Application of material with abnormal piezocaloric effect in solid-state refrigeration and/or heat storage
A solid-state refrigeration and thermal effect technology, which is applied to machines using waste heat, heat storage equipment, indirect heat exchangers, etc., can solve problems such as energy loss, achieve heat transfer, improve energy utilization efficiency, and have great application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Negative thermal expansion material NH 4 Anomalous barocaloric effect of SCN
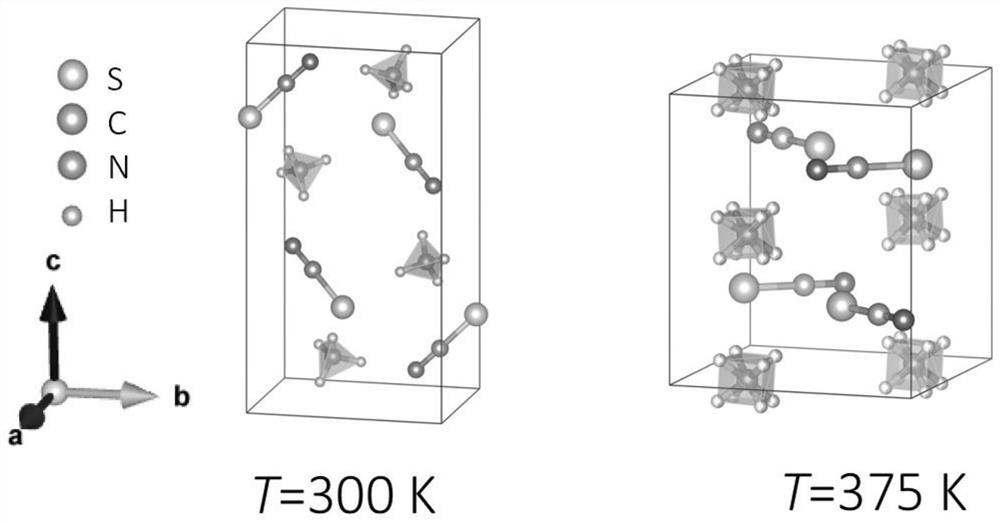
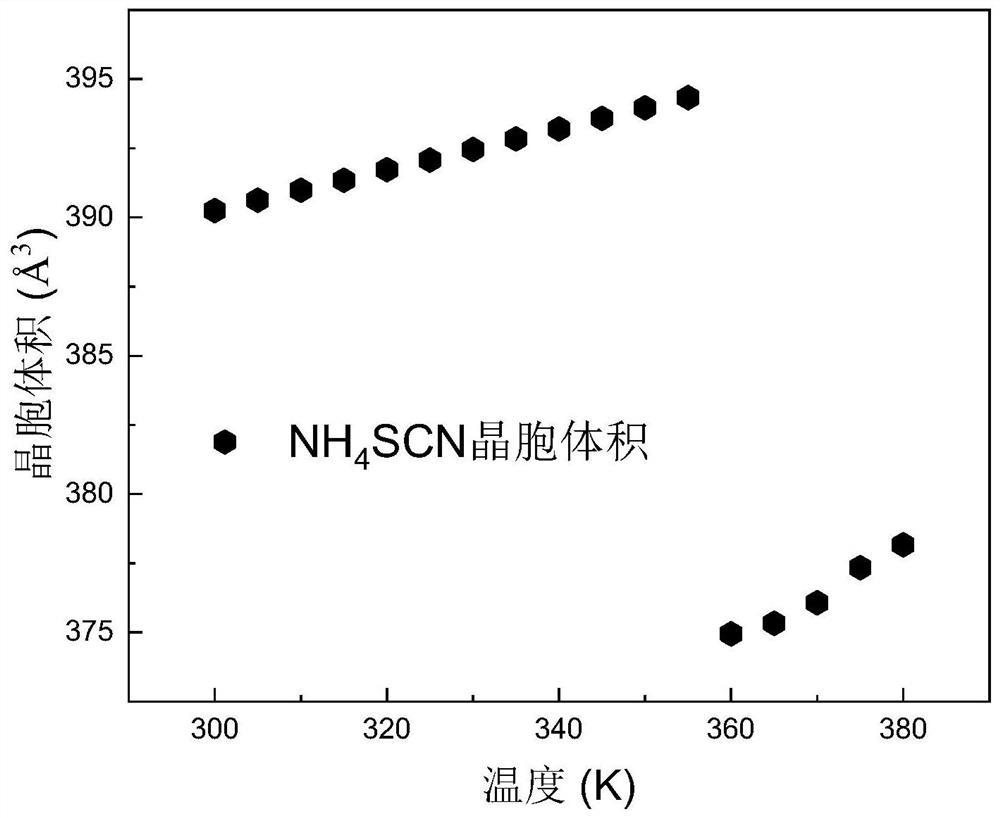
[0031] NH 4 SCN has two phase transitions at 360K and 390K respectively. Among them, a structural phase transition from ordered to disordered structural units occurs at 360K, and its crystal structure is shown in the attached figure 1 As shown, from 300K low-temperature monoclinic phase to 375K medium-temperature orthorhombic phase, where NH 4 + The phase is ordered at low temperature, while the phase is orientationally disordered at medium temperature. This phase change process is negative thermal expansion, that is, during the temperature-rising phase change process, the volume after the phase change is smaller than the volume before the phase change. attached figure 2 is NH 4 The variation of the volume of the SCN unit cell with temperature, the volume of the unit cell decreases sharply at 360K, and its negative thermal expansion rate is calculated as (V 2 -V 1 ) / V 1 = -4.9%. N...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Applications of materials with anomalous barothermic effect in solid-state refrigeration and / or heat storage
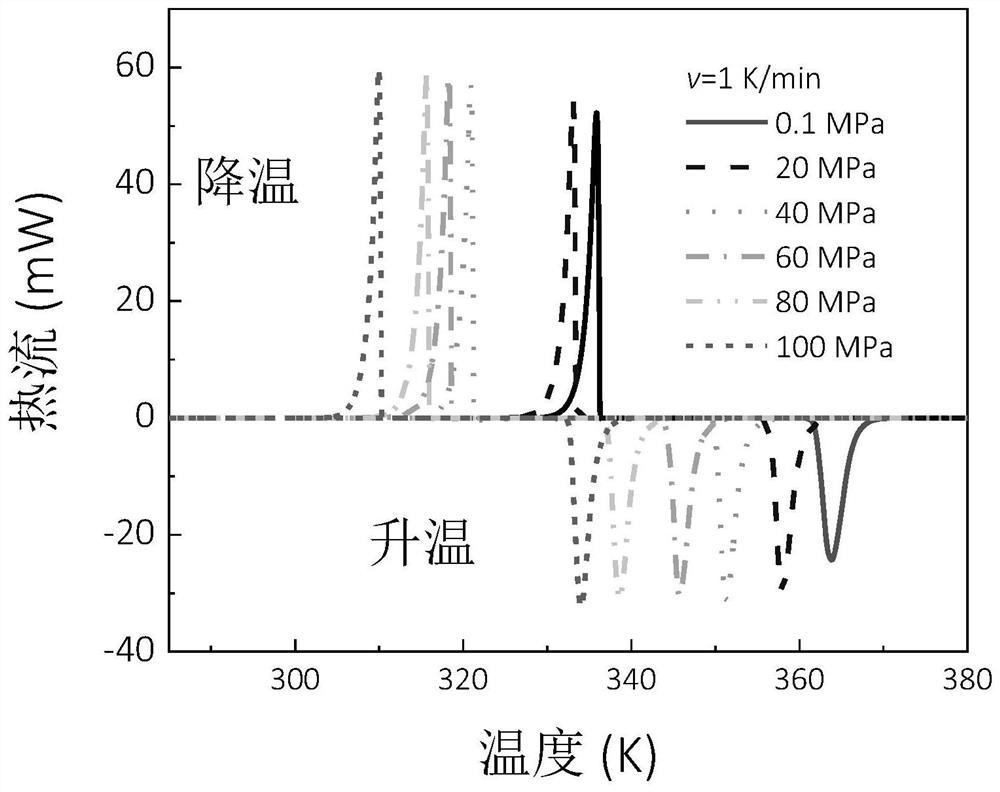
[0034] attached Figure 5 is based on the attached image 3 NH calculated from heat flow data at different pressures 4 Diagram of SCN autoclaving effect. P 0 is the atmospheric pressure, and P corresponds to 20MPa, 40MPa, 60MPa, 80MPa and 100MPa respectively. to NH 4 When pressure is applied to the SCN, the material undergoes an order-to-disorder endothermic phase transition. As the pressure increases, the entropy change of the barothermal effect increases. It reaches a saturated maximum value of 128.7J kg when the driving pressure is only 80MPa -1 K -1 . The depressurization process corresponds to the exothermic phase transition from disorder to order. Combining existing anomalous barocaloric materials with NH 4 SCN for comparison, the results are shown in the appendix Figure 6 . It can be seen that NH 4 The pressure-driven isothermal entropy cha...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Applications of materials with anomalous barothermic effect in solid-state refrigeration and / or heat storage
[0037] attached Figure 10 NH 4 SCN measured pressure and heat flow data. Fill the sample cell with nitrogen so that the initial pressure of the sample cell is 8.2MPa. Then pressurize it to 90MPa at a temperature of 349K to undergo an endothermic phase transition, and the enthalpy of this process becomes 43.01kJ kg -1 . When the pressure is stabilized at 90MPa, the temperature of the material is lowered to 313K. After the pressure is unloaded, an exothermic phase transition occurs, and the phase transition enthalpy becomes -45.2kJ kg -1 . In the cooling process, the heat flow curve in the figure is a straight line, which proves that there is no obvious heat loss at a constant pressure of 90MPa, so the heat transfer can be realized by controlling the pressure. attached Figure 11 Application scenario 2 for materials with anomalous barothermal effect in so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com