Human pulmonary infection assessment method based on intestinal flora in excrement sample and application of human pulmonary infection assessment method
A technology for fecal samples and intestinal flora, applied in the field of biomedicine, to reduce patient pain, improve prognosis, and high detection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
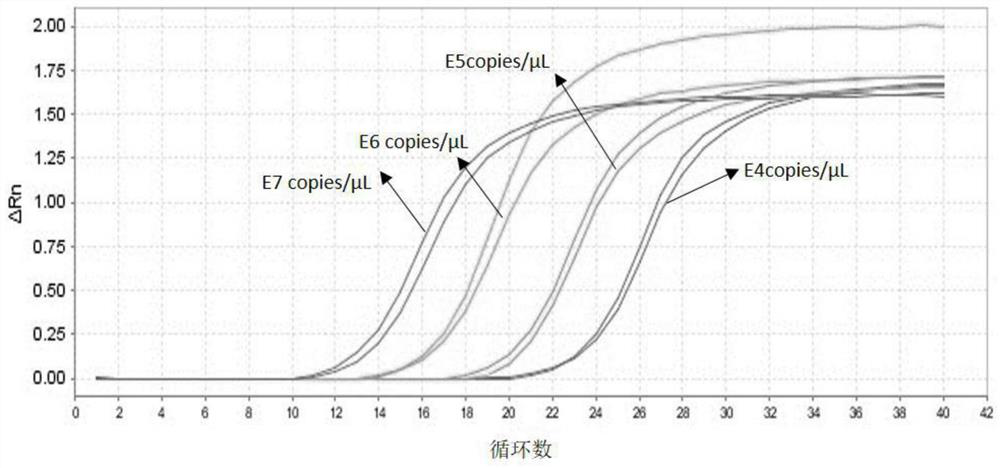
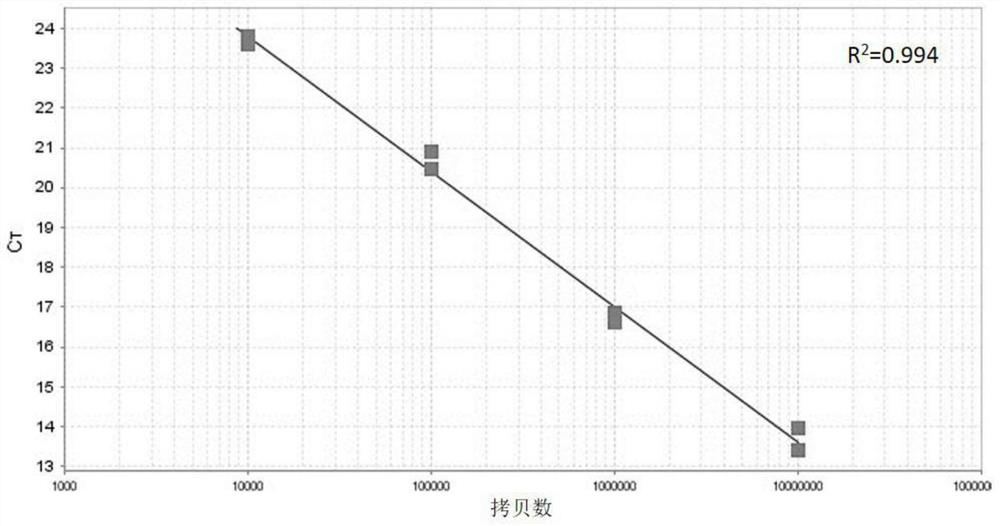
[0026] A method for evaluating human lung infection based on intestinal flora in stool samples of the present invention comprises the following steps:
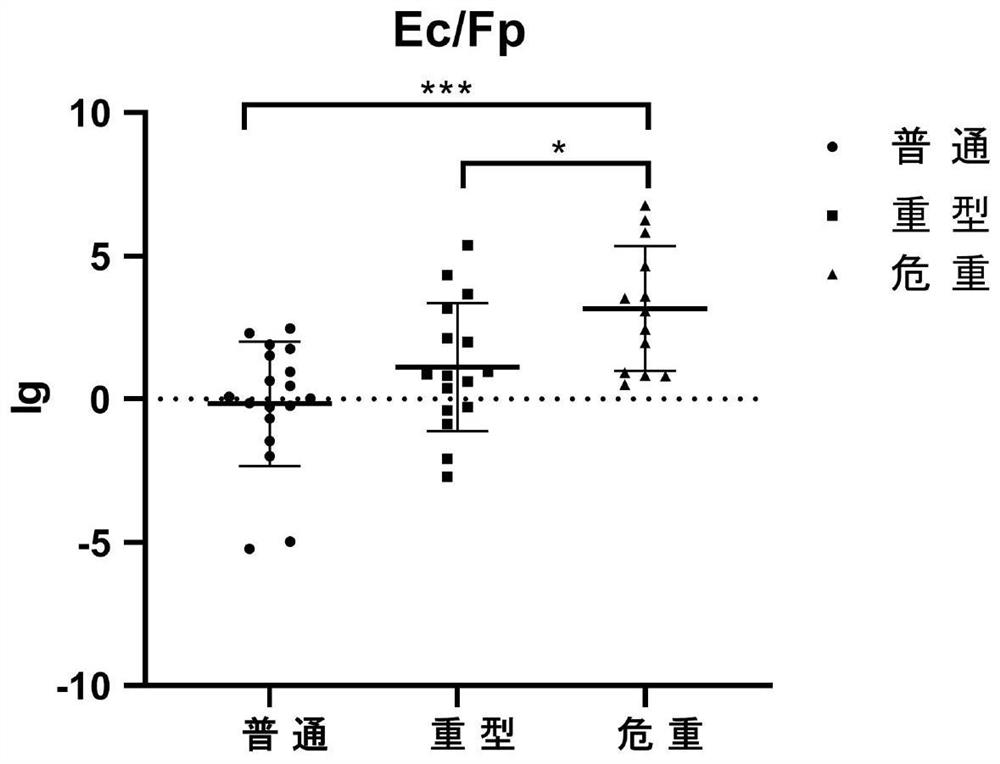
[0027] The first step is to collect the stool samples of the test personnel and extract DNA. Use the stool genomic DNA extraction kit (DP328) of Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. and extract the stool sample DNA as the template DNA according to the instructions. The selected test personnel include 20 ordinary patients with new coronary pneumonia, 19 severe patients and 17 critical patients were recorded as ordinary group, severe group and critical group respectively. The average age of 20 ordinary patients with new coronary pneumonia was 59 years old, and the age range was 53-63 years old. There were 8 males and 12 females; the average age of the 19 critically ill patients was 66 years old, and the age range was 61-74 years old, 9 males and 10 females; the average age of the 17 critically ill patients was 61 years old, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com