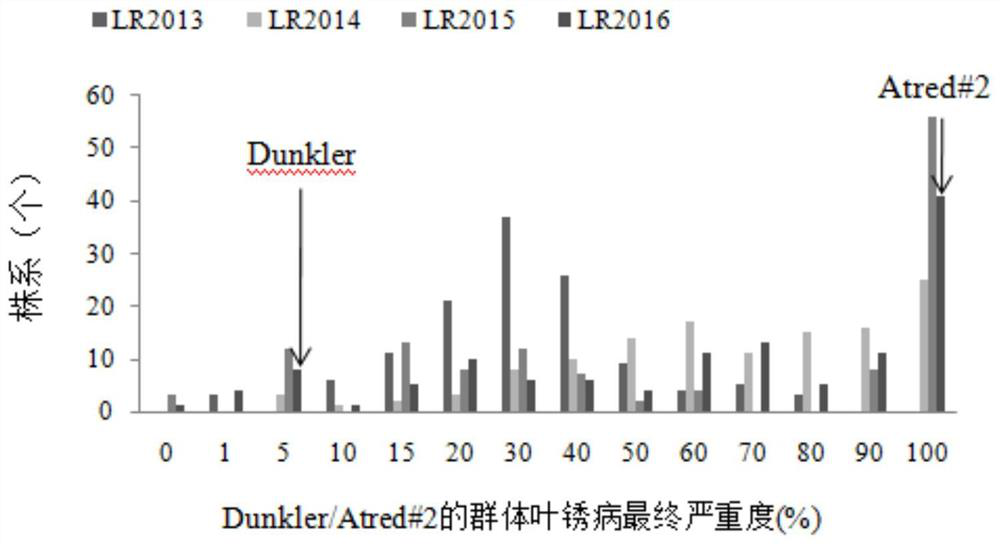
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Wheat leaf rust" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wheat leaf rust is a fungal disease that affects wheat, barley and rye stems, leaves and grains. In temperate zones it is destructive on winter wheat because the pathogen overwinters. Infections can lead up to 20% yield loss, which is exacerbated by dying leaves, which fertilize the fungus. The pathogen is Puccinia rust fungus. Puccinia triticina causes "black rust", P. recondita causes "brown rust", and P. striiformis causes "yellow rust". It is the most prevalent of all the wheat rust diseases, occurring in most wheat growing regions. It causes serious epidemics in North America, Mexico and South America and is a devastating seasonal disease in India. All three types of Puccinia are heteroecious requiring two distinct and distantly related hosts (alternate hosts). Rust and the similar smut are members of the class Pucciniomycetes but rust is not normally a black powdery mass.
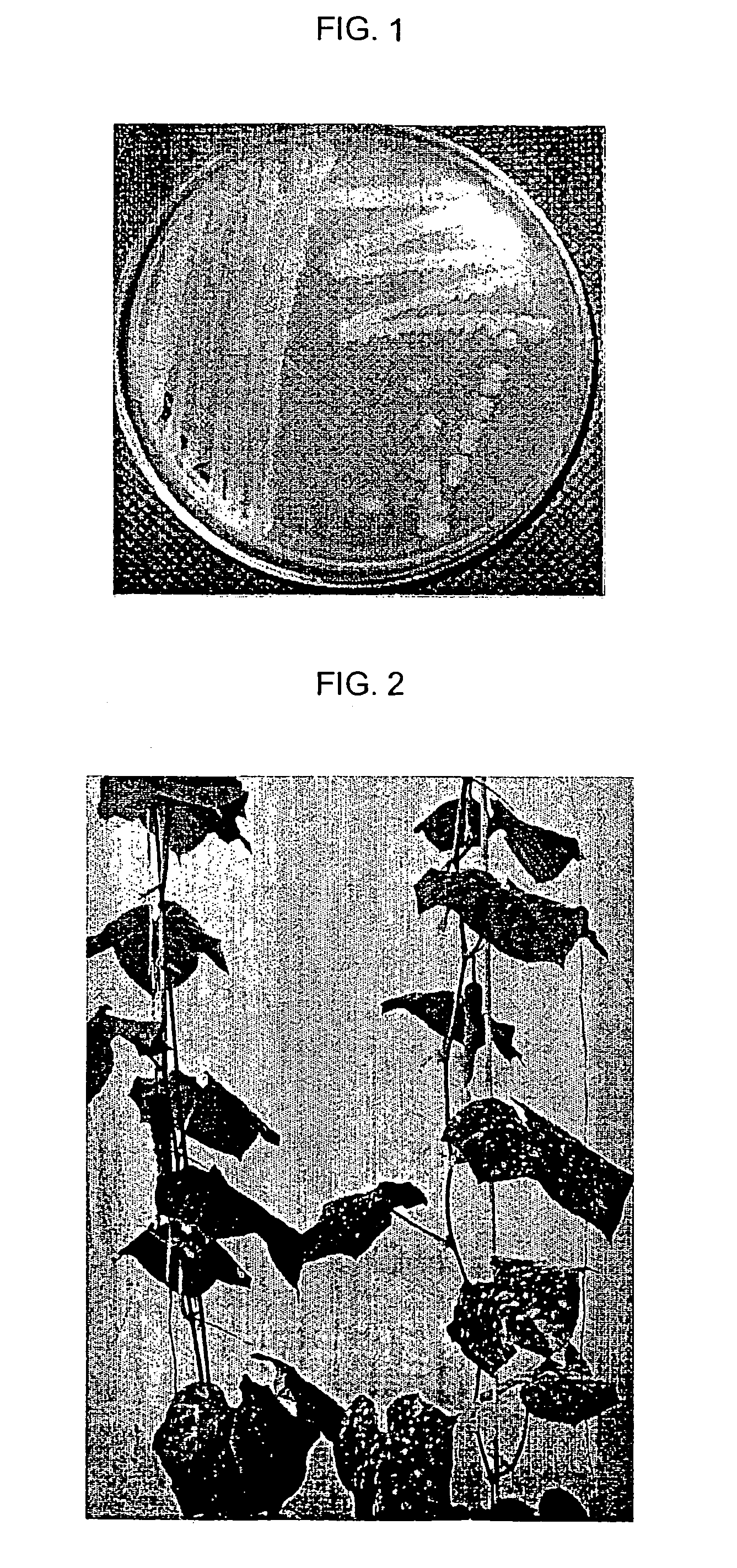
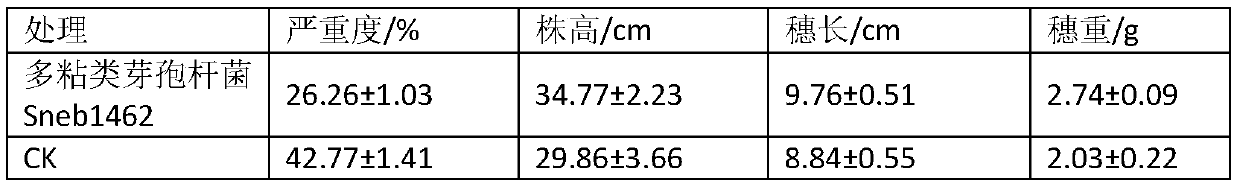
Bacillus subtilis strain having antagonistic activity for controlling plant diseases
A novel strain of Bacillus subtilis EB120 shows high antagonistic activity for controlling various plant diseases including barley powdery mildew, cucumber powdery mildew, red pepper anthracnose, rice blast, tomato gray mold, tomato late blight and wheat leaf rust, it can be effectively used as a microbioside for biologically controlling the plant diseases.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
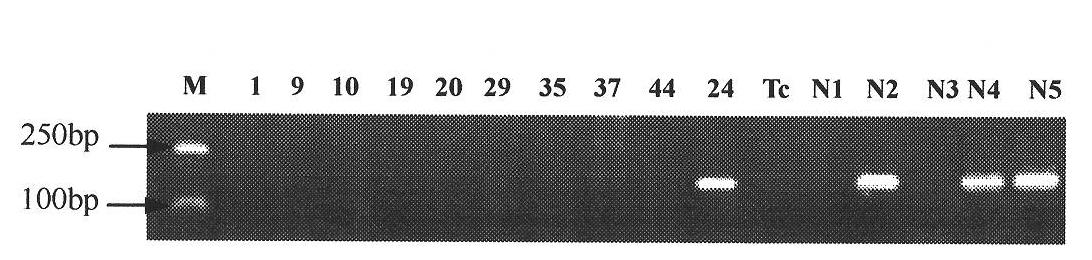
Method and special primer for screening wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr24
InactiveCN101967518AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide sequencing
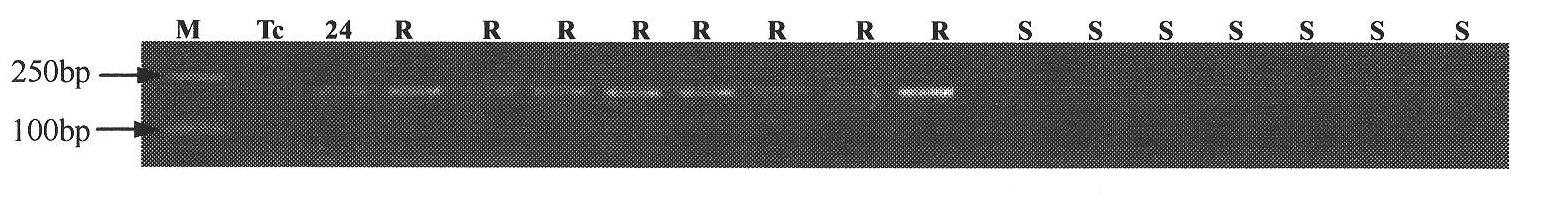
The invention discloses a method and a special primer for screening a wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr24. The special primer is a primer pair consisting of nucleotide sequences in a sequence 1 and a sequence 2 in a sequence list. The method for screening wheat containing the leaf rust resistance gene Lr24 is to perform polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using the genome DNA of a wheat variety to be tested as a template under the guidance of the primer pair consisting of the nucleotide sequences in the sequence 1 and the sequence 2 in the sequence list according to claim 1, wherein the product of the amplification contains wheat which has a strip size of 212bp and has the Lr24 gene. A method for detecting the amplification products comprises the steps of performing 2.0 percent agarose gel electrophoresis on the amplification products and developing by using an electronic beam (EB) or Goldview. The method and the special primer for screening the wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr24 are expected to play an important role in the wheat leaf rust resistance breeding.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Thaumatin-like protein related to wheat leaf rust resistance and encoding gene and application thereof
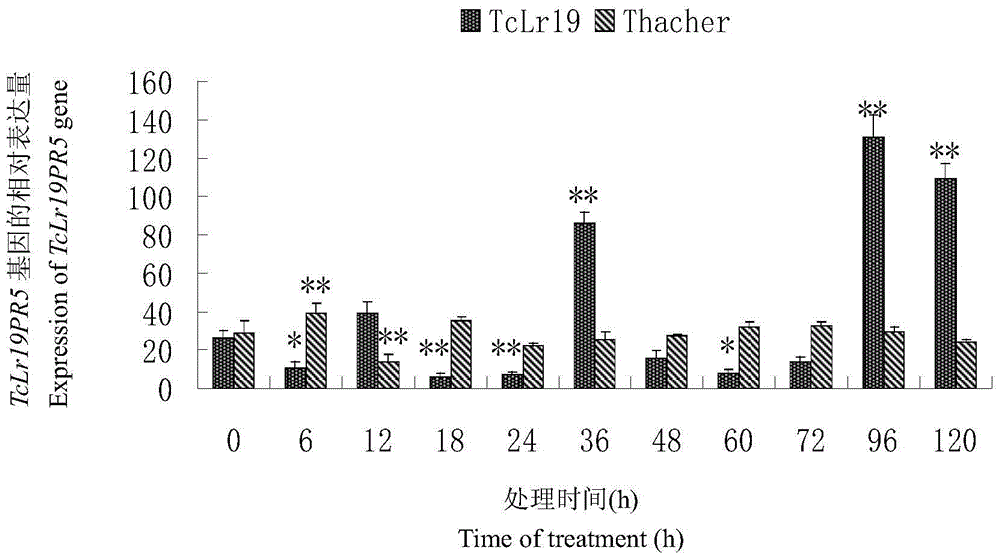
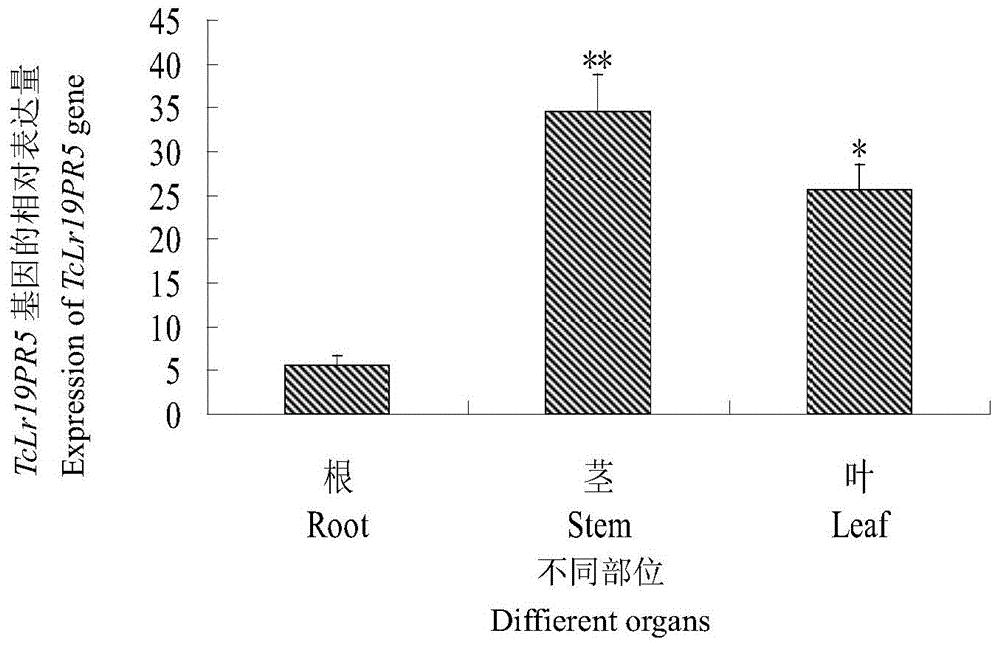
The invention discloses a thaumatin-like protein gene TcLr19PR5 related to wheat leaf rust resistance and a gene encoded through the thaumatin-like protein gene TcLr19PR5. Through RT-PCR and the electronic cloning technology, a 516bp thaumatin-like protein gene is cloned, and 171 amino acid residues are coded; and real-time fluorescence quantification PCR analysis shows that at different time points after puccinia triticina is inoculated, the expression quantity of the gene in non-affine combinations is higher than that of the gene in affine combinations, it is indicated that expressions are induced through the wheat puccinia triticina, the expression amount of stems is higher than the expressions of the leaves and the roots, and meanwhile it is clear that the expressions are induced by adversity signal molecules of abscisic acid (ABA) and salicylic acid (SA). According to the thaumatin-like protein gene and the gene, basic data are provided for in-depth exploration of wheat and puccinia triticina interaction molecular mechanisms, and the theory basis is provided for cultivating leaf-rust-resistance wheat varieties.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Method for identifying wheat leaf rust single sorus by utilizing nested PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
InactiveCN102586427AEasy to prepareSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyWheat Rust
The invention relates to a method for identifying a wheat leaf rust single sorus by utilizing nested PCR (polymerase chain reaction). The method comprises the following steps: designing and synthesizing a primer, extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the single sorus, performing amplification and separation on target genes, performing separation and identification on an amplified final product, then performing sequencing, comparing in a Genbank and determining the wheat leaf rust single sorus. The method for identifying the wheat leaf rust single sorus by utilizing the nested PCR is simple to operate and rapid and accurate in identification result, and can be applied into actual production.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bacillus subtilis strain having antagonistic activity for controlling plant diseases
A novel strain of Bacillus subtilis EB120 shows high antagonistic activity for controlling various plant diseases including barley powdery mildew, cucumber powdery mildew, red pepper anthracnose, rice blast, tomato gray mold, tomato late blight and wheat leaf rust, it can be effectively used as a microbioside for biologically controlling the plant diseases.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
Water dispersible granules containing pyraclostrobin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105707097ASimple preparation processReduce manufacturing costBiocideDead animal preservationDispersityWater dispersible
The invention relates to water dispersible granules containing pyraclostrobin. The water dispersible granules containing pyraclostrobin comprise the following ingredients: 5%-80% of active ingredients, 1%-10% of a dispersing agent, 1%-8% of a wetting agent, 1%-10% of a disintegrating agent, 1%-5% of a binding agent and the balance of a filler. The preparation method comprises the steps of performing uniform mixing, ultrafine grinding, granulation, drying and sieving on the raw materials to obtain the water dispersible granules. The two compounded granules have an obvious synergistic effect than a mono-agent, the problems of difficult disintegration and the like of single pyraclostrobin or compounded water dispersible granules due to low melting point is solved, and the defects of dust flying and the like of wettable powder during production and use processes are overcome; the water dispersible granules have the advantages of high active ingredient content, high disintegration speed, good dispersity, high thermal stability, less environmental pollution and the like, has good control effects on wheat leaf rust, powdery mildew of cucumber, alternania mail Roberts and macrophoma musae when in use, and is high in safety.
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPOSION AGROCHEM
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site of anti-wheat leaf rust gene Lr13 and application of SNP site
ActiveCN111073993AAccelerate the breeding process for disease resistanceHigh combinatorial throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDisease resistantWheat leaf rust
The invention relates to an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site of an anti-wheat leaf rust gene Lr13 and application of the SNP site. The SNP site is positioned at a 157695819 locus of a 2B chromosome of wheat, and a KASP (kompetitive allele specific polymerase chain reaction) primer combination capable of amplifying the SNP site comprise three primers of SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ IDNO.4. The SNP site interlinked with the anti-wheat leaf rust gene Lr13 is screened, designed and developed, in addition, the KASP primer combination is designed for the SNP site, the type of the SNP site can be accurately identified through the KASP primer combination, then a wheat strain with the anti-wheat leaf rust gene Lr13 can be screened, the selection efficiency can be improved, the anti-disease breeding progress of wheat can be accelerated, and the target of pyramiding breeding of multiple anti-disease genes can be achieved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Specific polymerase chain reaction markers of competitive allele of leaf rust-resistant locus of durum wheat adult-plant and application of specific polymerase chain reaction markers of competitive allele of leaf rust-resistant locus of durum wheat adult-plant
InactiveCN110592260AGood genetic stabilityHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
The invention provides wheat leaf rust resistance-related KASP molecular markers and application thereof. The KASP molecular markers are selected from BA00138075 and / or BA00606902, wherein base sequences of BA00138075 and BA00606902 are as shown in a table 1 as shown in the specification respectively. According to the provided KASP molecular markers, the selectivity of a locus can be enhanced, theaccuracy of selection of a leaf rust-resistant breeding material is improved, and the provided KASP molecular markers have important significance for achieving molecular marker-assisted selection breeding and improving the selection efficiency of durum wheat breeding.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
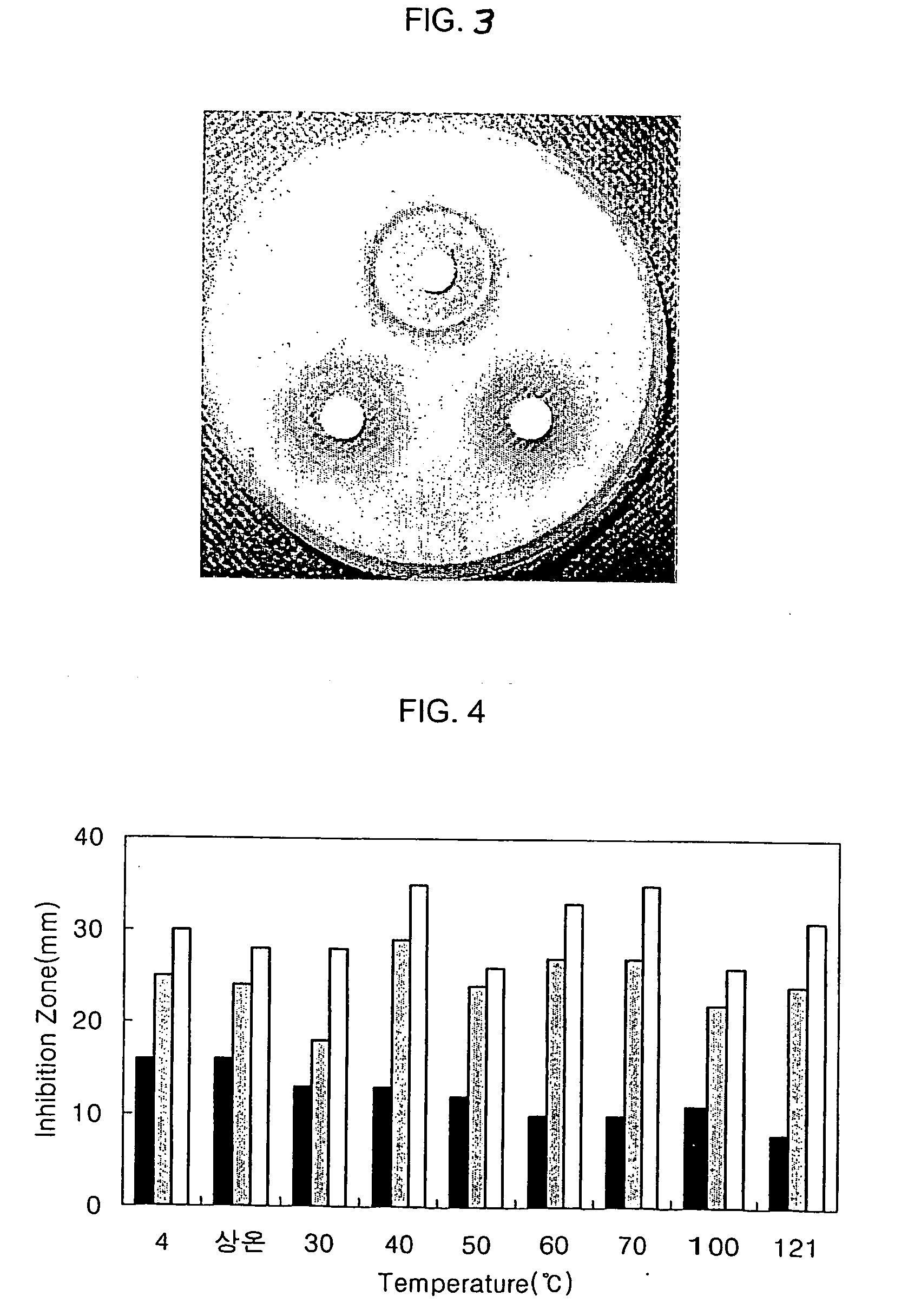
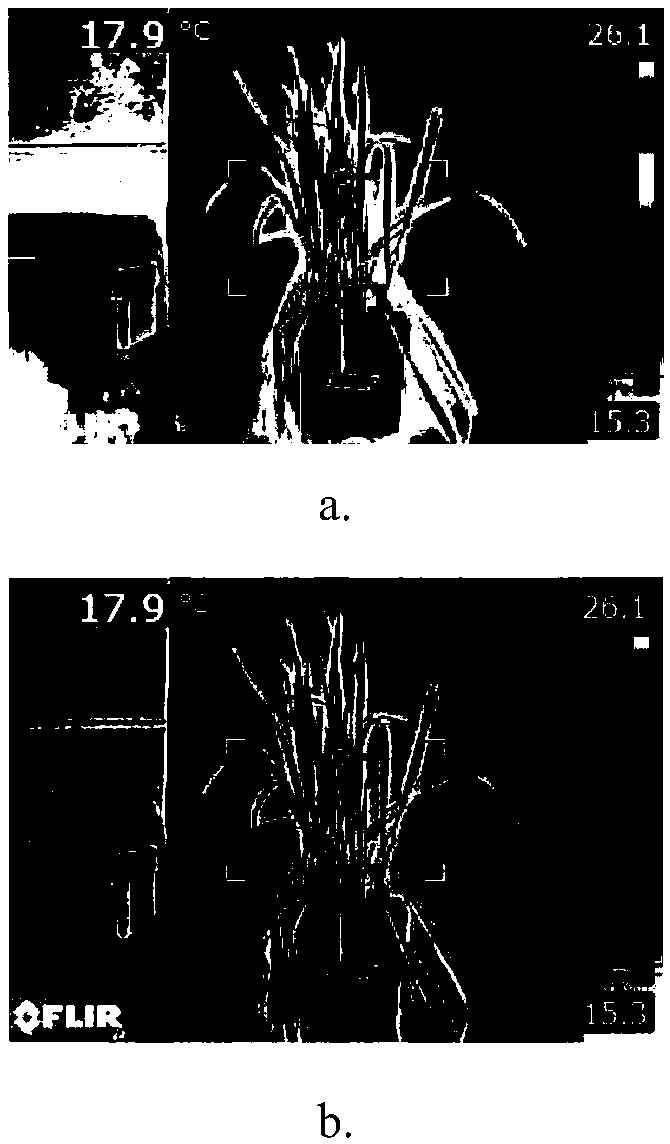
Grading method of wheat leaf rust based on infrared thermal imaging edge detection
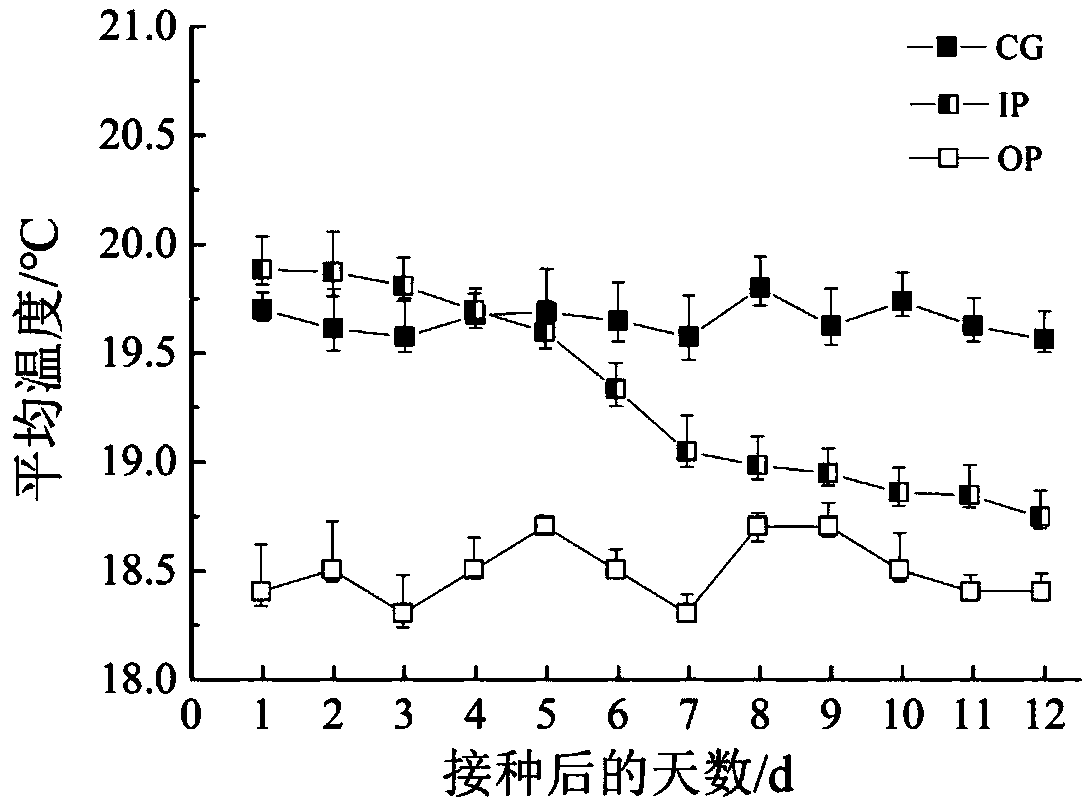
The invention discloses a method for grading wheat leaf rust based on infrared thermal imaging edge detection processing, which relates to the technical field of wheat rust detection. Firstly, the infrared thermogram of the whole wheat sample was collected to calculate the average leaf temperature of healthy plants, incubated plants and symptomatic plants, respectively, and to find out the temperature change rule in the process of fungal invasion. Then the regions of infrared thermogram which were pretreated by histogram equalization and median filter were extracted from the infrared thermogram. The proportion of lesion area in the total thermal imaging area of the whole plant was calculated by dividing the temperature region, extracting the low temperature region and segmenting the threshold value. The correlation coefficient was 0.9755, RMSE was 9.79%, and the overall recognition rate was 90%. Compared with the general near-infrared detection method, the invention has the advantagesof fast detection speed and earlier detection of diseases.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Primer for screening wheat leaf rust resistance QTL and application of primer
InactiveCN104911272AAccumulateImprove disease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceResistant genes
The invention discloses a primer for screening wheat leaf rust resistance QTL and an application of the primer, and relates to the technical field of determination or detection method of nucleic acid. The primer is a primer pair consisting of upstream and downstream nucleotide sequences of primers wmc692 and wmca657. The invention provides novel SSR markers wmc692 and wmc657 of the wheat leaf rust resistance QTL-(i) QLr.zh-4B. A molecular marker which is tightly linked to the QTL can be utilized to perform the assistant marker selection for the QTL, so that the accumulation of a plurality of active disease-resistant genes can be realized, and the disease resistance of a species can be prolonged. The novel leaf rust resistance QTL and the special primer can play an important role in the long-term disease resistance breeding of wheat.
Owner:BAODING UNIV
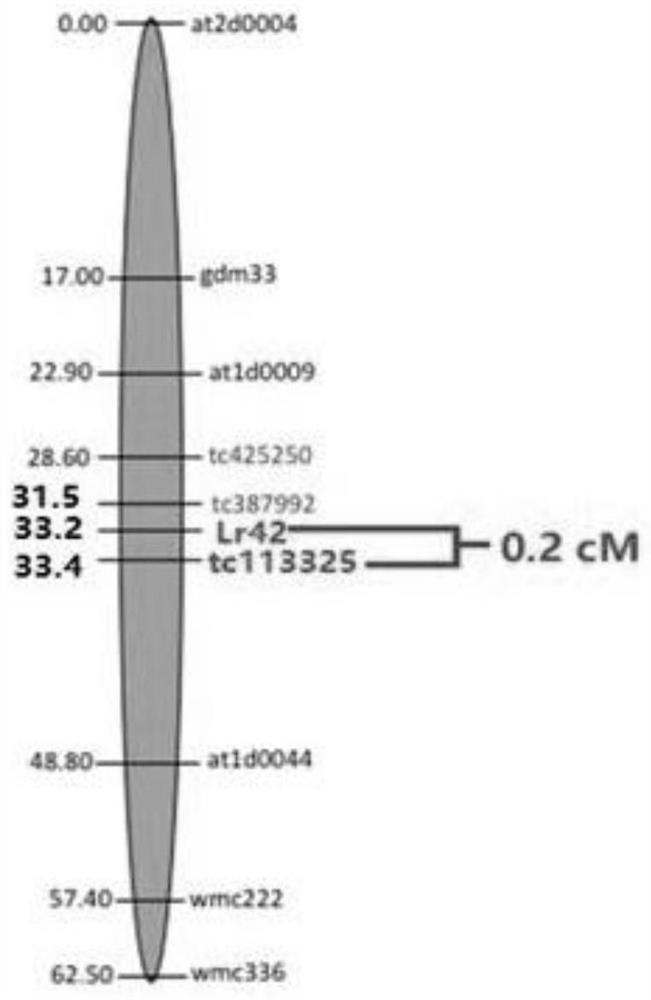
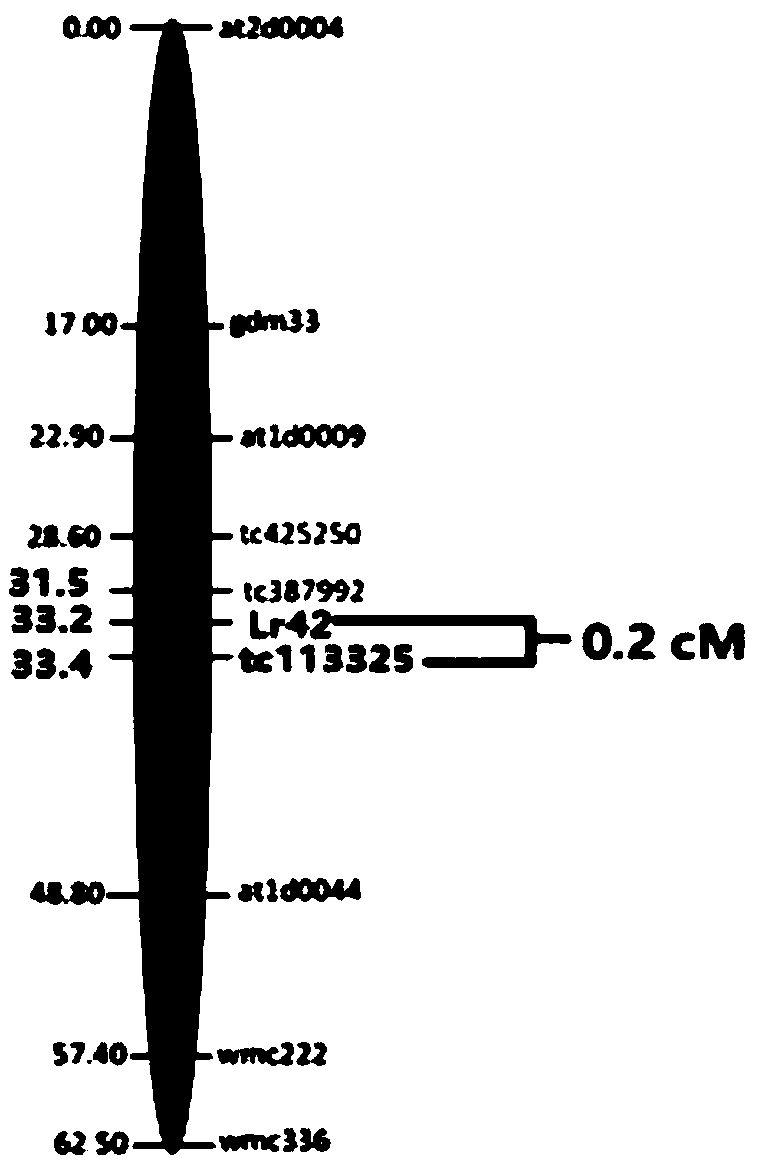
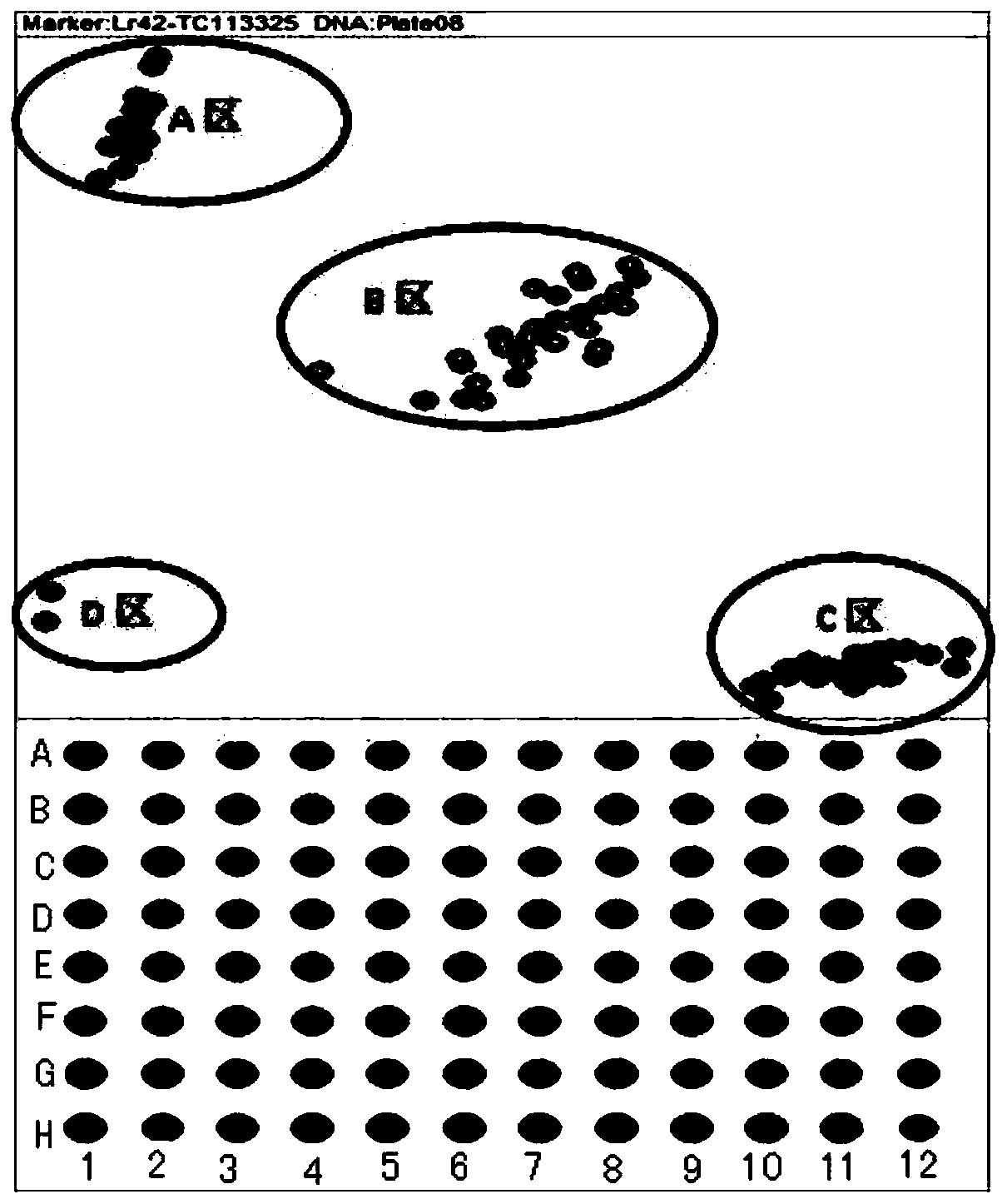
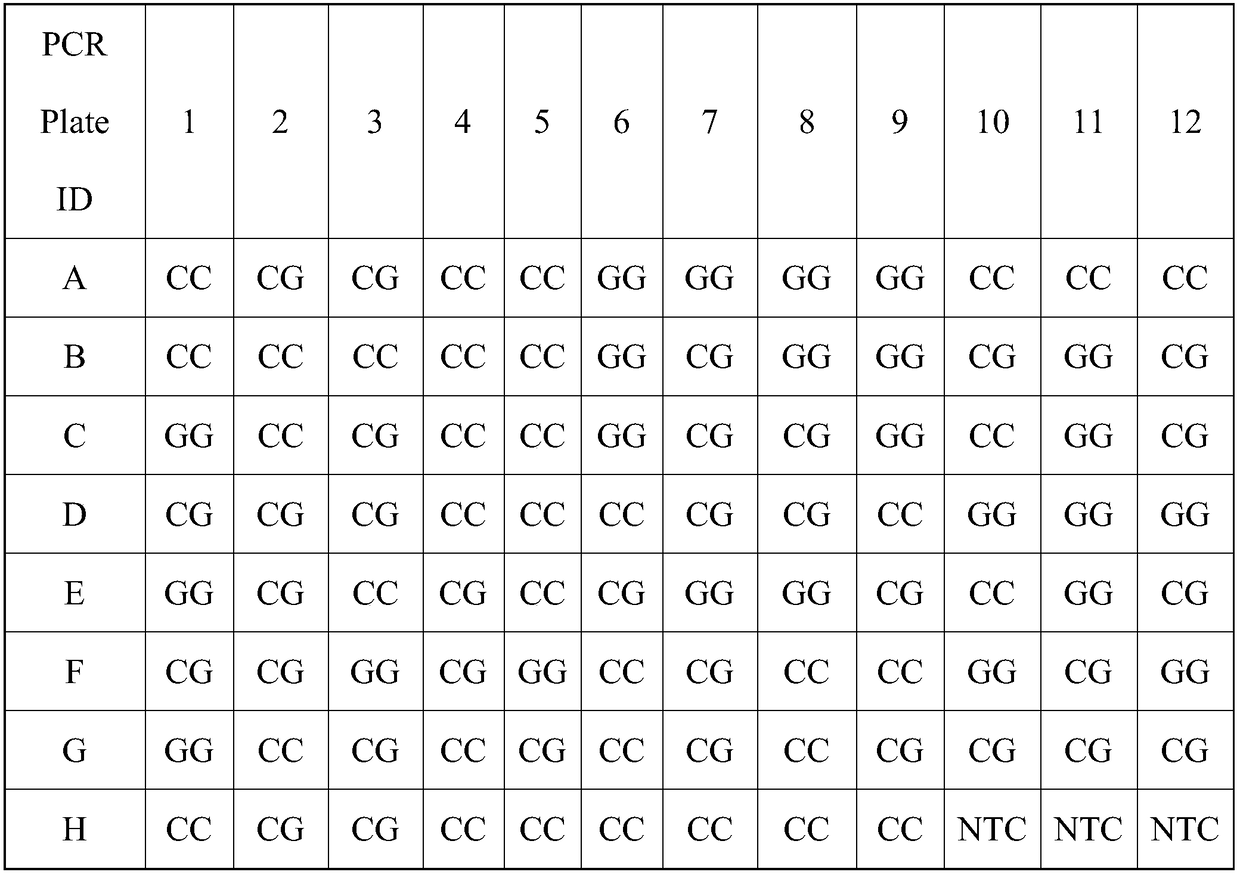
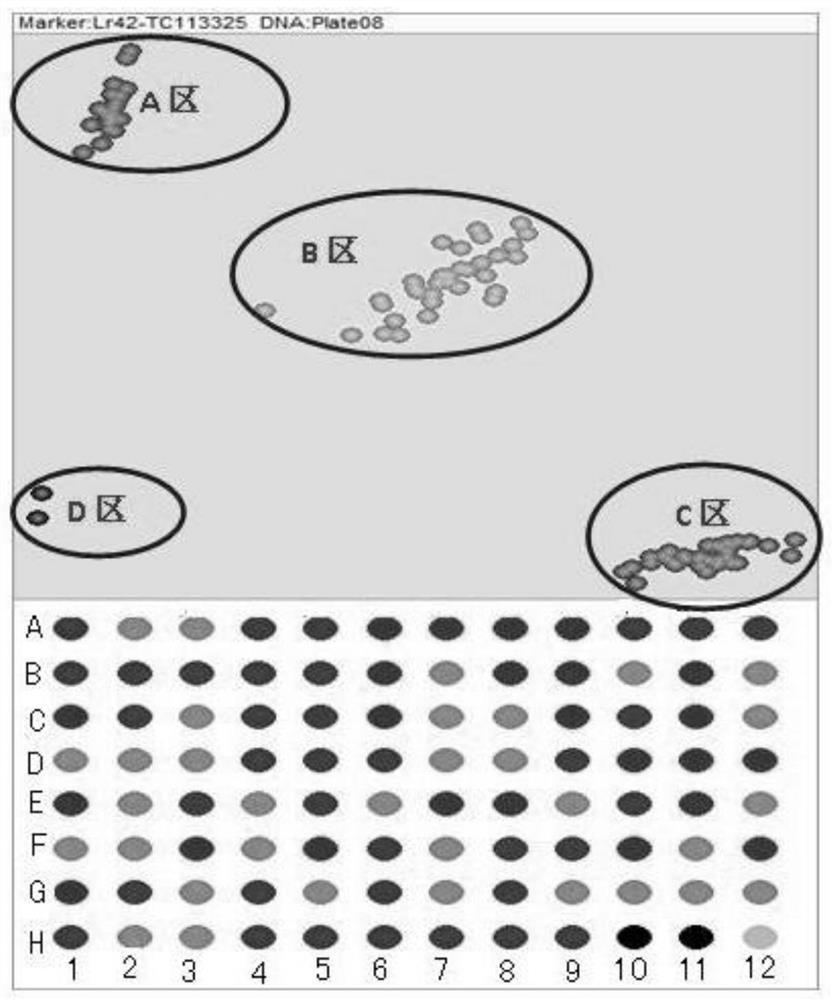
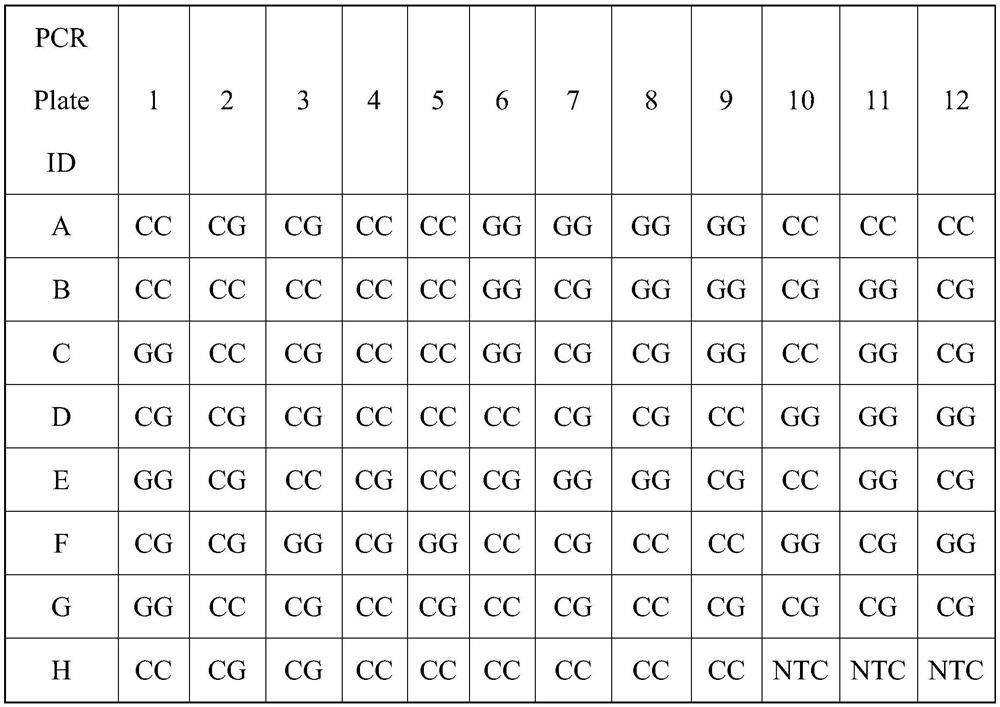
SNP molecular marker of wheat leaf rust resistant gene Lr42, detection method and application
ActiveCN109161609AHigh detection throughputShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceResistant genes
The invention discloses an SNP molecular marker TC113325, of a wheat leaf rust resistant gene Lr42, a method of detecting the wheat leaf rust resistant gene Lr42 by using the molecular marker and application thereof. The molecular marker is obtained by amplifying the following primers, wherein the upstream primer sequences are as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and SEQ ID NO. 3 and a downstream primer sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3. The method of detecting the wheat leaf rust resistant gene Lr42 by using the molecular marker TC113325 has the characteristics of being high in detection flux, short in time, high in accuracy, easy to implement automation, low in cost, environmentally friendly and the like, and is applied on a large scale in breeding work favorably.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI XIAOMAI INST
Colloidal gold test strip used for detecting wheat leaf rust
ActiveCN105001326AEasy to operateReduce economic lossMicroorganism based processesTissue cultureBiotechnologyAntigen
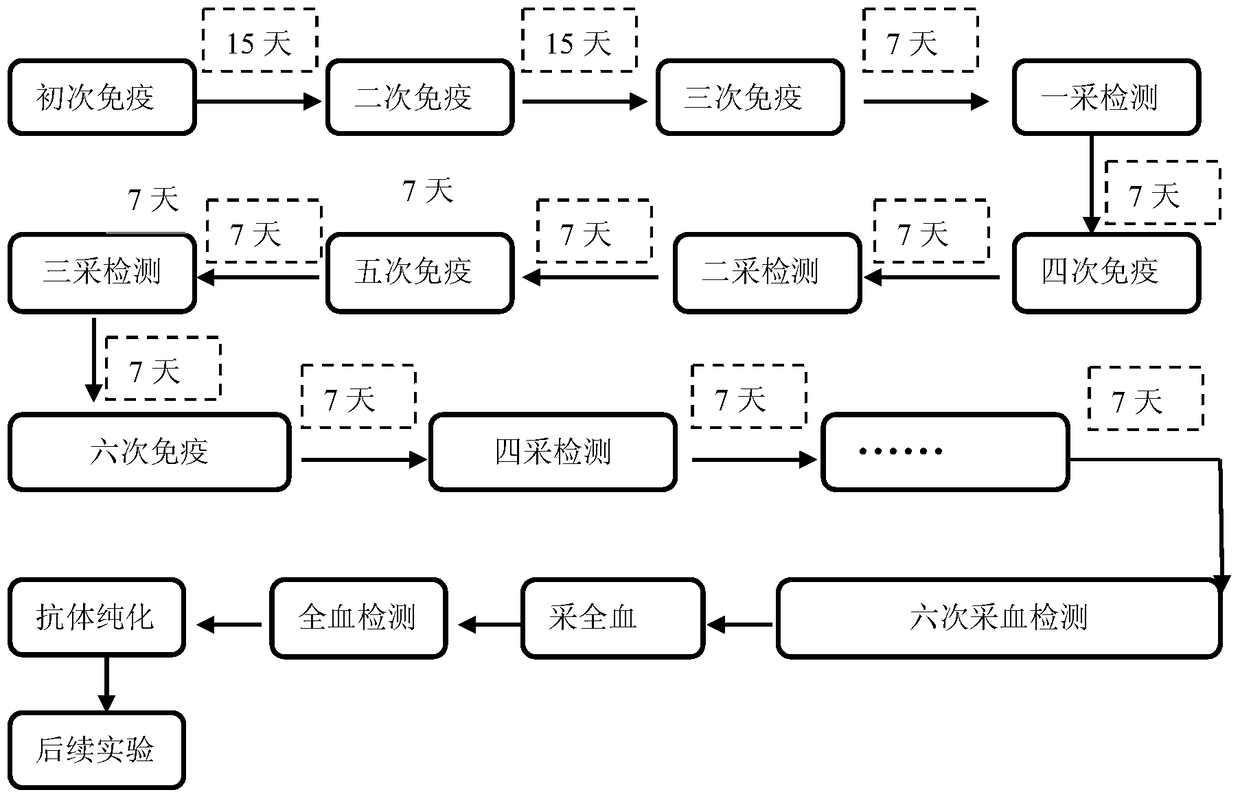
The invention provides a colloidal gold test strip used for detecting wheat leaf rust. The colloidal gold test strip comprises a sample pad, a colloidal-gold pad, an NC membrane, absorbent paper and a PS base plate, wherein the sample pad, the colloidal-gold pad, the NC membrane and the absorbent paper are successively arranged on the PS base plate along the chromatographic direction of a sample, the colloidal-gold pad is coated by a colloidal gold-labeled monoclonal antibody against Puccinia triticina, the NC membrane successively comprises a detection line and a quality control line along the chromatographic direction of the sample, the detection line is coated with Puccinia triticina antigen protein that the monoclonal antibody can specifically recognize, and the quality control line is coated with a goat anti-mouse secondary antibody. The monoclonal antibody against Puccinia triticina is secreted by a hybridoma cell with an accession number of CGMCC No. 10884. When the test strip is used for detection, the process from sampling to obtainment of detection results only takes 15 min, operation is simple and convenient, the results are accurate, early warning of wheat leaf rust can be realized, and economic loss caused by diseases is reduced.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Indel molecular marker of wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr13 and application thereof
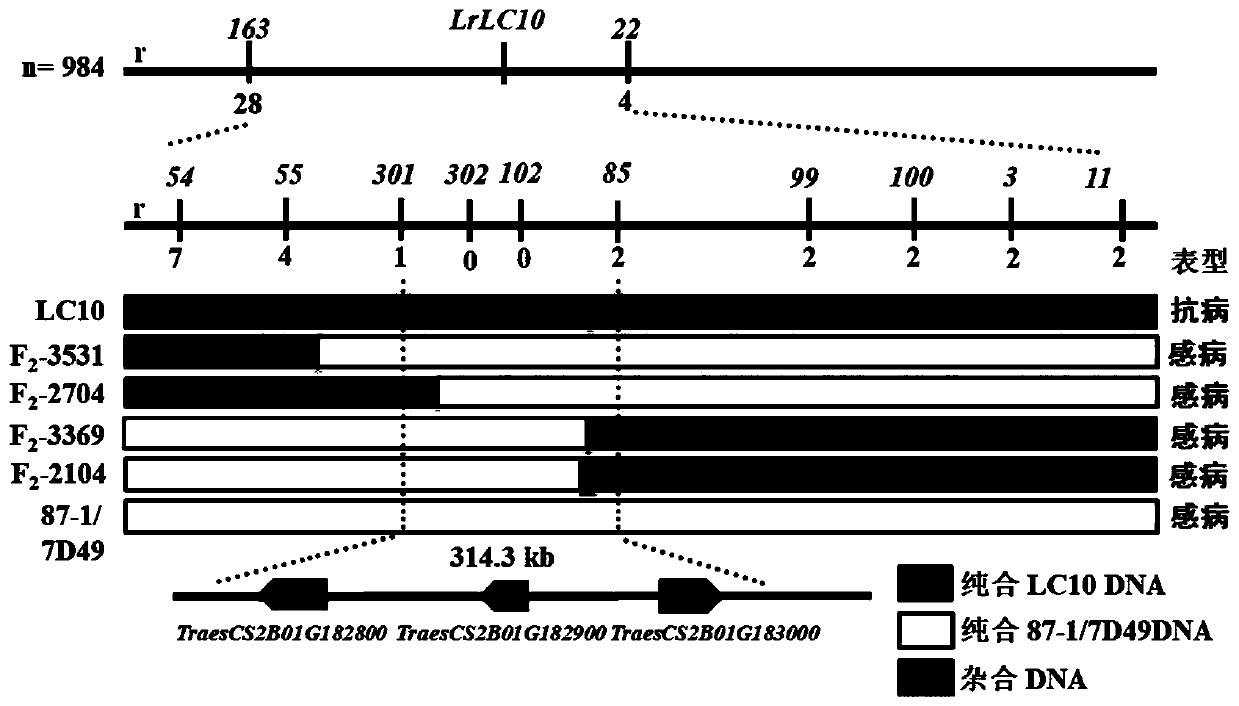
ActiveCN111041122AAchieving the goal of aggregation breedingImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationNucleotideGenetic linkage map
The invention relates to an indel molecular marker of a wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr13 and an application of the indel molecular marker. The indel molecular marker is located at the 1577558888thsite of a wheat 2B chromosome, and the nucleotide sequence of the indel molecular marker is shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO.1. According to the invention, genetic analysis is carried out on disease-resistant and susceptible wheat, the interval position of the leaf rust resistance gene Lr13 is determined by constructing a genetic linkage map, an indel molecular marker linked with the gene is correspondingly developed, the indel molecular marker is highly linked with the wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr13, a wheat strain containing the wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr13 can be screened out through the indel molecular marker, the selection efficiency is improved, the wheat disease-resistant breeding process is accelerated, and the purpose of polymerization breeding of multiple disease-resistant genes is achieved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
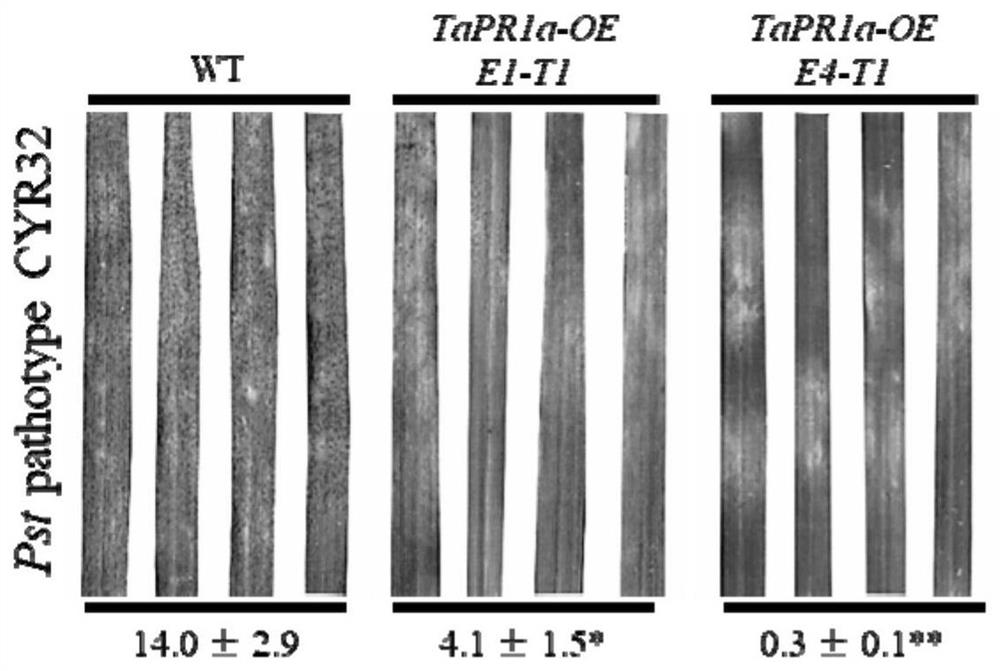
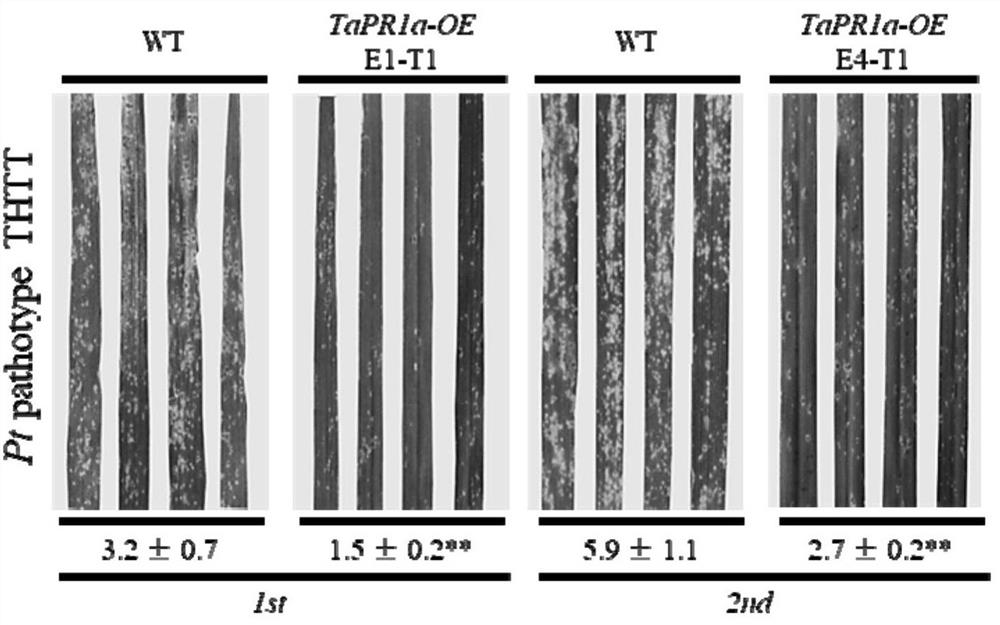
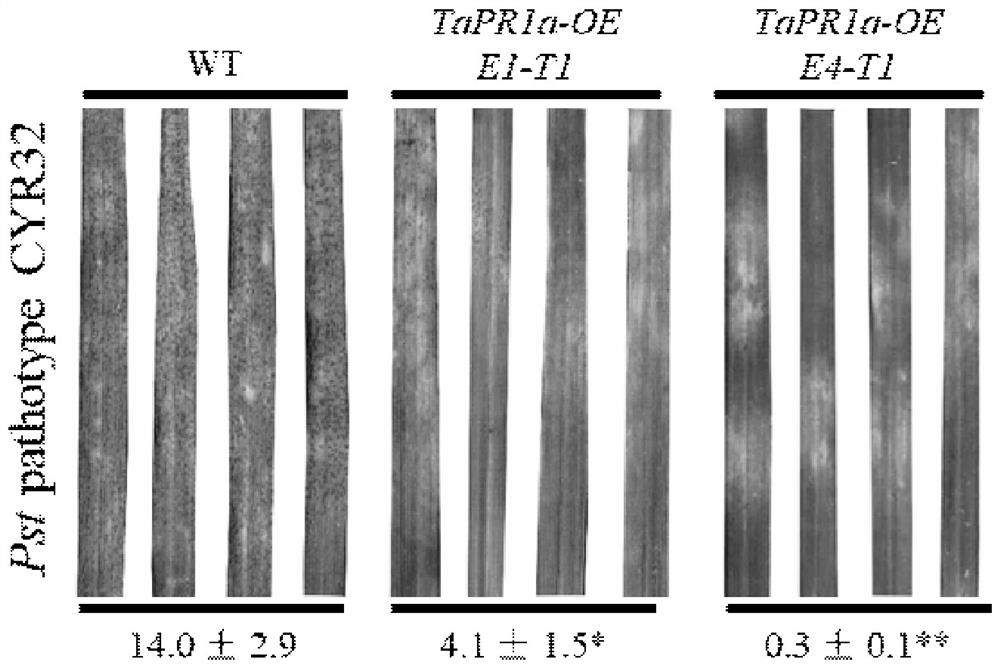
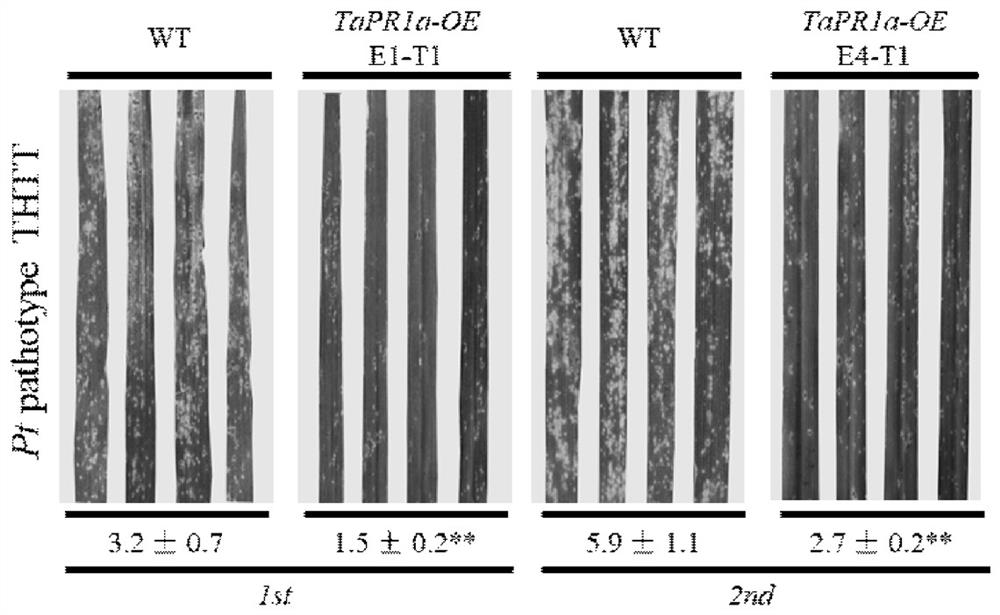
Wheat disease course related protein TaPR1a gene and application thereof in wheat stripe rust and leaf rust resistance
The invention provides a wheat disease course related protein TaPR1a gene and an application thereof in wheat stripe rust and leaf rust resistance. The invention relates to a genetic sequence, and particularly discloses the wheat pathogenesis related protein TaPR1a gene with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and a preparation process of a wheat transgenic material for overexpressing the TaPR1a gene. Experiments prove that the TaPR1a gene can significantly improve the resistance level of wheat to wheat stripe rust and wheat leaf rust.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
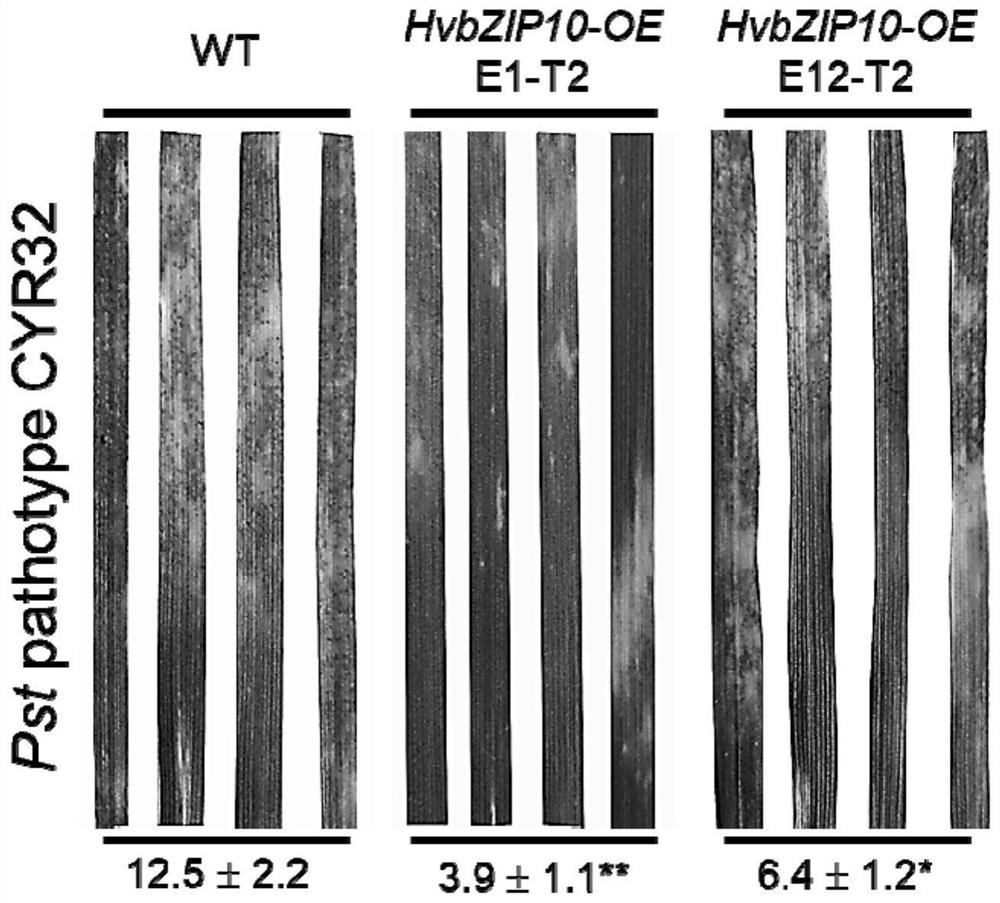
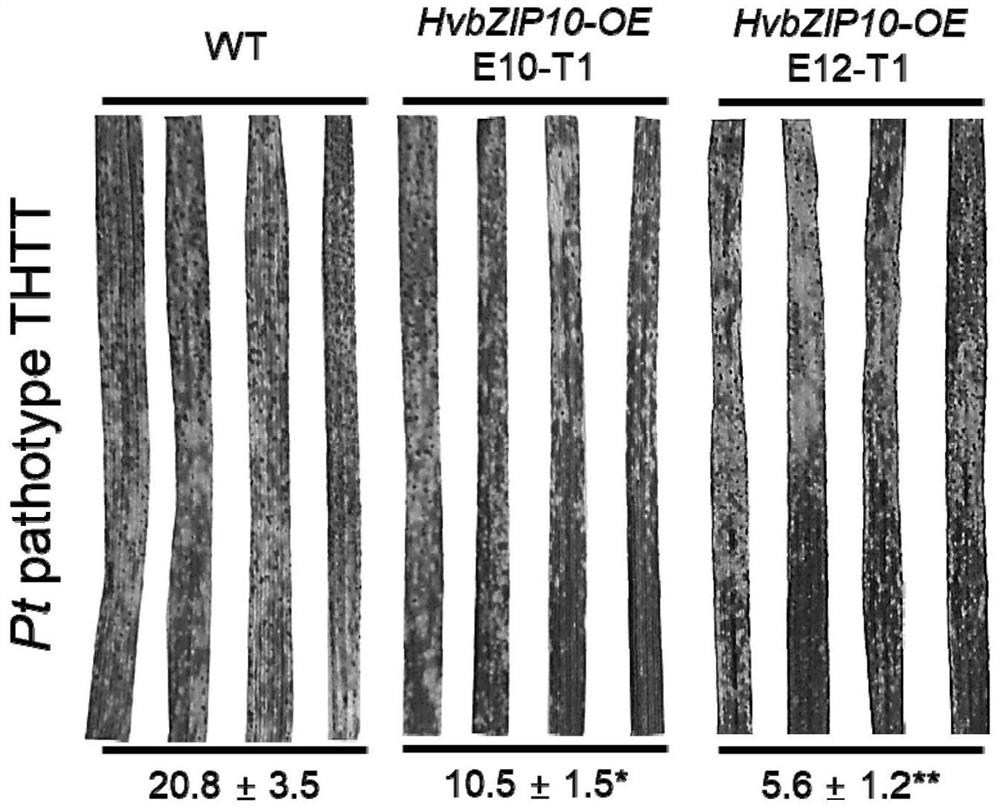
Barley Transcription Factor hvbzip10 Gene and Its Application in Wheat Resistance to Stripe Rust and Leaf Rust
The invention provides a barley transcription factor HvbZIP10 gene and its application in wheat resistance to stripe rust and leaf rust. The invention relates to gene sequences, and specifically discloses barley transcription factor HvbZIP10, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the preparation process of wheat transgenic materials overexpressing HvbZIP10. The invention verifies through experiments that the HvbZIP10 gene can significantly improve the resistance level of wheat to wheat stripe rust and wheat leaf rust.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
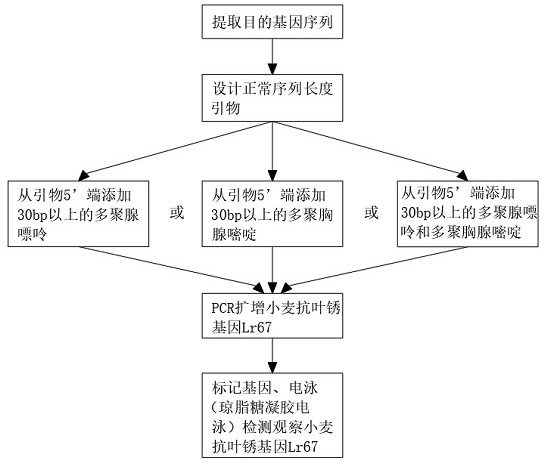
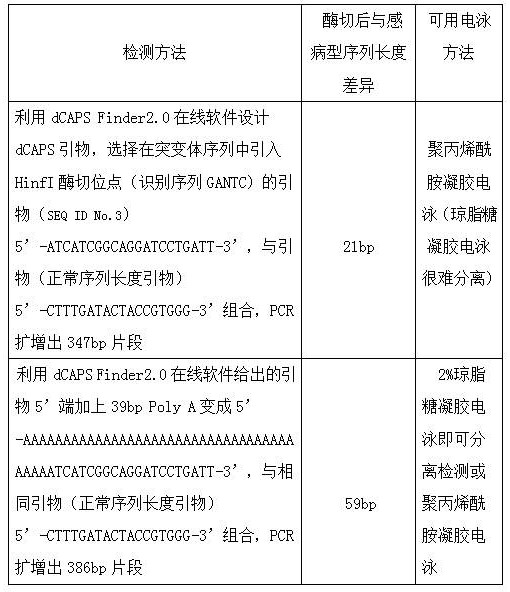
Method for improving dcaps marker detection efficiency
ActiveCN112322708AImprove detection efficiencyThe detection method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionWild type
The invention provides a method for improving dcaps marker detection efficiency, and relates to the technical field of molecular biology. The method for improving the dcaps marker detection efficiencycomprises the following steps: S1, selecting a target gene sequence: extracting a known wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr67 and a wild type susceptibility gene thereof; S2, designing a dCAPS primer:extracting the wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr67 in S1 to be matched with dCAPS Finder2.0 equipment to prepare a primer with a normal sequence length; and S3, amplifying the primer sequence length: amplifying the primer prepared in S2. According to the method for improving the dcaps marker detection efficiency, enzyme cutting sites are introduced into primers of dCAPS, and the length of the primers is generally about 20 bp, so that fragments which are about 20 bp shorter than original fragments are generated after PCR enzyme cutting, and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is generally adopted for separation so as to distinguish the difference of the fragments of 20 bp. According to the invention, a tail sequence of 30bp or above is added to the 5' end of each primer, so that the fragment size difference between a wild type and a mutant after enzyme digestion is increased to 50bp or above.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A molecular marker and its application for rapid detection of leaf rust resistance gene in Thiopyrum elongatum
ActiveCN107630107BImprove breeding efficiencyEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWheat leaf rust
The present invention provides a molecular marker and its application for rapid detection of the leaf rust resistance gene of E. elongatum. With the aid of the induced short-segment translocation line of E. elongatum for resistance to leaf rust, combined with the reference sequence of the wheat D genome, The molecular marker Xsdau798 closely linked to it was designed and developed for wheat leaf rust resistance breeding and early molecular marker-assisted selection of leaf rust resistance traits to improve breeding efficiency.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method and special primer for screening wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr24
InactiveCN101967518BMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a method and a special primer for screening a wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr24. The special primer is a primer pair consisting of nucleotide sequences in a sequence 1 and a sequence 2 in a sequence list. The method for screening wheat containing the leaf rust resistance gene Lr24 is to perform polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using the genome DNA of a wheat variety to be tested as a template under the guidance of the primer pair consisting of the nucleotide sequences in the sequence 1 and the sequence 2 in the sequence list according to claim 1, wherein the product of the amplification contains wheat which has a strip size of 212bp and has the Lr24 gene. A method for detecting the amplification products comprises the steps of performing 2.0 percent agarose gel electrophoresis on the amplification products and developing by using an electronic beam (EB) or Goldview. The method and the special primer for screening the wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr24 are expected to play an important role in the wheat leaf rust resistance breeding.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
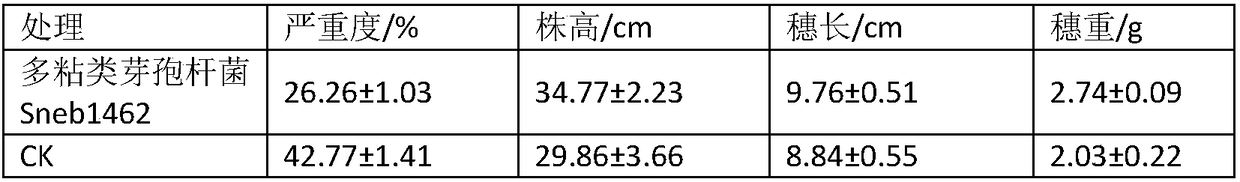
Paenibacillus polymyxa and its application for preventing and treating wheat leaf rust
The invention relates to a Paenibacillus polymyxa used for preventing and treating wheat leaf rust and its application, belonging to the technical field of microbial pesticides. The bacterial strain Paenibacillus polymyxa involved in the invention Paenibacillus polymyxa , was deposited in the General Microorganism Center of China Committee for the Collection of Microorganisms on November 14, 2017, and the preservation number is: CGMCC No.14879. Paenibacillus polymyxa can be made into a biocontrol agent for the prevention and treatment of wheat leaf rust, which can effectively control the infection of wheat leaf rust, the effect is remarkable, and at the same time, it can promote plant growth, and has a good application prospect in the prevention and treatment of wheat leaf rust .
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Antigens and polyclonal antibodies for differentiating between wheat leaf rust and bacillus rust
ActiveCN105367638BSimple and fast operationConvenient and effective detectionSerum immunoglobulinsSerum albuminPuccinia reconditaEuropean rabbit
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Wheat Process-related Protein tapr1a Gene and Its Application in Wheat Resistance to Stripe Rust and Leaf Rust
The invention provides a wheat disease process-related protein TaPR1a gene and its application in wheat resistance to stripe rust and leaf rust. The invention relates to a gene sequence, and specifically discloses a wheat disease process-related protein TaPR1a gene, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and a preparation process of a wheat transgenic material overexpressing the TaPR1a gene. The invention verifies through experiments that the TaPR1a gene can significantly improve the resistance level of wheat to wheat stripe rust and wheat leaf rust.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Colloidal gold test strips for detecting wheat leaf rust
ActiveCN105001326BEasy to operateReduce economic lossMicroorganism based processesTissue cultureBiotechnologyAntigen
The invention provides a colloidal gold test strip used for detecting wheat leaf rust. The colloidal gold test strip comprises a sample pad, a colloidal-gold pad, an NC membrane, absorbent paper and a PS base plate, wherein the sample pad, the colloidal-gold pad, the NC membrane and the absorbent paper are successively arranged on the PS base plate along the chromatographic direction of a sample, the colloidal-gold pad is coated by a colloidal gold-labeled monoclonal antibody against Puccinia triticina, the NC membrane successively comprises a detection line and a quality control line along the chromatographic direction of the sample, the detection line is coated with Puccinia triticina antigen protein that the monoclonal antibody can specifically recognize, and the quality control line is coated with a goat anti-mouse secondary antibody. The monoclonal antibody against Puccinia triticina is secreted by a hybridoma cell with an accession number of CGMCC No. 10884. When the test strip is used for detection, the process from sampling to obtainment of detection results only takes 15 min, operation is simple and convenient, the results are accurate, early warning of wheat leaf rust can be realized, and economic loss caused by diseases is reduced.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Paenibacillus polymyxa for controlling puccinia triticina of wheat and application of paenibacillus polymyxa
The invention relates to paenibacillus polymyxa for controlling puccinia triticina of wheat and an application of the paenibacillus polymyxa and belongs to the technical field of microbial pesticides.The bacterial strain paenibacillus polymyxa is preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) with preservation number being CGMCC No.14879 on November 14, 2017. An antibiological inoculant for controlling puccinia recondite of wheat can be prepared from the paenibacillus polymyxa, infection of puccinia recondite of wheat can be controlled effectively, the effect isremarkable, meanwhile, plant growth can be promoted, and the paenibacillus polymyxa has good application prospect in the aspect of control for puccinia recondite of wheat.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
SNP Molecular Marker, Detection Method and Application of Wheat Leaf Rust Resistance Gene lr42
ActiveCN109161609BHigh detection throughputShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWheat leaf rust
The invention discloses a SNP molecular marker TC113325 of wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr42, a method for detecting wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr42 using the molecular marker and its application. The molecular marker is amplified by the following primers, wherein the sequence of the upstream primer is as follows: As shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, the downstream primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.3, using the above SNP molecular marker TC113325 to detect wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr42 has high detection throughput, short time and accuracy High, easy to realize automation, low cost, environment-friendly and other characteristics, it is conducive to large-scale application in breeding work.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI XIAOMAI INST
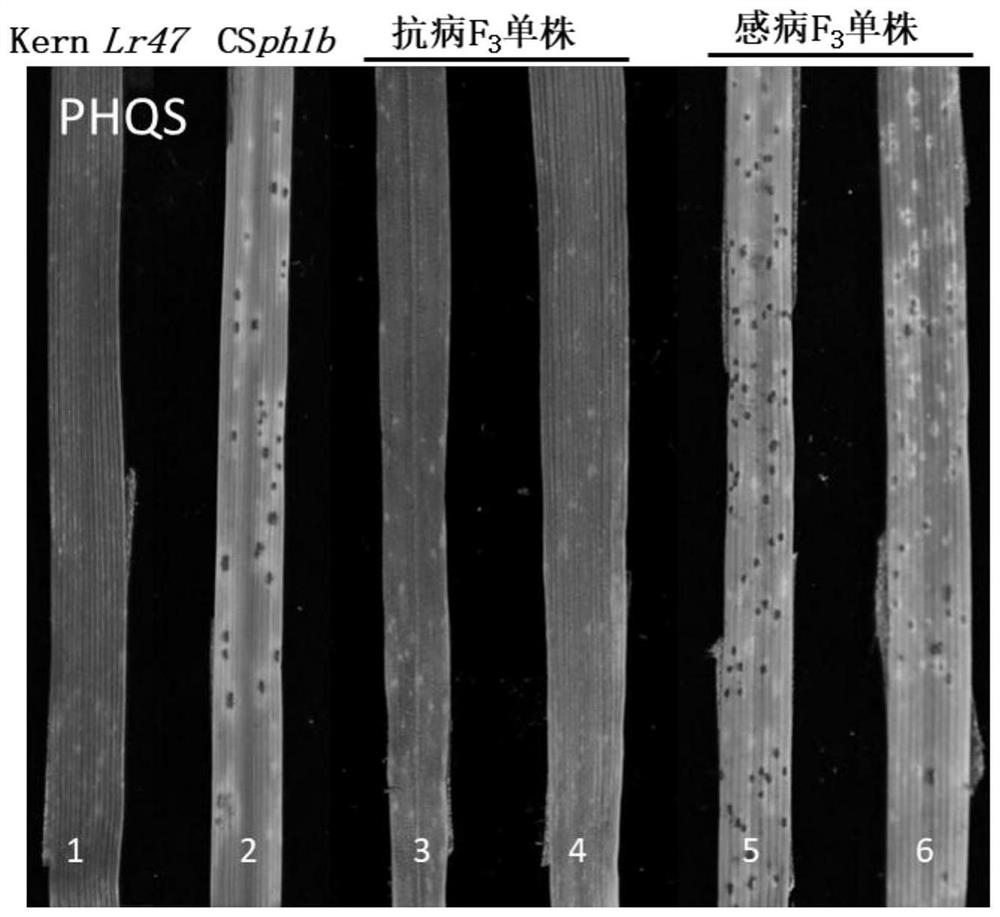
Molecular marker for detecting wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr47, detection method and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN114480709AReduce the difficulty of detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyResistant genes
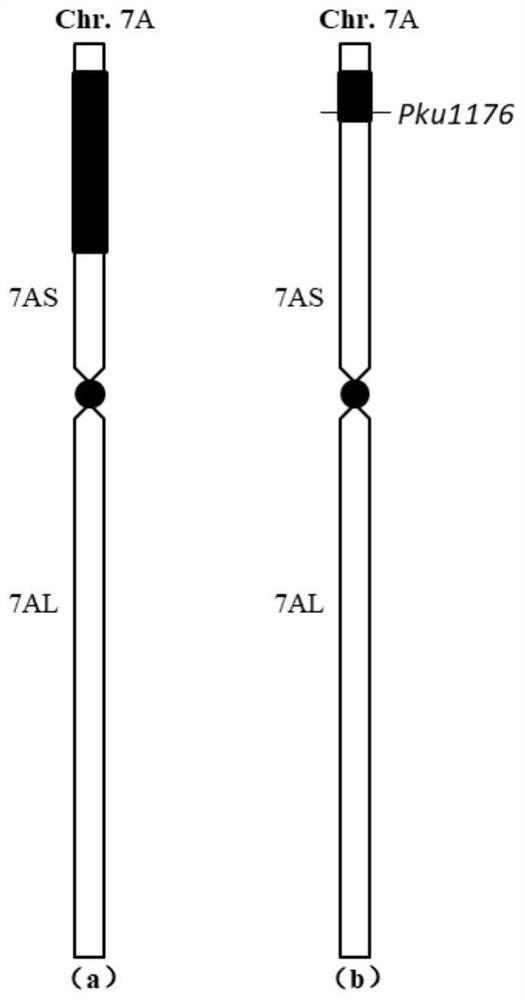
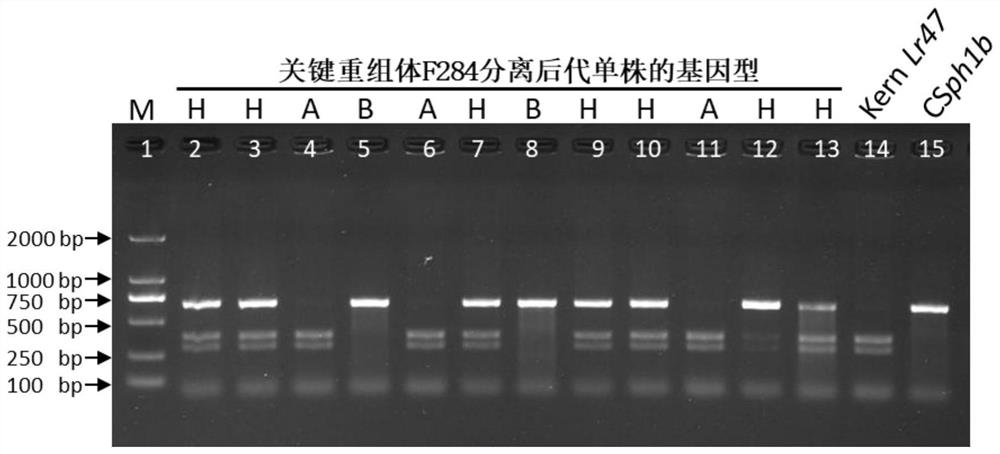
The invention provides a molecular marker for detecting a wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr47, a detection method and application of the molecular marker. The invention develops a molecular marker Pku1176 closely linked with a leaf rust resistant gene Lr47 by means of an induced wheat-Aegilops spelltuifolia leaf rust resistant short fragment translocation line and in combination with reference sequences of wheat and Aegilops spelltuifolia. By utilizing the molecular marker, translocated short fragment 7S chromosomes under different wheat backgrounds can be accurately and quickly detected, the early molecular assisted selection of the leaf rust resistant gene Lr47 is realized, and the wheat disease-resistant breeding efficiency is improved. The method solves the problem of high difficulty in detecting the wheat rust-resistant gene in the prior art, and is suitable for the field of molecular genetic breeding.
Owner:PEKING UNIV INST OF ADVANCED AGRI SCI
Primers and their application for screening wheat leaf rust resistance qtl
InactiveCN105385772BAccumulateImprove disease resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMarker-assisted selection
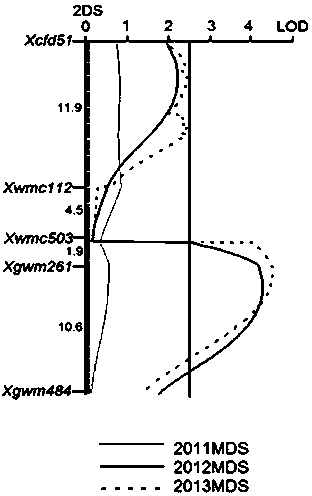
The invention discloses a primer used for screening wheat brown leaf rust resisting QTL and application thereof and relates to the technical field of nucleic acid determination or test methods. The QTL is located on a chromosome 2DS, the marker interval is Xgwm261-Xgwm484, and the QTL is from a susceptible parent Thatcher; the primer is a primer pair composed of upstream and downstream nucleotide sequences of a primer wms261 and a primer wms484. The primer is used for screening wheat brown leaf rust resisting QTL-QLr.hebau-2DS, and molecular markers in close linkage with the QTL can be used for marking the QTL for auxiliary selection, so that accumulation of multiple effective anti-disease genes are achieved, and disease resistance of varieties is improved. The discovered novel brown leaf rust resisting QTL and the special primer play an important role in wheat disease resisting breeding process.
Owner:BAODING UNIV
The SNP Loci of Wheat Leaf Rust Resistance Gene lr13 and Its Application
ActiveCN111073993BAccelerate the breeding process for disease resistanceHigh combinatorial throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWheat RustDisease resistant
The present invention relates to the SNP site of wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr13 and its application. The SNP site is located at the 157695820th position of wheat 2B chromosome. The KASP primer combination that can amplify the SNP site includes SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO. Three primers of ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4. The present invention screens, designs and develops a SNP site linked to the wheat rust resistance gene Lr13, and designs a KASP primer combination for the SNP site, and can accurately identify the type of the SNP site through the KASP primer combination, thereby screening out the SNP site containing The wheat line of the wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr13 improves the selection efficiency and accelerates the process of wheat disease resistance breeding, and realizes the goal of multi-disease resistance gene aggregation breeding.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Organic matter farmland improver
InactiveCN112266294AReduce contentContent supplementPlant growth regulatorsBiocideLand improvementOrganic acid
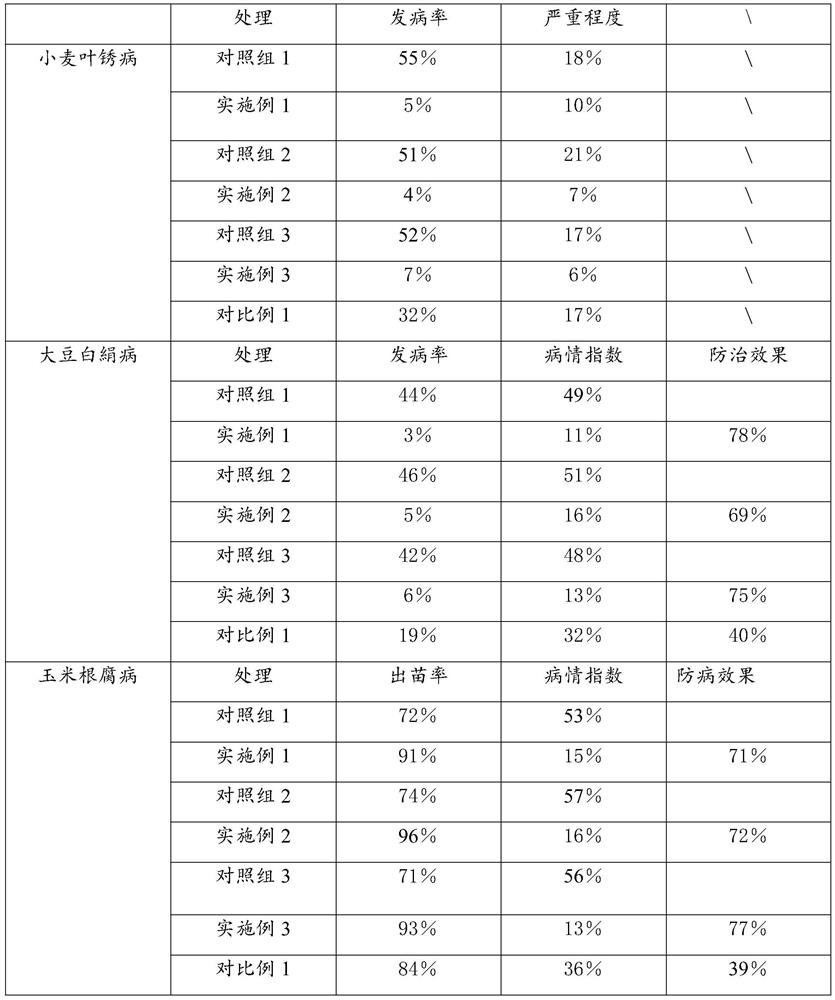
The invention discloses an organic matter farmland improver, which belongs to the technical field of land improvement. The organic matter farmland improver is prepared from chitin, humic acid, potassium fulvic acid, organic acid, a metal ion chelating agent and vermiculite. By applying the organic matter farmland improver to fields, soil organic matter can be supplemented, and wheat leaf rust, soybean white wilt and corn root rot can be effectively inhibited.
Owner:武汉市秀谷科技有限公司
Primer set of wheat leaf rust est-ssr molecular marker and its detection method and application
InactiveCN107058602BAmplification results are stablePolymorphism richMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyPuccinia recondita
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Competitive allele-specific polymerase chain reaction markers of leaf rust resistance loci in durum wheat and their applications
InactiveCN110592260BGood genetic stabilityHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com