Metschnikowia bicuspidate and method for treating high-salinity wastewater
A high-salt wastewater and yeast technology, applied in the direction of microbial-based methods, chemical instruments and methods, and food industry wastewater treatment, can solve problems such as high cost and affect the production efficiency of processing plants, and achieve low cost and simple operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] In the present invention, after separation, purification, identification, optimization and screening, the strain that can utilize the organic matter of high-salt wastewater is M. trichomes ( Metschnikowia bicuspidate ) , It has been deposited in the General Microbiology Center of the China Microorganism Culture Collection Management Committee, codenamed WSKeW-M, and the deposit number is CGMCC No.18674.
[0025] The method for processing high-salt wastewater with the above-mentioned M. biloba is carried out according to the following steps:
[0026] a. Gradually expand the seed solution of the above-mentioned M. biloba (CGMCC No.18674);
[0027] b. Add 8 times the volume of the expanded bacterial solution to the high-salt wastewater produced by kelp processing and the high-salt wastewater produced by wakame processing at a volume percentage of 5%, and shake at 120 r / min at 20 °C. Incubate for 60 hours.
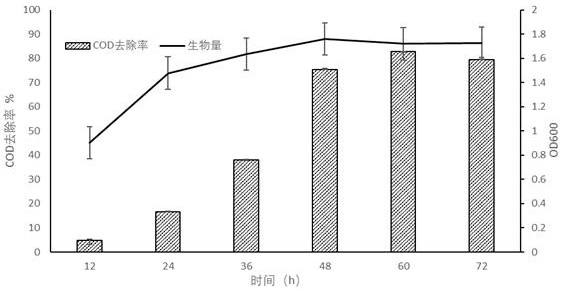
[0028] Measure the high-salt waste water produced by kelp proc...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The method for processing high-salt wastewater with the above-mentioned M. biloba is carried out according to the following steps:
[0031] a. Combine the above-mentioned M. biloba (CGMCC No. 18674) with the Pichia moniliformes with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 18675 ( Meyerozyma guilliermondii ) according to the volume ratio of 1:1 to make compound seed solution and gradually expand the culture;
[0032] b. Add 8 times the volume of the expanded bacterial solution to the high-salt wastewater produced by kelp processing at a volume percentage of 3%, and culture at 20 °C with a shaker at 150 r / min for 60 hours.
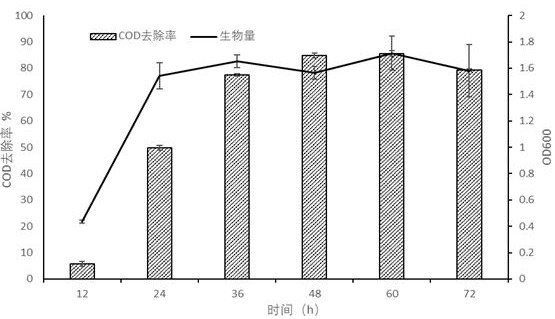
[0033] The high-salt waste water produced by the processing of kelp processed by the above-mentioned method is measured, and the results are as follows: image 3 shown. The results showed that the COD removal rate of high-salt wastewater produced by kelp processing was 85.98%.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The method for processing high-salt wastewater with the above-mentioned M. biloba is carried out according to the following steps:
[0036] a. Combine the above-mentioned M. biloba (CGMCC No. 18674) with Halomonas with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 20812 ( Cobetia sp. ) according to the volume ratio of 2:1 to make compound seed solution and gradually expand the culture;
[0037] b. Add the 20-fold volume of the bacterial solution to the high-salt wastewater from wakame processing at a volume percentage of 1%, and culture at 20 °C with a shaker at 150 r / min for 60 hours.
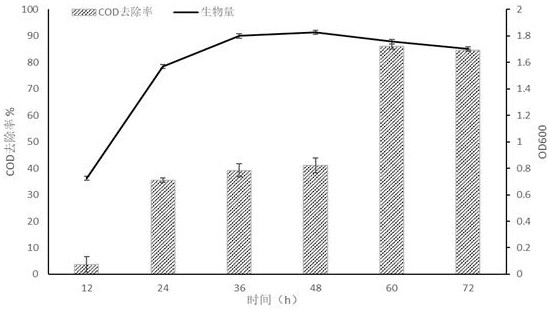
[0038] Using potassium permanganate oxidation method to carry out COD determination on the high-salt wastewater produced by wakame processing that has been processed by the above method, the results are as follows: Figure 4 shown. The results showed that the COD removal rate of high-salt wastewater from wakame processing was 86.24%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com