of the BSA solution of each concentration obtained in step 3, add 1000uL of absolute ethanol that was also pre-cooled at 4°C, turn over and mix well, p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com