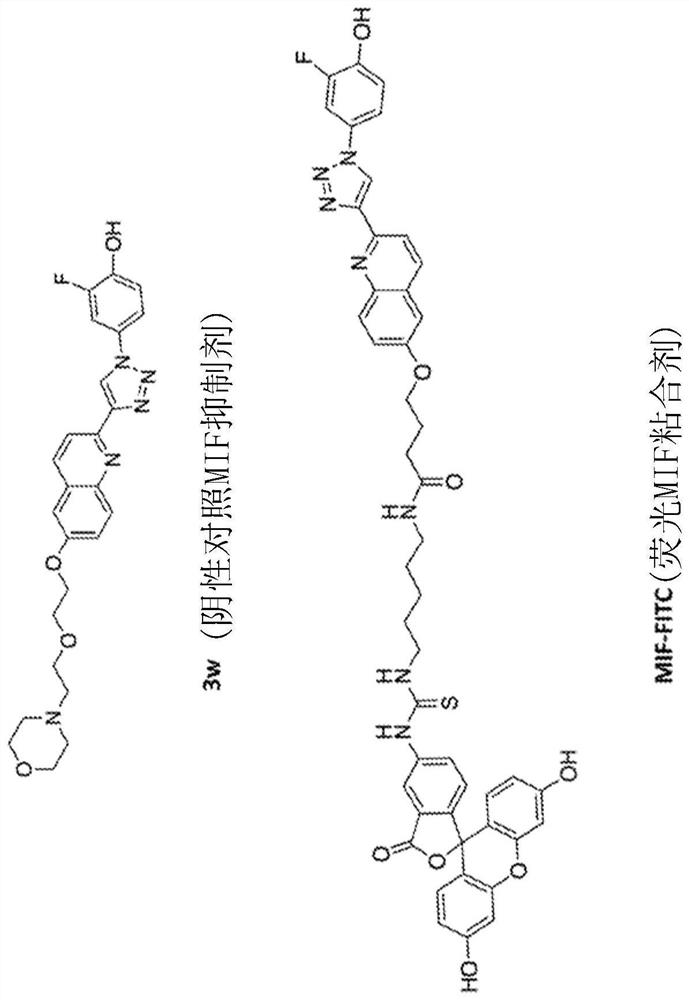
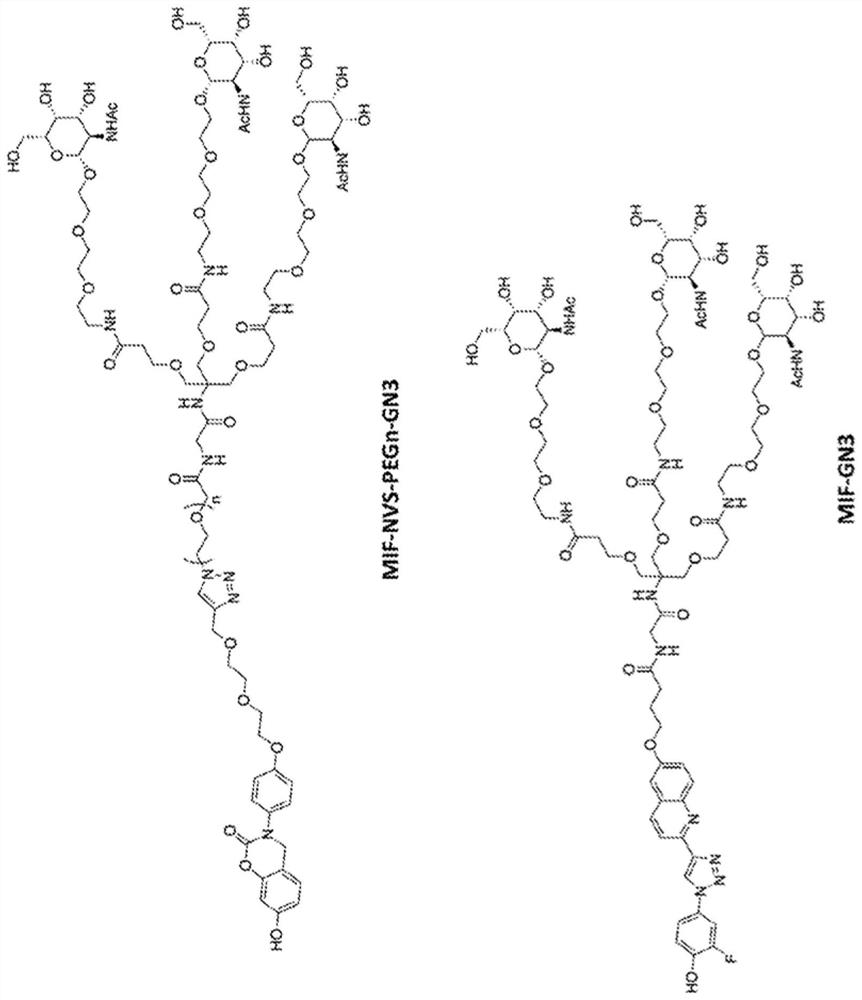
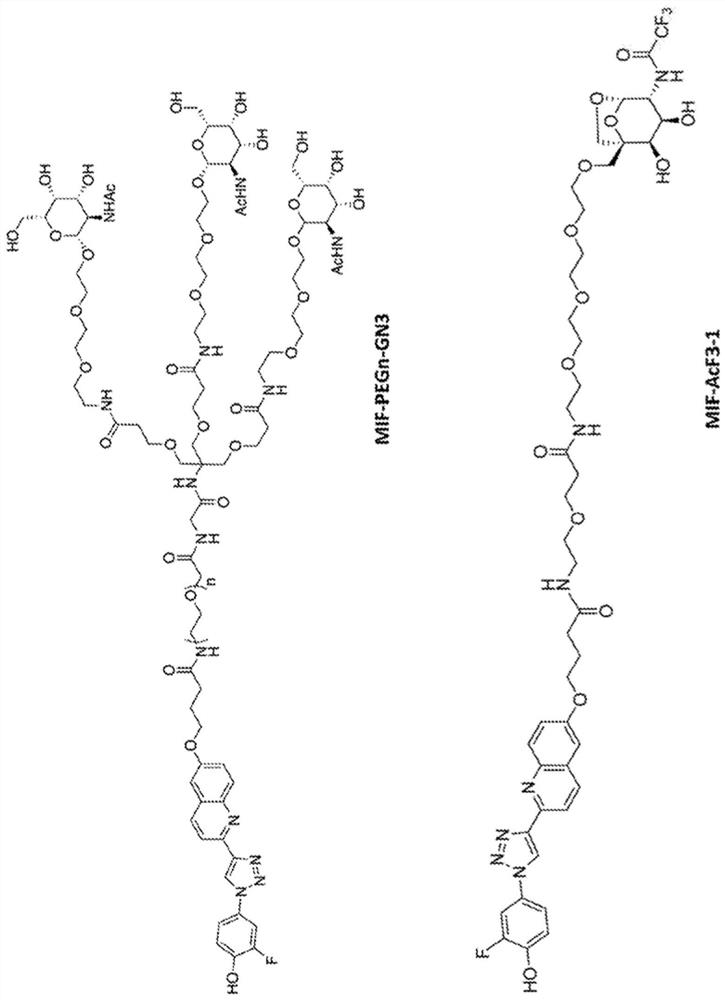
Bifunctional small molecules to target the selective degradation of circulating proteins
A protein, bifunctional technology, applied in the direction of organic active ingredients, allergic diseases, non-central analgesics, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0547] Proper protein secretion (section) and turnover are necessary processes to maintain homeostasis. Newly synthesized proteins targeted for secretion are first transported to the endoplasmic reticulum, where they are post-translationally modified with sialic acid-terminal N-linked glycan chains (1). As proteins age, terminal sialic acid residues are removed by circulating endogenous glycosidases (2). This natural protein aging process exposes galactose and N-acetylgalactose (GalNAc) residues, which bind to the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR) on the surface of hepatocytes (3-5).
[0548] ASGPR is a C-type lectin that removes aged circulating proteins as well as exposed GalNAc residues from circulation by transporting them into lysosomes. Display of multiple galactose or GalNAc residues on the protein surface is essential for high affinity binding - and subsequent endocytosis by - ASGPR (6, 7). Once these proteins are endocytosed, they are released from ASGPR by deplet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com