Method for improving dcaps marker detection efficiency
A label detection and high efficiency technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of low detection efficiency and difficult separation of actual labels, and achieve the effects of reducing detection time, simplifying detection methods, and improving detection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
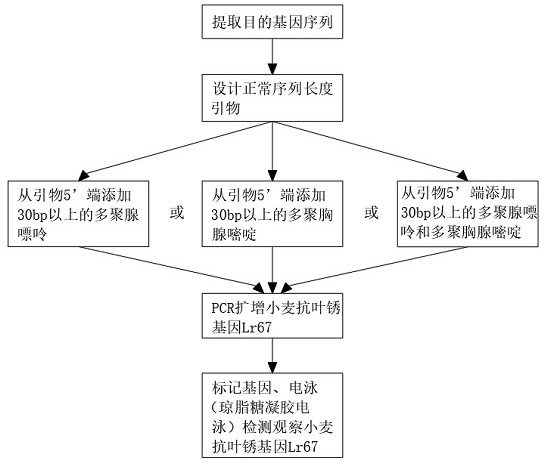
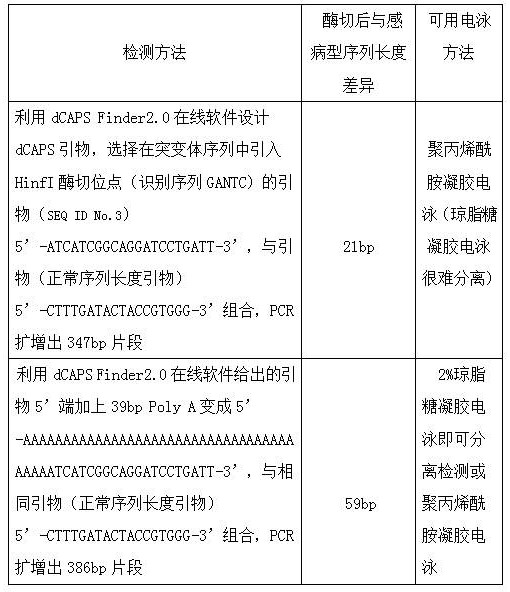
[0025] Embodiment 1, a method for improving the detection efficiency of dcaps markers, comprising the following steps: Step 1, selecting the target gene sequence: extracting the known wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr67 and its wild-type disease-susceptible gene, providing the basic raw materials required for the experiment, Step 2, dCAPS primer design: extract the wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr67 in step 1 and cooperate with dCAPS Finder2.0 equipment to prepare primers with normal sequence lengths, and prepare the raw materials required for the experiment. Step 3, primer sequence length amplification: use the primers prepared in step 2 Carry out a certain sequence length amplification, sequence length amplification is by introducing the primer of Hinfl restriction site into the sequence of wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr67, at the same time, add more than 30bp polynucleotides to the 5' end of the introduced Hinfl restriction site primer Polypurine or polypyrimidine is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com